2000 DODGE NEON coolant level
[x] Cancel search: coolant levelPage 4 of 1285

MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES................3
SPECIFICATIONS
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION................3SCHEDULE ± A...........................3
SCHEDULE ± B...........................4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service for your vehicle.
First is Schedule ±A. It lists all the scheduled
maintenance to be performed under ªnormalº operat-
ing conditions.
Second is Schedule ±B. It is a schedule for vehi-
cles that are operated under the following conditions:
²Frequent short trip driving less than 5 miles (8
km)
²Frequent driving in dusty conditions
²Extensive idling
²More than 50% of the driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90É F (32É C)
SPECIFICATIONS
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION
At Each Stop For Fuel
²Check engine oil level and add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add as
required.
Once A Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten termi-
nals as required.
²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transmission.
Add fluid as required.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponent boots and seals.²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on Schedule ± A (7,500 miles - 12 000 km) or
every other interval on Schedule ± B (6,000 miles -
10 000 km).
²Check the engine coolant level, hoses, and
clamps.
If mileage is less than 7,500 miles (12 000 km)
yearly, replace the engine oil filter at each oil change.
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
The scheduled emission maintenance listed inbold
typeon the Maintenance Schedules, must be done at
the mileage specified to assure the continued proper
functioning of the emission control system. These,
and all other maintenance services included in this
manual, should be done to provide the best vehicle
performance and reliability. More frequent mainte-
nance may be needed for vehicles in severe operating
conditions such as dusty areas and very short trip
driving.
FLUID FILL POINTS AND LUBRICATION
LOCATIONS
The fluid fill/check locations and lubrication loca-
tions are located in each applicable group.
SCHEDULE ± A
7,500 Miles (12 000 km) or at 6 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km) or at 12 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
22,500 Miles (36 000 km) or at 18 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 3
Page 180 of 1285
COOLING SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLING SYSTEM........................1
COOLANT...............................2
COOLANT PERFORMANCE..................2
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM..............3
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.....................3
RADIATOR..............................3
RADIATOR COOLING FAN MODULE...........3
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP..........4
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS............5
WATER PUMP...........................5
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER.....6
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS.................6
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER...................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS..............7
ENGINE THERMOSTAT TESTING............14
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS........14
WATER PUMP DIAGNOSIS................15
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK...........15
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR TEST...............15
COOLANT CONCENTRATION TESTING........15
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS.....15
PRESSURE CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK...............16
PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP.......................16
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION...........17
DEAERATION...........................17
TEMPERATURE GAUGE INDICATION.........17
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER..................17
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE.........17COOLANTÐADDING ADDITIONAL...........18
COOLANT LEVELÐSERVICING.............18
COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING.............19
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING............19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WATER PUMP..........................19
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE................20
ENGINE THERMOSTAT....................20
RADIATOR.............................21
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK...................22
COOLING FAN MODULE...................22
COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER..........23
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER..................24
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS................24
AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY....26
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
COOLING FAN MODULE...................26
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
WATER PUMP..........................28
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT INSPECTION.......28
COOLING SYSTEM CAP...................28
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING..............28
RADIATOR FLUSHING....................28
REVERSE FLUSHING.....................29
CHEMICAL CLEANING....................29
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION..........................29
SPECIFICATIONS
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY..............30
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.................30
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING..............................30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of an engine cooling
module, thermostat, coolant, and a water pump to
circulate the coolant. The engine cooling module may
consist of a radiator, electric fan motor, fan, shroud,
coolant reserve system, transmission oil cooler, hoses,clamps, air conditioning condenser and transmission
oil lines.
²When the Engine is cold: The thermostat is
closed and the cooling system has no flow through
the radiator. The coolant flows through the engine,
heater system and bypass.
²When the Engine is warm: Thermostat is open
and the cooling system has flow through the radiator,
engine, heater system, and bypass.
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 182 of 1285

protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is
recommended for best engine cooling without corro-
sion. When mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. The system provides space for expansion
and contraction. Also, the system provides a conve-
nient and safe method for checking and adjusting the
coolant level at atmospheric pressure without remov-
ing the pressure cap. It also provides some reserve
coolant to compensate for minor leaks and evapora-
tion or boiling losses. All vehicles are equipped with
this system (Fig. 2).
Refer to Coolant Level Check, Deaeration, and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine thermostat is located on the front of
the engine (radiator side) in the thermostat housing/
engine outlet connector. The thermostat has an air
bleed (vent) located in the flange and a O-ring for
sealing incorporate on it. There is a relief in the ther-
mostat housing/outlet connector for the O-ring.
The engine thermostat is a wax pellet driven,
reverse poppet choke type. It is designed to provide
the fastest warm up possible by preventing leakage
through it and to guarantee a minimum engine oper-
ating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC (192 to 199ÉF). Also,
the thermostat will automatically reach wide open, to
accommodate unrestricted flow to the radiator astemperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the radiator, fan,
and ambient temperatureÐnot the thermostat.
A thermostats primary purpose is to maintain
engine temperature in a range that will provide sat-
isfactory engine performance and emission levels
under all expected driving conditions. It also provides
hot water (coolant) for heater performance. It does
this by transferring heat from engine metal and
automatic transmission oil cooler (if equipped) to
coolant, moving this heated coolant to the heater core
and radiator, and then transferring this heat to the
ambient air.
RADIATOR
The radiator is a down-flow type (vertical tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength,
as well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep
the engine coolant within operating temperatures.
The radiator functions as a heat exchanger, using
air flow across the exterior of the radiator tubes. This
heat is then transferred from the coolant and into
the passing air.
The radiator has an aluminum core with plastic
tanks. Although stronger than brass, plastic tanks
are subject to damage by impact. Always handle radi-
ator with care.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN MODULE
The radiator cooling fan is a single speed electric
motor driven fan. The fan module includes an electric
motor, fan blade, and a support shroud that is
attached to the radiator (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 Coolant Recovery System
1 ± RECOVERY HOSE
2 ± ENGINE COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 ± PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 3 Radiator Fan
1 ± SCREWS
2 ± LOWER MOUNTS
3 ± FAN MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 186 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
LOW1. Has a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) been set indicating a stuck
open engine thermostat?1. Refer to On Board Diagnostic in
Group 25. Replace thermostat, if
necessary. If a (DTC) has not been
set, the problem may be with the
temperature gauge.
2. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) connected to the
temperature gauge coolant sensor
on the engine?2. Check the connector at the
engine coolant sensor. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
3. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) operating OK?3. Check Gauge operation. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
4. Coolant level low during cold
ambient temperature, accompanied
by poor heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the coolant
recovery/reserve container and the
radiator. Inspect the system for
leaks. Repair as necessary. Refer to
WARNINGS in this section before
removing pressure cap.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM.1. Trailer being towed, a steep hill
being climbed, vehicle being
operated in slow moving traffic, or
engine idling during high ambient
(outside) temperatures with air
conditioning on. High altitudes
Could aggravate these conditions.1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and drive the vehicle
without any of the previous
conditions. Observe the temperature
gauge the gauge should return to
the normal range. If the gauge does
not return to the normal range,
determine the cause of the
overheating and repair. Refer to
POSSIBLE CAUSES in this section.
2. Is temperature gauge (if
equipped) reading correctly?2. Check gauge. Refer to Group 8E.
Repair as necessary.
3. Is temperature warning lamp (if
equipped) illuminating
unnecessarily?3. Check warning lamp operation.
Refer to Group 8E. Repair as
necessary.
4. Coolant low in recovery/reserve
container and radiator?4. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary. Refer to
Checking Cooling System for Leaks
in this section.
5. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered. Also refer
to the following step 6.5. Tighten cap.
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 7
Page 187 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM. (CONT.)6. Poor seals at radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator cap
Inspection. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck. If
neck is bent or damaged, replace
neck.
7. Coolant level low in radiator, but
not in coolant recovery/reserve
container. This indicates the
radiator is not drawing coolant from
the coolant recovery/reserve
container as the engine cools. As
the engine cools, a vacuum is
formed inside the cooling system. If
the radiator cap seals are defective,
or the cooling system has a leak, a
vacuum cannot be formed.7. (a) Check condition of radiator
cap and cap seals. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck.
Replace if damaged.
(c) Check condition of hose from
filler neck to coolant container. It
should be tight at both ends without
any kinks or tears. Replace hose as
necessary.
(d) Check coolant recovery/reserve
container and hose for blockage.
Repair as necessary.
8. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture ratio may be too
rich.8. Check coolant concentration.
Refer to Coolant Concentration
Testing in this section. Adjust
glycol-to-water ration as required.
9. Coolant not flowing through
system.9. Check for coolant flow at filler
neck with some coolant removed,
engine warm, and thermostat open.
Coolant should be observed flowing
through filler neck. If flow is not
observed, determine reason for lack
of flow and repair as necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.10. Clean obstruction from fins.
11. Radiator core is plugged or
corroded.11. Replace or re-core radiator.
12. Fuel or ignition system
problems.12. Refer to Fuel and Ignition
System groups for diagnosis. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedure manual.
13. Dragging Brakes. 13. Inspect brake system and repair
as necessary. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for diagnosis.
14 Bug screen or other aftermarket
accessory is being used causing
reduced air flow.14. Remove bug screen or
accessory.
15. Thermostat partially or
completely closed. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.15. Check thermostat operation and
replace as necessary. Refer to
thermostat in this section for
procedure.
7 - 8 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 188 of 1285
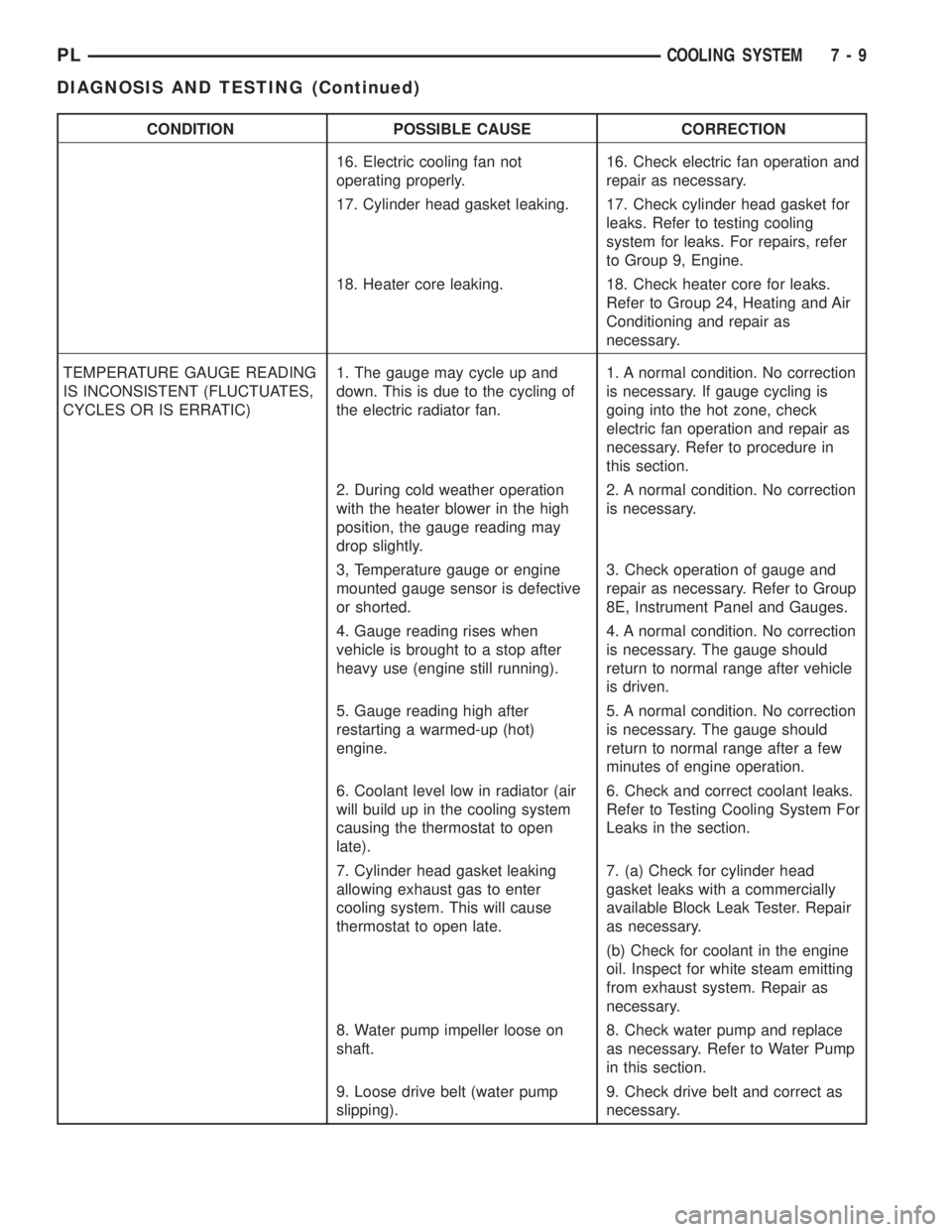
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
16. Electric cooling fan not
operating properly.16. Check electric fan operation and
repair as necessary.
17. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 17. Check cylinder head gasket for
leaks. Refer to testing cooling
system for leaks. For repairs, refer
to Group 9, Engine.
18. Heater core leaking. 18. Check heater core for leaks.
Refer to Group 24, Heating and Air
Conditioning and repair as
necessary.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
IS INCONSISTENT (FLUCTUATES,
CYCLES OR IS ERRATIC)1. The gauge may cycle up and
down. This is due to the cycling of
the electric radiator fan.1. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. If gauge cycling is
going into the hot zone, check
electric fan operation and repair as
necessary. Refer to procedure in
this section.
2. During cold weather operation
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.2. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary.
3, Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor is defective
or shorted.3. Check operation of gauge and
repair as necessary. Refer to Group
8E, Instrument Panel and Gauges.
4. Gauge reading rises when
vehicle is brought to a stop after
heavy use (engine still running).4. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. The gauge should
return to normal range after vehicle
is driven.
5. Gauge reading high after
restarting a warmed-up (hot)
engine.5. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. The gauge should
return to normal range after a few
minutes of engine operation.
6. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open
late).6. Check and correct coolant leaks.
Refer to Testing Cooling System For
Leaks in the section.
7. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system. This will cause
thermostat to open late.7. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks with a commercially
available Block Leak Tester. Repair
as necessary.
(b) Check for coolant in the engine
oil. Inspect for white steam emitting
from exhaust system. Repair as
necessary.
8. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.8. Check water pump and replace
as necessary. Refer to Water Pump
in this section.
9. Loose drive belt (water pump
slipping).9. Check drive belt and correct as
necessary.
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 189 of 1285
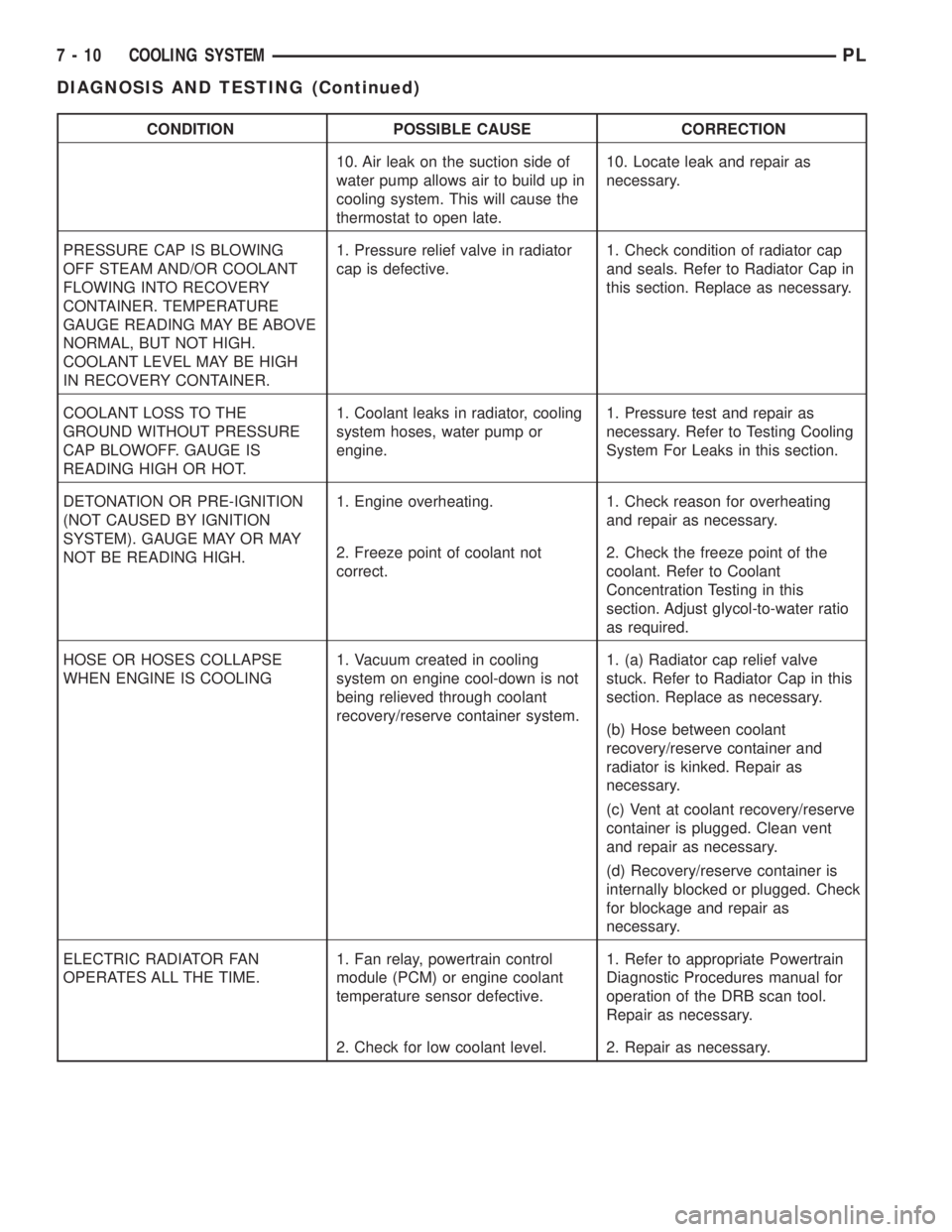
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
10. Air leak on the suction side of
water pump allows air to build up in
cooling system. This will cause the
thermostat to open late.10. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT
FLOWING INTO RECOVERY
CONTAINER. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE READING MAY BE ABOVE
NORMAL, BUT NOT HIGH.
COOLANT LEVEL MAY BE HIGH
IN RECOVERY CONTAINER.1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and seals. Refer to Radiator Cap in
this section. Replace as necessary.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT PRESSURE
CAP BLOWOFF. GAUGE IS
READING HIGH OR HOT.1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump or
engine.1. Pressure test and repair as
necessary. Refer to Testing Cooling
System For Leaks in this section.
DETONATION OR PRE-IGNITION
(NOT CAUSED BY IGNITION
SYSTEM). GAUGE MAY OR MAY
NOT BE READING HIGH.1. Engine overheating. 1. Check reason for overheating
and repair as necessary.
2. Freeze point of coolant not
correct.2. Check the freeze point of the
coolant. Refer to Coolant
Concentration Testing in this
section. Adjust glycol-to-water ratio
as required.
HOSE OR HOSES COLLAPSE
WHEN ENGINE IS COOLING1. Vacuum created in cooling
system on engine cool-down is not
being relieved through coolant
recovery/reserve container system.1. (a) Radiator cap relief valve
stuck. Refer to Radiator Cap in this
section. Replace as necessary.
(b) Hose between coolant
recovery/reserve container and
radiator is kinked. Repair as
necessary.
(c) Vent at coolant recovery/reserve
container is plugged. Clean vent
and repair as necessary.
(d) Recovery/reserve container is
internally blocked or plugged. Check
for blockage and repair as
necessary.
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME.1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM) or engine coolant
temperature sensor defective.1. Refer to appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
Repair as necessary.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Repair as necessary.
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 191 of 1285
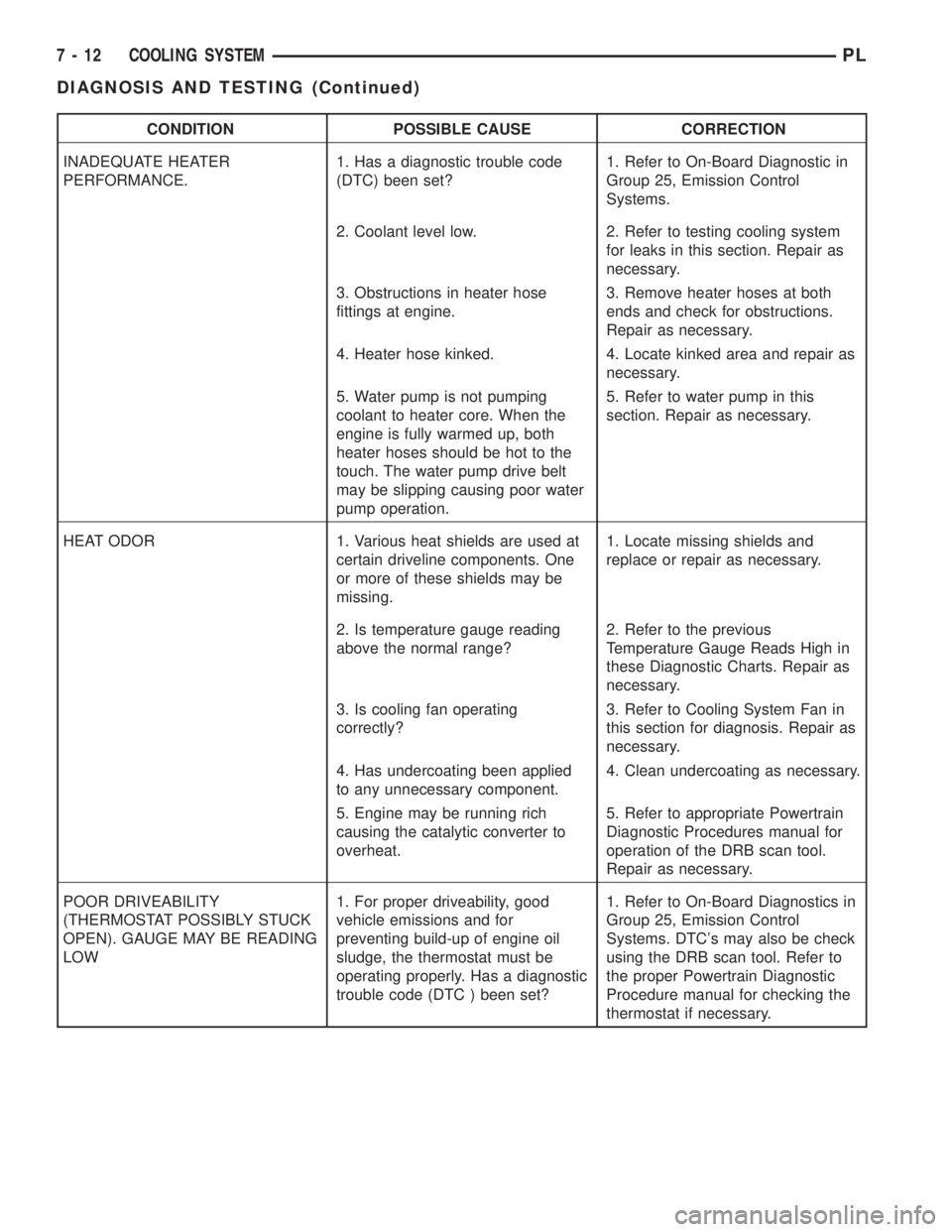
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE.1. Has a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) been set?1. Refer to On-Board Diagnostic in
Group 25, Emission Control
Systems.
2. Coolant level low. 2. Refer to testing cooling system
for leaks in this section. Repair as
necessary.
3. Obstructions in heater hose
fittings at engine.3. Remove heater hoses at both
ends and check for obstructions.
Repair as necessary.
4. Heater hose kinked. 4. Locate kinked area and repair as
necessary.
5. Water pump is not pumping
coolant to heater core. When the
engine is fully warmed up, both
heater hoses should be hot to the
touch. The water pump drive belt
may be slipping causing poor water
pump operation.5. Refer to water pump in this
section. Repair as necessary.
HEAT ODOR 1. Various heat shields are used at
certain driveline components. One
or more of these shields may be
missing.1. Locate missing shields and
replace or repair as necessary.
2. Is temperature gauge reading
above the normal range?2. Refer to the previous
Temperature Gauge Reads High in
these Diagnostic Charts. Repair as
necessary.
3. Is cooling fan operating
correctly?3. Refer to Cooling System Fan in
this section for diagnosis. Repair as
necessary.
4. Has undercoating been applied
to any unnecessary component.4. Clean undercoating as necessary.
5. Engine may be running rich
causing the catalytic converter to
overheat.5. Refer to appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
Repair as necessary.
POOR DRIVEABILITY
(THERMOSTAT POSSIBLY STUCK
OPEN). GAUGE MAY BE READING
LOW1. For proper driveability, good
vehicle emissions and for
preventing build-up of engine oil
sludge, the thermostat must be
operating properly. Has a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC ) been set?1. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics in
Group 25, Emission Control
Systems. DTC's may also be check
using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
the proper Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedure manual for checking the
thermostat if necessary.
7 - 12 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)