2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER reset
[x] Cancel search: resetPage 3215 of 4284
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
VERIFICATION
(1) Place gearshift lever in gated park (P).
(2) Attempt to move vehicle by rocking back and
forth on level ground. If vehicle does not move,
attempt to start engine. If engine starts, the park
position is correct.
(3) Set parking brake.
(4) Turn key to on/run and depress brake pedal.
Place gearshift lever in neutral (N).
(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine starts in
both neutral (N) or park (P), gearshift cable is
adjusted properly. No adjustment is required.
(6) If engine does not start in either park (P) or
neutral (N), perform adjustment procedure.
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in gated park (P) and
remove ignition key.
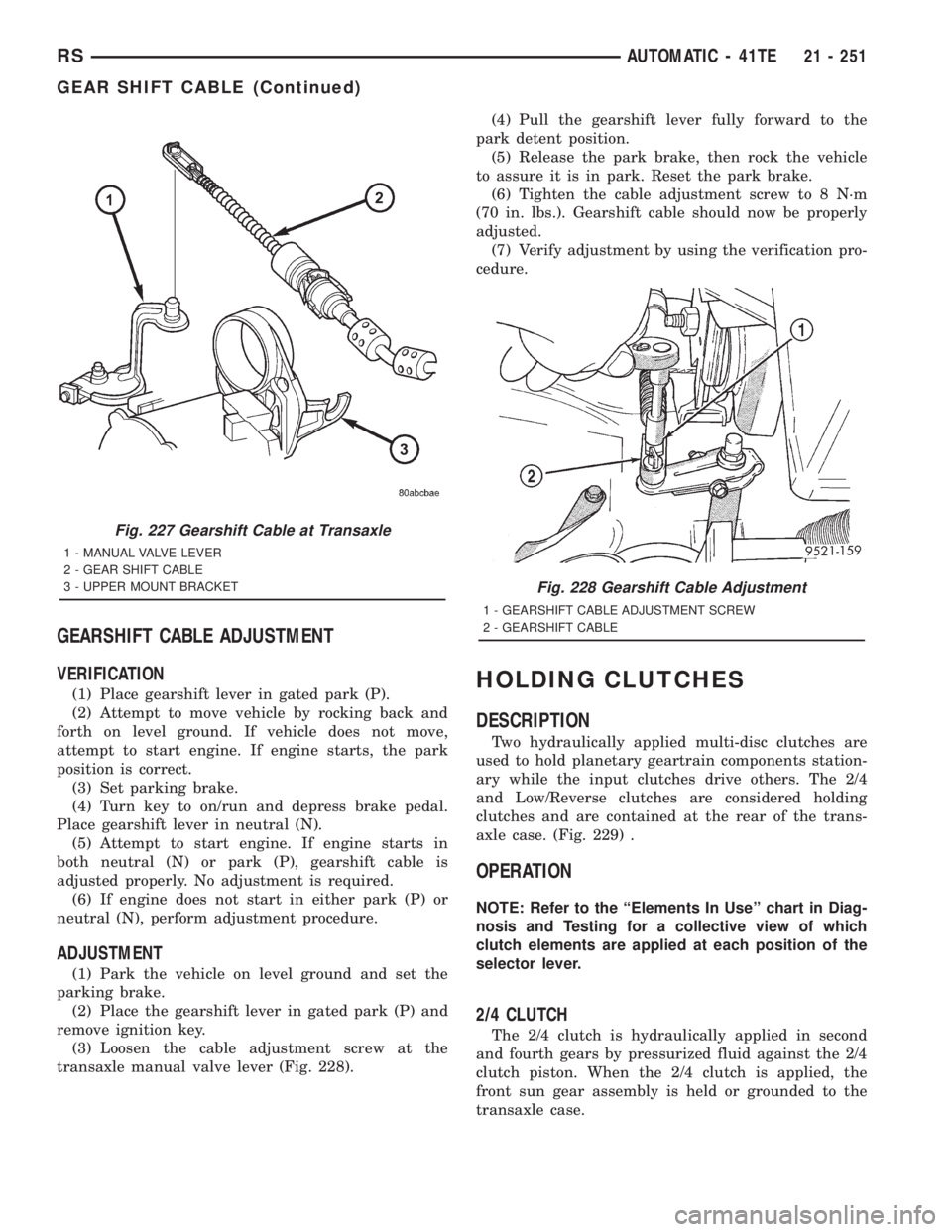
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 228).(4) Pull the gearshift lever fully forward to the
park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park. Reset the park brake.
(6) Tighten the cable adjustment screw to 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.). Gearshift cable should now be properly
adjusted.
(7) Verify adjustment by using the verification pro-
cedure.
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION
Two hydraulically applied multi-disc clutches are
used to hold planetary geartrain components station-
ary while the input clutches drive others. The 2/4
and Low/Reverse clutches are considered holding
clutches and are contained at the rear of the trans-
axle case. (Fig. 229) .
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the ªElements In Useº chart in Diag-
nosis and Testing for a collective view of which
clutch elements are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
2/4 CLUTCH
The 2/4 clutch is hydraulically applied in second
and fourth gears by pressurized fluid against the 2/4
clutch piston. When the 2/4 clutch is applied, the
front sun gear assembly is held or grounded to the
transaxle case.
Fig. 227 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 228 Gearshift Cable Adjustment
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT SCREW
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 251
GEAR SHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 3250 of 4284

The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If torque conveter assembly is being
replaced, it is necessary to restart the TCC Break-In
Strategy. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If torque conveter is being replaced, it is
necessary to restart the TCC Break-In Strategy.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 339). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(10) If torque conveter was replaced, it is neces-
sary to reset the TCC Break-In Strategy. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 339 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3251 of 4284

TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 340) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is
supplied to the solenoid pack and the transmission is
in ªlimp-inº mode. After a controller reset (ignition
key turned to the ªrunº position or after cranking
engine), the TCM energizes the relay. Prior to this,
the TCM verifies that the contacts are open by check-
ing for no voltage at the switched battery terminals.
After this is verified, the voltage at the solenoid pack
pressure switches is checked. After the relay is ener-
gized, the TCM monitors the terminals to verify that
the voltage is greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle and
can only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 341) .
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 342) .
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 341)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the TCM
as a combination of open and closed switches. Each
shift lever position has an assigned combination of
switch states (open/closed) that the TCM receives
from four sense circuits. The TCM interprets this
information and determines the appropriate trans-
axle gear position and shift schedule.
Fig. 340 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERYFig. 341 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 287
Page 3798 of 4284

3.2.3 OTHER CONTROLS
CHARGING SYSTEM
The charging system is turned on when the
engine is started and ASD relay energized. When
the ASD relay is on, ASD output voltage is supplied
to the ASD sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is
connected in some cases, through the PCM and
supplied to one of the generator field terminals
(Gen Source +). All others, the Gen field is con-
nected directly to the ASD output voltage. The
amount of current produced by the generator is
controlled by the Electronic Voltage Regulator
(EVR) circuitry, in the PCM. Battery temperature is
determined from IAT. This temperature along with
sensed line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary the
battery charging rate. This is done by cycling the
ground path to the other generator field terminal
(Gen field driver).
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
The PCM controls vehicle speed by operation of
the speed control servo vacuum and vent solenoids.
Energizing the vacuum solenoid applies vacuum to
the servo to increase throttle position. Operation of
the vent solenoid slowly releases the vacuum allow-
ing throttle position to decrease. A special dump
solenoid allows immediate release of throttle posi-
tion caused by braking, cruise control switch turned
off, shifting into neutral, excessive RPM (tires spin-
ning) or ignition off.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP SYSTEM (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection pump is a device that pressur-
izes the evaporative system to determine if there
are any leaks. When certain conditions are met, the
PCM will activate the pump and start counting
pump strokes. If the pump stops within a calibrated
number of strokes, the system is determined to be
normal. If the pump does not stop or stops too soon,
a DTC will be set.
3.2.4 PCM OPERATING MODES
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
wide open throttle. There are several different
modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two types of engine control operation:
open loopandclosed loop.
Inopen loopoperation, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset program-
ming. Inputs from the heated oxygen sensors are
not monitored.Inclosed loopoperation, the PCM monitors the
inputs from the heated oxygen sensors. This input
indicates to the PCM whether or not the calculated
injector pulse width results in the ideal air-fuel
ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel. By monitoring
the exhaust oxygen content through the oxygen
sensor, the PCM can fine tune injector pulse width.
Fine tuning injector pulse width allows the PCM to
achieve the lowest emission levels while maintain-
ing optimum fuel economy.
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
and wide open throttle modes are open loop modes.
Under most operating conditions, closed loop modes
occur with the engine at operating temperature.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ENGINE OFF) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
1. The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic
fuel strategy.
2. The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input.
The PCM modifies fuel strategy based on this
input.
When the key is in the on position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the auto shutdown relay
and fuel pump relay are not energized. Therefore,
voltage is not supplied to the fuel pump, ignition
coil, and fuel injectors.
Engine Start-up ModeÐ This is an open loop
mode. The following actions occur when the starter
motor is engaged:
1. The auto shutdown and fuel pump relays are
energized. If the PCM does not receive the cam-
shaft and crankshaft signal within approxi-
mately one second, these relays are de-
energized.
2. The PCM energizes all fuel injectors until it
determines crankshaft position from the cam-
shaft and crankshaft signals. The PCM deter-
mines crankshaft position within one engine
revolution. After the camshaft position has been
determined, the PCM energizes the fuel injectors
in sequence. The PCM adjusts the injector pulse
width and synchronizes the fuel injectors by
controlling the fuel injectors' ground paths.
3. Once the engine idles within 64 rpm of its target
engine speed, the PCM compares the current
MAP sensor value with the value received dur-
ing the ignition switch on (zero rpm) mode. A
diagnostic trouble code is written to PCM mem-
ory if a minimum difference between the two
values is not found.
4
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 3802 of 4284

powertrain control module checks that circuit or
function. Procedures in this manual verify if the
DTC is a hard code at the beginning of each test.
When it is not a hard code, an intermittent test
must be performed.
DTC's that are for Euro Stage III OBD monitors
will not set with just the ignition key on. Comparing
these to non-emission DTC's, they will seem like an
intermittent. These DTC's require a set of parame-
ters to be performed (The DRBIIItpre-test screens
will help with this for MONITOR DTC's), this is
called a TRIP. All Euro Stage III OBD DTCs will be
set after one or in some cases two trip failures, and
the MIL will be turned on. These DTC's require
three successful, no failures, TRIPS to extinguish
the MIL, followed by 40 warm-up cycles to erase the
DTC.
3.3.2 INTERMITTENT CODE
A diagnostic trouble code that is not there every
time the PCM checks the circuit is an intermittent
DTC. Most intermittent DTC's are caused by wiring
or connector problems. Defects that come and go
like this are the most difficult to diagnose; they
must be looked for under specific conditions that
cause them. The following checks may assist you in
identifying a possible intermittent problem:
²Visually inspect related wire harness connectors.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded
terminals.
²Visually inspect the related harnesses. Look for
chafed, pierced, or partially broken wire.
²Refer to any technical service bulletins that may
apply.
²Use the DRBIIItdata recorder or co-pilot.
3.3.3 DISTANCE SINCE MI SET
The Euro Stage III OBD directive requires that
the distance traveled by the vehicle while theMIis
activated must be available at any instant through
the serial port on the standard data link connector.
This feature works as follows:1. If the MI is illuminated due to a fault, the
distance count is updated (i.e. it is counting).
2. If there is a9stale9MI fault (i.e. the fault is still
frozen in memory but the MI has heen extin-
guished due to 3 good trips), the distance count is
held (i.e. frozen).
3. If the distance count is being held due to (Item
2.) and the fault is cleared, the distance is
cleared (set to zero).
4. If the distance count is being held due to (Item
2.) and another MI occurs, the distance count is
reset (to 0) and begins updating anew.
5. If a fault occurs while the MI is already illumi-
nated due to a previous fault (the distance count
is updating), then the distance count continues
to update w/out interruption.
6. If the MI is flashing due to activate misfire and
there is and9active9fault (i.e. matured fault for
which 3 good trips have not occurred), the dis-
tance count behaves as the MI in ON.
7. If the MI is flashing due to active misfire and
there is no9active9fault (i.e. the MI is flashing
for a 1 malf.), the distance count behaves as if
the MI is off (because it is not yet a matured
fault).
8. The distance count is cleared whenever the fault
is cleared. (Via 40 warm up cycles, or via scan
tool).
3.3.4 HANDLING NO DTC PROBLEMS
Symptom checks cannot be used properly unless
the driveability problem characteristic actually
happens while the vehicle is being tested.
Select the symptom that most accurately de-
scribes the vehicle's driveability problem and then
perform the test routine that pertains to this symp-
tom. Perform each routine test in sequence until the
problem is found. For definitions, see Section 6.0
Glossary Of Terms.
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSTIC TEST
HARD START CHECKING THE FUEL PRESSURE
CHECKING THE ECT SENSOR
CHECKING THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CHECKING IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
CHECKING IAT SENSOR
8
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 3810 of 4284

Symptom:
P0622-GENERATOR FIELD NOT SWITCHING PROPERLY
When Monitored and Set Condition:
P0622-GENERATOR FIELD NOT SWITCHING PROPERLY
When Monitored: With the ignition on. Engine running.
Set Condition: When the PCM tries to regulate the generator field with no result during
monitoring.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
WIRING HARNESS INTERMITTENT
INSPECT WIRING HARNESS
ASD RELAY OUTPUT CIRCUIT OPEN
GENERATOR FIELD DRIVER CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND
GENERATOR FIELD DRIVER CIRCUIT OPEN
GENERATOR
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, actuate the Generator Field Driver circuit.
Using a 12-volt test light connected to ground, backprobe the Generator Field Driver
circuit in the back of the Generator.
Does the test light illuminate brightly and flash?All
Ye s®Go To 2
No®Go To 4
2 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIItactuate the Generator Field Driver circuit.
Wiggle the wiring harness from the Generator to PCM.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTC's.
Did the DTC reset?All
Ye s®Repair as necessary .
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER - 3.
No®Go To 3
3 Turn the ignition off.
Using the schematic as a guide, inspect the Wiring and Connectors.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s®Repair as necessary.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER - 3.
No®Test Complete.
16
CHARGING
Page 3819 of 4284

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
5 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRB III, display the VIN that is programmed in the PCM.
Was the correct VIN programmed into the PCM?All
Ye s®Go To 6
No®Replace and program the Powertrain Control Module in accor-
dance with the Service Information.
Perform SKIS VERIFICATION TEST.
6 Turn the ignition off.
Replace and program the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module in accordance with the
Service Information.
Turn the ignition on.
With the DRB III, erase all SKIM and PCM DTCs.
Attempt to start and idle the engine.
With the DRB III, read the PCM DTCs.
Does the DRB III display this code?All
Ye s®Replace and program the Powertrain Control Module in accor-
dance with the Service Information.
Perform SKIS VERIFICATION TEST.
No®Test Complete.
7NOTE: This DTC could have been set if the SKIM harness connector was
disconnected, or if the SKIM was replaced recently.
NOTE: All keys that the customer uses for this vehicle must be tested to
verify they are operating properly.
Turn the ignition on.
Verify the correct VIN is programmed into the PCM and SKIM.
Turn the ignition off.
With the next customer key turn the ignition key on and crank the engine to start.
With the DRB III, read the PCM DTCs. Look for P1685
Is the Starts Since Set counter for DTC P1685 displayed and equal to 0?All
Ye s®Replace the Ignition Key.
Perform SKIS VERIFICATION TEST.
No®Test Complete.
NOTE: If this DTC cannot be reset, it could have been an actual theft
attempt.
25
COMMUNICATION
P1685-WRONG OR INVALID KEY MSG RECEIVED FROM SKIM Ð
Continued
Page 3822 of 4284

Symptom:
P1695-NO CCD/J1850 MESSAGE FROM BODY CONTROL MODULE
When Monitored and Set Condition:
P1695-NO CCD/J1850 MESSAGE FROM BODY CONTROL MODULE
When Monitored: With the ignition on. Battery voltage greater than 10.0 volts.
Set Condition: No BUS messages recieved from the BCM for 20 seconds.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
INTERMITTENT CONDITION
COMMUNICATE WITH BCM
PCM
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, erase DTCs.
Cycle the ignition key on and off several times.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTC's.
Does the DTC reset?All
Ye s®Go To 2
No®Go To 3
2 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, attempt to communicate with the BCM.
Can communication be established with the BCM?All
Ye s®Replace and program the Powertrain Control Module in accor-
dance with the Service Information.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER-1.
No®Refer to the Communication Category and perform the appropri-
ate symptom related to no communication with BCM.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER-1.
28
COMMUNICATION