Page 274 of 3051
NBR423
1. Remove master cylinder reservoir cap.
2. Remove brake cable lock spring.
3. Release parking brake control lever, then disconnect cable
from the caliper.
4. Remove upper pin bolt.
NBR426
5. Open cylinder body downward. Then remove pads inner and
outer shims.
Standard pad thickness:
9.3 mm (0.366 in)
Pad wear limit:
2.0 mm (0.079 in)
SBR641
6. When installing new pads, push piston into cylinder body by
gently turning piston clockwise, as shown.
Carefully monitor brake fluid level because brake fluid will
return to reservoir when pushing back piston.
NBR374
7. Adjust the piston to the right angle as shown in the figure.
NBR375
8. As shown in the figure, align the piston’s concave to the pad’s
convex, then install the cylinder body to the torque member.
9. Install brake cable, brake cable mounting bolt, lock spring and
master cylinder reservoir cap.
REAR DISC BRAKE (BALL & RAMP TYPE)
Pad Replacement (Cont’d)
BR-37
Page 275 of 3051
NBR427
RemovalNLBR0152WARNING:
Clean brake pads with a vacuum dust collector to minimize the
hazard of airborne particles or other materials.
1. Remove brake cable lock spring.
2. Release parking brake control lever, then disconnect cable
from the caliper.
3. Remove torque member fixing bolts and connecting bolt.
4. Remove brake hose connecting bolt.
5. Plug off the brake hose and cylinder body to prevent air enter-
ing the system.
CAUTION:
Care should be taken as not to let:
+Air enter the cylinder body and brake hose.
+Brake fluid spill from the cylinder body and brake hose.
DisassemblyNLBR0153Remove pin bolts and pins.
NOTE:
Cylinder body can not be disassembled.
InspectionNLBR0154CALIPERNLBR0154S01CAUTION:
Do not drain any brake fluid from cylinder body. Cylinder body
can not be disassembled.
Cylinder BodyNLBR0154S0101Check cylinder body for score, rust, wear, damage or presence of
foreign materials. If any of the above conditions are observed,
replace cylinder body.
Torque MemberNLBR0154S0102Check for wear, cracks or other damage. Replace if necessary.
Pin and Pin BootNLBR0154S0104Check for wear, cracks or other damage.
Replace if any of the above conditions are observed.
REAR DISC BRAKE (BALL & RAMP TYPE)
Removal
BR-38
Page 276 of 3051

SBR219C
ROTORNLBR0154S02Rubbing SurfaceNLBR0154S0201Check rotor for roughness, cracks or chips.
RunoutNLBR0154S02021. Secure rotor to wheel hub with two nuts (M12 x 1.25).
2. Check runout using a dial indicator.
Make sure that axial end play is within the specifications
before measuring. Refer to AX section (“REAR WHEEL
BEARING”,“On-vehicle Service”).
3. Change relative positions of rotor and wheel hub so that runout
is minimized.
Maximum runout:
0.07 mm (0.0028 in)
ThicknessNLBR0154S0203Rotor repair limit:
Standard thickness
10 mm (0.39 in)
Minimum thickness
9 mm (0.35 in)
Thickness variation (At least 8 portions)
Maximum 0.02 mm (0.0008 in)
NBR374
NBR375
InstallationNLBR0156CAUTION:
+Refill with new brake fluid“DOT 4”.
+Never reuse drained brake fluid.
+Do not drain (factory) filled brake fluid from (new) caliper
assemblies.
1. Install caliper assembly.
+As shown in the figure, align the piston’s concave to the pad’s
convex, then install the cylinder body to the torque member.
2. Remove the plug from the cylinder body and brake hose.
CAUTION:
Care should be taken as not to let:
+Air enter the cylinder body and brake hose.
+Brake fluid spill from the cylinder body and brake hose.
3. Install brake hose to caliper securely.
4. Install all parts and secure all bolts.
5. Bleed air. Refer to“Bleeding Brake System”, BR-8 and“Air
Bleeding Procedure”, CL-10.
REAR DISC BRAKE (BALL & RAMP TYPE)
Inspection (Cont’d)
BR-39
Page 281 of 3051
This components controls the hydraulic circuit and increases, holds
or decreases hydraulic pressure to all or individual wheels. The
ABS actuator and electric unit can not be disassemble and will be
service as an assembly.
ABS Actuator OperationNLBR0087S0301
Inlet solenoid
valveOutlet solenoid
valve
Normal brake operation OFF (Open) OFF (Closed)Master cylinder brake fluid pressure is directly
transmitted to caliper via the inlet solenoid valve.
ABS operationPressure hold ON (Closed) OFF (Closed)Hydraulic circuit is shut off to hold the caliper brake
fluid pressure.
Pressure
decreaseON (Closed) ON (Open)Caliper brake fluid is sent to reservoir via the outlet
solenoid valve. Then it is pushed up to the master
cylinder by pump.
Pressure
increaseOFF (Open) OFF (Closed)Master cylinder brake fluid pressure is transmitted
to caliper.
DESCRIPTIONABS
System Description (Cont’d)
BR-44
Page 300 of 3051
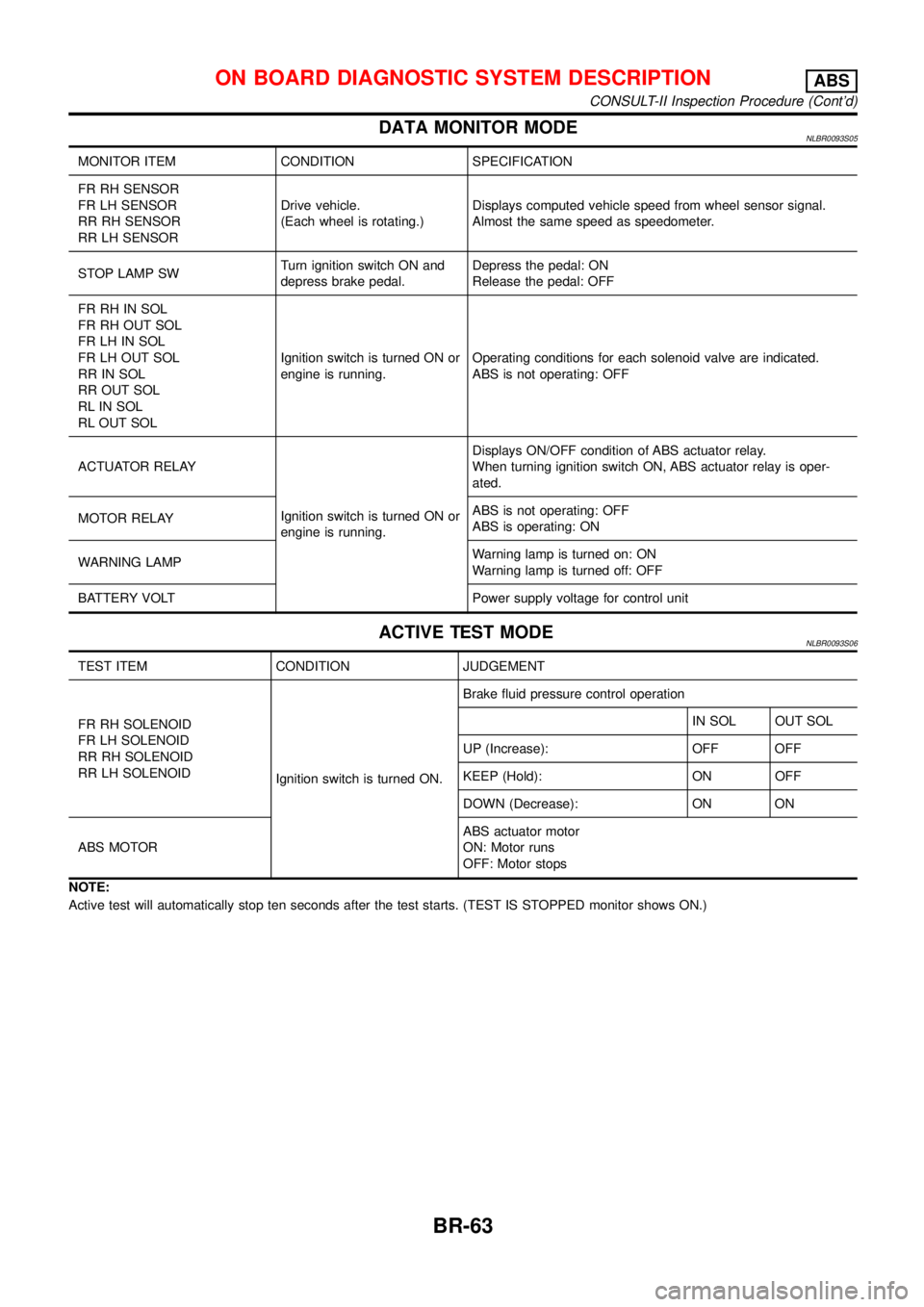
DATA MONITOR MODENLBR0093S05
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
FR RH SENSOR
FR LH SENSOR
RR RH SENSOR
RR LH SENSORDrive vehicle.
(Each wheel is rotating.)Displays computed vehicle speed from wheel sensor signal.
Almost the same speed as speedometer.
STOP LAMP SWTurn ignition switch ON and
depress brake pedal.Depress the pedal: ON
Release the pedal: OFF
FR RH IN SOL
FR RH OUT SOL
FR LH IN SOL
FR LH OUT SOL
RR IN SOL
RR OUT SOL
RL IN SOL
RL OUT SOLIgnition switch is turned ON or
engine is running.Operating conditions for each solenoid valve are indicated.
ABS is not operating: OFF
ACTUATOR RELAY
Ignition switch is turned ON or
engine is running.Displays ON/OFF condition of ABS actuator relay.
When turning ignition switch ON, ABS actuator relay is oper-
ated.
MOTOR RELAYABS is not operating: OFF
ABS is operating: ON
WARNING LAMPWarning lamp is turned on: ON
Warning lamp is turned off: OFF
BATTERY VOLT Power supply voltage for control unit
ACTIVE TEST MODENLBR0093S06
TEST ITEM CONDITION JUDGEMENT
FR RH SOLENOID
FR LH SOLENOID
RR RH SOLENOID
RR LH SOLENOID
Ignition switch is turned ON.Brake fluid pressure control operation
IN SOL OUT SOL
UP (Increase): OFF OFF
KEEP (Hold): ON OFF
DOWN (Decrease): ON ON
ABS MOTORABS actuator motor
ON: Motor runs
OFF: Motor stops
NOTE:
Active test will automatically stop ten seconds after the test starts. (TEST IS STOPPED monitor shows ON.)
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONABS
CONSULT-II Inspection Procedure (Cont’d)
BR-63
Page 301 of 3051

SEF233G
SEF234G
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses for Quick
and Accurate Repair
NLBR0094INTRODUCTIONNLBR0094S01The ABS system has an electronic control unit to control major
functions. The control unit accepts input signals from sensors and
instantly drives actuator. It is essential that both kinds of signals are
proper and stable. It is also important to check for conventional
problems: such as air leaks in the booster or lines, lack of brake
fluid, or other problems with the brake system.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a problem that occurs intermit-
tently rather than continuously. Most intermittent problems are
caused by poor electric connections or faulty wiring. In this case,
careful checking of suspicious circuits may help prevent the
replacement of good parts.
A visual check only may not find the cause of the problems, so a
road test should be performed.
Before undertaking actual checks, take just a few minutes to talk
with a customer who approaches with a ABS complaint. The cus-
tomer is a very good source of information on such problems;
especially intermittent ones. Through the talks with the customer,
find out what symptoms are present and under what conditions
they occur.
Start your diagnosis by looking for“conventional”problems first.
This is one of the best ways to troubleshoot brake problems on an
ABS controlled vehicle. Also check related Service Bulletins for
information.
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS—INTRODUCTIONABS
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses for Quick and Accurate Repair
BR-64
Page 302 of 3051
Preliminary CheckNLBR0095
1 CHECK BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
Check brake fluid level in reservoir tank.
Low fluid level may indicate brake pad wear or leakage from brake line.
NBR376
Is brake fluid filled between MAX and MIN lines on reservoir tank and/or has brake fluid been contaminated?
Ye s©GO TO 2.
No©Repair. GO TO 2.
2 CHECK BRAKE LINE
Check brake line for leakage.
SBR389C
Is leakage present at or around brake lines, tubes or hoses or are any of these parts cracked or damaged?
Ye s©GO TO 3.
No©Repair. GO TO 3.
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS—BASIC INSPECTIONABS
Preliminary Check
BR-65
Page 304 of 3051
5 RECHECK BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
Check brake fluid level in reservoir tank again.
NBR376
Is brake fluid filled between MAX and MIN lines on reservoir tank and/or has brake fluid been contaminated?
Ye s©GO TO 6.
No©Fill up brake fluid.
6 CHECK WARNING LAMP ACTIVATION
Check warning lamp activation.
SBR759E
Does warning lamp turn on when ignition switch is turned“ON”?
Ye s©GO TO 7.
No©Check fuse, warning lamp bulb and warning lamp circuit.
7 CHECK WARNING LAMP DEACTIVATION
Check warning lamp for deactivation after engine is started.
Does warning lamp turn off when engine is started?
Ye s©GO TO 8.
No©Go to Self-diagnosis. Refer to BR-56, 58.
8 DRIVE VEHICLE
Drive vehicle at speeds over 30 km/h (19 MPH) for at least one minute.
Does warning lamp remain off after vehicle has been driven at 30 km/h (19 MPH) for at least one minute?
Ye s©END
No©Go to Self-diagnosis. Refer to BR-56, 58.
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS—BASIC INSPECTIONABS
Preliminary Check (Cont’d)
BR-67