Page 2212 of 4592
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±61
DTC P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunc-
tion
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Camshaft position sensor (G signal) consists of magnet, iron core and pickup coil.
The G signal plate has one tooth on its outer circumference and is installed on the camshaft timing pulley.
When the camshafts rotate, the protrusion on the signal plate and the air gap on the pickup coil change,
causing fluctuations in the magnetic field and generating an electromotive force in the pickup coil.
The NE signal plate has 34 teeth and is installed on the crankshaft timing pulley. The NE signal sensor gener-
ates 34 signals at every engine revolution. The ECM detects the standard crankshaft angle based on the
G signal and the actual crankshaft angle and the engine speed by the NE signal.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0340
No camshaft position sensor signal to ECM during cranking
(2 trip detection logic)�Open or short in camshaft position sensor circuit
�Camshaft position sensor
P0340No camshaft position sensor signal to ECM with engine speed
600 rpm or more
�Camshaft osition sensor
�Camshaft timing pulley
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 on page DI±59.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio was lean
or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check resistance of camshaft position sensor (See Pub. No. RM654U, page
IG±1).
Reference: INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
Refer to DTC P0335 on page DI±59.
NG Replace camshaft position sensor.
OK
2 Check for open and short in harness and connector between ECM and camshaft
position sensor (See page IN±29).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
DI014±11
Page 2237 of 4592

DI±86
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DTC P1190 Fuel Pressure Regulator Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator regulates the fuel pressure by reducing the pressure of the compressed fuel from
the fuel tank to the fuel injection pressure, which is 785 kPa (8 kgf/cm
2, 114 psi).
Similar to the fuel shutoff valve for the fuel tank, a fuel shutoff valve is provided on the fuel inlet side of the
fuel pressure regulator to shutoff the supply of fuel when the engine is stopped or during abnormal condi-
tions.
A reservoir that traps the moisture and oil in the fuel is provided on the low pressure side.
A built±in relief valve is provided to protect the parts located on the low pressure side.
While the fuel pressure is being reduced by the fuel pressure regulator, the Joule±Thompson effect
associated with the expansion of the fuel causes the fuel pressure regulator to be cooled excessively, exert-
ing unfavorable influence on the rubber parts such as diaphragms and fuel hoses.
Therefore, to raise the fuel temperature, a water passage is provided in the fuel pressure regulator to allow
the engine coolant to warm the regulator.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P1190After engine is warmed up, detection of pressure control
malfunction (2 trip detection logic)
�Open or short in fuel shutoff valve circuit for fuel tank
�Fuel shutoff valve for fuel tank
�Open or short in fuel shutoff valve circuit for fuel pressure
regulator
�Fuel shutoff valve for fuel pressure regulator
�Fuel fuel pressure regulator
�Open or short in fuel shutoff valve circuit for fuel delivery
pipe
�Fuel shutoff valve for fuel delivery pipe
�ECM
DI64X±01
Page 2253 of 4592
DI±102
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DTC P1300 Igniter Circuit Malfunction (No.1)
DTC P1310 Igniter Circuit Malfunction (No.2)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ECM determines the ignition timing, turns on Tr1 at a predetermined angle (°CA) before the desired
ignition timing and outputs and ignition signal (IGT) 1 to the igniter.
Since the width of the IGT signal is constant, the dwell angle control circuit in the igniter determines the time
the control circuit starts primary current flow to the ignition coil based on the engine rpm and ignition timing
one revolution ago, that is, the time the Tr2 turns on.
When it reaches the ignition timing, the ECM turns Tr1 off and outputs the IGT signal O.
This turns Tr2 off, interrupting the primary current flow and generating a high voltage in the secondary coil
which causes the spark plug to spark. Also, the counter electromotive force is generated when the primary
current is interrupted, the igniter sends an ignition confirmation signal (IGF) to the ECM. The ECM stops fuel
injection as a fail safe function when the IGF signal is not input to the ECM.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P1300No IGF signal to ECM for 4 consecutive IGT1 signals during
engine running
�Ignition system
�Open or short in IGF or IGT1 circuit from No.1 ignition coil
with igniter to ECM
�No.1 ignition coil with igniter
�ECM
P1310No IGF signal to ECM for 4 consecutive IGT2 signals during
engine running
�Ignition system
�Open or short in IGF or IGT2 circuit from No.2 ignition coil
with igniter to ECM
�No.2 ignition coil with igniter
�ECM
HINT:
No.1 ignition coil with igniter is for cylinder No.1 and No.4, and No.2 ignition coil is for cylinder No.2 and No.3.
DI01G±07
Page 2254 of 4592
A09399
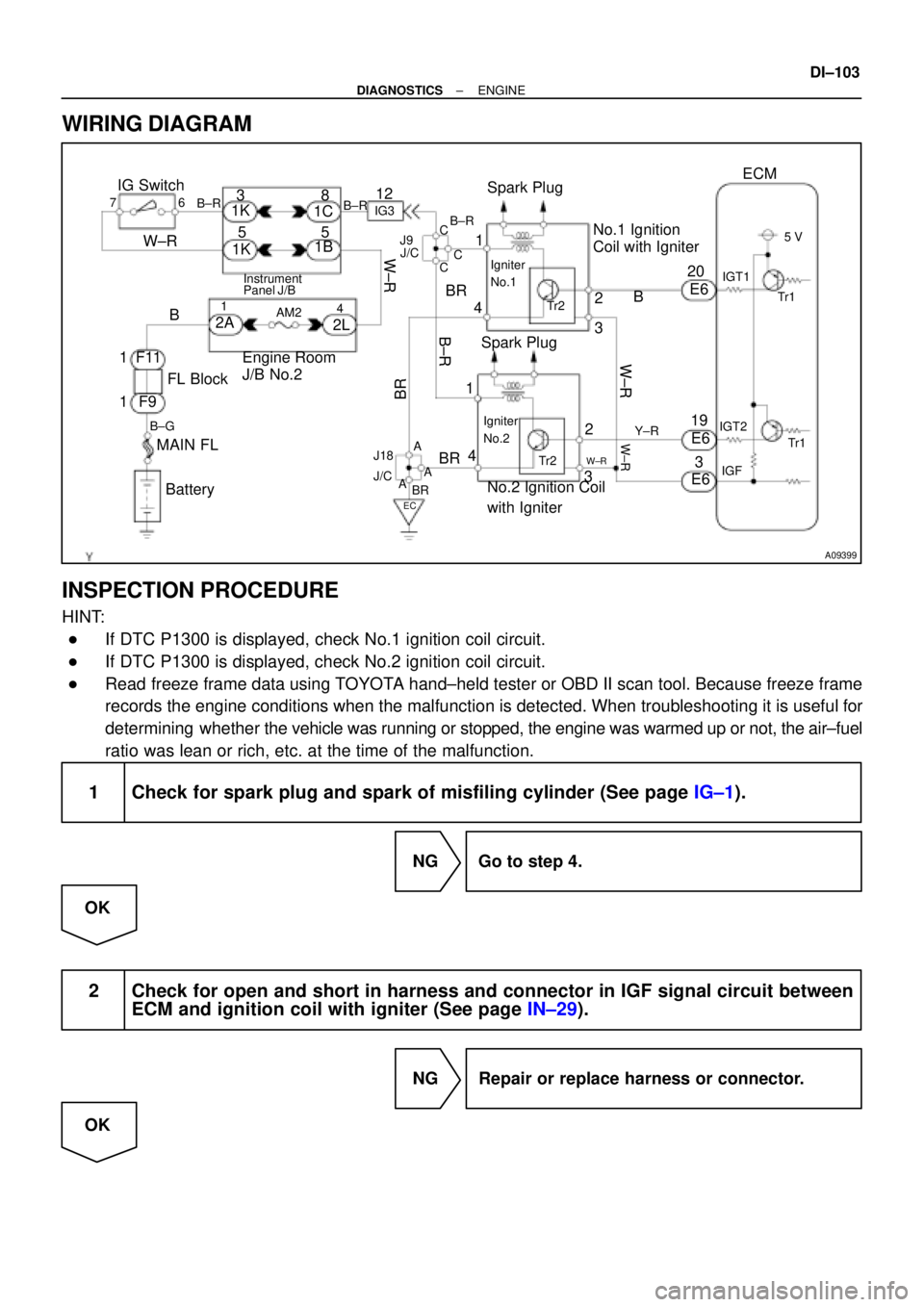
IG Switch
B±R
BatteryEngine Room
J/B No.2
763
1IG3
B
BR
Spark Plug
Spark Plug
2
3 2
3 4
Tr2 Igniter
No.1
No.1 Ignition
Coil with Igniter
FL Block
Y±R
BR
C
20
19
IGT2
Tr1
E6
E6
E6
W±R
IGT1
IGF5 V
Tr1
No.2 Ignition Coil
with Igniter
Igniter
No.2
AA A
EC
Tr2
W±R
B±R 5
1B 1K
Instrument
W±RW±R
2L 2A
4 1
AM2B
F9 F11 1
1
B±G
MAIN FL
3 1
4
J/C J9
ECM
W±R
Panel J/BC
CBR
BR J18
J/C
558
1C
1K
B±R
B±R12
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±103
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTC P1300 is displayed, check No.1 ignition coil circuit.
�If DTC P1300 is displayed, check No.2 ignition coil circuit.
�Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame
records the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting it is useful for
determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel
ratio was lean or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check for spark plug and spark of misfiling cylinder (See page IG±1).
NG Go to step 4.
OK
2 Check for open and short in harness and connector in IGF signal circuit between
ECM and ignition coil with igniter (See page IN±29).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
Page 2255 of 4592
A09288BE6653A09269
ON
IGF
(±) (+)
A09287BE6653A09268
START
IGT2
IGT1
(±) (+) DI±104
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
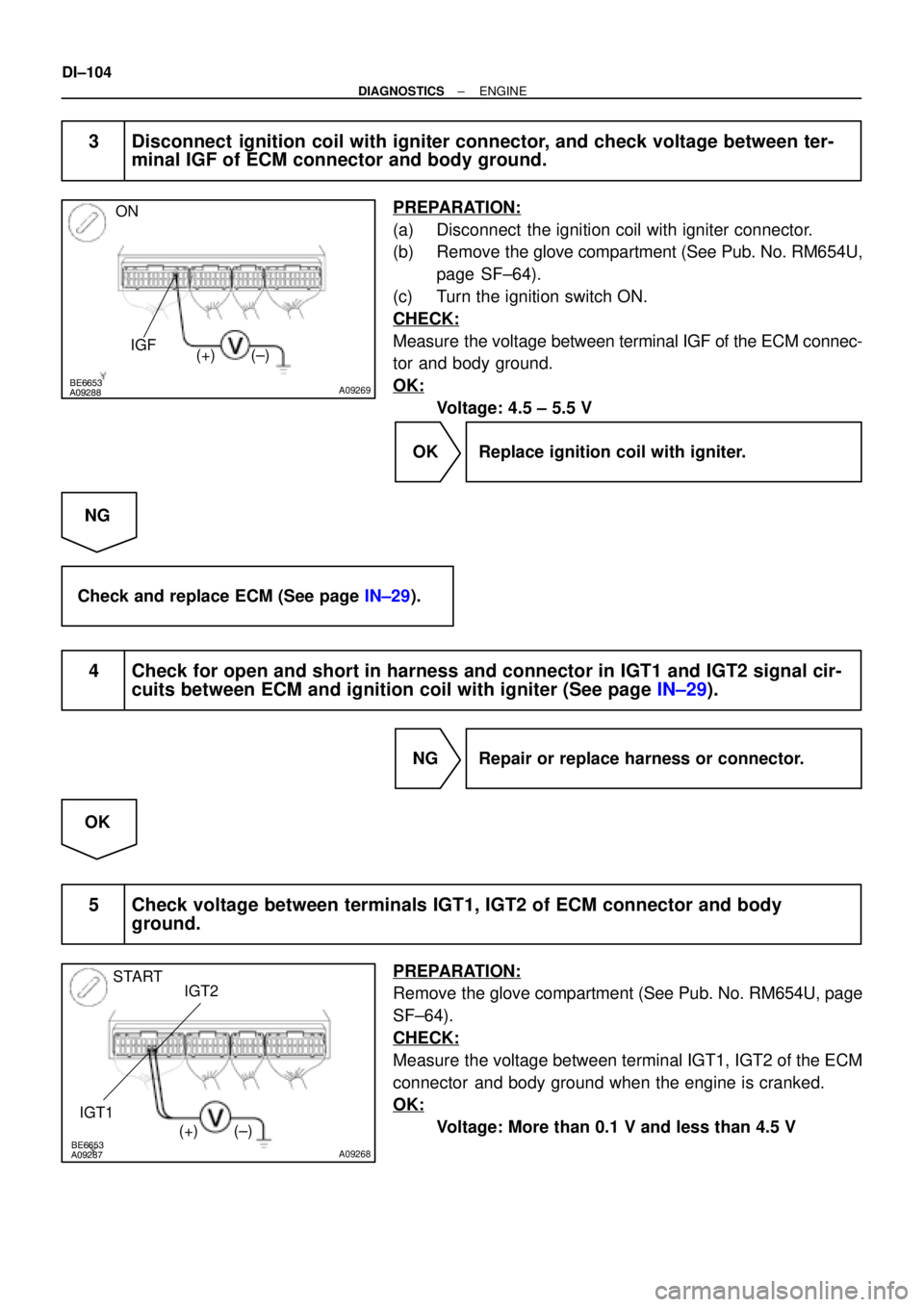
3 Disconnect ignition coil with igniter connector, and check voltage between ter-
minal IGF of ECM connector and body ground.
PREPARATION:
(a) Disconnect the ignition coil with igniter connector.
(b) Remove the glove compartment (See Pub. No. RM654U,
page SF±64).
(c) Turn the ignition switch ON.
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminal IGF of the ECM connec-
tor and body ground.
OK:
Voltage: 4.5 ± 5.5 V
OK Replace ignition coil with igniter.
NG
Check and replace ECM (See page IN±29).
4 Check for open and short in harness and connector in IGT1 and IGT2 signal cir-
cuits between ECM and ignition coil with igniter (See page IN±29).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
5 Check voltage between terminals IGT1, IGT2 of ECM connector and body
ground.
PREPARATION:
Remove the glove compartment (See Pub. No. RM654U, page
SF±64).
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminal IGT1, IGT2 of the ECM
connector and body ground when the engine is cranked.
OK:
Voltage: More than 0.1 V and less than 4.5 V
Page 2256 of 4592
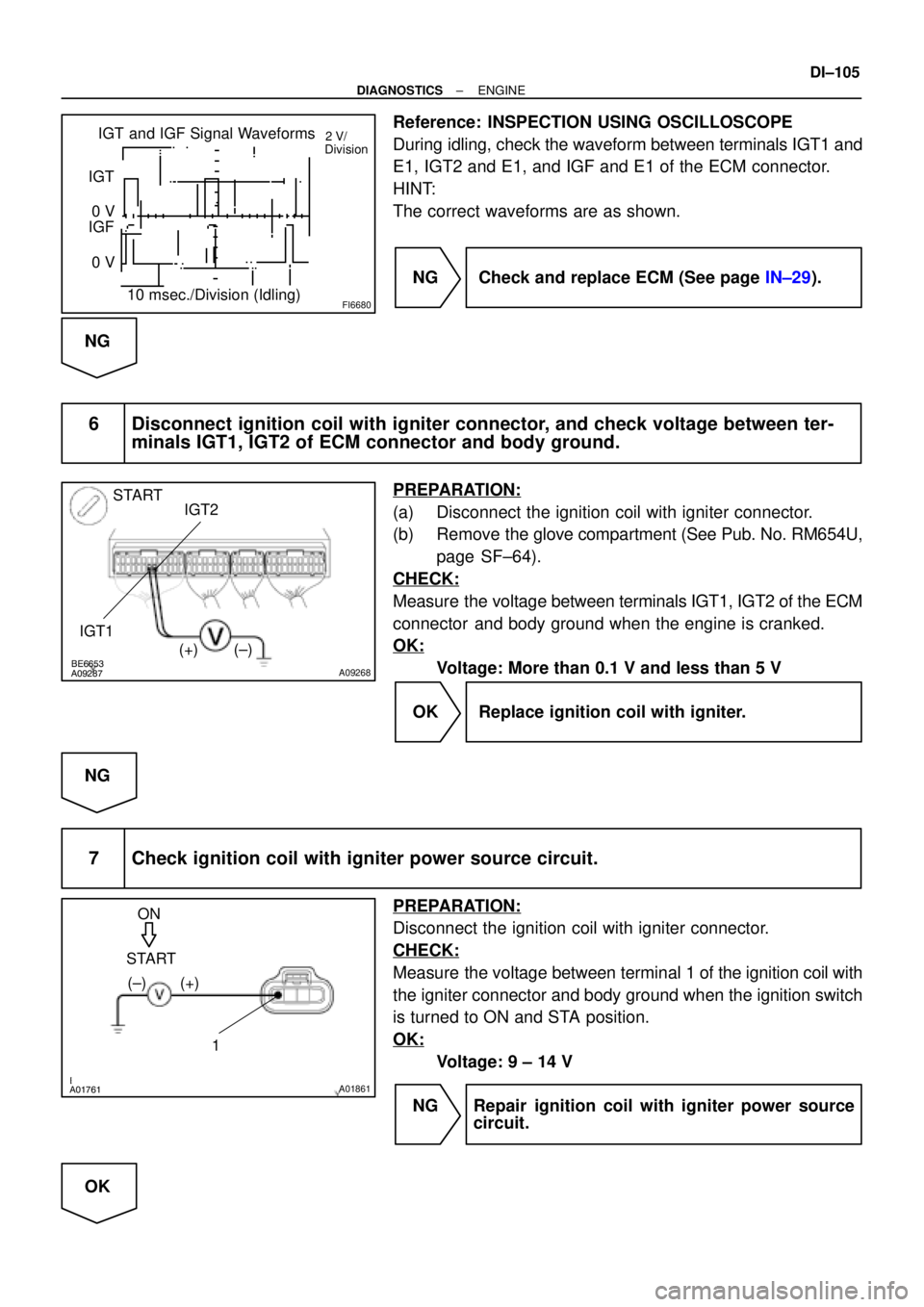
FI6680
IGT and IGF Signal Waveforms
10 msec./Division (Idling) IGT
0 V
IGF
0 V2 V/
Division
A09287BE6653A09268
START
IGT2
IGT1
(±) (+)
BE6653A01761A01861
ON
START
1 (±) (+)
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±105
Reference: INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
During idling, check the waveform between terminals IGT1 and
E1, IGT2 and E1, and IGF and E1 of the ECM connector.
HINT:
The correct waveforms are as shown.
NG Check and replace ECM (See page IN±29).
NG
6 Disconnect ignition coil with igniter connector, and check voltage between ter-
minals IGT1, IGT2 of ECM connector and body ground.
PREPARATION:
(a) Disconnect the ignition coil with igniter connector.
(b) Remove the glove compartment (See Pub. No. RM654U,
page SF±64).
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminals IGT1, IGT2 of the ECM
connector and body ground when the engine is cranked.
OK:
Voltage: More than 0.1 V and less than 5 V
OK Replace ignition coil with igniter.
NG
7 Check ignition coil with igniter power source circuit.
PREPARATION:
Disconnect the ignition coil with igniter connector.
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminal 1 of the ignition coil with
the igniter connector and body ground when the ignition switch
is turned to ON and STA position.
OK:
Voltage: 9 ± 14 V
NG Repair ignition coil with igniter power source
circuit.
OK
Page 2257 of 4592
DI±106
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
8 Check for open and short in harness and connector between ignition switch and
ignition coil with igniter (See page IN±29).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
Replace ignition coil with igniter.
Page 2268 of 4592
A09403
ECM
+B 12
E4 B±Y J/C
B
J24 J23B
B±Y
Instrument
Panel J/B 22J 2K7
W±R EFI
Relay 1 3
52
2F4
W±B
2A 1
AM2
42L
B
FL
Block
MAIN
FL
B±GEngine
J/B No.2
5
1B
531K71W
IGN
1K
Room
W±R
IG
Switch
7 6
E6
BR
B±R
EC
E1
F11
F9EB
1
1
EFI
J20
J/C A
A
Battery
BR
16 B±R DI±116
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
ECM Power Source Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the ignition switch is turned ON, battery positive voltage is applied to the coil, closing the contacts of
the EFI main relay (Marking: EFI) and supplying power to terminal +B of the ECM.
WIRING DIAGRAM
DI01L±07