2001 NISSAN ALMERA N16 Starting
[x] Cancel search: StartingPage 7 of 2493

SEF289H
+Before starting repairs which do not require battery power:
Turn off ignition switch.
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
SGI233
+To prevent serious burns:
Avoid contact with hot metal parts.
Do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot.
SGI234
+Before servicing the vehicle:
Protect fenders, upholstery and carpeting with appropriate cov-
ers.
Take caution that keys, buckles or buttons do not scratch paint.
+Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly.
+Replace oil seals, gaskets, packings, O-rings, locking washers,
cotter pins, self-locking nuts, etc. with new ones.
+Replace inner and outer races of tapered roller bearings and
needle bearings as a set.
+Arrange the disassembled parts in accordance with their
assembled locations and sequence.
+Do not touch the terminals of electrical components which use
microcomputers (such as ECMs).
Static electricity may damage internal electronic components.
+After disconnecting vacuum or air hoses, attach a tag to indi-
cate the proper connection.
+Use only the fluids and lubricants specified in this manual.
+Use approved bonding agent, sealants or their equivalents
when required.
+Use tools and recommended special tools where specified for
safe and efficient service repairs.
+When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust
systems, check all affected lines for leaks.
+Dispose of drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning parts in
an appropriate manner.
PRECAUTIONS
Precautions (Cont'd)
GI-5
Page 159 of 2493
NJEM0051
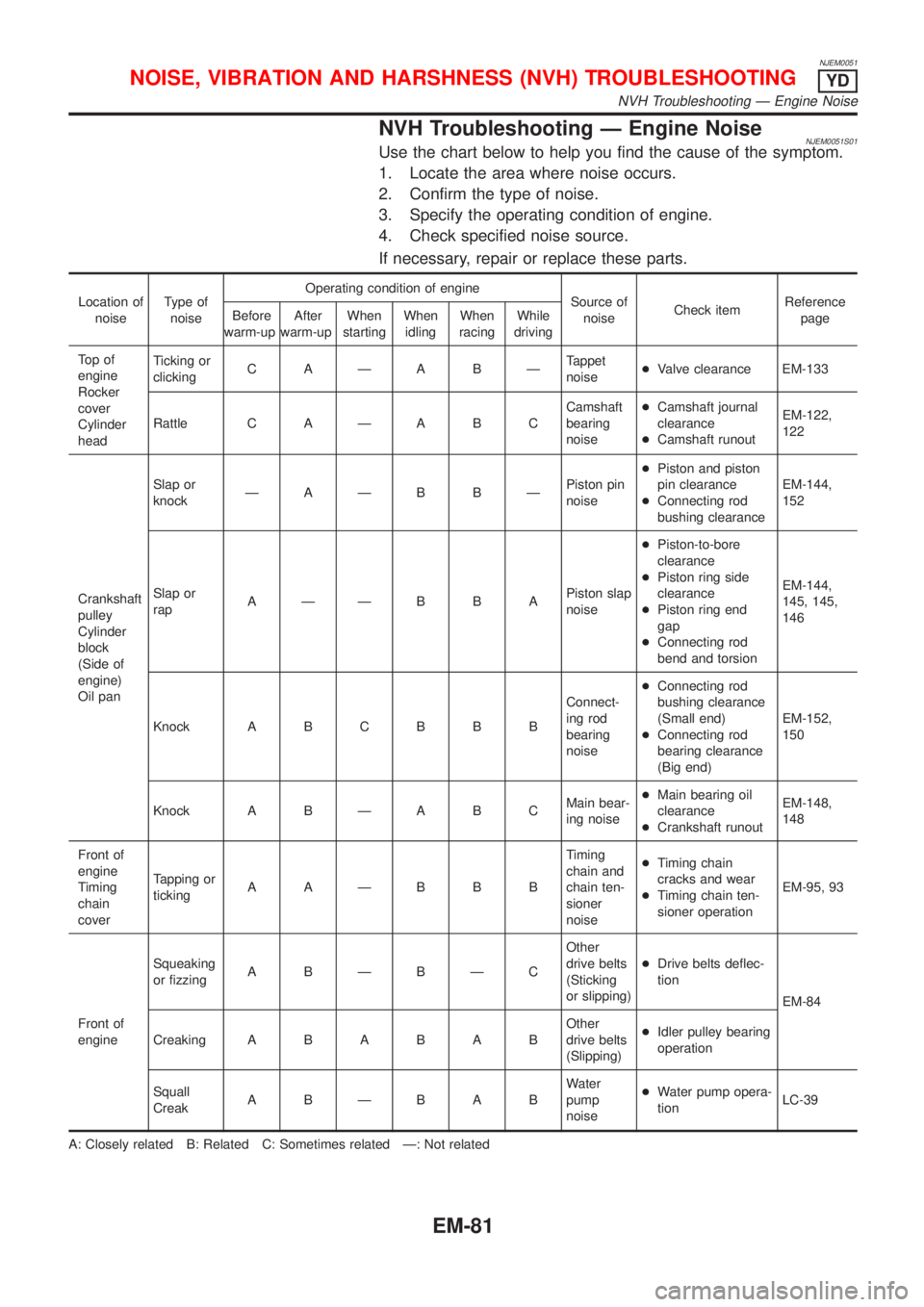
NVH Troubleshooting Ð Engine NoiseNJEM0051S01Use the chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom.
1. Locate the area where noise occurs.
2. Confirm the type of noise.
3. Specify the operating condition of engine.
4. Check specified noise source.
If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
Location of
noiseType of
noiseOperating condition of engine
Source of
noiseCheck itemReference
page Before
warm-upAfter
warm-upWhen
startingWhen
idlingWhen
racingWhile
driving
To p o f
engine
Rocker
cover
Cylinder
headTicking or
clickingC AÐA BÐTappet
noise+Valve clearance EM-133
Rattle C A Ð A B CCamshaft
bearing
noise+Camshaft journal
clearance
+Camshaft runoutEM-122,
122
Crankshaft
pulley
Cylinder
block
(Side of
engine)
Oil panSlap or
knockÐAÐB BÐPiston pin
noise+Piston and piston
pin clearance
+Connecting rod
bushing clearanceEM-144,
152
Slap or
rapAÐÐB B APiston slap
noise+Piston-to-bore
clearance
+Piston ring side
clearance
+Piston ring end
gap
+Connecting rod
bend and torsionEM-144,
145, 145,
146
Knock A B C B B BConnect-
ing rod
bearing
noise+Connecting rod
bushing clearance
(Small end)
+Connecting rod
bearing clearance
(Big end)EM-152,
150
Knock A B Ð A B CMain bear-
ing noise+Main bearing oil
clearance
+Crankshaft runoutEM-148,
148
Front of
engine
Timing
chain
coverTapping or
tickingAAÐBBBTiming
chain and
chain ten-
sioner
noise+Timing chain
cracks and wear
+Timing chain ten-
sioner operationEM-95, 93
Front of
engineSqueaking
or fizzingA BÐBÐCOther
drive belts
(Sticking
or slipping)+Drive belts deflec-
tion
EM-84
CreakingABABABOther
drive belts
(Slipping)+Idler pulley bearing
operation
Squall
CreakABÐBABWater
pump
noise+Water pump opera-
tionLC-39
A: Closely related B: Related C: Sometimes related Ð: Not related
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGYD
NVH Troubleshooting Ð Engine Noise
EM-81
Page 203 of 2493
SEM934C
JEM157G
VALVE SEATSNJEM0065S10+Before starting this check, confirm that the dimensions of valve
guides and valves are as specified.
+Apply red lead primer on contacting surfaces of valve seat and
of valve face to examine the conditions of contacting surfaces.
+Check that the paint on contacting surfaces is continuous
along the entire circumference.
+If there are abnormal indications, grind the valve and check the
contact again. If abnormal indications still persist, replace
valve seat.
SEM795A
REPLACING VALVE SEAT FOR SERVICE PARTSNJEM0065S111. Bore out old seat until it collapses. Boring should not continue
beyond the bottom face of the seat recess in cylinder head. Set
the machine depth stop to ensure this.
2. Ream cylinder head recess for service valve seat.
Oversize [0.5 mm (0.020 in)]:
Intake 30.500 - 30.516 mm (1.2008 - 1.2014 in)
Exhaust 29.500 - 29.516 mm (1.1614 - 1.1620 in)
Be sure to ream in circles concentric to the valve guide
center.
This will enable valve seat to fit correctly.
CYLINDER HEADYD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-125
Page 216 of 2493

SEM189G
+Make sure that support is stable with the use of safety
blocks.
16. Install hooks of lifting chain into engine slingers and tighten
chain so that engine still remains on transmission jacks with-
out being lifted up.
17. Remove engine mount insulator RH.
18. Remove through-bolt of engine mount insulator LH.
19. Remove bolts securing center member at front and rear.
JEM190G
20. Carefully lower transmission jacks in accordance with the low-
ering pace of the hoist, and remove engine and transaxle
assembly from vehicle.
+While working, check that no parts of engine assembly
interfere with adjacent parts on the vehicle.
+While working, make sure that parts requiring disconnec-
tion are not left connected, and that no parts interfere with
vehicle.
+To prevent vehicle from falling down, perform operation
carefully so that the center of gravity of the vehicle will not
shift.
21. Remove center member.
+Before starting removal operation, first place the assem-
bly on a level surface and securely support the bottom
surface with wood blocks. Using a hoist, lift engine
slingers, and make sure the assembly is stable.
22. Separate engine and transaxle.
INSTALLATIONNJEM0069S02Install in the reverse order of removal, observing the following:
+While installing, be careful to keep mount insulators free of oil
smear and damage.
+When parts require specified installation directions/positions,
install by using the identifying marks indicating up or front.
+While keeping the mount insulators free of twists or distortions,
start tightening from the through-bolt on the engine mount
insulator LH. This mount is used as the reference position.
ENGINE ASSEMBLYYD
Removal and Installation (Cont'd)
EM-138
Page 292 of 2493

+While filling, if coolant from engine side spills out, be sure to
reconnect the heater hose.
+Fill coolant to the level of the radiator cap at a rate of 2!(1-3/4
Imp qt)/min or lower.
(Close the air relief plugs in order starting with the location from
where the coolant began spilling out.)
CAUTION:
If the filling rate is too fast, this could lead to air being mixed
in the coolant. Be sure to fill the coolant slowly according to
the rate indicated above.
+Replace the copper washer of the air bleeding plug.
Air relief plug:
: 6.7 - 7.9 N´m (0.68 - 0.81 kg-m, 59 - 70 in-lb)
+Use genuine Nissan anti-freeze coolant or equivalent
mixed with water (distilled or demineralized).
SMA182B
SMA412B
Refer to MA-20, ªRECOMMENDED FLUIDS AND LUBRI-
CANTSº.
Engine coolant capacity (With reservoir tank):
8.7!(7-5/8 Imp qt)
Reservoir tank capacity:
0.7!(5/8 Imp qt)
+Pour coolant through coolant filler neck slowly to allow air
in system to escape.
4. Fill radiator and reservoir tank to specified level.
5. Warm up engine to normal operating temperature without
radiator cap installed.
+If coolant overflows radiator filler hole, install radiator cap.
6. Run engine at 3,000 rpm for 10 seconds and return to idle
speed with radiator cap installed.
+Repeat two or three times.
Watch coolant temperature gauge so as not to overheat the
engine.
7. Stop engine and cool it down.
+Cool down using a fan to reduce the time.
+If necessary, refill radiator up to filler neck with coolant.
8. Refill reservoir tank to MAX level line with coolant.
9. Repeat steps 4 through 7 two or more times with radiator cap
installed until coolant level no longer drops.
10. Check cooling system for leaks with engine running.
11. Warm up engine, and check for sound of coolant flow while
running engine from idle up to 3,000 rpm with heater tempera-
ture controller set at several positions between COOL and
HOT.
+Sound may be noticeable at heater water cock.
12. If sound is heard, bleed air from cooling system by repeating
steps 4 through 7 until coolant level no longer drops
+Clean excess coolant from engine.
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEMYD
Changing Engine Coolant (Cont'd)
LC-44
Page 315 of 2493

SEF605X
+Do not operate fuel pump when there is no fuel in lines.
+Tighten fuel hose clamps to the specified torque.
SEF709Y
+Do not depress accelerator pedal when starting.
+Immediately after starting, do not rev up engine unneces-
sarily.
+Do not rev up engine just prior to shutdown.
SEF708Y
+When installing C.B. ham radio or a mobile phone, be sure
to observe the following as it may adversely affect elec-
tronic control systems depending on installation location.
1)Keep the antenna as far as possible from the electronic
control units.
2)Keep the antenna feeder line more than 20 cm (8 in) away
from the harness of electronic controls.
Do not let them run parallel for a long distance.
3)Adjust the antenna and feeder line so that the standing-
wave ratio can be kept smaller.
4)Be sure to ground the radio to vehicle body.
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble DiagnosisNJEC0006When you read Wiring diagrams, refer to the following:
+GI-12, ªHOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMSº
+EL-10, ªPOWER SUPPLY ROUTINGº for power distribution
circuit
When you perform trouble diagnosis, refer to the following:
+GI-31, ªHOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUP IN TROUBLE
DIAGNOSISº
+GI-21, ªHOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR
AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENTº
PRECAUTIONSQG
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System (Cont'd)
EC-19
Page 325 of 2493

Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0014Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0014S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Fuel injec-
tion & mix-
ture ratio
controlInjector Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Throttle position sensorThrottle position
Throttle valve idle position
PNP switch Gear position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Ignition switch Start signal
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Knock sensor Engine knocking condition
Electrical load Electrical load signal
Battery Battery voltage
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
Heated oxygen sensor 2 (rear)* Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
* Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
Basic Multiport Fuel Injection SystemNJEC0014S02The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of
time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). The amount of fuel injected is a program value in the
ECM memory. The program value is preset by engine operating conditions. These conditions are determined
by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from both the camshaft position sensor and the mass air
flow sensor.
Various Fuel Injection Increase/Decrease CompensationNJEC0014S03In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance under various oper-
ating conditions as listed below.
+During warm-up
+When starting the engine
+During acceleration
+Hot-engine operation
+When selector lever is changed from ªNº to ªDº (A/T models)
+High-load, high-speed operation
+During deceleration
+During high engine speed operation
+During high vehicle speed operation (M/T models)
+Extremely high engine coolant temperature
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
EC-29
Page 326 of 2493

Mixture Ratio Feedback Control (Closed loop control)NJEC0014S04
SEF336WA
The mixture ratio feedback system provides the best air-fuel mixture ratio for driveability and emission con-
trol. The three way catalyst can then better reduce CO, HC and NOx emissions. This system uses a heated
oxygen sensor 1 (front) in the exhaust manifold to monitor if the engine operation is rich or lean. The ECM
adjusts the injection pulse width according to the sensor voltage signal. For more information about the heated
oxygen sensor 1 (front), refer to EC-176. This maintains the mixture ratio within the range of stoichiometric
(ideal air-fuel mixture).
This stage is referred to as the closed loop control condition.
Heated oxygen sensor 2 (rear) is located downstream of the three way catalyst. Even if the switching char-
acteristics of the heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) shift, the air-fuel ratio is controlled to stoichiometric by the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor 2 (rear).
Open Loop ControlNJEC0014S05The open loop system condition refers to when the ECM detects any of the following conditions. Feedback
control stops in order to maintain stabilized fuel combustion.
+Deceleration and acceleration
+High-load, high-speed operation
+Malfunction of heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) or its circuit
+Insufficient activation of heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) at low engine coolant temperature
+High engine coolant temperature
+During warm-up
+When starting the engine
Mixture Ratio Self-learning ControlNJEC0014S06The mixture ratio feedback control system monitors the mixture ratio signal transmitted from the heated oxy-
gen sensor 1 (front). This feedback signal is then sent to the ECM. The ECM controls the basic mixture ratio
as close to the theoretical mixture ratio as possible. However, the basic mixture ratio is not necessarily con-
trolled as originally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot film) and charac-
teristic changes during operation (i.e., injector clogging) directly affect mixture ratio.
Accordingly, the difference between the basic and theoretical mixture ratios is monitored in this system. This
is then computed in terms of ªinjection pulse durationº to automatically compensate for the difference between
the two ratios.
ªFuel trimº refers to the feedback compensation value compared against the basic injection duration. Fuel trim
includes short term fuel trim and long term fuel trim.
ªShort term fuel trimº is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the mixture ratio at its theoretical
value. The signal from the heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) indicates whether the mixture ratio is RICH or LEAN
compared to the theoretical value. The signal then triggers a reduction in fuel volume if the mixture ratio is
rich, and an increase in fuel volume if it is lean.
ªLong term fuel trimº is overall fuel compensation carried out long-term to compensate for continual deviation
of the short term fuel trim from the central value. Such deviation will occur due to individual engine differences,
wear over time and changes in the usage environment.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System (Cont'd)
EC-30