2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2914 of 4284

FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is located
under the vehicle in front of the rear axle assembly
(Fig. 5). The 12±volt electric vane-type pump is oper-
ated and controlled by the Engine Control Module
(ECM) .
OPERATION
The purpose of the fuel transfer pump is to supply
(transfer) a low-pressure fuel source:fromthe fuel
tank,throughthe fuel filter/water separator andto
the fuel injection pump. Here, the low-pressure is
raised to a high-pressure by the fuel injection pump
for operation of the high-pressure fuel injectors.The fuel transfer pump is controlled by the Engine
Control Module(ECM). The ECM turns the fuel
transfer pump on for 30 seconds when the ignition
ket is turned ªONº.
With the ignition ªONº and fuel tranfer pump run-
ning, the low-pressure fuel pressure should be 13-17 psi.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
A radial-piston pump is used as the high pressure
pump for fuel pressure generation (Fig. 6).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL)
(3) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
(4) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(6) Support engine and remove right engine mount
assembly.
(7) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Using special tool VM.1055, remove injection
pump sprocket retaining nut (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5 FUEL TRANSFER(LIFT) PUMP LOCATION
1 - LIFT PUMP RETAINING BOLTS
2 - LIFT PUMP
3 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR HOUSING
4 - FUEL HEATER
5 - CHECK BALL
6 - O-RING
7 - FLOW DIVERTER
8 - FUEL FILTER
9 - O-RING
10 - FUEL FILTER BOWL ASSEMBLY
Fig. 6 FUEL INJECTION PUMP
1 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
2 - INJECTION PUMP PRESSURE SOLENOID
14a - 6 FUEL DELIVERYRG
Page 2915 of 4284

NOTE: The use of special tool VM.1067 will allow
you to remove the injection pump without removing
the timing belt from the engine. This will allow you
to remove and install the injection pump without
altering injection pump timing.
(9) Install feet from VM.1067 in injection pump
sprocket as shown (Fig. 8).
(10) Install inner flange of special tool VM.1067 on
injection pump sprocket as shown (Fig. 9). Secure
flange to feet in injection pump sprocket with allen
bolts supplied with tool.
(11) Screw injection pump sprocket holding plate
assembly into flange of VM.1067 (Fig. 10) Using LHD
threaded bolt supplied, secure holding plate assembly
to timing belt inner cover.(12) Remove generator (Fig. 11). (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
REMOVAL)
(13) Disconnect fuel supply and return lines at
injection pump (Fig. 11)
(14) Disconnect fuel pressure solenoid electrical
connector at injection pump (Fig. 11)
(15) Remove injection pump retaining nuts.
(16) While holding injection pump, tighten bolt in
center of injection pump holding plate (Fig. 10).This
will push the injection pump out of the injection
pump sprocket.
Fig. 7 INJECTION PUMP SPROCKET
RETAINING NUT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1 - IDLER PULLEY
2 - TIMING BELT
3 - VM.1055
4 - INJECTION PUMP SPROCKET
Fig. 8 VM.1067 FEET INSTALLATION
1 - OUTER TIMING BELT SEALING SURFACE
2 - TIMING BELT
3 - TIMING BELT SPROCKET
4 - FEET FOR SPECIAL TOOL VM.1067
5 - INNER TIMING BELT COVER
RGFUEL DELIVERY14a-7
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2916 of 4284
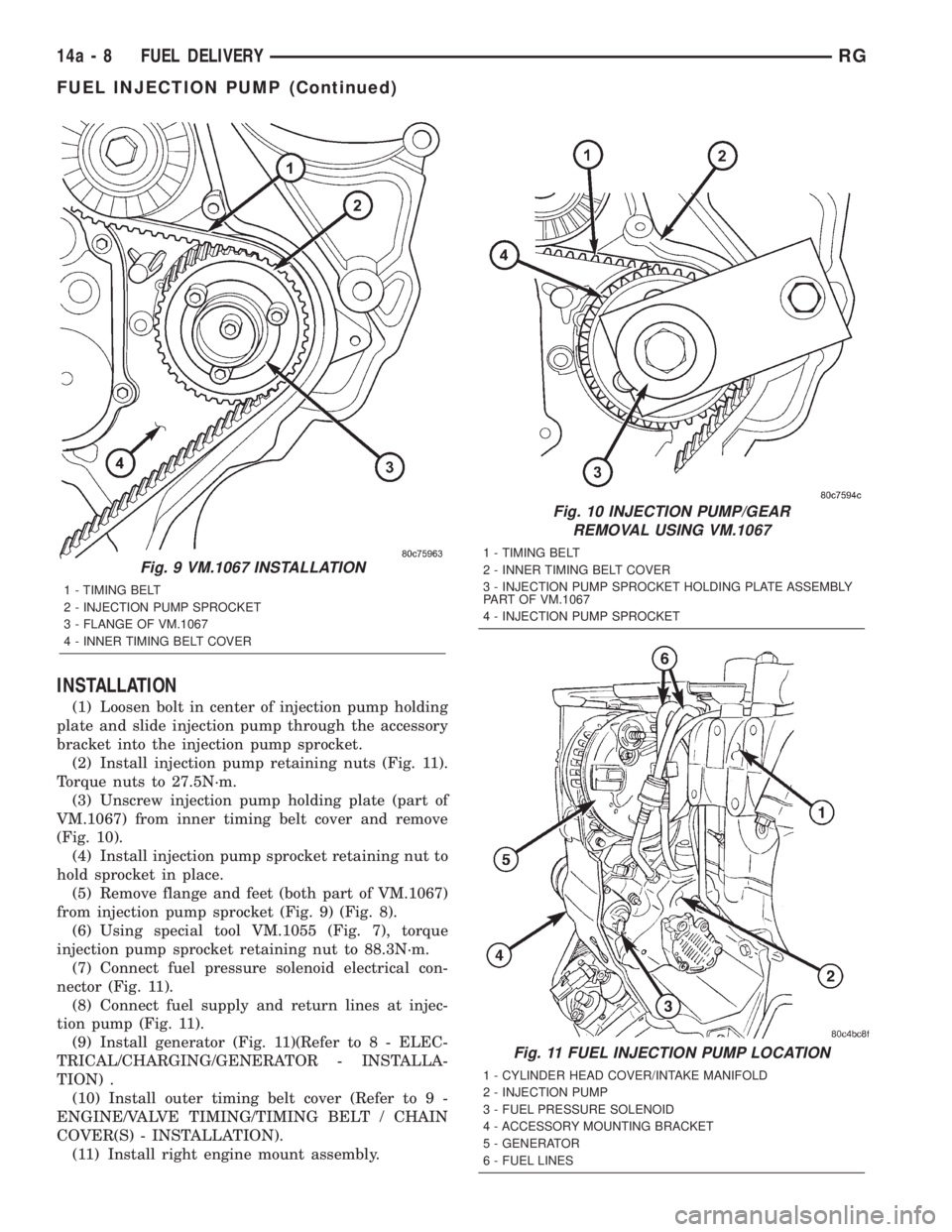
INSTALLATION
(1) Loosen bolt in center of injection pump holding
plate and slide injection pump through the accessory
bracket into the injection pump sprocket.
(2) Install injection pump retaining nuts (Fig. 11).
Torque nuts to 27.5N´m.
(3) Unscrew injection pump holding plate (part of
VM.1067) from inner timing belt cover and remove
(Fig. 10).
(4) Install injection pump sprocket retaining nut to
hold sprocket in place.
(5) Remove flange and feet (both part of VM.1067)
from injection pump sprocket (Fig. 9) (Fig. 8).
(6) Using special tool VM.1055 (Fig. 7), torque
injection pump sprocket retaining nut to 88.3N´m.
(7) Connect fuel pressure solenoid electrical con-
nector (Fig. 11).
(8) Connect fuel supply and return lines at injec-
tion pump (Fig. 11).
(9) Install generator (Fig. 11)(Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLA-
TION) .
(10) Install outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install right engine mount assembly.
Fig. 9 VM.1067 INSTALLATION
1 - TIMING BELT
2 - INJECTION PUMP SPROCKET
3 - FLANGE OF VM.1067
4 - INNER TIMING BELT COVER
Fig. 10 INJECTION PUMP/GEAR
REMOVAL USING VM.1067
1 - TIMING BELT
2 - INNER TIMING BELT COVER
3 - INJECTION PUMP SPROCKET HOLDING PLATE ASSEMBLY
PART OF VM.1067
4 - INJECTION PUMP SPROCKET
Fig. 11 FUEL INJECTION PUMP LOCATION
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - INJECTION PUMP
3 - FUEL PRESSURE SOLENOID
4 - ACCESSORY MOUNTING BRACKET
5 - GENERATOR
6 - FUEL LINES
14a - 8 FUEL DELIVERYRG
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2917 of 4284

(12) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(15) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect negative battery cable.
WATER IN FUEL SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The WIF sensor is located in the bowl assembly of
the fuel filter/water separator.
OPERATION
The sensor sends an input to the Engine Control
Module (ECM) when it senses water in the fuel filter/
water separator. As the water level in the filter/sep-
arator increases, the resistance across the WIF
sensor decreases. This decrease in resistance is sent
as a signal to the ECM and compared to a high
water standard value. Once the value reaches 30 to
40 kilohms, the ECM will activate the water-in-fuel
warning lamp through CCD bus circuits. This all
takes place when the ignition key is initially put in
the ON position. The ECM continues to monitor the
input at the end of the intake manifold air heater
post-heat cycle.
RGFUEL DELIVERY14a-9
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2918 of 4284
FUEL INJECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION...........................10
OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................12
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................12
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................13
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................13
OPERATION.............................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................13BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR.............13
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................13
OPERATION.............................13
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................14
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................14
OPERATION.............................14
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................14
OPERATION.............................15
REMOVAL..............................15
INSTALLATION...........................15
FUEL INJECTOR
FUEL INJECTOR
There are individual fuel injectors for all four cyl-
inders. These fuel injectors are used to spray fuel
into the combustion chamber (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The injector operation can be subdivided into four
operating states with the engine running and the
high-pressure pump generating pressure:
²Injector closed (with high pressure applied)
²Injector opens (start of injection)
²Injector opened fully
²Injector closes (end of injection)
Injector closed (with high pressure applied)
With the injector closed (at-rest state), the solenoid
valve is not energized and is therefore closed. With
the bleed orifice closed, the valve spring forces the
armature's ball onto the bleed-orifice seat. The rail's
high pressure build up in the valve control chamber,
and the same pressure is also present in the nozzle's
chamber volume. The rail pressure applied at the
control plunger's end face, together with the force of
the nozzle spring, maintain the nozzle in the closed
position against the opening forces applied to its
pressure stage (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 FUEL INJECTOR
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - NOZZLE
3 - FUEL INLET FITTING
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
14a - 10 FUEL INJECTIONRG
Page 2919 of 4284

Injector opens (start of injection)
The solenoid valve is energized with the pickup
current which serves to ensure that it open quickly.
The force exerted by the triggered solenoid now
exceeds that of the valve spring and the armature
opens the bleed orifice. Almost immediately, the high-level pick-up current is reduced to the lower holding
current required for the electromagnet. This is possi-
ble due to the magnetic circuit's air gap now being
smaller. When the bleed orifice opens, fuel can flow
from the valve control chamber into the cavity situ-
ated above it, and from there via the fuel return to
the tank. The bleed orifice prevents complete pres-
sure balance, and the pressure in the valve control
chamber sinks as a result. This leads to the pressure
in the valve-control chamber being lower than that in
the nozzle's chamber volume which is still at the
same pressure level as the rail. The reduced pressure
in the valve-control chamber causes a reduction in
the force exerted on the control plunger, the nozzle
needle open as a result, and injection starts (Fig. 2).
Injector opens fully
The control plunger reaches its upper stop where it
remains supported by a cushion of fuel which is gen-
erated by the flow of fuel between the bleed and feed
orifices. The injector nozzle has now opened fully,
and the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber
at a pressure almost equal to that in the fuel rail
(Fig. 2).
Injector closes (end of injection)
As soon as the solenoid valve is no longer trig-
gered, the valve spring forces the armature down-
wards and the ball closes the bleed orifice. The
armature is a 2±piece design. Here, although the
armature plate is guided by a driver shoulder in its
downward movement, it can ªoverspringº with the
return spring so that it exerts no downwards-acting
forces on the armature and the ball. The closing of
the bleed orifice lead to pressure build up in the con-
trol chamber via the input from the feed orifice. This
pressure is the same as that in the rail and exerts an
increased force on the control plunger through its
end face. This force, together with that of the spring,
now exceeds the force exerted by the chamber volume
and the nozzle needle closes. Injection ceases as soon
as the nozzle needle comes up against its bottom stop
again (Fig. 2).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect injector electrical connector.
(4) Remove fuel return line from injector (Fig. 3).
(5) Remove fuel injector high pressure line (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove fuel injector retainer and retaining
bolt (Fig. 3).
(7) Remove fuel injector from cylinder head (Fig.
3).
Fig. 2 INJECTOR COMPONENTS
1 - INJECTOR CLOSED (AT-REST STATUS)
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
3 - TRIGGERING ELEMENT (SOLENOID VALVE)
4 - FUEL INLET (HIGH PRESSURE) FROM THE RAIL
5 - VALVE BALL
6 - BLEED ORIFICE
7 - FEED ORIFICE
8 - VALVE CONTROL CHAMBER
9 - VALVE CONTROL PLUNGER
10 - FEED PASSAGE TO THE NOZZLE
11 - NOZZLE NEEDLE
RGFUEL INJECTION14a-11
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 2920 of 4284

INSTALLATION
NOTE: Be sure the copper washer is installed on
end of injector before installing in cylinder head.
(1) Install fuel injector in cylinder head.
(2) Install fuel injector retainer and bolt (Fig. 3).
Torque bolt to 32.4 N´m.
(3) Install fuel injector high pressure line (Fig. 3).(4) Install fuel return line to injector (Fig. 3).
(5) Connect fuel injector electrical connector.
(6) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - INSTALLATION).
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The accelerator pedal position sensor mounts to
the accelerator pedal bracket (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The accelerator pedal position sensor contains a
potentiometer that is operated by the accelerator
pedal. As the accelerator pedal is depressed and
released, the sensor provides a variable voltage sig-
nal to the engine control module. This voltage signal
is directly proportional to accelerator pedal position.
When the pedal is fully depressed, the voltage signal
is high.
REMOVAL - PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (LHD)
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect pedal position sensor electrical con-
nector (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL RAIL RETAINING BOLT
2 - FUEL RAIL RETAINING STUD
3 - FUEL RAIL RETURN LINE
4 - FUEL RAIL
5 - FUEL RAIL SUPPLY LINE
6 - IDLER PULLEY
7 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
8 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY RETAINING BOLTS
9 - BELT TENSIONER RETAINING BOLT
10 - BELT TENSIONER
11 - FUEL INJECTOR RETAINER
12 - FUEL INJECTOR RETURN LINE
13 - FUEL INJECTOR RETAINING BOLT
14 - FUEL INJECTORS
15 - FUEL INJECTOR HIGH PRESSURE SUPPLY LINESFig. 4 ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
LOCATION (TYPICAL)
1 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
2 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
3 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL
4 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL MOUNTING BRACKET
14a - 12 FUEL INJECTIONRG
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 2921 of 4284

(3) Remove 2 pedal position sensor retaining nuts
(Fig. 4).
(4) Remove pedal position sensor from vehicle.
REMOVAL - PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (RHD)
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect pedal position sensor electrical con-
nector (Fig. 4).
(3) Remove 2 pedal position sensor retaining nuts
(Fig. 4).
(4) Remove pedal position sensor from vehicle.
INSTALLATION - PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
(LHD)
(1) Position pedal position sensor in vehicle.
(2) Install pedal position sensor retaining nuts
(Fig. 4).
(3) Connect pedal position sensor electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(4) Connect negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
(RHD)
(1) Position pedal position sensor in vehicle.
(2) Install 2 pedal position sensor retaining nuts
(Fig. 4).
(3) Connect pedal position sensor electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(4) Connect negative battery cable.
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The boost pressure sensor is mounted to the top of
the intake manifold. The sensor allows the ECM to
monitor air pressure within the intake manifold. The
boost pressure sensor is also used as an intake air
temperature sensor (Fig. 5).
OPERATION
When the intake manifold pressure is low (high
vacuum) sensor voltage output is 0.25-1.8 volts at the
ECM. When the intake manifold pressure is high due
to turbo boost, sensor voltage output is 2.0-4.7 volts.
The sensor receives a 5-volts reference from the
ECM. Sensor ground is also provides by the ECM.
The ECM uses boost pressure combined with intake
air temerature to determine the volume of air enter-
ing the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BOOST PRESSURE
SENSOR
If the boost pressure sensor fails, the ECM records
a DTC into memory and continues to operate theengine in one of the three limp-in modes. When the
ECM is operating in this mode, a loss of power will
be present, as if the turbocharger was not operating.
The best method for diagnosing faults with the boost
pressure sensor is with the DRB IIItscan tool. Refer
to the Diesel Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for more
information.
Refer to On-Board Diagnostics in Emissions Con-
trol System for a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTC's) for certain fuel system components.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The boost pressure sensor/intake air temperature
sensor is located in the top of the intake manifold
(Fig. 6). The intake air temperature sensor is used to
measure the intake air temperature. The intake air
temperture sensor is a dual purpose sensor. It is also
used as a boost pressure sensor.
OPERATION
The intake air temperature sensor is a negative
temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor (resistance
varies inversly with temperature). This means at
cold air temperature its resistance is high, sothe volt-
age signal will be high. As intake air temperature
increases, sensor resistance decreases and the signal
voltage will be low. This allows the sensor to provide
an analog voltage signal (0.2-4.8 volts) to the ECM.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover retaining bolts and cover-
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE COVER - REMOVAL).
Fig. 5 BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR/INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
RGFUEL INJECTION14a-13
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)