2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER wheel torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel torquePage 1592 of 4284

HALF SHAFT - REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT - REAR
DESCRIPTION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................16
HALF SHAFT..........................16
REMOVAL..............................16INSTALLATION...........................17
SPECIFICATIONS........................18
CV BOOT - INNER/OUTER
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................20
HALF SHAFT - REAR
DESCRIPTION
The inner and outer joints of both half shaft
assemblies are tripod joints. The tripod joints are
true constant velocity (CV) joint assemblies, which
allow for the changes in half shaft length through
the jounce and rebound travel of the rear suspension.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer
CV joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to deter-
mine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both half shafts is bolted
rear differential assembly's output flanges. The outer
CV joint has a stub shaft that is splined into the
wheel hub and retained by a steel hub nut.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT
VEHICLE INSPECTION
(1) Check for grease in the vicinity of the inboard
tripod joint and outboard CV joint; this is a sign of
inner or outer joint seal boot or seal boot clamp dam-
age.
(2) A light film of grease may appear on the right
inner tripod joint seal boot; this is considered normal
and should not require replacement of the seal boot.
NOISE AND/OR VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise and/or a vibration in turns could
be caused by one of the following conditions:
²Damaged outer CV or inner tripod joint seal
boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the loss
and/or contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint.
²Noise may also be caused by another component
of the vehicle coming in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of one of the following
conditions:²A torn seal boot on the inner or outer joint of the
half shaft assembly.
²A loose or missing clamp on the inner or outer
joint of the half shaft assembly.
²A damaged or worn half shaft CV joint.
SHUDDER OR VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This problem could be a result of:
²A worn or damaged half shaft inner tripod joint.
²A sticking tripod joint spider assembly (inner tri-
pod joint only).
²Improper wheel alignment. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of:
²Foreign material (mud, etc.) packed on the back-
side of the wheel(s).
²Out of balance tires or wheels. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
²Improper tire and/or wheel runout. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
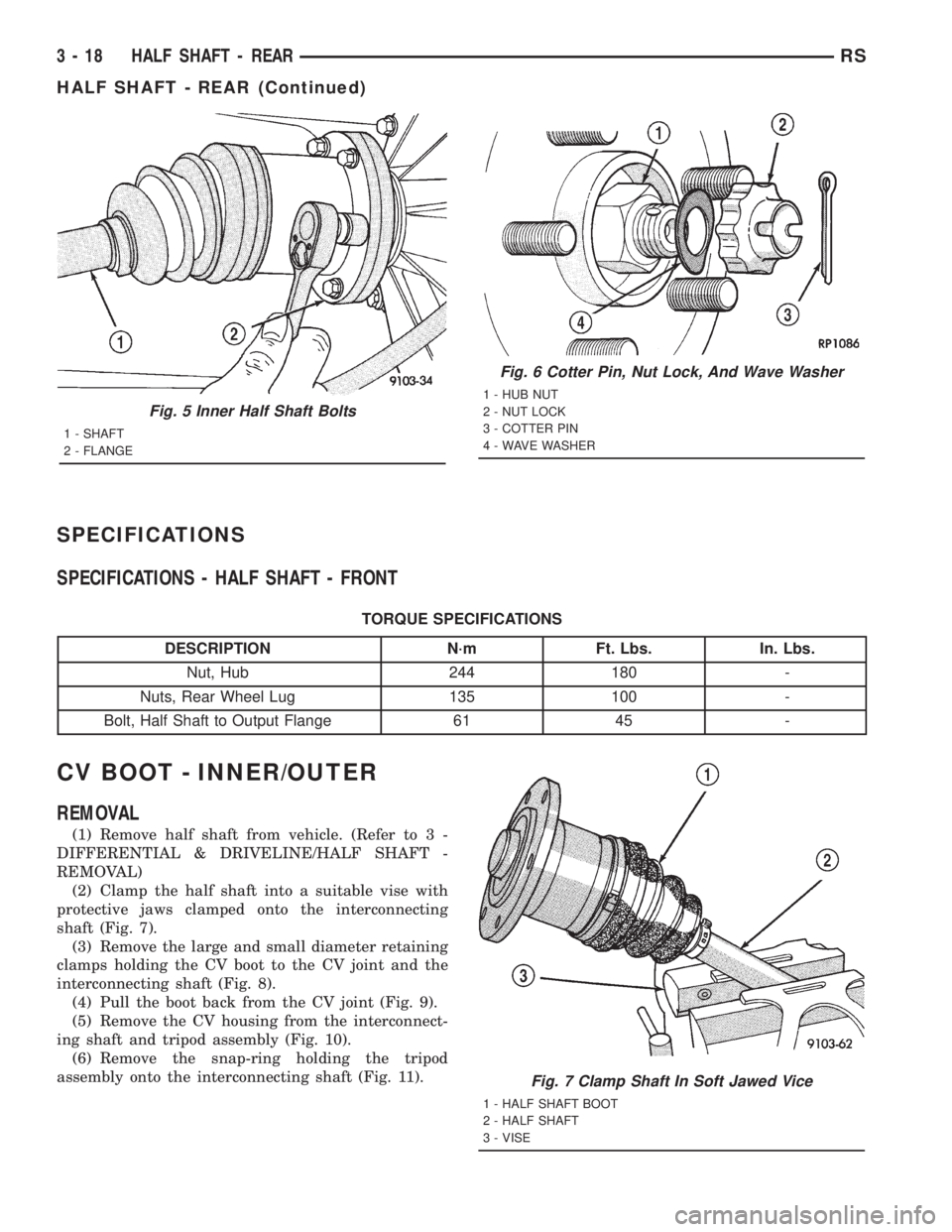
REMOVAL
(1) Lift vehicle on hoist so that the wheels hang
freely.
(2) Remove rear wheel.
(3) Remove cotter pin, nut lock, and wave washer
(Fig. 1).
(4) Remove hub nut and washer.
CAUTION: The half shaft outer CV joint, when
installed, acts as a bolt and secures the hub/bear-
ing assembly. If the vehicle is to be supported or
moved on its wheels, install and torque a bolt
through the hub. This will ensure that the hub/bear-
ing assembly cannot loosen.
(5) Remove inner half shaft retaining bolts (Fig. 2).
3 - 16 HALF SHAFT - REARRS
Page 1593 of 4284

(6) The half shaft is spring loaded. Compress inner
half shaft joint slightly and pull downward to clear
rear differential output flange. Then pull half shaft
assembly outward to remove (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the outer CV joint stub shaft through
the hub bearing (Fig. 4).
(2) The half shaft is spring loaded. Compress inner
half shaft joint slightly and push upward until the
inner CV joint flange engages the rear differential
output flange.(3) Install the inner half shaft retaining bolts (Fig.
5). Torque the bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft.lbs.).
(4) Install the half shaft washer and hub nut.
Torque the hub nut to 244 N´m (180 ft.lbs.).
(5) Install the wave washer, nut lock, and a new
cotter pin (Fig. 6). Be sure to wrap the cotter pin
prongs tightly around the hub nut lock.
(6) Install rear wheel. Torque the lug nuts to 135
N´m (100 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 1 Cotter Pin, Nut Lock, And Wave Washer
1 - HUB NUT
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - WAVE WASHER
Fig. 2 Inner Half Shaft Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 3 Half Shaft Removal
1 - BRAKE BACKING PLATE
2 - HALF SHAFT
Fig. 4 Half Shaft Installation
1 - BRAKE BACKING PLATE
2 - HALF SHAFT
RSHALF SHAFT - REAR3-17
HALF SHAFT - REAR (Continued)
Page 1594 of 4284
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - HALF SHAFT - FRONT
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Nut, Hub 244 180 -
Nuts, Rear Wheel Lug 135 100 -
Bolt, Half Shaft to Output Flange 61 45 -
CV BOOT - INNER/OUTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove half shaft from vehicle. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(2) Clamp the half shaft into a suitable vise with
protective jaws clamped onto the interconnecting
shaft (Fig. 7).
(3) Remove the large and small diameter retaining
clamps holding the CV boot to the CV joint and the
interconnecting shaft (Fig. 8).
(4) Pull the boot back from the CV joint (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove the CV housing from the interconnect-
ing shaft and tripod assembly (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove the snap-ring holding the tripod
assembly onto the interconnecting shaft (Fig. 11).
Fig. 5 Inner Half Shaft Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 6 Cotter Pin, Nut Lock, And Wave Washer
1 - HUB NUT
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - WAVE WASHER
Fig. 7 Clamp Shaft In Soft Jawed Vice
1 - HALF SHAFT BOOT
2 - HALF SHAFT
3 - VISE
3 - 18 HALF SHAFT - REARRS
HALF SHAFT - REAR (Continued)
Page 1602 of 4284

REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................26
OPERATION.............................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE NOISE.........27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE OPERATION....29
REMOVAL..............................29
DISASSEMBLY...........................30
ASSEMBLY.............................32
INSTALLATION...........................36
SPECIFICATIONS........................37
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................37
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................38
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION...........................43
OPERATION.............................43FLUID - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................44
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY FLUID CHANGE . . 44
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................44
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING FLUID
CHANGE..............................44
VISCOUS COUPLER
DESCRIPTION...........................45
OPERATION.............................45
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................47
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................47
OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL..............................49
INSTALLATION...........................50
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The rear driveline module assembly (Fig. 1) con-
sists of four main components:
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Viscous Coupling
²Differential Assembly
²Torque Arm
The viscous coupling and bi-directional overrun-
ning clutch are contained within an overrunning
clutch housing, which fastens to the differential
assembly. The overrunning clutch housing and differ-
ential assembly have unique fluid sumps, each
requiring their own type and capacity of fluid. The
overrunning clutch housing requires MopartATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equiv-
alent. The differential assembly requires
Driveline module service is limited to the following
components:
²Differential Assembly (serviced only as assem-
bly)
²Viscous Coupling
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Overrunning Clutch Housing
²Seals (Input Flange, Output Flange, Overrun-
ning Clutch Housing O-rings)
²Input Flange/Shield²Torque Arm
²Vents
²FastenersOPERATION
The primary benefits of All Wheel Drive are:
²Superior straight line acceleration, and corner-
ing on all surfaces
²Better traction and handling under adverse con-
ditions, resulting in improved hill climbing ability
and safer driving.
The heart of the system is an inter-axle viscous
coupling. The vehicle retains predominantly front-
wheel drive characteristics, but the All Wheel Drive
capability takes effect when the front wheels start to
slip. Under normal level road, straight line driving,
100% of the torque is allocated to the front wheels.
The viscous coupling controls and distributes torque/
power to the rear wheels. The viscous coupling trans-
mits torque to the rear wheels in proportion of the
amount of the slippage at the front wheels. Thais
variable torque distribution is automatic with no
driver inputs required. The coupling is similar to a
multi-plate clutch. It consists of a series of closely
spaced discs, which are alternately connected to the
front and rear drive units. The unit is totally sealed
and partially filled with silicone fluid. There is no
3 - 26 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
Page 1603 of 4284

adjustment, maintenance or fluid checks required
during the life of the unit.
The overrunning clutch allows the rear wheels to
overrun the front wheels during a rapid front wheel
lock braking maneuver. The overrunning action pre-
vents any feed-back of front wheel braking torque to
the rear wheels. It also allows the braking system to
control the braking behavior as a two wheel drive
(2WD) vehicle.
The overrunning clutch housing has a separate oil
sump and is filled independently from the differen-
tial. The fill plug is located on the side of the over-
running clutch case. When filling the overrunning
clutch with lubricant use MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equivalent.
The differential assembly contains a conventional
open differential with hypoid ring gear and pinion
gear set. The hypoid gears are lubricated by SAE
80W-90 gear lubricant.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE NOISE
Different sources can be the cause of noise that the
rear driveline module assembly is suspected of mak-
ing. Refer to the following causes for noise diagnosis.
DRIVELINE MODULE ASSEMBLY NOISE
The most important part of driveline module ser-
vice is properly identifying the cause of failures and
noise complaints. The cause of most driveline module
failures is relatively easy to identify. The cause of
driveline module noise is more difficult to identify.
If vehicle noise becomes intolerable, an effort
should be made to isolate the noise. Many noises that
are reported as coming from the driveline module
may actually originate at other sources. For example:
Fig. 1 AWD Driveline Module Assembly
1 - TORQUE ARM
2 - INPUT FLANGE
3 - FLANGE NUT
4 - WASHER
5 - SHIELD
6 - VENT
7 - O-RING
8 - WASHER
9 - BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (BOC)
10 - VISCOUS COUPLER11 - SHIM (SELECT)
12 - O-RING
13 - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
14 - PLUG-DIFFERENTIAL FILL
15 - PLUG-OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING DRAIN
16 - SNAP RING
17 - BEARING
18 - OVERRUNING CLUTCH HOUSING
19 - SEAL-INPUT FLANGE
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1605 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE OPERATION
Driveline module operation requires relatively
straight-forward diagnosis. Refer to the following
chart:
DRIVELINE MODULE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Rear wheels not
overrunning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft turning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
2) Viscous coupling failure 2) Replace viscous coupling
3) Rear differential failure 3) Replace the rear differential
assembly
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft not turning1) Power transfer unit failure. 1) Replace power transfer unit
components as necessary
Vibration at all speeds,
continuous torque transfer1) Mis-matched tires, worn tires on
front axle.1) Replace worn or incorrect
(mis-matched) tires with same
make and size
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Drain fluid from overrunning clutch housing
and/or differential assembly if necessary.
(3) Remove propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(4) Disconnect left and right rear halfshafts from
output flanges (Fig. 2).(5) Remove torque arm mount to body bolts.
(6) Position transmission jack to driveline module
assembly and secure assembly to jack.
(7) Remove two driveline module-to-body bolts
(Fig. 3).
(8) Lower driveline module from vehicle and
remove from jack.
Fig. 2 Half Shaft Mounting Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 3 Rear Drive Line Module Assembly Mounting
Bolts
1 - DRIVELINE MODULE RETAINING BOLT (2)
2 - RUBBER ISOLATOR
3 - WASHER
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-29
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1613 of 4284
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Driveline Module-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Bolt, Halfshaft-to-Ouput Flange 61 45 Ð
Bolt, Overrunning Clutch Housing-to-
Differential60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm-to-Differential Assembly 60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm Mount-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Nut, Input Flange 135 100 Ð
Plug, Differential Drain/Fill 35 26 Ð
Plug, Overrunning Clutch Housing Drain/Fill 30 22 Ð
Vent, Differential/Overrunning Clutch
Housing12 Ð 110
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS
BI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The bi-directional overrunning clutch (BOC) (Fig.
28) works as a mechanical disconnect between the
front and rear axles, preventing torque from being
transferred from the rear axle to the front. The BOC
is a simply an overrunning clutch which works in
both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations. This
means that when the output (the rear axle) is rotat-
ing faster in one direction than the input (front axle),
there is no torque transmission. But when the input
speed is equal to the output speed, the unit becomes
locked. The BOC provides significant benefits regard-
ing braking stability, handling, and driveline durabil-
ity. Disconnecting the front and the rear driveline
during braking helps to maintain the braking stabil-
ity of an AWD vehicle. In an ABS/braking event, the
locking of the rear wheels must be avoided for stabil-
ity reasons. Therefore brake systems are designed to
Tool 6958
Tool 8493
Tool 8802
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-37
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1614 of 4284

lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on a
slippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
through to the rear wheels. The rear driveline mod-
ule, with the BOC, will perform the same as a front
wheel drive vehicle during these events. The gear
ratio offset between the front and rear differentials
force the BOC into the overrunning mode most of the
time. This allows BOC to significantly reduce the
rolling resistance of the vehicle, which improves fuel
consumption, allows the downsizing of the driveline
components, and prevents the PTU and propshaft
joints from overheating.
OPERATION
In order to achieve all-wheel drive operation in
reverse, the overrunning clutch locking functional
direction must be reversible. The bi-directional over-
running clutch (BOC) changes the operational mode
direction depending on the propeller shaft direction.
The propeller shaft rotates in the clockwise (when
viewed from the front) direction when the vehicle is
moving forward, which indexes the BOC to the for-
ward overrunning position. When the vehicle is in
reverse, the propeller shaft will rotate counter-clock-
wise and index the BOC to the reverse overrunning
position.
The BOC acts as a mechanical stator. It is active
(transmitting torque), or it is not active and in over-
running mode (not transmitting torque). This ªall or
nothingº approach to torque transfer would cause a
sudden application of all available power to the rear
wheels, which is not desirable. Therefore it is run in
series with a viscous coupler to smooth, dampen, and
limit the transmission of torque to the rear axle and
to prevent a step style torque input to the rear axle.
STEADY STATE, LOW TO MODERATE SPEED, NO
FRONT WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
During normal driving conditions, (no wheel slip),
the inner shaft (front axle) and outer race (viscous
coupler) are running at different speeds due to the
different gear ratios between the front and rear dif-
ferentials. In this condition, the outer race is always
spinning faster (overdriving between 5-32 rpm) than
the inner shaft. When the BOC (Fig. 29) is running
under these conditions, at low vehicle speeds the
drag shoes and the cage keep the rollers up on the
left side (forward side) of the inner shaft flats. This is
what is known as ªoverrunning mode.º Notice that
when the clutch is in overrunning mode, the rollers
are spinning clockwise and with the outer race, thus
no torque is being transferred.
NOTE: Low speed, forward and reverse operation is
identical, just in opposite directions. (Fig. 29)
shows forward direction in reverse the rollers are
on the other side of the flats due to a reversal of
the cage force.
TRANSIENT CONDITION (BOC LOCKED), FRONT
WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
When the front wheels lose traction and begin to
slip, the propeller shaft and rear axle pinion speed
difference decreases to zero. At this point the input
shaft (cam) becomes the driving member of the BOC
(Fig. 30), compressing the rollers against the outer
race. This locks the input shaft with the outer race
and transmits torque to the housing of the viscous
coupler, that in turn transmits torque to the rear
axle pinion. It should also be noted that when the
device is locked, the inner shaft and the outer race
are rotating at the same speed. The rollers are
pinched at this point and will stay locked until a
torque reversal (no front wheel slip) occurs. When
locked, the viscous coupler slips during the torque
transfer and the amount of torque transferred is
dependent on the coupling characteristic and the
amount of front wheel slip.
3 - 38 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)