2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 1839 of 4284
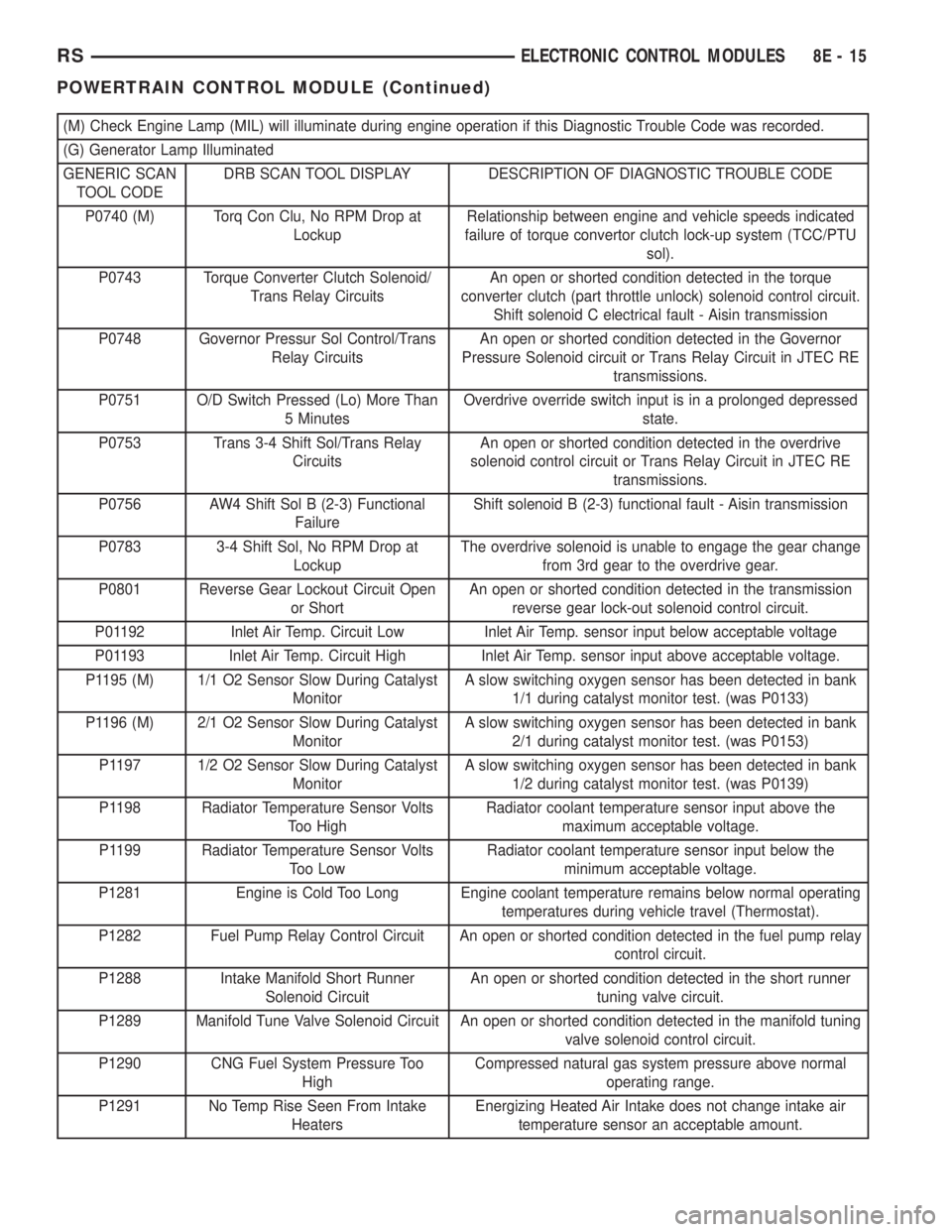
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC SCAN
TOOL CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0740 (M) Torq Con Clu, No RPM Drop at
LockupRelationship between engine and vehicle speeds indicated
failure of torque convertor clutch lock-up system (TCC/PTU
sol).
P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter clutch (part throttle unlock) solenoid control circuit.
Shift solenoid C electrical fault - Aisin transmission
P0748 Governor Pressur Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Governor
Pressure Solenoid circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC RE
transmissions.
P0751 O/D Switch Pressed (Lo) More Than
5 MinutesOverdrive override switch input is in a prolonged depressed
state.
P0753 Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the overdrive
solenoid control circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC RE
transmissions.
P0756 AW4 Shift Sol B (2-3) Functional
FailureShift solenoid B (2-3) functional fault - Aisin transmission
P0783 3-4 Shift Sol, No RPM Drop at
LockupThe overdrive solenoid is unable to engage the gear change
from 3rd gear to the overdrive gear.
P0801 Reverse Gear Lockout Circuit Open
or ShortAn open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
reverse gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P01192 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit Low Inlet Air Temp. sensor input below acceptable voltage
P01193 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit High Inlet Air Temp. sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal operating
temperatures during vehicle travel (Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump relay
control circuit.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner
Solenoid CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short runner
tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the manifold tuning
valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 CNG Fuel System Pressure Too
HighCompressed natural gas system pressure above normal
operating range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1843 of 4284

OPERATION - SENSOR RETURN - PCM INPUT
The sensor return circuit provides a low electrical
noise ground reference for all of the systems sensors.
The sensor return circuit connects to internal ground
circuits within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
OPERATION - SCI RECEIVE - PCM INPUT
SCI Receive is the serial data communication
receive circuit for the DRB scan tool. The Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) receives data from the DRB
through the SCI Receive circuit.
OPERATION - IGNITION SENSE - PCM INPUT
The ignition sense input informs the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) that the ignition switch is in
the crank or run position.
OPERATION - PCM GROUND
Ground is provided through multiple pins of the
PCM connector. Depending on the vehicle there may
be as many as three different ground pins. There are
power grounds and sensor grounds.
The power grounds are used to control the ground
side of any relay, solenoid, ignition coil or injector.
The signal ground is used for any input that uses
sensor return for ground, and the ground side of any
internal processing component.
The SBEC III case is shielded to prevent RFI and
EMI. The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the case is also
grounded separately from the ground pins.
OPERATION - 8-VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 8 volts to the crankshaft posi-
tion sensor, camshaft position sensor.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Throttle position sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid
OPERATION - MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than 0.745
volts or less than 0.1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-19
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1844 of 4284

PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
If the PCM does not receive both signals within
approximately one second, it will not energize the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel
pump relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sen-
sors.
²The PCM energizes the injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²MAP
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²O2 sensors
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
8E - 20 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1845 of 4284

²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in response to MAP
sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are used by
the PCM:
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - OBTAINING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check. When the key is in the power on, but
engine off position, the MIL will remain illuminated
for regulatory purposes.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-21
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1849 of 4284

²Output Shaft Speed Sensor
Some examples ofindirect inputsto the TCM
are:
²Engine/Body Identification
²Manifold Pressure
²Target Idle
²Torque Reduction Confirmation
²Speed Control ON/OFF Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Ambient/Battery Temperature
²Brake Switch Status
²DRB Communication
Based on the information received from these var-
ious inputs, the TCM determines the appropriate
shift schedule and shift points, depending on the
present operating conditions and driver demand.
This is possible through the control of various direct
and indirect outputs.
Some examples of TCMdirect outputsare:
²Transmission Control Relay
²Solenoids (LR/CC, 2/4, OD and UD)
²Vehicle Speed (to PCM)
²Torque Reduction Request (to PCM)
An example of a TCMindirect outputis:
²Transmission Temperature (to PCM)
In addition to monitoring inputs and controlling
outputs, the TCM has other important responsibili-
ties and functions:
²Storing and maintaining Clutch Volume Indices
(CVI)
²Storing and selecting appropriate Shift Sched-
ules
²System self-diagnostics²Diagnostic capabilities (with DRB scan tool)
CLUTCH VOLUME INDEX (CVI)
An important function of the TCM is to monitor
Clutch Volume Index (CVI). CVIs represent the vol-
ume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
The TCM monitors gear ratio changes by monitor-
ing the Input and Output Speed Sensors. The Input,
or Turbine Speed Sensor sends an electrical signal to
the TCM that represents input shaft rpm. The Out-
put Speed Sensor provides the TCM with output
shaft speed information.
By comparing the two inputs, the TCM can deter-
mine transaxle gear ratio. This is important to the
CVI calculation because the TCM determines CVIs
by monitoring how long it takes for a gear change to
occur (Fig. 14).
Gear ratios can be determined by using the DRB
Scan Tool and reading the Input/Output Speed Sen-
sor values in the ªMonitorsº display. Gear ratio can
be obtained by dividing the Input Speed Sensor value
by the Output Speed Sensor value.
For example, if the input shaft is rotating at 1000
rpm and the output shaft is rotating at 500 rpm,
then the TCM can determine that the gear ratio is
Fig. 13 Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
Fig. 14 Example of CVI Calculation
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - CLUTCH PACK
4 - SEPARATOR PLATE
5 - FRICTION DISCS
6 - INPUT SHAFT
7 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
8 - PISTON AND SEAL
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-25
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1851 of 4284

Schedule Condition Expected Operation
HotOil temperature at start-up above
80É F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± Full EMCC, no PEMCC except to
engage FEMCC (except at closed
throttle at speeds above 70-83 mph)
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift (25-32 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (41-48 mph)
± 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
± 3rd gear PEMCC from 27-31 mph
Super OverheatOil temperature above 260É F ± All9Overheat9shift schedule
features apply
± 2nd gear PEMCC above 22 mph
± Above 22 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PINION FACTOR
SETTING
NOTE: This procedure must be performed if the
Transmission Control Module (TCM) has been
replaced with a NEW or replacement unit. Failure to
perform this procedure will result in an inoperative
or improperly calibrated speedometer.
The vehicle speed readings for the speedometer are
taken from the output speed sensor. The TCM must
be calibrated to the different combinations of equip-
ment (final drive and tires) available. Pinion Factor
allows the technician to set the Transmission Control
Module initial setting so that the speedometer read-
ings will be correct. To properly read and/or reset the
Pinion Factor, it is necessary to use a DRB scan tool.
(1) Plug the DRB scan tool into the diagnostic con-
nector located under the instrument panel.
(2) Select the Transmission menu.
(3) Select the Miscellaneous menu.
(4) Select Pinion Factor. Then follow the instruc-
tions on the DRB scan tool screen.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK LEARN
PROCEDURE
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRB scan tool. This program allows the electronic
transaxle system to recalibrate itself. This will pro-
vide the best possible transaxle operation.NOTE: The quick learn procedure should be per-
formed if any of the following procedures are per-
formed:
²Transaxle Assembly Replacement
²Transmission Control Module Replacement
²Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or Recondition
To perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the DRB
indicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
(1) Plug the DRB scan tool into the diagnostic con-
nector. The connector is located under the instrument
panel.
(2) Go to the Transmission screen.
(3) Go to the Miscellaneous screen.
(4) Select Quick Learn Procedure. Follow the
instructions of the DRB to perform the Quick Learn
Procedure.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-27
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1875 of 4284

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION...........................21
OPERATION.............................21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................22
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.........22
SPECIFICATIONS........................22
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................23
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................23
OPERATION.............................23
REMOVAL..............................23
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................23
OPERATION.............................23REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................24
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY
DESCRIPTION...........................25
OPERATION.............................25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................25
GENERATOR DECOUPLER...............25
REMOVAL..............................25
INSTALLATION...........................26
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................26
OPERATION.............................26
REMOVAL..............................26
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION - CHARGING SYSTEM
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Decoupler Pulley (If equipped)
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch (refer to the Ignition System sec-
tion for information)
²Battery (refer to the Battery section for informa-
tion)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Voltmeter (refer to the Instrument Cluster sec-
tion for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to the
Wiring section for information)
²Accessory drive belt (refer to the Cooling section
for more information)
OPERATION - CHARGING SYSTEM
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is connected
through the PCM and supplied to one of the genera-
tor field terminals (Gen. Source +) at the back of the
generator.
The generator is driven by the engine through a
serpentine belt and pulley or decoupler pulley
arrangement.The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the EVR (field control) circuitry
contained within the PCM. This circuitry is con-
nected in series with the second rotor field terminal
and ground.
A battery temperature sensor is used to sense bat-
tery temperature. This temperature data, along with
data from monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM
to vary the battery charging rate. This is done by
cycling the ground path to control the strength of the
rotor magnetic field. The PCM then compensates and
regulates generator current output accordingly to
maintain system voltage at the targeted system volt-
age based on battery temperature.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostics in the Electronic Control Mod-
ules(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE - DESCRIPTION) section for more DTC
information.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the PCI bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to the Instrument Cluster section for additional
information.
RSCHARGING8F-21
Page 1927 of 4284

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER..................1
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................11
CLUSTER LENS
REMOVAL..............................12INSTALLATION...........................12
MECHANICAL TRANSMISSION RANGE
INDICATOR
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................12
RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................12
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrumentation gauges are contained in a
subdial assembly within the instrument cluster. The
individual gauges are not serviceable. If one of the
cluster gauges becomes faulty, the entire cluster
would require replacement.
The mechanical instrument cluster with a tachom-
eter is equipped with a electronic vacuum fluorescent
transmission range indicator (PRND3L), odometer,
and trip odometer display.
The mechanical instrument cluster without a
tachometer is equipped with a cable operated trans-
mission range indicator (PRND21) and a vacuum
flourescent odometer display.
The instrument cluster is equipped with the follow-
ing warning lamps.
²Lift Gate Ajar
²Low Fuel Level
²Low Windshield Washer Fluid Level
²Cruise
²Battery Voltage
²Fasten Seat Belt
²Door Ajar
²Headlamp Out
²Coolant Temperature
²Anti-Lock Brake
²Brake
²Airbag
²Traction Control
²Autostick
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for operation
instructions and conditions for the Instrument Clus-
ter Gauges.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS
The instrument clusters are equipped with a self
diagnostic test feature to help identify electronic
problems. Prior to any test, perform the Self-Diag-
nostic Test. The self diagnostic system displays
instrument cluster stored fault codes in the odometer
display, sweeps the gauges to the calibration points,
and bulb checks the warning indicators. When the
key is in the ON position with the engine not run-
ning, the MIL will remain illuminated for regulatory
purposes.
To activate the Self-Diagnostic program:
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position,
depress the TRIP ODOMETER RESET button.
(2) Continue to hold the TRIP ODOMETER
RESET button untilSofand a number (software ver-
sion number (i.e.Sof 3.2) appears in the odometer
window (about five seconds) then release the button.
If a fault code is present, the cluster will display it in
the odometer display. When all fault codes have been
displayed, the cluster will displayªendºin the odom-
eter display. Refer to the table to determine what
each trouble code means.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-1