2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2998 of 4284

(5) Low line pressure in all positions indicates a
defective pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure
regulator valve.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE
Test only if transaxle shifts at wrong vehicle
speeds when throttle cable is correctly adjusted.
(1) Connect a 100 psi gauge to governor pressure
port. It is located at lower right side of case, below
differential cover (Fig. 2).
(2) Operate transaxle in third gear to read pres-
sures. The governor pressure should respond
smoothly to changes in mph and should return to 0
to 3 psi when vehicle is stopped. High pressure
(above 3 psi) at standstill will prevent the transaxle
from downshifting.
THROTTLE PRESSURE
No gauge port is provided for throttle pressure.
Incorrect throttle pressure should be suspected if
part throttle upshift speeds are either delayed or
occur too early in relation to vehicle speed. Engine
runaway on shifts can also be an indicator of low
throttle pressure setting, or misadjusted throttle
cable.
In no case should throttle pressure be adjusted
until the transaxle throttle cable adjustment has
been verified to be correct.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 3).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill, or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 3). Pump
o-ring or pump body leaks follow the same path as a
seal leak. Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally
deposited on the inside of the converter housing and
not on the converter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaksusually travel down the inside of the converter hous-
ing (Fig. 3).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 4).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 4 Converter Leak PointsÐTypical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
21 - 34 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3000 of 4284

KICKDOWN SERVO (FRONT)
Direct air pressure into KICKDOWN SERVO ON
passage. Operation of servo is indicated by a tighten-
ing of front band. Spring tension on servo piston
should release the band.
LOW AND REVERSE SERVO (REAR)
Direct air pressure into LOW-REVERSE SERVO
APPLY passage. Operation of servo is indicated by a
tightening of rear band. Spring tension on servo pis-
ton should release the band.
If clutches and servos operate properly, no upshift
indicates that a malfunction exists in the valve body.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
axle case and valve body can be repaired by the use
of Heli-Coils, or equivalent. This repair consists of
drilling out the worn-out damaged threads. Then tap-
ping the hole with a Heli-Coil tap, or equivalent, and
installing a Heli-Coil insert, or equivalent, into the
hole. This brings the hole back to its original thread
size.
Heli-Coil, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove fluid level indicator tube bolt and tube/
indicator assembly (Fig. 6). Plug opening to prevent
debris intrusion.
(3) Disconnect torque converter clutch solenoid
(TCC) connector.
(4) Disconnect kickdown cable from lever and
bracket (Fig. 7). Position out of way.
(5) Disconnect gearshift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 8). Position out
of way.
(6) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(7) Remove upper two (2) transaxle-to-engine bolts.
(8) Remove three (3) rear mount bracket-to-trans-
axle case bolts (Fig. 9).
(9) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(10) Remove halfshafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(11) Remove starter motor assembly (Fig. 10).
Fig. 6 Fluid Level Indicator Assembly
1 - INDICATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - BOLT
3 - KICKDOWN CABLE BRACKET
4 - SEAL
Fig. 7 Throttle Valve Cable at Transaxle
1 - LEVER
2 - BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
21 - 36 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3002 of 4284

(12) Remove front mount and bracket (Fig. 11).
(13) Cut transaxle oil cooler lines flush with fit-
tings. a service kit will be installed upon reintalla-
tion. Plug lines and fittings to prevent debris
intrusion.
(14) Remove structural collar (Fig. 12).
(15) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor connector.
(16) Remove rear mount shield (Fig. 13).
(17) Remove rear mount thru-bolt.
(18) Support engine with screw jack and wood
block.
(19) Remove cradle plate.
(20) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(21) Remove left wheel splash shield.
(22) Remove left upper mount thru-bolt (Fig. 14).
(23) Lower engine/transaxle assembly.
(24) Obtain transmission jack and helper.
(25) Remove remaining transaxle-to-engine bolts
and remove transaxle assembly from vehicle.
Fig. 11 Front Mount and Bracket
1 - BRACKET - FRONT MOUNT
2 - NUT
3 - BOLT
4 - MOUNT - FRONT INSULATOR
5 - BOLT
6 - BOLT
7 - FRONT CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 12 Structural Collar
1 - BOLT - COLLAR TO OIL PAN
2 - BOLT - COLLAR TO TRANSAXLE
3 - STRUCTURAL COLLAR
4 - OIL PAN
Fig. 13 Rear Mount Heat Shield
1 - BOLT - HEAT SHIELD
2 - HEAT SHIELD
3 - CLIP
4 - REAR MOUNT
21 - 38 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3023 of 4284

(40) Install oil filter and gasket into position (Fig.
93).
(41) Install oil filter-to-valve body screws (Fig. 94)
and torque to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.) torque.
(42) Install an 1/8º bead of Moparž Silicone Rub-
ber Adhesive Sealant to the transaxle oil pan (Fig.
95). Install oil pan to case and immediately install
and torque oil pan-to-case bolts (Fig. 96) to 19 N´m
(165 in. lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transaxle assembly to engine using a
transmission jack and helper.
(2) Install and torque transaxle-to-engine bolts to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3) Using screw jack and wood block, raise engine/
transaxle assembly into position and install left
upper mount thru-bolt (Fig. 97). Torque bolt to 75
N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 93 Oil Filter and Gasket
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - GASKET
3 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 94 Oil Filter Screws
1 - SCREWDRIVER HANDLE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4553
3 - OIL FILTER SCREWS (2)
4 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 95 Transaxle Oil Pan
1 - TRANSAXLE OIL PAN
2 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 96 Transaxle Oil Pan Bolts
1 - TRANSAXLE OIL PAN
2 - OIL PAN BOLTS
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-59
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3037 of 4284
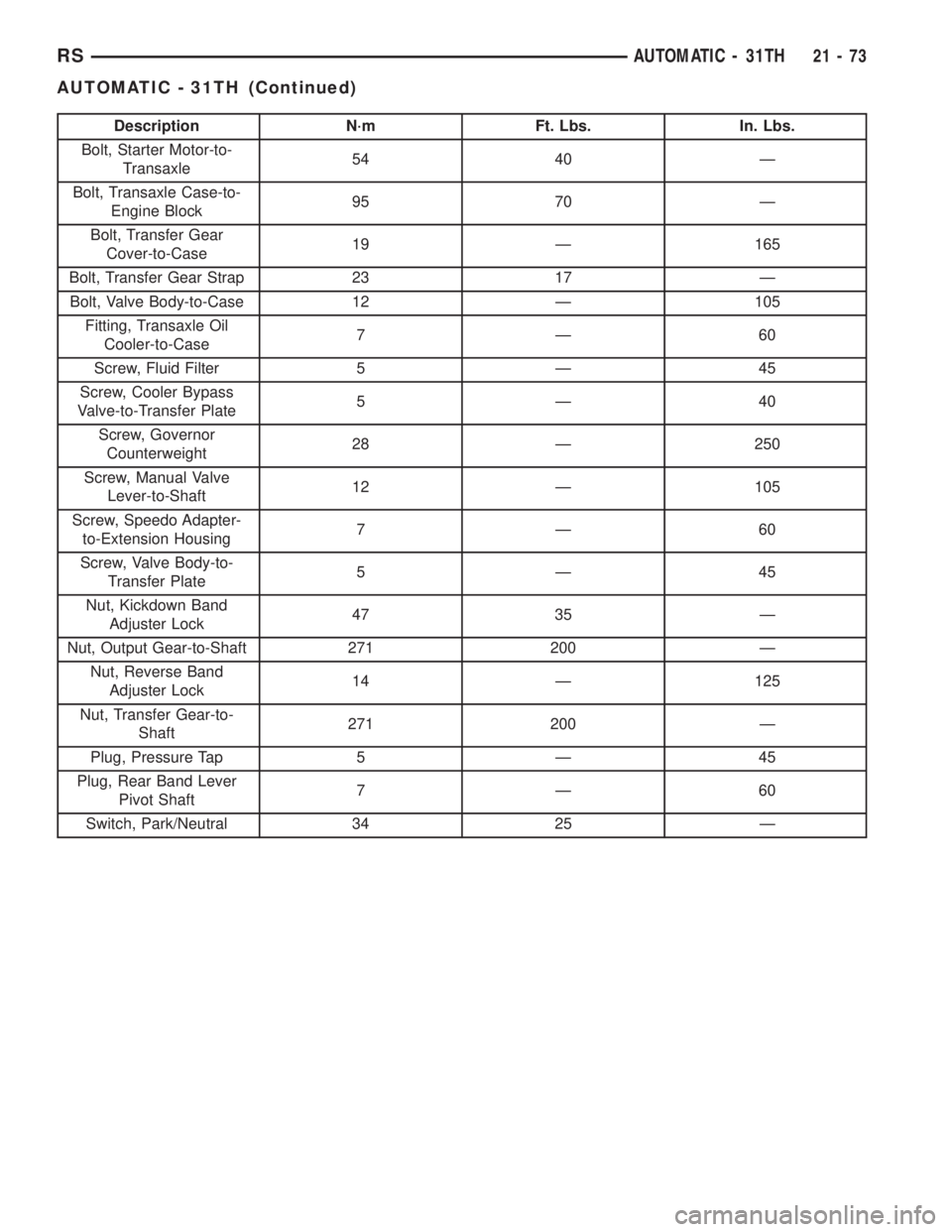
Description N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Starter Motor-to-
Transaxle54 40 Ð
Bolt, Transaxle Case-to-
Engine Block95 70 Ð
Bolt, Transfer Gear
Cover-to-Case19 Ð 165
Bolt, Transfer Gear Strap 23 17 Ð
Bolt, Valve Body-to-Case 12 Ð 105
Fitting, Transaxle Oil
Cooler-to-Case7Ð60
Screw, Fluid Filter 5 Ð 45
Screw, Cooler Bypass
Valve-to-Transfer Plate5Ð40
Screw, Governor
Counterweight28 Ð 250
Screw, Manual Valve
Lever-to-Shaft12 Ð 105
Screw, Speedo Adapter-
to-Extension Housing7Ð60
Screw, Valve Body-to-
Transfer Plate5Ð45
Nut, Kickdown Band
Adjuster Lock47 35 Ð
Nut, Output Gear-to-Shaft 271 200 Ð
Nut, Reverse Band
Adjuster Lock14 Ð 125
Nut, Transfer Gear-to-
Shaft271 200 Ð
Plug, Pressure Tap 5 Ð 45
Plug, Rear Band Lever
Pivot Shaft7Ð60
Switch, Park/Neutral 34 25 Ð
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-73
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3044 of 4284

(5) Back off front band adjusting screw 2ò turns.
(6) Hold adjuster screw in position and tighten
locknut to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install air cleaner assembly.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
ADJUSTMENTS - REAR BAND
The transmission oil pan must be removed for
access to the rear (low/reverse) band adjusting screw.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid (Fig.
111) (Fig. 112).(3) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut 5-6 turns.
Be sure adjusting screw turns freely in lever.
(4) Tighten adjusting screw to 5 N´m (41 in. lbs.)
(Fig. 113).
(5) Back off adjusting screw 3 turns.
(6) Hold adjusting screw in place and tighten lock-
nut to 14 N´m (125 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install a bead of Moparž Silicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant to the oil pan and install to case imme-
diately.
(8) Install oil pan-to-case bolts and torque to 19
N´m (165 in. lbs.).
(9) Lower vehicle and refill transmission with
Moparž ATF Plus 4, Type 9602, fluid.
CLUTCH - FRONT
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 119) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil
pump. It is considered a driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
Fig. 111 Transaxle Oil Pan Bolts
1 - TRANSAXLE OIL PAN
2 - OIL PAN BOLTS
Fig. 112 Transaxle Oil Pan
1 - TRANSAXLE OIL PAN
2 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 113 Adjust Low/Reverse Band
1 - LOW-REVERSE BAND LEVER
2 - ADJUSTING SCREW
3 - STRUT
4 - LOW-REVERSE BAND
5 - LOCK NUT
6 - LEVER (SHORT)
21 - 80 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
BANDS (Continued)
Page 3049 of 4284

(5) Using feeler gauge, measure front clutch clear-
ance (Fig. 125).Front clutch clearance should be
within 1.27-2.79 mm (0.050-0.110 in.) and is not
adjustable.
CLUTCH - REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear clutch assembly (Fig. 132) is composed of
the input shaft, rear clutch retainer, pressure plate,
clutch plates, driving discs, piston, Belleville spring,
and snap-rings. The Belleville spring acts as a lever
to multiply the force applied on to it by the apply pis-
ton. The increased apply force on the rear clutch
pack, in comparison to the front clutch pack, is
needed to hold against the greater torque load
imposed onto the rear pack. The rear clutch is
directly behind the front clutch and is considered a
driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack. In
some transmissions, the snap-ring is selective and
used to adjust clutch pack clearance.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
Fig. 124 Front Clutch Waved Snap Ring
1 - WAVED SNAP RING
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 125 Measuring Front Clutch Plate Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-85
CLUTCH - FRONT (Continued)
Page 3062 of 4284

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL AND
CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground. This will assure complete oil level sta-
bilization between differential and transmis-
sion.The fluid should be at normal operating
temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.). The
fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region (cross-
hatched area) on the fluid level indicator (Fig. 165).
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle dipstick where it may be mistaken for a
leak.Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check.
Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown. This is normal. A dark brown/black fluid
accompanied with a burnt odor and/or deterioration
in shift quality may indicate fluid deterioration or
transmission component failure.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
CHANGE
NOTE: For the recommended maintenance (fluid/fil-
ter change) intervals for this transaxle, (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled Moparž
ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Place a drain con-
tainer with a large opening, under transaxle oil pan.
Fig. 165 Fluid Level Indicator Markings
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 98 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS