Page 377 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH55
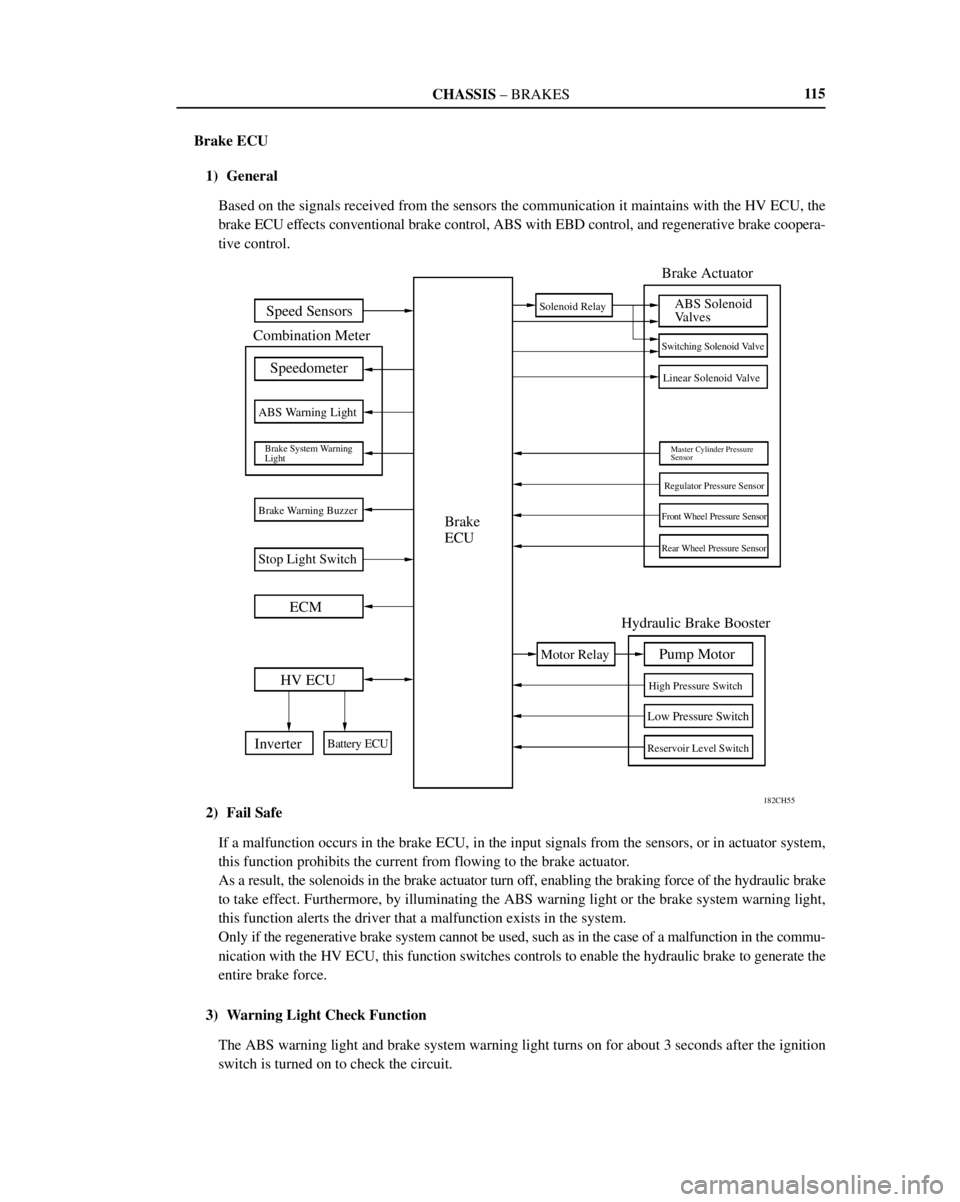
Speed Sensors
Combination Meter
Speedometer
ABS Warning Light
Brake System Warning
Light
Brake Warning Buzzer
Stop Light Switch
ECM
HV ECU
Inverter
Battery ECU
Brake
ECU
Solenoid Relay
Motor Relay
Brake Actuator
ABS Solenoid
Valves
Switching Solenoid Valve
Linear Solenoid Valve
Master Cylinder Pressure
Sensor
Regulator Pressure Sensor
Front Wheel Pressure Sensor
Rear Wheel Pressure Sensor
Pump Motor
High Pressure Switch
Low Pressure Switch
Reservoir Level Switch
Hydraulic Brake Booster11 5
Brake ECU
1) General
Based on the signals received from the sensors the communication it maintains with the HV ECU, the
brake ECU effects conventional brake control, ABS with EBD control, and regenerative brake coopera-
tive control.
2) Fail Safe
If a malfunction occurs in the brake ECU, in the input signals from the sensors, or in actuator system,
this function prohibits the current from flowing to the brake actuator.
As a result, the solenoids in the brake actuator turn off, enabling the braking force of the hydraulic brake
to take effect. Furthermore, by illuminating the ABS warning light or the brake system warning light,
this function alerts the driver that a malfunction exists in the system.
Only if the regenerative brake system cannot be used, such as in the case of a malfunction in the commu-
nication with the HV ECU, this function switches controls to enable the hydraulic brake to generate the
entire brake force.
3) Warning Light Check Function
The ABS warning light and brake system warning light turns on for about 3 seconds after the ignition
switch is turned on to check the circuit.
Page 378 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH79
Port A
Pressure
Holding
Valve
To
Wheel
Cylinder
Port B
Pressure
Preduction
ValveTo
Reservoir
and Pump
From Wheel Cylinder
182CH80 182CH81
11 6
4) Self-Diagnosis
If the brake ECU detects a malfunction in the brake system, the ABS warning light and brake system
warning light will light up and alert the driver that a malfunction has occurred. The ECU will also store
the codes of malfunctions. See the 2001 Prius Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM778U) for the DTC (Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code) check method, DTC and DTC clearance.
Brake System Control
1) ABS with EBD control
a. General
The EBD control utilizes ABS, realizing the proper brake force distribution between front and rear
wheels in accordance with the driving conditions. In addition, during cornering braking, it also controls
the brake forces of right and left front wheels, helping to maintain the vehicle stability.
The distribution of the brake force is performed under electrical control of the brake ECU, which pre-
cisely controls the brake force in accordance with the vehicle's driving conditions.
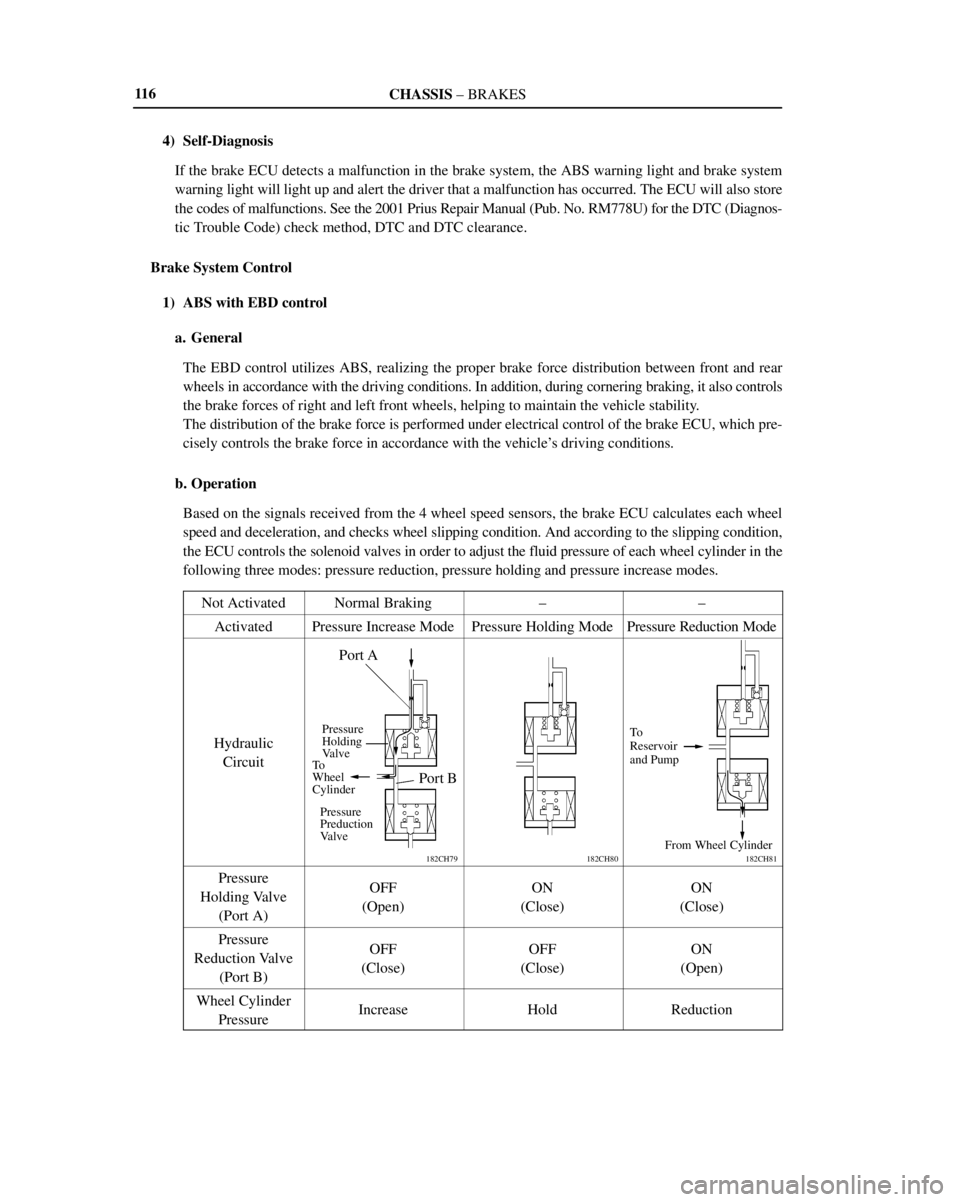
b. Operation
Based on the signals received from the 4 wheel speed sensors, the brake ECU calculates each wheel
speed and deceleration, and checks wheel slipping condition. And according to the slipping condition,
the ECU controls the solenoid valves in order to adjust the fluid pressure of each wheel cylinder in the
following three modes: pressure reduction, pressure holding and pressure increase modes.
Not Activated
Normal Braking±±
ActivatedPressure Increase ModePressure Holding ModePressure Reduction Mode
Hydraulic
Circuit
Pressure
Holding Valve
(Port A)OFF
(Open)ON
(Close)ON
(Close)
Pressure
Reduction Valve
(Port B)OFF
(Close)OFF
(Close)ON
(Open)
Wheel Cylinder
PressureIncreaseHoldReduction
Page 379 of 1943
CHASSIS ± BRAKES
182CH57
To Reservoir TankFrom Master Cylinder
Pressure
SensorPressure
Sensor
SLR
OFF
SLA
ON
SMC1
ON ONSMC2
Stroke
Simulator
ReservoirSS
ON
Pressure
SensorPressure
Sensor
SRrH
ONSFRH
ON
SRrR
ONSFRR
OFFSFLH
OFF
SFLR
OFF
Rear Wheel CylindersFront Wheel Cylinders P & B Valve11 7
� Sample of ABS control �
Page 384 of 1943
CHASSIS ± STEERING
182CH62
122
STEERING
�DESCRIPTION
�A vehicle-speed sensing type EMPS (Electric Motor-assisted Power Steering) has been adopted. The
EMPS uses the EMPS ECU to control a DC motor that is mounted on the steering gear in accordance with
the signals received from various sensors to provide power assist to the steering effort.
�A rack and pinion type steering gear and a stepless tilt steering have been adopted.
�The steering column has adopted an energy absorbing mechanism that uses energy absorbing plate.
� Specifications �
Gear Ratio (Overall)16.4 � 18.3
No. of Turns Lock to Lock3.99
Rack Stroke mm (in.)149.6 (5.89)
Page 391 of 1943
CHASSIS ± STEERING
182CH66
182CH67
Instrument Panel
Reinforcement
Main ShaftInstrument Panel
Reinforcement
Energy Absorbing Plate
Breakaway Bracket
DetachSecondary
Collision
Primary
CollisionContractDeform
After Collision
Before Collision129
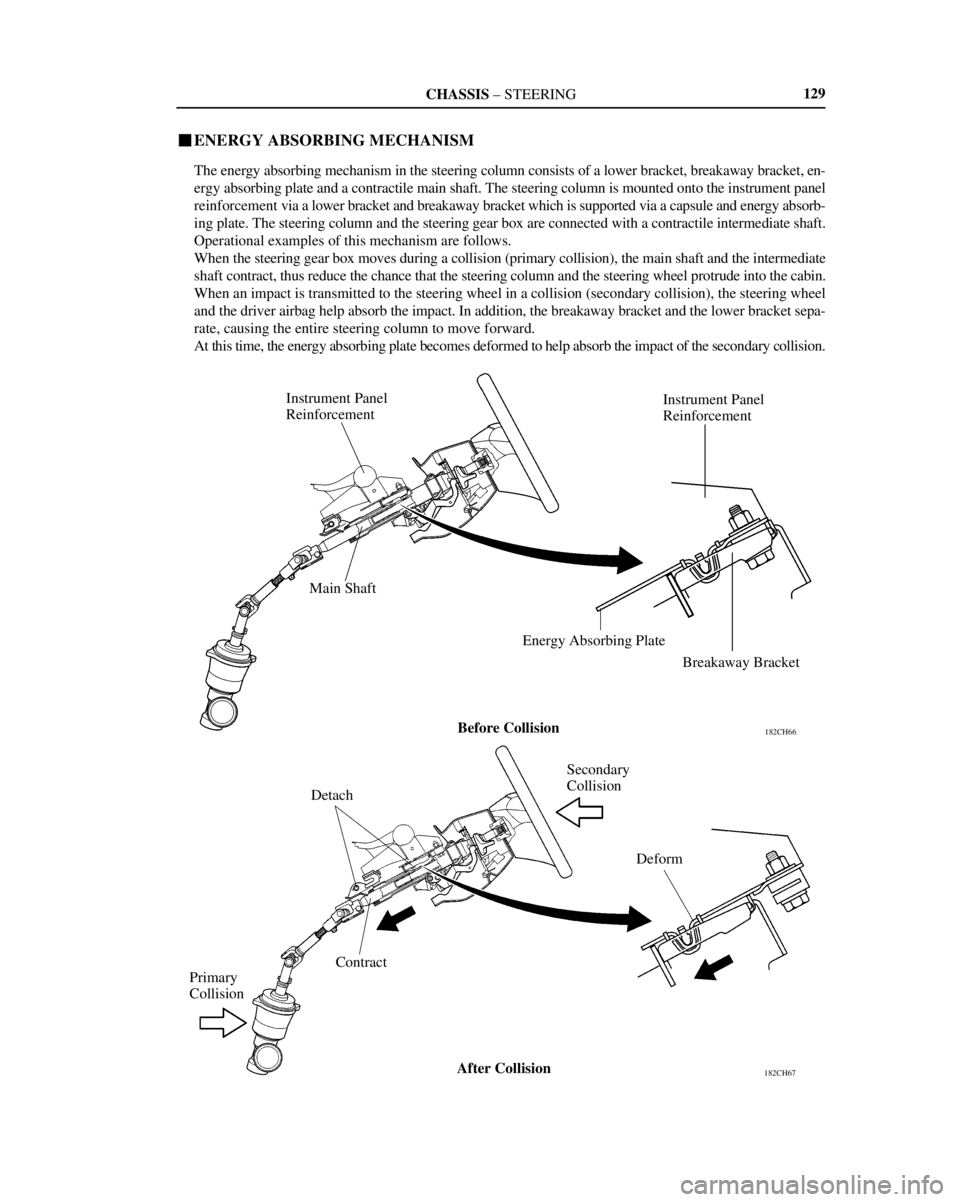
�ENERGY ABSORBING MECHANISM
The energy absorbing mechanism in the steering column consists of a lower bracket, breakaway bracket, en-
ergy absorbing plate and a contractile main shaft. The steering column is mounted onto the instrument panel
reinforcement via a lower bracket and breakaway bracket which is supported via a capsule and energy absorb-
ing plate. The steering column and the steering gear box are connected with a contractile intermediate shaft.
Operational examples of this mechanism are follows.
When the steering gear box moves during a collision (primary collision), the main shaft and the intermediate
shaft contract, thus reduce the chance that the steering column and the steering wheel protrude into the cabin.
When an impact is transmitted to the steering wheel in a collision (secondary collision), the steering wheel
and the driver airbag help absorb the impact. In addition, the breakaway bracket and the lower bracket sepa-
rate, causing the entire steering column to move forward.
At this time, the energy absorbing plate becomes deformed to help absorb the impact of the secondary collision.
Page 394 of 1943
BODY ± BODY STRUCTURE
182BO03
� Impact Absorbing Structure for Front Collision �
Front
Impact
Energy 132
�SAFETY FEATURES
1. Impact Absorbing Structure
General
The impact absorbing structure of the Prius provides a body construction that can effectively helps absorb
the energy of impact in the event of a front, or side collision. Also, it realizes a high level of occupant protec-
tion performance through the use of reinforcements and members that help to minimize cabin deformation.
Construction
1) Impact Absorbing Structure for Front Collision
In conjunction with the high level of impact absorbing structure for a front collision, the front bumper
reinforcement, the side members, the reinforcements and members that surround the cabin have been
optimally allocated.
Accordingly, the frameworks of the underbody and cabin help to absorb and dissipate the impact energy
efficiently, and to realize the minimized cabin deformation, in case of a front collision.
Page 395 of 1943
BODY ± BODY STRUCTURE
182BO04
182BO05
� Impact Absorbing Structure for Side Collision �
�
Head Impact Protection Structure �
Energy Absorbing
Urethane PadEnergy Absorbing Material
Side Impact
Protection Beams
Side Impact Energy
Side Impact Protection Beam
: Energy Absorbing Rib
: Aluminum Energy
Absorbing Material133
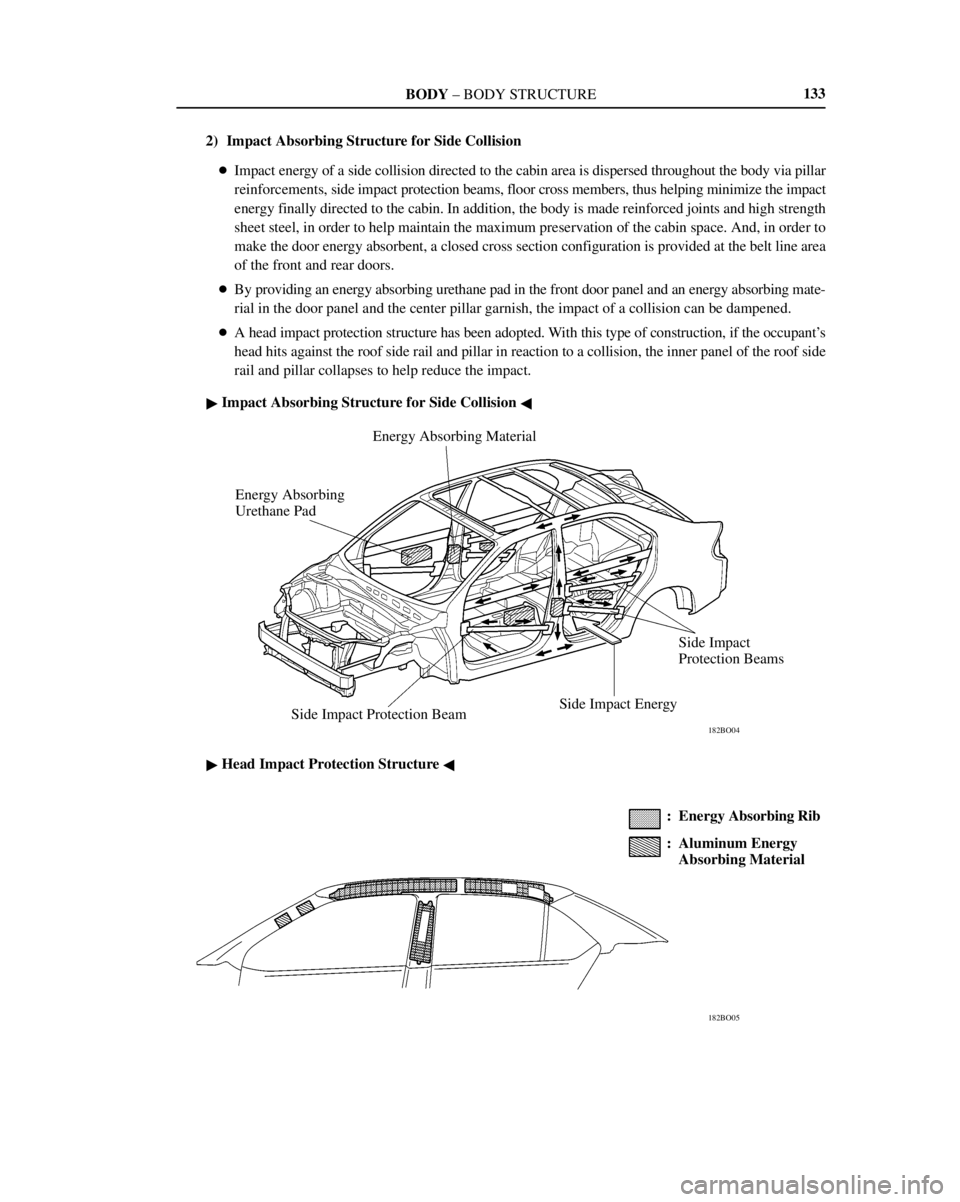
2) Impact Absorbing Structure for Side Collision
�Impact energy of a side collision directed to the cabin area is dispersed throughout the body via pillar
reinforcements, side impact protection beams, floor cross members, thus helping minimize the impact
energy finally directed to the cabin. In addition, the body is made reinforced joints and high strength
sheet steel, in order to help maintain the maximum preservation of the cabin space. And, in order to
make the door energy absorbent, a closed cross section configuration is provided at the belt line area
of the front and rear doors.
�By providing an energy absorbing urethane pad in the front door panel and an energy absorbing mate-
rial in the door panel and the center pillar garnish, the impact of a collision can be dampened.
�A head impact protection structure has been adopted. With this type of construction, if the occupant's
head hits against the roof side rail and pillar in reaction to a collision, the inner panel of the roof side
rail and pillar collapses to help reduce the impact.
Page 398 of 1943
BODY ± LOW VIBRATION AND LOW NOISE BODY
182BO09
182BO10
: Roof Silenser Pad
Foamed Urethane
Sponge
: Foamed Seal Material
: Felt
Dash Panel Silencer
Floor Silencer (RSPP)
:
136
�LOW VIBRATION AND LOW NOISE BODY
1. General
Effective application of vibration damping and noise suppresant materials reduces engine and road noise.
2. Sound Absorbing and Vibration Damping Materials
�Adoption of the dash panel silencer made the reduction of the engine and road noise and improved the
quietness in the compartment.
�Foamed urethane sponge, foamed seal material, felt and roof silencer pad are applied onto the roof panel
and pillars to reduce wind and road noise.
�The adoption of the floor silencer realized the reduction of the engine and road noise. Also, the adoption
of RSPP (Recycled Sound Proof Products) for raw material realized the improvement of recylability.