Page 278 of 5135
A58692
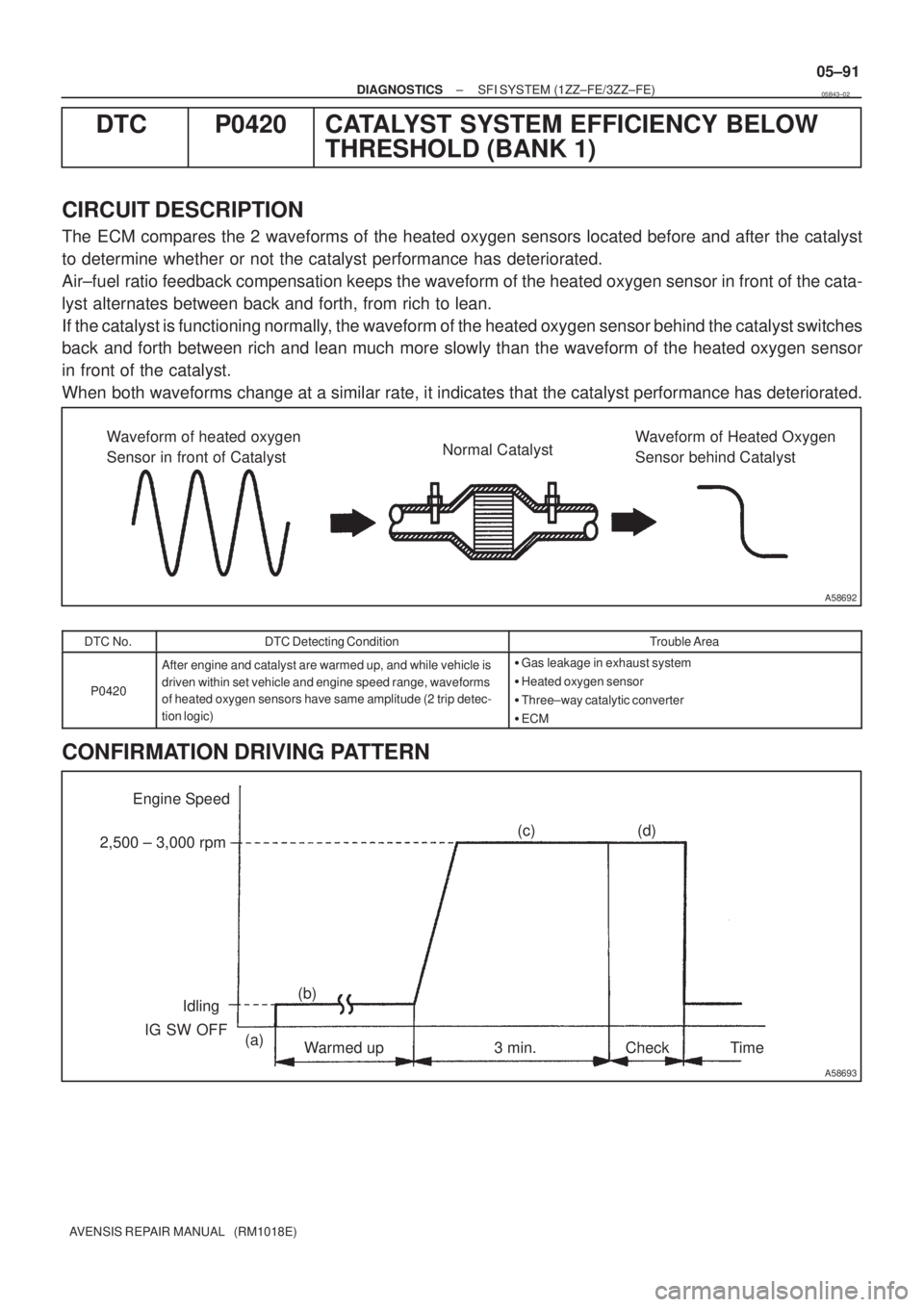
Waveform of heated oxygen
Sensor in front of CatalystNormal CatalystWaveform of Heated Oxygen
Sensor behind Catalyst
A58693
Engine Speed
2,500 ± 3,000 rpm
Idling
IG SW OFF
Warmed up 3 min. Check Time (a)(b)(c) (d)
± DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
05±91
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW
THRESHOLD (BANK 1)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ECM compares the 2 waveforms of the heated oxygen sensors located before and after the catalyst
to determine whether or not the catalyst performance has deteriorated.
Air±fuel ratio feedback compensation keeps the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor in front of the cata-
lyst alternates between back and forth, from rich to lean.
If the catalyst is functioning normally, the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor behind the catalyst switches
back and forth between rich and lean much more slowly than the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor
in front of the catalyst.
When both waveforms change at a similar rate, it indicates that the catalyst performance has deteriorated.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0420
After engine and catalyst are warmed up, and while vehicle is
driven within set vehicle and engine speed range, waveforms
of heated oxygen sensors have same amplitude (2 trip detec-
tion logic)�Gas leakage in exhaust system
�Heated oxygen sensor
�Three±way catalytic converter
�ECM
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
05B43±02
Page 279 of 5135

A58694
OX Signal Waveform (Oscilloscope)
1.0 V
0 V 200 msec. /Division
05±92
±
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM(1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
(a)Connect the hand±held tester to the DLC3, or connect the probe of the oscilloscope between terminals HT1A,
HT1B, OX1A, OX1B and E1 of the ECM connector.
(b)Start the engine and warm it up with all the accessories switched OFF until the engine coolant temperature is
stable.
(c)Run the engine at 2,500 to 3,000 rpm for about 3 min.
(d)After confirming that the waveform of the heated oxygen
sensor (bank 1 sensor 1 (OX)) which oscillates around 0.5
V during feedback to the ECM, check the waveform of the
heated oxygen sensor (bank 1 sensor 2 (OX)).
HINT:
�If there is a malfunction in the system, the waveform of the
heated oxygen sensor (bank 1 sensor 2 (OX)) is similar
to the wave from of the heated oxygen sensor (bank 1
sensor 1 (OX)) snown in the diagram on the left.
�There are some cases that, even though a malfunction
exists, the CHK ENG may not be illuminated.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using \f���� ����\b�\f��\f�
� Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determi\
ning whether the vehicle was running
or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio was lea\
n or rich, etc. at the time of the mal-
function.
1READ OUTPUT DTC(BESIDES P0420)
(a)Read the DTC using the hand±held tester. Result:
Display (DTC output)Proceed to
Only ºP0420º is outputA
ºP0420º and other DTCs are outputB
HINT:
If any other codes besides ºP0420º are output, perform the troublesh\
ooting for those DTCs first.
BGO TO RELEVANT DTC CHART(See page 05±16)
A
Page 281 of 5135

A63955
GND
CH1
(G2)
CH2
(NE+) GND
05±88
±
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM(1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
DTCP0340CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position sensor (G2 signal) consists of a magnet, iron core \
and pickup coil.
The G2 signal plate has 3 teeth on its outer circumference and is instal\
led on the camshaft timing pulley.
When the camshafts rotate, the protrusion on the signal plate and the air gap on the pickup coil changes,
causing fluctuations in the magnetic field and generating an electromoti\
ve force in the pickup coil.
The NE signal plate (crankshaft timing pulley) has 34 teeth and is instal\
led to the crankshaft. The NE signal
sensor generates 34 signals at every engine revolution. The ECM detects \
the crankshaft angle and the en-
gine revolution based on the NE signals, and the cylinder and the angle of the VVT based on the combination
of the G2 and NE signals.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0340
�No camshaft position sensor signal to the ECM during crank-
ing
� Open in NE± circuit
�Open or short in camshaft position sensor circuit
� Camshaft position sensor
� Intake camshaft
� Timing chain has jumped a tooth
� ECM
Reference: Inspection using the oscilloscope.
HINT:
The correct waveform is as shown on the left.
ItemContents
TerminalCH1: G2 ± NE±
CH2: NE+ ± NE±
Equipment Set5V/DIV, 20ms/DIV
ConditionDuring cranking or idling
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 on page05±84.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using \f�� �� ����\b� \f��\f�
� Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determi\
ning whether the vehicle was running
or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio was lea\
n or rich, etc. at the time of the mal-
function.
05B42±03
Page 285 of 5135
A79089
C1
Camshaft Position Sensor(Shielded)
1 2ECM
(Shielded) 1
2
EHR
NE+NE± G2 W
G C6
Crankshaft Position Sensor
R RE13
E13
E1326
34
27
BR E
J12
Junction
ConnectorE E
± DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
05±85
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�Read freeze frame data using ��� �� ������ �����
� Freeze frame data records the engine conditions
when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determining whether the vehicle
was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio was lean or rich, etc. at
the time of the malfunction.
�Perform troubleshooting on ºDTC P0335º first. If no trouble is found, troubleshoot the following me-
chanical system.
Page 289 of 5135

A65745
E12
ECM ConnectorFKN+
FKN±
A65745
E12
ECM ConnectorFKN+
FKN±
05±82
±
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM(1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using \f���� ����\b�\f��\f�
� Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determi\
ning whether the vehicle was running
or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio was lea\
n or rich, etc. at the time of the mal-
function.
1CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR
(a)Disconnect the E12 ECM connector.
(b)Check for continuity between the wire harness side con- nectors.
Standard (Check for short):
Symbols (Terminal No.)Specified condition
FKN+ (E12±1) ± FKN± (E12±2)No continuity
OKGo to step 3
NG
2INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR (See page 10±3)
NG REPLACE KNOCK SENSOR
OK
3 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(ECM ± KNOCK SENSOR)
(a) Disconnect the E12 ECM connector.
(b) Disconnect the knock sensor connector.
(c) Check for continuity between the wire harness side con- nectors.
Standard (Check for open):
Symbols (Terminal No.)Specified condition
FKN+ (E12±1) ± Knock sensor (K1±2)ContinuityFKN± (E12±2) ± Knock sensor (K1±1)Continuity
Standard (Check for short):
Symbols (Terminal No.)Specified condition
FKN+ (E12±1) or Knock sensor (K1±2) ± Body groundNo continuityFKN± (E12±2) or Knock sensor (K1±1) ± Body groundNo continuity
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
OK
Page 291 of 5135
05C6Q±01
05±168
±
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM(1AZ±FE)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
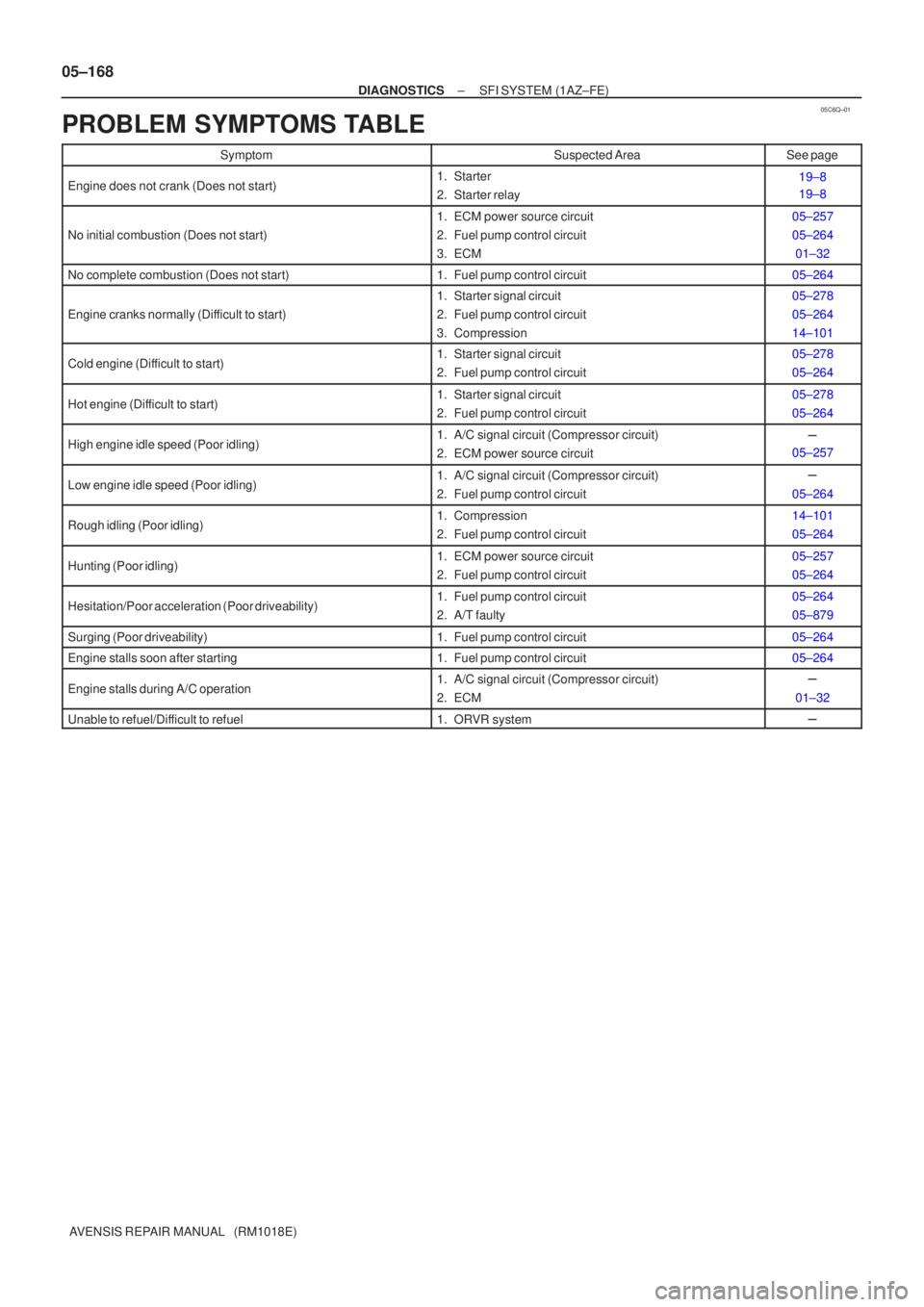
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
SymptomSuspected AreaSee page
Engine does not crank (Does not start)1. Starter
2. Starter relay19±8
19±8
No initial combustion (Does not start)
1. ECM power source circuit
2. Fuel pump control circuit
3. ECM05±257
05±264 01±32
No complete combustion (Does not start)1. Fuel pump control circuit05±264
Engine cranks normally (Difficult to start)
1. Starter signal circuit
2. Fuel pump control circuit
3. Compression05±278
05±264
14±101
Cold engine (Difficult to start)1. Starter signal circuit
2. Fuel pump control circuit05±278
05±264
Hot engine (Difficult to start)1. Starter signal circuit
2. Fuel pump control circuit05±278
05±264
High engine idle speed (Poor idling)1. A/C signal circuit (Compressor circuit)
2. ECM power source circuit�
05±257
Low engine idle speed (Poor idling)1. A/C signal circuit (Compressor circuit)
2. Fuel pump control circuit�
05±264
Rough idling (Poor idling)1. Compression
2. Fuel pump control circuit14±101
05±264
Hunting (Poor idling)1. ECM power source circuit
2. Fuel pump control circuit05±257
05±264
Hesitation/Poor acceleration (Poor driveability)1. Fuel pump control circuit
2. A/T faulty05±264
05±879
Surging (Poor driveability)1. Fuel pump control circuit05±264
Engine stalls soon after starting1. Fuel pump control circuit05±264
Engine stalls during A/C operation1. A/C signal circuit (Compressor circuit)
2. ECM�
01±32
Unable to refuel/Difficult to refuel1. ORVR system�
Page 294 of 5135
05C6O±01
A76850
Combination Meter
Fuel Pump
DLC3
Circuit Opening Relay
Engine Room J/B No.1
Engine Room R/B No.1 Variable Resister (*1)
ECM
VSV (EVAP)
Mass Air Flow Meter
Engine Room J/B No.4
Engine Room R/B No.4
Idle Speed Control Valve
Canshaft Position Sensor
Engine Coolamt
Temperature SensorThrottle Body
Knock Sensor
Neutral Start Switch Injector Camshaft Oil Control Valve
Ignition Coli and Igniter
Crank Position Sensor
A/F Sensor
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank 1 Sensor 2) A/F Sensor
(Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
*1: Leaded Only
± DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1AZ±FE)
05±165
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
LOCATION
Page 309 of 5135
± DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ±FE/3ZZ±FE)
05±135
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the engine is cranked, the intake air flow becomes slow, so fuel vaporization is poor. A rich mixture
is therefore necessary in order to achieve good startability. While the engine is being cranked, the battery
voltage is applied to terminal STA of the ECM. The starter signal is mainly used to increase the fuel injection
volume for the starting injection control and after±start injection control.
05C6I±01