2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 3197 of 4284

OPERATION
The function of an accumulator is to cushion the
application of a frictional clutch element. When pres-
surized fluid is applied to a clutch circuit, the appli-
cation force is dampened by fluid collecting in the
respective accumulator chamber against the piston
and spring(s). The intended result is a smooth, firm
clutch application.
AUTOSTICK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Autostick is a driver-interactive transaxle feature
that offers manual gear shifting capability. The con-
trol switch is part of the transaxle gear shift lever as
shown in (Fig. 175). It can only be serviced by replac-
ing the gearshift lever assembly. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/GEAR SHIFT LEVER -
REMOVAL)
OPERATION
When the shift lever is moved into the Autostick
position (as indicated by the Shift Lever Position
Indicator in the cluster), the transaxle remains in
whatever gear it was using before Autostick was acti-
vated. The TCM sends a 5 volt signal through the
switch and then monitors the signal for voltage drop.
Each switch state (driver command) results in a spe-
cific voltage reading sensed by the TCM. The TCM
then determines transaxle operation (upshift/down-
shift/OD Lockout) based on their corresponding volt-
age. Refer to the following chart for corresponding
switch states and voltage readings:
Switch State Voltage Reading
Autostick DOWN
depressed0.3V-1.6V
Autostick UP depressed 1.6V-2.8V
Overdrive OFF9Lockout9
depressed2.8V-3.8V
All switches open 3.8V-4.8V
-Voltage values <.3V and >4.8V are considered
INVALID and will result in a DTC
Moving the switch up causes an upshift and mov-
ing the switch down causes a downshift. The instru-
ment cluster will illuminate the selected gear. The
vehicle can be launched in 1st, 2nd, or 3rd gear while
in the Autostick mode. The speed control is operable
Fig. 173 Low/Reverse Accumulator Assembly
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - SEAL RINGS
3 - RETURN SPRINGS
4 - (NOTE NOTCH)
Fig. 174 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
Fig. 175 Autostick Switch Location (if equipped)
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 233
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 3236 of 4284
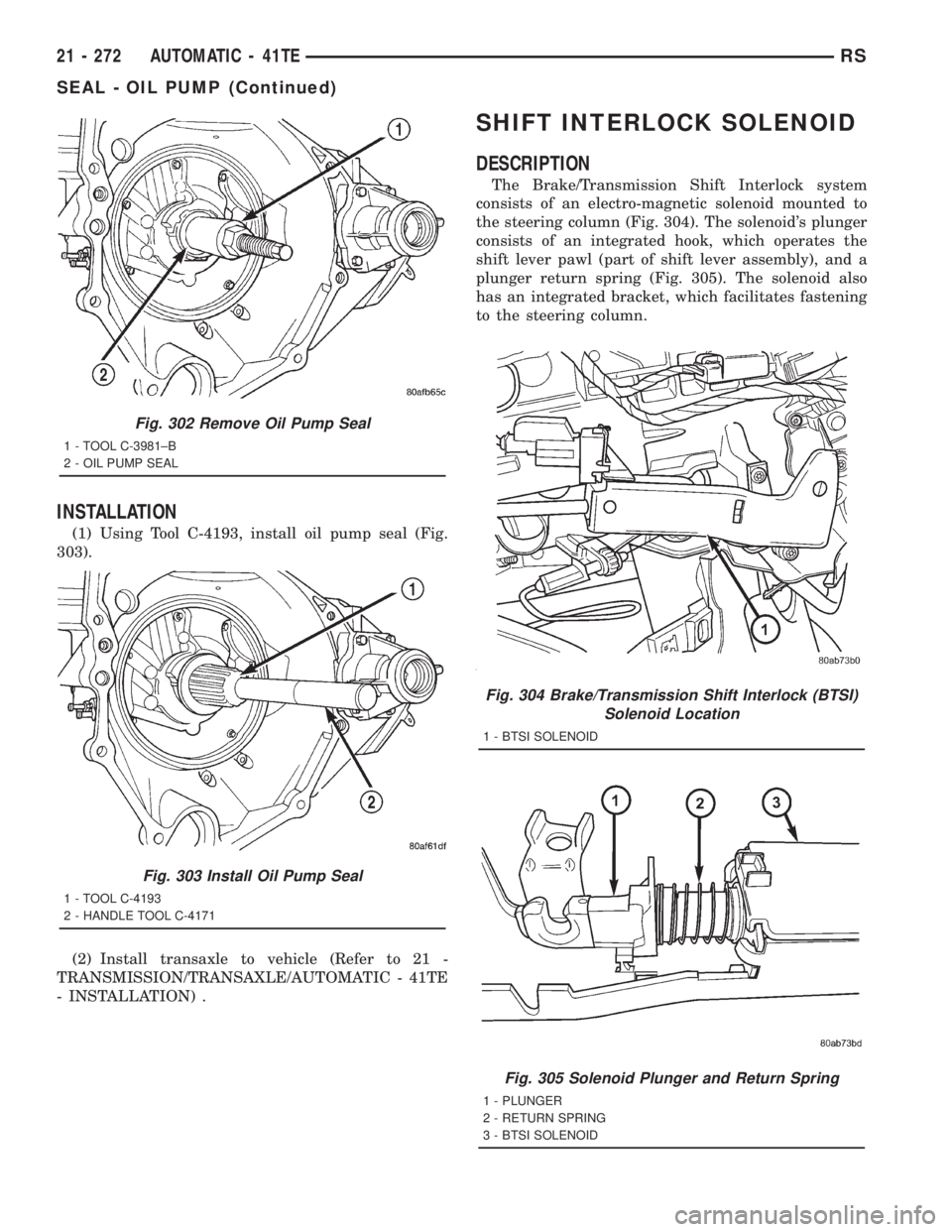
INSTALLATION
(1) Using Tool C-4193, install oil pump seal (Fig.
303).
(2) Install transaxle to vehicle (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE
- INSTALLATION) .
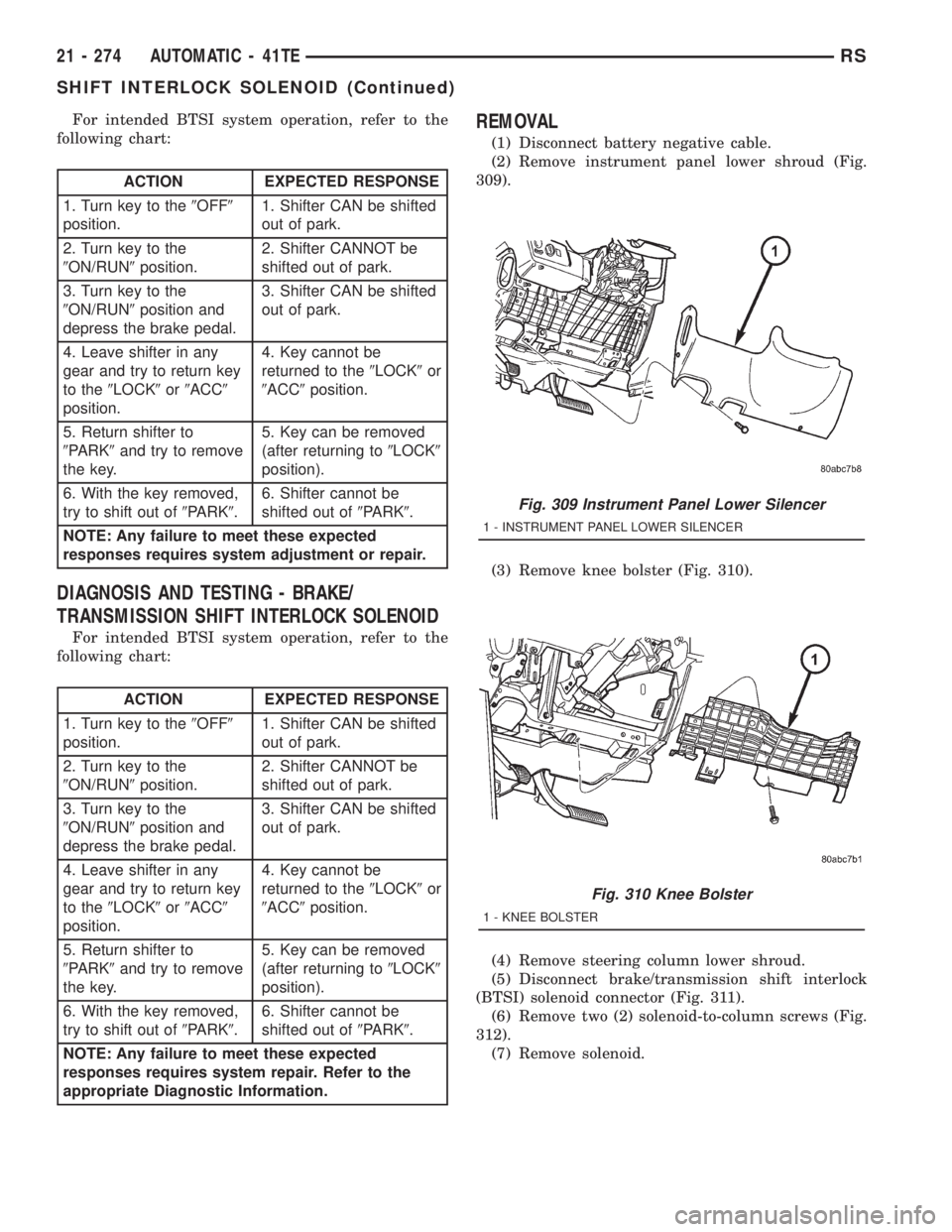
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock system
consists of an electro-magnetic solenoid mounted to
the steering column (Fig. 304). The solenoid's plunger
consists of an integrated hook, which operates the
shift lever pawl (part of shift lever assembly), and a
plunger return spring (Fig. 305). The solenoid also
has an integrated bracket, which facilitates fastening
to the steering column.
Fig. 302 Remove Oil Pump Seal
1 - TOOL C-3981±B
2 - OIL PUMP SEAL
Fig. 303 Install Oil Pump Seal
1 - TOOL C-4193
2 - HANDLE TOOL C-4171
Fig. 304 Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid Location
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
Fig. 305 Solenoid Plunger and Return Spring
1 - PLUNGER
2 - RETURN SPRING
3 - BTSI SOLENOID
21 - 272 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
SEAL - OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 3238 of 4284
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
309).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 310).
(4) Remove steering column lower shroud.
(5) Disconnect brake/transmission shift interlock
(BTSI) solenoid connector (Fig. 311).
(6) Remove two (2) solenoid-to-column screws (Fig.
312).
(7) Remove solenoid.
Fig. 309 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 310 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
21 - 274 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3240 of 4284
(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 315).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
316).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)SOLENOID/PRESSURE
SWITCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly (Fig. 317)
is external to the transaxle and mounted to the
transaxle case. The assembly consists of four sole-
noids that control hydraulic pressure to the LR/CC,
2/4, OD, and UD friction elements. The reverse
clutch is controlled by line pressure from the manual
valve in the valve body. The solenoids are contained
within the Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly, and
can only be serviced by replacing the assembly.
The solenoid assembly also contains pressure
switches that monitor and send hydraulic circuit
information to the TCM. Likewise, the pressure
switches can only be service by replacing the assem-
bly.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The TCM energizes or operates the solenoids individ-
ually by grounding the return wire of the solenoid
needed. When a solenoid is energized, the solenoid
valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or closed
(vented or applied), depending on its default operat-
Fig. 315 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 316 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCERFig. 317 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly
1 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 276 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3363 of 4284

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
TIRE AND WHEEL VIBRATION..............1
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................4
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE...............4
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING.......6
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION..............6
REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................7
TIRES
DESCRIPTION............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................9
TIRE NOISE............................9
TIRE/VEHICLE LEAD.....................9
TIRE WEAR PATTERNS..................11
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS...............11
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................11
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES.............11
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION...........................12TIRE LEAK REPAIRING..................12
CLEANING..............................13
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................13
WHEEL INSPECTION....................13
CLEANING..............................14
SPECIFICATIONS........................14
WHEEL COVER
DESCRIPTION...........................14
REMOVAL..............................14
INSTALLATION...........................14
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT
REMOVAL..............................15
INSTALLATION...........................16
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - REAR
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................17
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
VIBRATION
Tire and wheel imbalance, runout and force varia-
tion can cause vehicles to exhibit steering wheel
vibration.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visual inspection of the vehicle is recommended
prior to road testing or performing any other proce-
dure. Raise vehicle on a suitable hoist. Refer to
Hoisting in Lubrication and Maintenance.
Inspect for the following:
²Verify correct (OEM) wheel and tire, as well as
correct wheel weights. Aluminum wheels require
unique wheel weights. They are designed to fit the
contour of the wheel (Fig. 1).
²Inspect tires and wheels for damage, mud pack-
ing and unusual wear; correct as necessary.
²Check and adjust tire air pressure to the pres-
sure listed on the label attached to the rear face of
the driver's door.
ROAD TEST
Road test vehicle on a smooth road for a least five
miles to warm tires (remove any flat spots). Lightlyplace hands on steering wheel at the 10:00 and 2:00
positions while slowly sweeping up and down from 90
to 110 km/h (55 to 70 mph) where legal speed limits
allow.
Observe the steering wheel for:
²Visual Nibble (oscillation: clockwise/counter-
clockwise, usually due to tire imbalance)
Fig. 1 Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - WHEEL WEIGHT
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-1
Page 3371 of 4284

Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. For example, the letter
ªSº indicates that the tire is speed rated up to 112
mph (180 km/h). The speed rating is not always
printed on the tire sidewall.
²Q -up to 100 mph (160 km/h)
²S -up to 112 mph (180 km/h)
²T -up to 118 mph (190 km/h)
²U -up to 124 mph (200 km/h)
²H -up to 130 mph (210 km/h)
²V -up to 149 mph (240 km/h)
²Z -more than 149 mph (240 km/h) (consult the
tire manufacturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
& S or M-S (indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. It is recommended that tires from dif-
ferent manufacturers NOT be mixed. They may bemixed with a temporary spare tire when necessary. A
maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph) is recom-
mended while a temporary spare is in use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehicle.
The original equipment tires provide a proper com-
bination of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The temporary (convenience) spare tire is designed
for emergency use only. The original tire should be
repaired and reinstalled, or replaced with a new, at
the first opportunity.
The temporary (convenience) spare tire should be
inflated to the pressure listed on its sidewall. Do not
exceed speeds of 80 km/h (50 mph) when the tempo-
rary spare tire is in use on the vehicle. Refer to the
Owner's Manual for more details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
Unusual tire noise can be associated with tire and
wheel vibration or irregular tire wear. For vibration,
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For irregular tire wear, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS/TIRES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD
Use the following Vehicle Lead Diagnosis And Cor-
rection Chart to diagnose and correct a vehicle lead
or drift problem.
Fig. 17 Tire Identification
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-9
TIRES (Continued)
Page 3377 of 4284
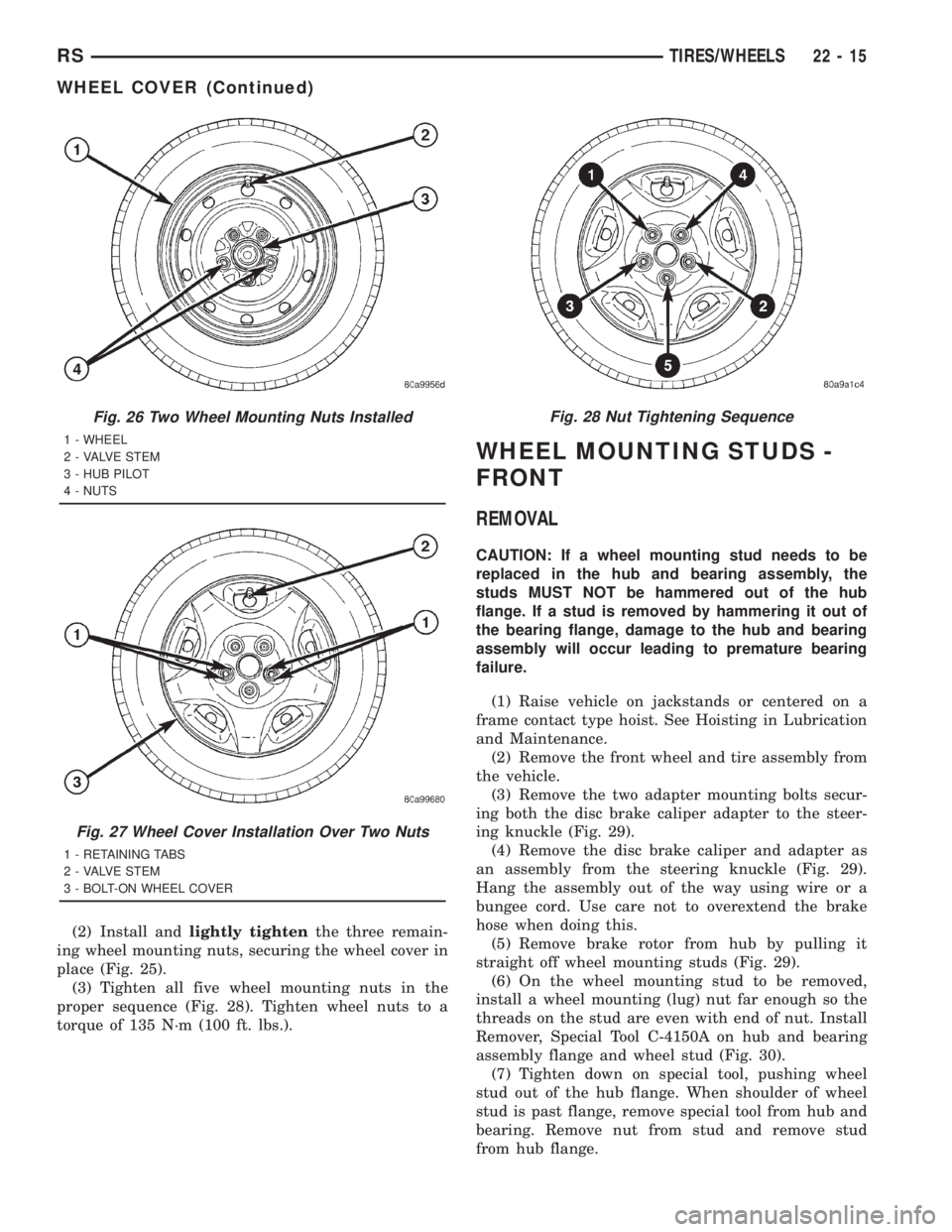
(2) Install andlightly tightenthe three remain-
ing wheel mounting nuts, securing the wheel cover in
place (Fig. 25).
(3) Tighten all five wheel mounting nuts in the
proper sequence (Fig. 28). Tighten wheel nuts to a
torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS -
FRONT
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If a wheel mounting stud needs to be
replaced in the hub and bearing assembly, the
studs MUST NOT be hammered out of the hub
flange. If a stud is removed by hammering it out of
the bearing flange, damage to the hub and bearing
assembly will occur leading to premature bearing
failure.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assembly from
the vehicle.
(3) Remove the two adapter mounting bolts secur-
ing both the disc brake caliper adapter to the steer-
ing knuckle (Fig. 29).
(4) Remove the disc brake caliper and adapter as
an assembly from the steering knuckle (Fig. 29).
Hang the assembly out of the way using wire or a
bungee cord. Use care not to overextend the brake
hose when doing this.
(5) Remove brake rotor from hub by pulling it
straight off wheel mounting studs (Fig. 29).
(6) On the wheel mounting stud to be removed,
install a wheel mounting (lug) nut far enough so the
threads on the stud are even with end of nut. Install
Remover, Special Tool C-4150A on hub and bearing
assembly flange and wheel stud (Fig. 30).
(7) Tighten down on special tool, pushing wheel
stud out of the hub flange. When shoulder of wheel
stud is past flange, remove special tool from hub and
bearing. Remove nut from stud and remove stud
from hub flange.
Fig. 26 Two Wheel Mounting Nuts Installed
1 - WHEEL
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - HUB PILOT
4 - NUTS
Fig. 27 Wheel Cover Installation Over Two Nuts
1 - RETAINING TABS
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
Fig. 28 Nut Tightening Sequence
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-15
WHEEL COVER (Continued)
Page 3378 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Install replacement wheel stud into flange of
hub and bearing assembly. Install washers on wheel
stud, then install a wheel mounting (lug) nut on stud
with flat side of lug nut against washers as shown
(Fig. 31).
(2) Tighten the nut, pulling the wheel stud into
the flange of the hub and bearing. When the head ofthe stud is fully seated against the rear of the hub
flange, remove nut and washers from stud.
(3) Install the brake rotor back on the hub and
bearing (Fig. 29).
(4) Install brake caliper and adapter back over
brake rotor aligning adapter with mounting holes on
steering knuckle (Fig. 29).
(5) Install the two adapter mounting bolts securing
the adapter to the steering knuckle. Tighten the
mounting bolts to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install wheel and tire assembly on vehicle.
Tighten the wheel mounting lug nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half specifica-
tion, then repeat the tightening sequence to the full
specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle to the ground.
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS -
REAR
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If a wheel attaching stud needs to be
replaced in the hub and bearing assembly the studs
MUST NOT be hammered out of the hub flange. If a
stud is removed by hammering it out of the bearing
flange, damage to the hub and bearing assembly
will occur leading to premature hub and bearing
failure.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
Fig. 29 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
Fig. 30 Wheel Stud Removal (Typical)
1 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
2 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4150A
4 - STEERING KNUCKLE
5 - WHEEL STUD
Fig. 31 Installing Wheel Stud (Typical)
1 - WASHERS
2 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
3 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
4 - STEERING KNUCKLE
22 - 16 TIRES/WHEELSRS
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT (Continued)