Page 440 of 4770

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The EGR system recirculates exhaust gas, which is controlled to the proper quantity to suit the
driving conditions, into the intake air mixture to slow down combustion, reduce the combustion
temperature and reduces NOx emissions. The amount of EGR is regulated by the EGR vacuum
modulator according to the engine load.
If even one of the following conditions is fulfilled,
the VSV is turned ON by a signal from the ECM.
This results in atmospheric air acting on the EGR
valve, closing the EGR valve and shutting off the
exhaust gas (EGR cut±OFF).
Under the following conditions, EGR is cut to
maintain driveability.
wEngine coolant temp. below 60�C (140�F).
wDuring deceleration (throttle valve closed).
wLight engine load (amount of intake air very
small).
wEngine speed over 4,400 rpm.
wEngine racing.
EG R gas temp. is 70�C (158�F) or below for 50
sec. under conditions (a) and (b).
(2 trip detection logic) *
(a) Engine coolant temp.: 80�C (176�F) or more.
(b) EGR operation possible (EX. A/T in 3rd speed
(5th for M/T), 55 ± 60 mph (88 ± 96 km/h),
Flat road).wOpen in EGR gas temp. sensor circuit.
wShort in VSV circuit for EGR.
wEGR hose disconnected, valve stuck.
wClogged EGR gas passage.
wECM Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
*: See page
EG1±307.Trouble Area DTC No.
DTC 71 EGR System Malfunction
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±390
Page 446 of 4770

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Park/Neutral Position Switch Signal*
The ECM uses the signals from the park/neutral position switch to determine whether the transmis±
sion is in park or neutral, or in some other gear.
Air Conditioning Switch Signal
The ECM uses the output from the air conditioning switch to determine whether or not the air
conditioning is operating so that it can increase the idling speed of the engine if necessary.
Throttle Position Sensor IDL Signal
The IDL contacts are mounted in the throttle position sensor, and detects the idle condition.
(1) 3 sec. or more after engine starts with closed
throttle position switch OFF (IDL).
(2) * Park/ Neutral position switch OFF.
(Shift position in ªRº, ªDº, ª2º or ªLº positions).
(3) A/C switch ON.
*: Only vehicles with A/T.
HINT: In this circuit, diagnosis can only be made in the test mode.
wThrottle position sensor IDL circuit
wAccelerator pedal and cable
wPark/Neutral position switch circuit
wA/C switch circuit
wECM Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
WIRING DIAGRAM
Trouble Area
DTC 51 Switch Condition Signal Circuit
DTC No.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±396
Page 511 of 4770
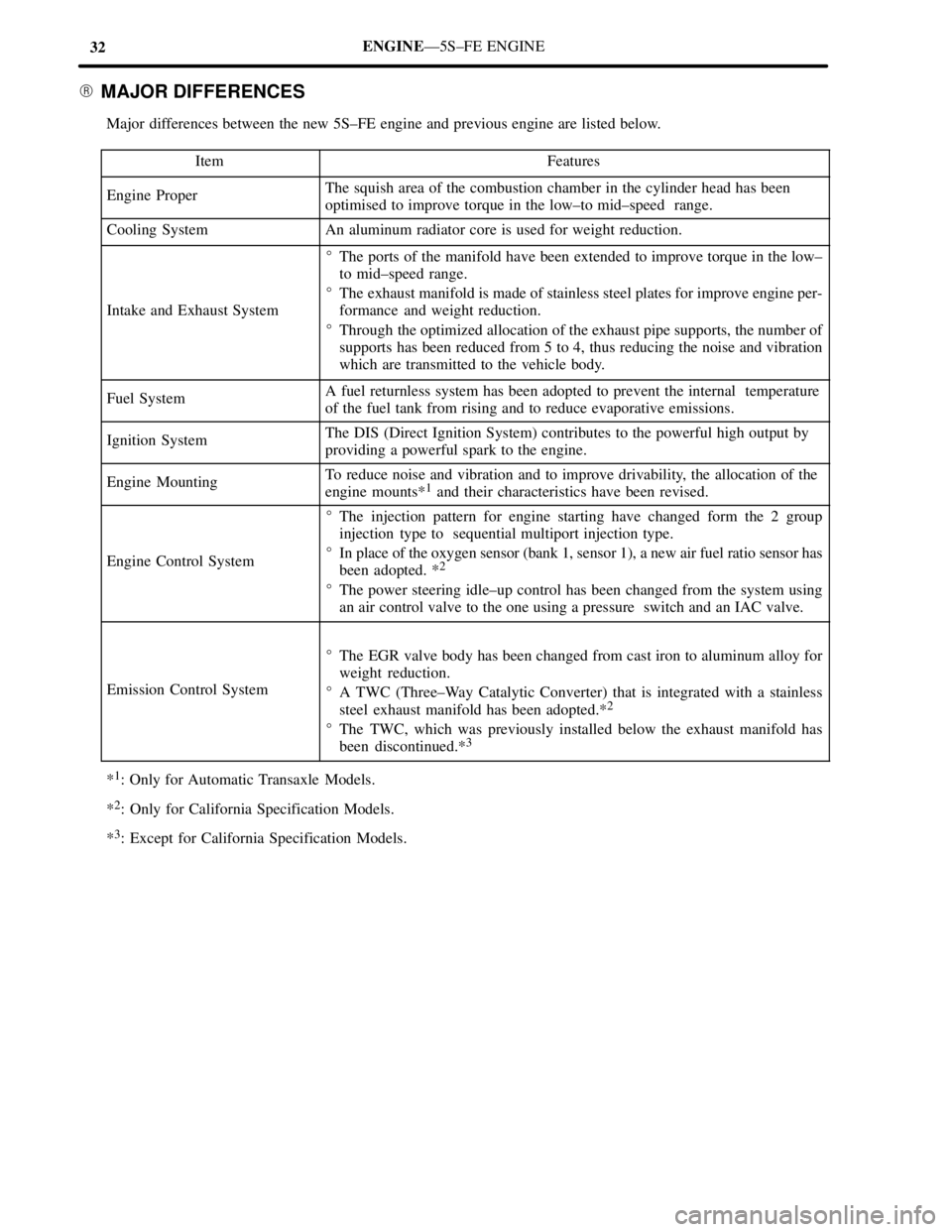
32ENGINEÐ5S±FE ENGINE
� MAJOR DIFFERENCES
Major differences between the new 5S±FE engine and previous engine are listed below.
Item
Features
Engine ProperThe squish area of the combustion chamber in the cylinder head has been
optimised to improve torque in the low±to mid±speed range.
Cooling SystemAn aluminum radiator core is used for weight reduction.
Intake and Exhaust System
�The ports of the manifold have been extended to improve torque in the low±
to mid±speed range.
�The exhaust manifold is made of stainless steel plates for improve engine per-
formance and weight reduction.
�Through the optimized allocation of the exhaust pipe supports, the number of
supports has been reduced from 5 to 4, thus reducing the noise and vibration
which are transmitted to the vehicle body.
Fuel SystemA fuel returnless system has been adopted to prevent the internal temperature
of the fuel tank from rising and to reduce evaporative emissions.
Ignition SystemThe DIS (Direct Ignition System) contributes to the powerful high output by
providing a powerful spark to the engine.
Engine MountingTo reduce noise and vibration and to improve drivability, the allocation of the
engine mounts*1 and their characteristics have been revised.
Engine Control System
�The injection pattern for engine starting have changed form the 2 group
injection type to sequential multiport injection type.
�In place of the oxygen sensor (bank 1, sensor 1), a new air fuel ratio sensor has
been adopted. *
2
�The power steering idle±up control has been changed from the system using
an air control valve to the one using a pressure switch and an IAC valve.
Emission Control System
�The EGR valve body has been changed from cast iron to aluminum alloy for
weight reduction.
�A TWC (Three±Way Catalytic Converter) that is integrated with a stainless
steel exhaust manifold has been adopted.*
2
�The TWC, which was previously installed below the exhaust manifold has
been discontinued.*3
*1: Only for Automatic Transaxle Models.
*
2: Only for California Specification Models.
*
3: Except for California Specification Models.
Page 515 of 4770
36ENGINEÐ5S±FE ENGINE
3. Spark Plugs
Twin grouond electrode platinum tipped spar plugs have been adopted to rreflect the change of the DIS system.
�Recommended Spark Plug Types�
NIPPONDENSO
PK20TR11
NGKBKR6EKPB11
Plug Gap1.0 ± 1.1 mm
(0.039 ± 0.043 in.)
� ENGINE MOUNTING
1. Manual Transaxle Models
The charasteristics of the front and rear mounts have been optimized.
2. Automatic Transaxle Models
�The fromt and rear mounts have been relocated upward to bring the engine's roll center closer to the engine's center
of gravity, resulting in reducing noise and vibration and improving drivability.
�The internal orifices of the front and rear mounts have been modified to improve riding comfort and to ensure a
quieter operatioon at idling.
Page 521 of 4770

42ENGINEÐ5S±FE ENGINE
5. Main Components of Engine Control System
The following table compares the main components of the new 5S±FE engine, and previous 5S±FE engine.
Model
NewPreviousComponentNewPrevious
Manifold Absolute Pressure SensorSemiconductoru
Throttle Position SensorLinear Typeu
Crankshaft Position SensorPick±Up Coil Type, 1u
Camshaft Position SensorPick±Up Coil Type, 1Ð
DistributorCamshaft PositionPick Up Coil Type 1DistributorSensorÐPick±Up Coil Type, 1
Knock SensorBuilt±In Piezoelectric
Element Type 1u
Oxygen Sensor
Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank 1, Sensor 1)*
1
(Bank 1, Sensor 2)
Air Fuel Ratio Sensor*
2
Oxygen Sensor
(Bank 1, Sensor 1)
(Bank 1, Sensor 2)
Injector2±Hole Typeu
IAC ValveRotary Solenoid Typeu
*1: Except for California Specification Models.
*
2: Only for California Specification Models.
Camshaft Position Sensor
The camshaft position sensor is mounted onto the
cylinder head. Using the protusion that is provided
on the timing pulley, the sensor generates 1 signal
for every revolution. This signal is then sent to the
ECM as a cranskshaft angle system.
Page 525 of 4770

46ENGINEÐ1MZ±FE ENGINE
� MAJOR DIFFERNCES
Major differences between the new 1MZ±FE engne and previous engine are listed below.
Item
Outline
Cooling SystemAn aluminum radiator core is used for weight reduction.
Intake and Exhaust System
Through the optimized allocation of the exhaust pipe supports, the number
number of supports has been reduced from 5 to 4, thus reducing the noise
and vibration which are transmitted to the vehicle body.
Fuel SystemA fuel returnless system has been adopted to prevent the internal temperature
of the fuel tank from rising, and to reduce evaporative emissions.
Engine MountingThe characteristics of the engine mounts, torque rod, and absorber have been
optimized to reduce noise and vibration.
Engine Control System
�A communication circuit has been provided between the ECM and the
ABS & TRAC ECU in conjunction with the adoption of the TRAC
(Traction Control) system.*
�The fuel pressure control has been discontinued in conjunction with the
adoption of the fuel returnless system.
�Instead of using the IDL signal input from the throttle position sensor,
the ECM now uses the VTA signal to detect the completely closed state of
the throttle valve.
�A new EGR system which uses a EGR valve position sensor is used.
�A communication method of the ECM and the hand±held tester has been
changed from the SAEJ1962 to the ISO 9141±2.
*: Applicable only to Vehicle Equipped with the TRAC System.
Page 526 of 4770
47 ENGINEÐ1MZ±FE ENGINE
� FUEL SYSTEM
1. Fuel Returnless System
The new Camry has adopted a fuel returnless system to reduce evaporative emissions. With the pressure regulator
housed inside the fuel tank, this system elimnates the return of fuel from the engine area. This prevents the internal
temperature of the fuel tank from risisng, and reduces evaporative emissions.
� ENGINE MOUNTING
1. General
�The internal ofifice of the fron tmount has been modified to improve the riding comfort and to ensure a quieter
operation at idling.
�The characteristics of the rear mount, left mount, torque rod, and absorber have been optimized.
Page 532 of 4770
53ENGINEÐ1MZ±FE ENGINE
2) VCV (Vacuum Control Valve)
The VCV is a valve that regulates the intake manifold
vacuum that is appllied to the VSV to a constant level
(±17 kPa, ±130 mm Hg.)
The intake manifold vacuum that is supplied
through the S port is applied to the diaphragm. If this
force becomes greater than the spring force, the
diaphragm moves downward, allowing the valve to
close the S port and the atmosphere supplied
through the filter. Conversely, if the vacuum that is
applied to the diaphragm becomes weaker, the
diaphragm moves upward, causing the valve to
open and to shut off the atmosphere and supply the
intake manifold vacuum. This process is repeated to
regulate the vacuum in the Z port to a constant level.
3) EGR Valve Position Sensor
The EGR valve position sensor is mounted on the EGR valve. This sensor converts the EGR valve opening into a
voltage and sends it to the ECM as the EGR valve position signal.