2000 DODGE NEON engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 847 of 1285

²Coolant temperature
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Engine run time
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²Transmission gear selection (park/neutral
switch)
²Vehicle distance (speed)
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays
are mounted externally, but turned on and off by the
PCM.
The crankshaft position sensor signal is sent to the
PCM. If the PCM does not receive the signal within
approximately one second of engine cranking, it deac-
tivates the ASD relay and fuel pump relay. When
these relays deactivate, power is shut off from the
fuel injectors, ignition coils, heating element in the
oxygen sensors and the fuel pump.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8 volts direct
current to power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5 volt direct current supply for
the manifold absolute pressure sensor and throttle
position sensor.
PCM GROUND
OPERATION
Ground is provided through multiple pins of the
PCM connector. Depending on the vehicle there may
be as many as three different ground pins. There are
power grounds and sensor grounds.
The power grounds are used to control the ground
side of any relay, solenoid, ignition coil or injector.
The signal ground is used for any input that uses
sensor return for ground, and the ground side of any
internal processing component.
The SBEC III case is shielded to prevent RFI and
EMI. The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the case is also
grounded separately from the ground pins.
5 VOLT SUPPLYÐPCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Throttle position sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid
8-VOLT SUPPLYÐPCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
The PCM supplies 8 volts to the crankshaft posi-
tion sensor, camshaft position sensor.
FUEL CORRECTION or ADAPTIVE MEMORIES
DESCRIPTION
In Open Loop, the PCM changes pulse width with-
out feedback from the O2 Sensors. Once the engine
warms up to approximately 30 to 35É F, the PCM
goes into closed loopShort Term Correctionand
utilitzes feedback from the O2 Sensors. Closed loop
Long Term Adaptive Memoryis maintained above
170É to 190É F unless the PCM senses wide open
throttle. At that time the PCM returns to Open Loop
operation.
OPERATION
Short Term
The first fuel correction program that begins func-
tioning is the short term fuel correction. This system
corrects fuel delivery in direct proportion to the read-
ings from the Upstream O2 Sensor.
The PCM monitors the air/fuel ratio by using the
input voltage from the O2 Sensor. When the voltage
reaches its preset high or low limit, the PCM begins
to add or remove fuel until the sensor reaches its
switch point. The short term corrections then begin.
The PCM makes a series of quick changes in the
injector pulse-width until the O2 Sensor reaches its
opposite preset limit or switch point. The process
then repeats itself in the opposite direction.
Short term fuel correction will keep increasing or
decreasing injector pulse-width based upon the
upstream O2 Sensor input. The maximum range of
authority for short term memory is 25% (+/-) of base
pulse-width.
Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
There are up to 16 cells. Two cells are used only
during idle, based upon TPS and Park/Neutral
switch inputs. There may be two other cells used for
deceleration, based on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle
speed. The other twelve cells represent a manifold
pressure and an rpm range. Six of the cells are high
rpm and the other six are low rpm. Each of these
cells is a specific MAP voltage range.
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 851 of 1285

signal to the PCM, allowing engine starter operation.
The interlock switch is not adjustable.
Clutch Pedal Upstop Switch
With the clutch pedal at rest, the clutch pedal
upstop switch is closed, allowing speed control oper-
ation. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the upstop
switch opens and signals the PCM to cancel speed
control operation, and enter a modified engine cali-
bration schedule to improve driveability during gear-
to-gear shifts. The upstop switch is not adjustable.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the front
of the engine block (Fig. 8).
OPERATION
The PCM determines what cylinder to fire from the
crankshaft position sensor input and the camshaft
position sensor input. The second crankshaft counter-
weight has two sets of four timing reference notches
including a 60 degree signature notch (Fig. 9). From
the crankshaft position sensor input the PCM deter-
mines engine speed and crankshaft angle (position).
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the output
voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.
The PCM uses the Crankshaft Position sensor to
calculate the following: Engine RPM, TDC number 1
and 4, Ignition coil synchronization, Injection Syn-
chronization, Camshaft-to-crankshaft misalignment
where applicable (Timing belt skipped 1 tooth or
more diagnostic trouble code).
The PCM sends approximately 9 volts to the Hall-
effect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the
Hall-effect chip and the electronics inside the sensor.
A ground for the sensor is provided through the sen-
sor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a
5 volt output reference circuit.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The coolant sensor threads into the rear of the cyl-
inder head, next to the camshaft position sensor (Fig.
10). New sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
The ECT Sensor is a Negative Thermal Coefficient
(NTC), dual range Sensor. The resistance of the ECT
Sensor changes as coolant temperature changes. This
results in different input voltages to the PCM. The
PCM also uses the ECT Sensor input to operate the
low and high speed radiator cooling fans.
Fig. 8 Crankshaft Position Sensor
14 - 30 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 852 of 1285

OPERATION
The combination coolant temperature sensor has
two elements. One element supplies coolant temper-
ature signal to the PCM. The other element supplies
coolant temperature signal to the instrument panel
gauge cluster. The PCM determines engine coolant
temperature from the coolant temperature sensor.
As coolant temperature varies the coolant temper-
ature sensors resistance changes resulting in a differ-
ent input voltage to the PCM and the instrument
panel gauge cluster.When the engine is cold, the PCM will provide
slightly richer air- fuel mixtures and higher idle
speeds until normal operating temperatures are
reached.
The PCM has a dual temperature range program
for better sensor accuracy at cold temperatures. At
key-ON the PCM sends a regulated five volt signal
through a 10,000 ohm resistor to the sensor. When
the sensed voltage reaches approximately 1.25 volts
the PCM turns on the transistor. The transistor con-
nects a 1,000 ohm resistor in parallel with the 10,000
ohm resistor. With this drop in resistance the PCM
recognizes an increase in voltage on the input circuit.
FUEL LEVEL SENSORÐPCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge level sending unit is attached to the
fuel pump module.
OPERATION
The fuel level sensor (fuel gauge sending unit)
sends a signal to the PCM to indicate fuel level. The
purpose of this feature is to prevent a false setting of
misfire and fuel system monitor trouble codes if the
fuel level is less than approximately 15 percent of its
rated capacity. It is also used to send a signal for fuel
gauge operation via the PCI bus circuits.
Fig. 9 Timing Reference Notches
1 ± MACHINED NOTCHES
2 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 10 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐSOHC
1 ± ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 ± CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 860 of 1285

PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
All vehicles use a proportional purge solenoid. The
solenoid regulates the rate of vapor flow from the
EVAP canister to the throttle body. The PCM oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The proportional purge solenoid operates at a fre-
quency of 200 hz and is controlled by an engine con-
troller circuit that senses the current being applied
to the proportional purge solenoid (Fig. 23) and then
adjusts that current to achieve the desired purge
flow. The proportional purge solenoid controls the
purge rate of fuel vapors from the vapor canister and
fuel tank to the engine intake manifold.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
Refer to the Battery section for information and
refer to the Charging section for information. The
PCM regulates the charging system voltage within a
range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. The charging system is
turned ON and OFF with the Ignition Switch. When
the Ignition Switch is turned to the ON position, bat-
tery voltage is applied to the generator rotor through
one of the two field terminals to produce a magnetic
field. The amount of DC current produced by the
generator is controlled by the Electronic Voltage Reg-
ulator (EVR) in the PCM. This circuitry is connectedin series with the second rotor field terminal and
ground.
The voltage determined by the PCM as the final
goal for the charging system is called ªtarget charg-
ing voltage.º The PCM monitors battery voltage. If
the sensed voltage is 0.5 volts or lower than the tar-
get voltage, the PCM grounds the field winding until
sensed battery voltage is 0.5 volts above target volt-
age.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is mounted on the
throttle body. The PCM operates the idle air control
motor (Fig. 24).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control motor pintle protrudes into the
air bypass passage and regulates air flow through it.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
IAC motor pintle in and out of the bypass passage.
The adjustments are based on inputs the PCM
receives. The inputs are from the throttle position
sensor, crankshaft position sensor, coolant tempera-
ture sensor, MAP sensor, vehicle speed sensor and
various switch operations (brake, park/neutral, air
conditioning).
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following functions:
²Off-idle dashpot
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
Target Idle
Target idle is determined by the following inputs:
²Gear position
²ECT Sensor
²Battery voltage
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor
²VSS
²TPS
²MAP Sensor
Fig. 23 Proportional Purge Solenoid
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 39
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 868 of 1285

(5) Install the wiring harness into the clips on the
side of the air cleaner box.
(6) Install air cleaner element on to throttle body
and push towards the throttle body and past lip in
air cleaner box bottom (Fig. 45).
(7) Install air duct.
(8) Install lid and tighten screws.
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove 5 screws from air cleaner element box
lid.(2) Remove lid from air cleaner box.
(3) Pull air cleaner up and out of air cleaner box.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air cleaner element on to throttle body
and push towards the throttle body and past lip in
air cleaner box bottom (Fig. 46).
(2) Install lid and tighten screws.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The engine coolant temperature sensor threads
into the rear of the cylinder head (Fig. 47).
REMOVAL
(1) With the engine cold, drain coolant until level
drops below cylinder head. Refer to the Cooling Sys-
tem section.
(2) Disconnect coolant sensor electrical connector.
(3) Remove coolant sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant sensor. Tighten sensor to 18
N´m (165 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
(3) Fill cooling system. Refer to the Cooling Sys-
tem section.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle speed sensor is located in the transmis-
sion extension housing (Fig. 48) or (Fig. 49).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove the sensor mounting bolt.
Fig. 44 Air Cleaner Box
Fig. 45 Air Cleaner Box Lip
1 ± LIP
Fig. 46 Air Cleaner Element
1 ± LIP
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 47
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 869 of 1285
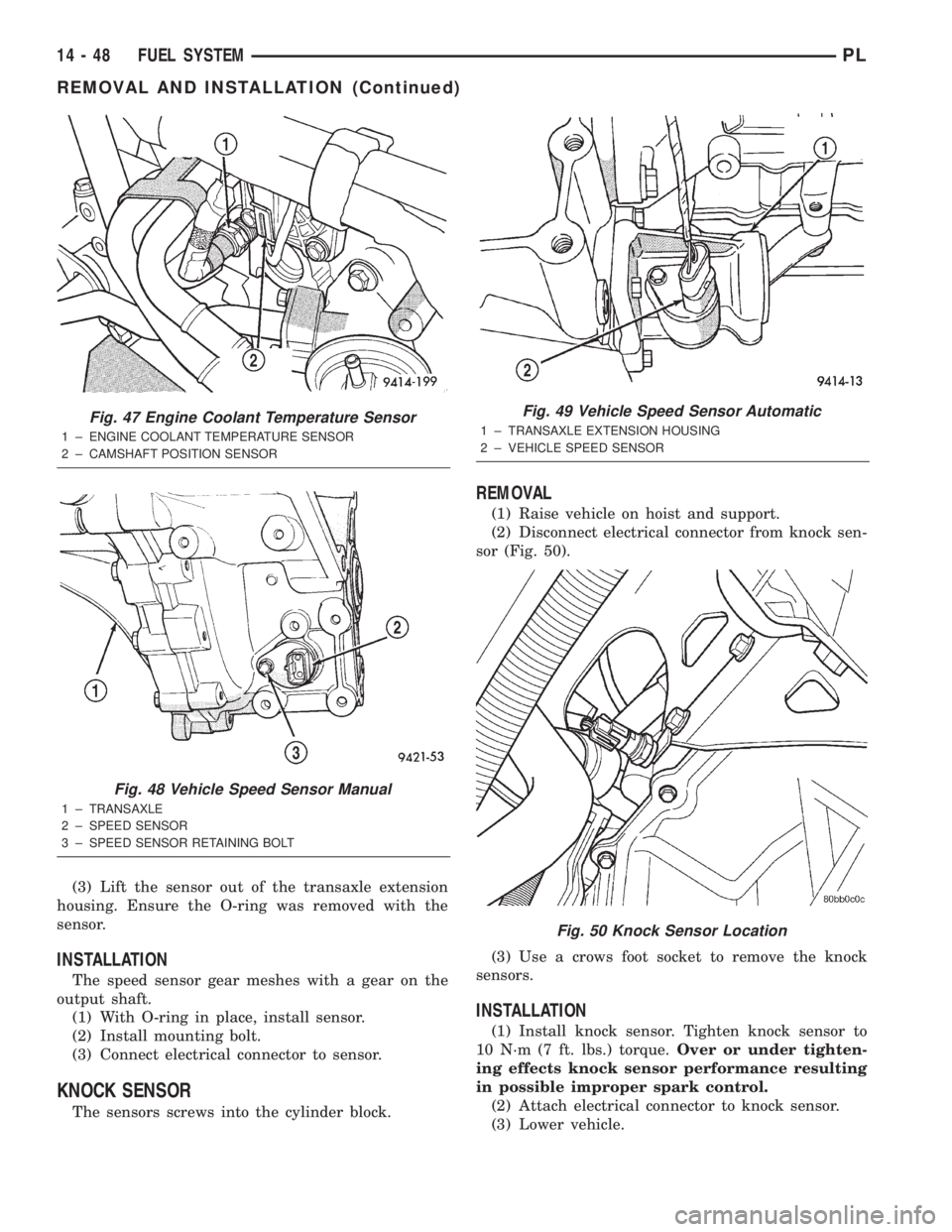
(3) Lift the sensor out of the transaxle extension
housing. Ensure the O-ring was removed with the
sensor.
INSTALLATION
The speed sensor gear meshes with a gear on the
output shaft.
(1) With O-ring in place, install sensor.
(2) Install mounting bolt.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
KNOCK SENSOR
The sensors screws into the cylinder block.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor (Fig. 50).
(3) Use a crows foot socket to remove the knock
sensors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance resulting
in possible improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
(3) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 47 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
1 ± ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 ± CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 48 Vehicle Speed Sensor Manual
1 ± TRANSAXLE
2 ± SPEED SENSOR
3 ± SPEED SENSOR RETAINING BOLT
Fig. 49 Vehicle Speed Sensor Automatic
1 ± TRANSAXLE EXTENSION HOUSING
2 ± VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 50 Knock Sensor Location
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 870 of 1285

SPECIFICATIONS
VECI LABEL
Always use the information found on the Vehicle
Emission Control Information (VECI) label. The
VECI label is located in the engine compartment.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Air Cleaner Lid Screws...... 3.9N´m(35in.lbs.)
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mounting Bolts . . 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.)
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor...... 18N´m
(165 in. lbs.)
IAC Motor-To-Throttle Body Bolts....... 4.5N´m
(40 in. lbs.)
MAP Sensor............... 4.5N´m(40in.lbs.)
Oxygen Sensor............. 28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Mounting
Screws.................. 4N´m(35in.lbs.)
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts........... 23N´m
(200 in. lbs.)
Throttle Position Sensor Mounting Screws . . 2 N´m
(20 in. lbs.)
Vehicle Speed Sensor Mounting Bolt..... 2.2N´m
(20 in. lbs.)
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL
Extractor C±4334
Pressure Gauge Assembly C±4799±B
Fuel Pressure Test Adapter 6539
Spanner Wrench 6856
Metering Orifice
Fuel Line Adapter 1/4
O2S (Oxygen Sensor) Remover/InstallerÐC-4907
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 49
Page 1091 of 1285

²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Alternate Good Trip
Alternate Good Trips are used in place of Global
Good Trips for Comprehensive Components and
Major Monitors. If the Task Manager cannot run a
Global Good Trip because a component fault is stop-
ping the monitor from running, it will attempt to
count an Alternate Good Trip.
The Task Manager counts an Alternate Good Trip
for Comprehensive components when the following
conditions are met:
²Two minutes of engine run time
²No other faults occur
The Task Manager counts an Alternate Good Trip
for a Major Monitor when the monitor runs and
passes. Only the Major Monitor that failed needs to
pass to count an Alternate Good Trip.
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
can determine under what vehicle operating condi-
tions the failure occurred.
The data stored in Freeze Frame is usually
recorded when a system fails the first time for twotrip faults. Freeze Frame data will only be overwrit-
ten by a different fault with a higher priority.
CAUTION: Erasing DTCs, either with the DRB III or
by disconnecting the battery, also clears all Freeze
Frame data.
Similar Conditions Window
The Similar Conditions Window displays informa-
tion about engine operation during a monitor. Abso-
lute MAP (engine load) and Engine RPM are stored
in this window when a failure occurs. There are two
different Similar conditions Windows: Fuel System
and Misfire.
FUEL SYSTEM
²Fuel System Similar Conditions WindowÐ
An indicator that 'Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys Fail'
and 'RPM When Fuel Sys Failed' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys FailÐ The
stored MAP reading at the time of failure. Informs
the user at what engine load the failure occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Fuel Sys FailÐ The stored RPM
reading at the time of failure. Informs the user at
what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM uti-
lizes both Short Term Compensation and Long Term
Adaptive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor
for total fuel correction.
²Upstream O2S VoltsÐ A live reading of the
Oxygen Sensor to indicate its performance. For
example, stuck lean, stuck rich, etc.
²SCW Time in Window (Similar Conditions
Window Time in Window)Ð A timer used by the
PCM that indicates that, after all Similar Conditions
have been met, if there has been enough good engine
running time in the SCW without failure detected.
This timer is used to increment a Good Trip.
²Fuel System Good Trip CounterÐATrip
Counter used to turn OFF the MIL for Fuel System
DTCs. To increment a Fuel System Good Trip, the
engine must be in the Similar Conditions Window,
Adaptive Memory Factor must be less than cali-
brated threshold and the Adaptive Memory Factor
must stay below that threshold for a calibrated
amount of time.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates that the
monitor has already been run and completed during
the current trip.
25 - 4 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)