2003 DODGE RAM electrical
[x] Cancel search: electricalPage 1675 of 2895

REAR BUMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Remove the license plate.
(3) Remove the bolts behind the plate.
(4) Disconnect the license plate light electrical con-
nectors.
(5) Disconnect the trailer light connector electrical
connection, if equipped.
(6) Remove the two bolts along the front upper
edge of the bumper near the frame tips.
(7)
Support the bumper with a suitable lifting device.
(8) Remove the bolts attaching the bumper support
brackets to the trailer hitch. (Fig. 5)
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the holes in the bumpers to the trailer
hitch pins and install the bumper.
(2) Install the support bracket to the hitch bolts,
loosely.
(3) Install the front upper edge to the trailer hitch
bolts and tighten to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the license plate reinforcement to hitch
bolts and tighten to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(5) Tighten the left bumper bracket bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(6) Tighten the right bumper bracket bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(7) Connect the trailer light connector electrical
connection, if equipped.
(8) Connect the license plate light electrical con-
nectors.
(9) Install the license plate.
FRAME
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - LIGHT DUTY FRONT
FRAME RAIL TIP REPLACEMENT
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE EYE PROTECTION WHEN GRIND-
ING OR WELDING METAL, SERIOUS EYE INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FRAME REPAIR
INVOLVING GRINDING OR WELDING, VERIFY THAT
VEHICLE FUEL SYSTEM IS NOT LEAKING OR IN
CONTACT WITH REPAIR AREA, PERSONAL INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT ALLOW OPEN FLAME OR HEAT AND
METAL SPATTER FROM ARC WELDING, TO CON-
TACT PLASTIC BODY PANELS. FIRE OR EXPLO-
SION CAN RESULT.
²WHEN WELDED FRAME COMPONENTS ARE
REPLACED, ENSURE COMPLETE PENETRATION
WELD IS ACHIEVED DURING INSTALLATION. IF
NOT, DANGEROUS OPERATING CONDITIONS CAN
RESULT.
²STAND CLEAR OF CABLES OR CHAINS ON
PULLING EQUIPMENT DURING FRAME STRAIGHT-
ENING OPERATIONS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
²DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHI-
CLE THAT IS NOT SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: 1500 series Dodge Ram Trucks (2002 and
later) are not designed for snow plow equipment.
The front collision repair tips must not be installed
on any truck equipped with a snow plow, or even
intended to be equipped with a snow plow.
CAUTION: This procedure is designed to replace
the front frame rail tips that have been damaged in
the crush initiator zones. Prior to any cutting, the
vehicle must be mounted on the appropriate frame
repair equipment (ªframe rackº), checked with three
dimensional measuring equipment, and the neces-
sary pull corrections made. If damage remains in
the frame beyond the area covered by this service
part after the pull, the frame must be replaced in its
entirety.
Fig. 5 TRAILER HITCH
1 - HITCH
2 - HITCH BOLTS (4)
3 - BUMPER BRACKET BOLTS (4)
4 - BUMPER SUPPORT BRACKETS
13 - 4 FRAMES & BUMPERSDR
Page 1681 of 2895
(c) Apply a durable top coat to the outside of the
repair area.
(28) Tighten the front cab mounting bolt to the
FESM bracket to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(29) Install the stabilizer bar. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER BAR - INSTALLA-
TION)
(30) Install the front bumper. (Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER
- INSTALLATION)(31) Install the wire harness and ground strap if
previously removed and install the bolt.
(a) If necessary, re-drill and tap the ground
strap mounting hole
(32) Install the front wheelhouse splash shield.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION)
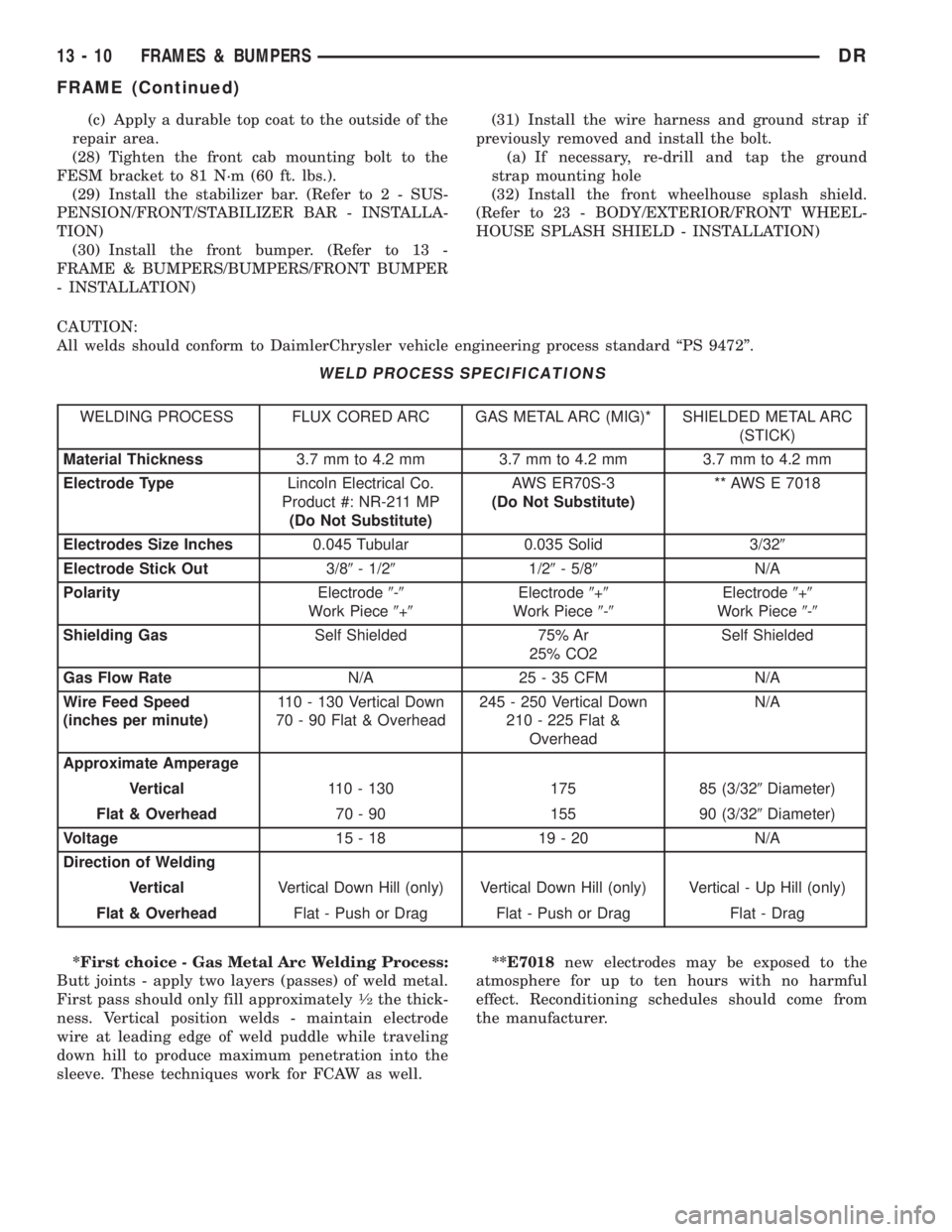
CAUTION:
All welds should conform to DaimlerChrysler vehicle engineering process standard ªPS 9472º.
WELD PROCESS SPECIFICATIONS
WELDING PROCESS FLUX CORED ARC GAS METAL ARC (MIG)* SHIELDED METAL ARC
(STICK)
Material Thickness3.7 mm to 4.2 mm 3.7 mm to 4.2 mm 3.7 mm to 4.2 mm
Electrode TypeLincoln Electrical Co.
Product #: NR-211 MP
(Do Not Substitute)AWS ER70S-3
(Do Not Substitute)** AWS E 7018
Electrodes Size Inches0.045 Tubular 0.035 Solid 3/329
Electrode Stick Out3/89- 1/291/29- 5/89N/A
PolarityElectrode9-9
Work Piece9+9Electrode9+9
Work Piece9-9Electrode9+9
Work Piece9-9
Shielding GasSelf Shielded 75% Ar
25% CO2Self Shielded
Gas Flow RateN/A 25 - 35 CFM N/A
Wire Feed Speed
(inches per minute)110 - 130 Vertical Down
70 - 90 Flat & Overhead245 - 250 Vertical Down
210 - 225 Flat &
OverheadN/A
Approximate Amperage
Vertical110 - 130 175 85 (3/329Diameter)
Flat & Overhead70 - 90 155 90 (3/329Diameter)
Voltage15-18 19-20 N/A
Direction of Welding
VerticalVertical Down Hill (only) Vertical Down Hill (only) Vertical - Up Hill (only)
Flat & OverheadFlat - Push or Drag Flat - Push or Drag Flat - Drag
*First choice - Gas Metal Arc Welding Process:
Butt joints - apply two layers (passes) of weld metal.
First pass should only fill approximately
1¤2the thick-
ness. Vertical position welds - maintain electrode
wire at leading edge of weld puddle while traveling
down hill to produce maximum penetration into the
sleeve. These techniques work for FCAW as well.**E7018new electrodes may be exposed to the
atmosphere for up to ten hours with no harmful
effect. Reconditioning schedules should come from
the manufacturer.
13 - 10 FRAMES & BUMPERSDR
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1683 of 2895

STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROFORM
FENDER RAIL REPAIR
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE EYE PROTECTION WHEN GRIND-
ING OR WELDING METAL, SERIOUS EYE INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FRAME REPAIR
INVOLVING GRINDING OR WELDING, VERIFY THAT
VEHICLE FUEL SYSTEM IS NOT LEAKING OR IN
CONTACT WITH REPAIR AREA, PERSONAL INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT ALLOW OPEN FLAME OR HEAT AND
METAL SPATTER FROM ARC WELDING, TO CON-
TACT PLASTIC BODY PANELS. FIRE OR EXPLO-
SION CAN RESULT.
²WHEN WELDED FRAME COMPONENTS ARE
REPLACED, ENSURE COMPLETE PENETRATION
WELD IS ACHIEVED DURING INSTALLATION. IF
NOT, DANGEROUS OPERATING CONDITIONS CAN
RESULT.
²STAND CLEAR OF CABLES OR CHAINS ON
PULLING EQUIPMENT DURING FRAME STRAIGHT-
ENING OPERATIONS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
²DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHI-
CLE THAT IS NOT SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Do not reuse damaged fasteners, quality
of repair would be suspect. Failure to use only pro-
duction fasteners or fasteners of equivalent hard-
ness can result in loosening or failure. Do not drill
holes in top or bottom frame rail flanges, frame rail
failure can result. When using heat to straighten
frame components do not exceed 566ÉC (1050ÉF),
metal fatigue can result.
CAUTION: This repair procedure assumes damage
to the right or left hydroform fender rail (Fig. 19).
Prior to any repairs, the vehicle must be mounted
on the appropriate frame repair equipment (ªframe
rackº), checked with three dimensional measuring
equipment, and necessary pull corrections made. If
damage exists in the hydroform fender rail, or cab
beyond the area covered by this service procedure
after dimensional corrections are made, the hydro-
form must be replaced in its entirety. Refer to 23 -
BODY/BODY STRUCTURE/WELD LOCATIONS -
SPECIFICATIONS, when replacing the entire hydro-
form.(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the front wheelhouse splash shield.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the fender. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/FRONT FENDER - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the A/C condenser, if required. (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING/A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the A/C lines, if required. Refer to the
Heating and Air Conditioning section of the manual
for recommended procedures.
(6) Remove the radiator assembly. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL)
(7) Remove the air cleaner and support bracket, if
required. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYS-
TEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove the integrated power module. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTE-
GRATED POWER MODULE - REMOVAL)
(9) Remove the bolts and position aside the wire
harness and grounds, if required.
(10) Remove the upper radiator crossmember.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/UPPER RADIATOR
CROSSMEMBER - REMOVAL)
(11) Remove the headlamp unit. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
HEADLAMP UNIT - REMOVAL)
(12) Remove the front cab mount to the Front End
Sheet Metal bracket (FESM) bolt.
(13) Remove the bolts attaching the lower radiator
crossmember to the hydroform fender rail. (Fig. 19)
CAUTION: Do not use any flame or plasma cutting
equipment to cut the frame in this procedure. The
inaccurate and high temperatures achieved during
flame or plasma cutting will change the metal char-
acteristics and may weaken the frame and/or repair
location.
(14) Using a reciprocating saw or equivalent, cut
the fender rail and shotgun at a straight and square
section of the hydroform and remove.
(15) Smooth and square the cut edges.
(16) Using the damaged structure as a reference
cut the service part at the same location as the first
cut. Smooth and square the cut edges.
NOTE: The repair structure should butt up to the
remaining structure and provide the same overall
vehicle geometry.
13 - 12 FRAMES & BUMPERSDR
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1685 of 2895

(26) Install the front cab mount bolt if previously
removed and tighten to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(27) Install the lower radiator crossmember bolts
and tighten to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(28) Install the headlamp unit. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEAD-
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(29) Install the upper radiator crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/UPPER RADIATOR
CROSSMEMBER - INSTALLATION)
(30) Install the wire harness and ground if previ-
ously removed and install the bolts.
(31) Install the integrated power module, if previ-
ously removed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DISTRIBUTION/INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
INSTALLATION)
(32) Install the air cleaner bracket and air cleaner,
if previously removed. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
INSTALLATION)(33) Install the radiator assembly. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION)
(34) Install the A/C lines, if previously removed.
Refer to the Heating and Air Conditioning section of
the manual for the recommended procedures.
(35) Install the A/C condenser, if previously
removed. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - INSTAL-
LATION)
(36) Install the fender. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/FRONT FENDER - INSTALLATION)
(37) Install the front wheelhouse splash shield.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION)
(38) Reconnect the battery ground.
Fig. 20 ENGINE COMPARTMENT/FRONT STRUCTURE
13 - 14 FRAMES & BUMPERSDR
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1688 of 2895

CAUTION:
All welds should conform to DaimlerChrysler vehicle engineering process standard ªps 9472º.
WELD PROCESS SPECIFICATIONS
WELDING PROCESS FLUX CORED ARC GAS METAL ARC (MIG)* SHIELDED METAL ARC
(STICK)
Material Thickness3.7 mm to 4.2 mm 3.7 mm to 4.2 mm 3.7 mm to 4.2 mm
Electrode TypeLincoln Electrical Co.
Product #: NR-211 MP
(Do Not Substitute)AWS ER70S-3
(Do Not Substitute)** AWS E 7018
Electrodes Size Inches.045 Tubular .035 Solid 3/329
Electrode Stick Out3/89- 1/291/29- 5/89N/A
PolarityElectrode9-9
Work Piece9+9Electrode9+9
Work Piece9-9Electrode9+9
Work Piece9-9
Shielding GasSelf Shielded 75% Ar
25% CO2Self Shielded
Gas Flow RateN/A 25 - 35 CFM N/A
Wire Feed Speed
(inches per minute)110 - 130 Vertical Down
70 - 90 Flat & Overhead245 - 250 Vertical Down
210 - 225 Flat &
OverheadN/A
Approximate Amperage
Vertical110 - 130 175 85 (3/329Diameter)
Flat & Overhead70 - 90 155 90 (3/329Diameter)
Voltage15-18 19-20 N/A
Direction of Welding
VerticalVertical Down Hill (only) Vertical Down Hill (only) Vertical - Up Hill (only)
Flat & OverheadFlat - Push or Drag Flat - Push or Drag Flat - Drag
*First choice - Gas Metal Arc Welding Process:
Butt joints - apply two layers (passes) of weld metal.
First pass should only fill approximately
1¤2the thick-
ness. Vertical position welds - maintain electrode
wire at leading edge of weld puddle while traveling
down hill to produce maximum penetration into the
sleeve. These techniques work for FCAW as well.
**E7018new electrodes may be exposed to the
atmosphere for up to ten hours with no harmful
effect. Reconditioning schedules should come from
the manufacturer.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FRAME DIMENSIONS
NOTE: Frame dimensions are listed in metric scale.
All dimensions are from center to center of Princi-
pal Locating Point (PLP), or from center to center of
PLP and fastener location.
VEHICLE PREPARATION
Position the vehicle on a level work surface. Using
screw or bottle jacks, adjust the vehicle PLP heights
to the specified dimension above a level work surface.
Vertical dimensions can be taken from the work sur-
face to the locations indicated were applicable.
INDEX
DESCRIPTION FIGURE
Frame Dimensional Graphics, Side
And Top View24
140.5 In Wheelbase - Heavy Duty -
2 Wheel Drive25
140.5 In Wheelbase - Heavy Duty -
4 Wheel Drive26
160.5 In Wheelbase - Heavy Duty -
2 Wheel Drive27
160.5 In Wheelbase - Heavy Duty -
4 Wheel Drive28
DRFRAMES & BUMPERS 13 - 17
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1704 of 2895

pump.Refer to Fuel Pump - Description and
Operation for more information.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 49.2 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source is supplied to the resistor track on the fuel
gauge sending unit. This is fed directly from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).NOTE: For
diagnostic purposes, this 12V power source can
only be verified with the circuit opened (fuel
pump module electrical connector unplugged).
With the connectors plugged, output voltages
will vary from about 0.6 volts at FULL, to about
8.6 volts at EMPTY (about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
for Jeep models, and about 7.0 volts at EMPTY
for Dodge Truck models).The resistor track is
used to vary the voltage (resistance) depending on
fuel tank float level. As fuel level increases, the float
and arm move up, which decreases voltage. As fuel
level decreases, the float and arm move down, which
increases voltage. The varied voltage signal is
returned back to the PCM through the sensor return
circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
REMOVAL
The fuel level sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of the fuel pump
module (Fig. 3).
(1) Remove fuel pump module from fuel tank.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
(2) To remove sending unit from pump module, lift
on plastic locking tab (Fig. 4) while sliding sending
unit tracks.
(3) Disconnect 4±wire electrical connector (Fig. 3)
from fuel pump module. Separate necessary sending
unit wiring from connector using terminal pick /
removal tool. Refer to Special Tools in 8W Wiring for
tool part numbers.
Fig. 3 LOCATION - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
1 - FUEL FILTER / FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE ASSEMBLY
3 - 4-WAY ELEC. CONNECT.
4 - FLOAT ARM
5 - ELEC. FUEL PUMP
6 - INLET FILTER
7 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
8 - GASKET (SEAL)
DRFUEL DELIVERY - GAS 14 - 7
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1705 of 2895

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect necessary wiring into electrical con-
nectors. Connect 4±wire electrical connector to pump
module.
(2) Position sending unit to pump module. Slide
and snap into place.
(3) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER A
CONSTANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM
HOSES, FITTINGS, LINES, OR MOST COMPO-
NENTS, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used toprevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Some are equipped with
safety latch clips. Some may require the use of a spe-
cial tool for disconnection and removal. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings Removal/Installation for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, clips)
of quick-connect fittings are not serviced sepa-
rately, but new plastic spacers are available for
some types. If service parts are not available, do
not attempt to repair the damaged fitting or fuel line
(tube). If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel line (tube) assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
Also refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps.
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Safety latch clips are
used on certain components/lines. Certain fittings
may require use of a special tool for disconnection.
DISCONNECTING
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSE,
FITTING OR LINE, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST
BE RELEASED. REFER TO FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of some types of quick-connect fitting are not
serviced separately. If service parts are not avail-
able, do not attempt to repair a damaged fitting or
fuel line. If repair is necessary, replace complete
fuel line assembly.
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Fig. 4 FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT - R/I
1 - SENDING UNIT
2 - LOCK TAB
3 - TRACKS
4 - NOTCH
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1709 of 2895

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The bottom section of
the fuel pump module contains a one-way check
valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to
maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm)
when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep
the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not
operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel
pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but
liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line
between the check valve and fuel injectors.Fuel
pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled
down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module assembly is located on the
top of the fuel tank (Fig. 1). The complete assembly
contains the following components:
²A combination fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator
²A separate fuel pick-up, or inlet filter
²An electric fuel pump
²A lockring to retain pump module to tank
²A soft gasket between tank flange and module
²A fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
²Fuel line connection
The fuel gauge sending unit may be serviced sepa-
rately. If the electrical fuel pump, primary inlet filter,
fuel filter or fuel pressure regulator require service,
the fuel pump module must be replaced.
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Pump, Inlet Filter, Fuel Filter / Fuel
Pressure Regulator and Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE, THE
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
(1) Drain and remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
(2) The plastic fuel pump module locknut (Fig. 15)
is threaded onto fuel tank. Install Special Tool 6856
to locknut and remove locknut (Fig. 16). The fuel
pump module will spring up slightly when locknut is
removed.
(3) Remove module from fuel tank.
Fig. 15 FUEL PUMP MODULE (TOP)
1 - FUEL FILTER / FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ALIGNMENT ARROW
3 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
4 - LOCKNUT
5 - ALIGNMENT MARKS
Fig. 16 LOCKNUT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION -
TYPICAL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6856
2 - LOCKNUT
14 - 12 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR