Page 1415 of 4592
P00495
Outside
Inside
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
DI±203
438 Author�: Date�:
2 Is engine cranked?
NO Proceed to page ST±18 and continue to trouble-
shoot.
YES
3 Does engine start?
NO Go to step 7.
YES
4 Check air filter.
PREPARATION:
Remove the air filter.
CHECK:
Visually check that the air filter is not dirty or excessive oily.
HINT:
If necessary, clean the filter with compressed air. First blow from
inside thoroughly, then blow from outside of the filter.
NG Repair or replace.
OK
Page 1418 of 4592
P23917
DI±206
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
441 Author�: Date�:
8 Check for spark.
PREPARATION:
(a) Remove the ignition coil or disconnect the high±tension
cord from the spark plug.
(b) Remove the spark plug.
(c) Install the spark plug to the ignition coil or high±tension
cord.
(d) Disconnect the injector connector.
(e) Hold the end about 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) from the ground.
CHECK:
Check if spark occurs while engine is being cranked.
NOTICE:
To prevent excess fuel being injected from the injectors
during this test, don't crank the engine for more than 5 ~ 10
seconds at a time.
OK:
Spark jumps across electrode gap.
NG Proceed to page IG±1 and continue to
troubleshoot.
OK
Proceed to problem symptoms table on page
DI±221.
Page 1421 of 4592
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
DI±209
444 Author�: Date�:
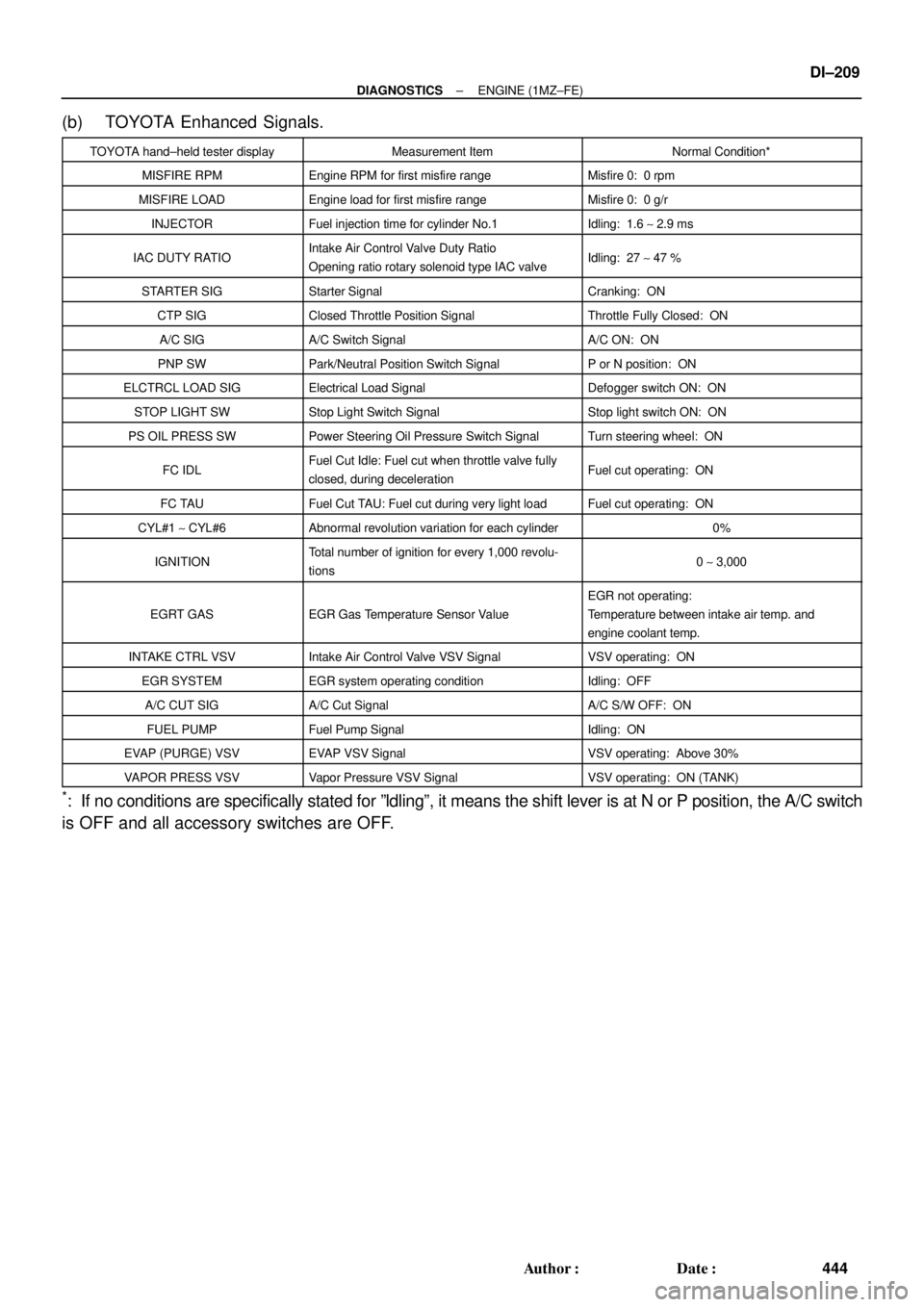
(b) TOYOTA Enhanced Signals.
TOYOTA hand±held tester displayMeasurement ItemNormal Condition*
MISFIRE RPMEngine RPM for first misfire rangeMisfire 0: 0 rpm
MISFIRE LOADEngine load for first misfire rangeMisfire 0: 0 g/r
INJECTORFuel injection time for cylinder No.1Idling: 1.6 ~ 2.9 ms
IAC DUTY RATIOIntake Air Control Valve Duty Ratio
Opening ratio rotary solenoid type IAC valveIdling: 27 ~ 47 %
STARTER SIGStarter SignalCranking: ON
CTP SIGClosed Throttle Position SignalThrottle Fully Closed: ON
A/C SIGA/C Switch SignalA/C ON: ON
PNP SWPark/Neutral Position Switch SignalP or N position: ON
ELCTRCL LOAD SIGElectrical Load SignalDefogger switch ON: ON
STOP LIGHT SWStop Light Switch SignalStop light switch ON: ON
PS OIL PRESS SWPower Steering Oil Pressure Switch SignalTurn steering wheel: ON
FC IDLFuel Cut Idle: Fuel cut when throttle valve fully
closed, during decelerationFuel cut operating: ON
FC TAUFuel Cut TAU: Fuel cut during very light loadFuel cut operating: ON
CYL#1 ~ CYL#6Abnormal revolution variation for each cylinder0%
IGNITIONTotal number of ignition for every 1,000 revolu-
tions0 ~ 3,000
EGRT GASEGR Gas Temperature Sensor Value
EGR not operating:
Temperature between intake air temp. and
engine coolant temp.
INTAKE CTRL VSVIntake Air Control Valve VSV SignalVSV operating: ON
EGR SYSTEMEGR system operating conditionIdling: OFF
A/C CUT SIGA/C Cut SignalA/C S/W OFF: ON
FUEL PUMPFuel Pump SignalIdling: ON
EVAP (PURGE) VSVEVAP VSV SignalVSV operating: Above 30%
VAPOR PRESS VSVVapor Pressure VSV SignalVSV operating: ON (TANK)
*: If no conditions are specifically stated for ºldlingº, it means the shift lever is at N or P position, the A/C switch
is OFF and all accessory switches are OFF.
Page 1491 of 4592

A00221P25779
P23917
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
DI±279
514 Author�: Date�:
2 Check spark plug and spark of misfiring cylinder.
PREPARATION:
(a) Remove the ignition coil (See page IG±7).
(b) Remove the spark plug.
CHECK:
(a) Check spark plug type.
(b) Check for carbon deposits on electrode.
(c) Check electrode gap.
OK:
(a) Twin ground electrodes type.
Recommended spark plug:
ND PK20TR11
NGK BKR6EKPB±11
(b) No large carbon deposit present.
Not wet with gasoline or oil.
(c) Electrode gap:
Standerd: 1.0 ± 1.1 mm (0.03937 ± 0.043 in.).
Maximum: 1.3 mm (0.051 in.).
PREPARATION:
(a) Install the spark plug to the ignition coil, and connect the
ignition coil the connector.
(b) Disconnect injector connector.
(c) Hold the end about 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) from the ground.
CHECK:
Check if spark occurs while engine is being cranked.
NOTICE:
To prevent excess fuel being injected from the
injectors during this test, don't crank the engine for more
than 5 ~ 10 sec. at a time.
OK:
Spark jumps across electrode gap.
NG Replace or check ignition system
(See page IG±1).
OK
Page 1499 of 4592
P25474
Camshaft Position Sensor
1
2
1
2B±W
B±RL
BR LECM
G22+
NE+
NE±
E2
E10
E10E11
2410
Crankshaft Position SensorB±R16
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
DI±287
522 Author�: Date�:
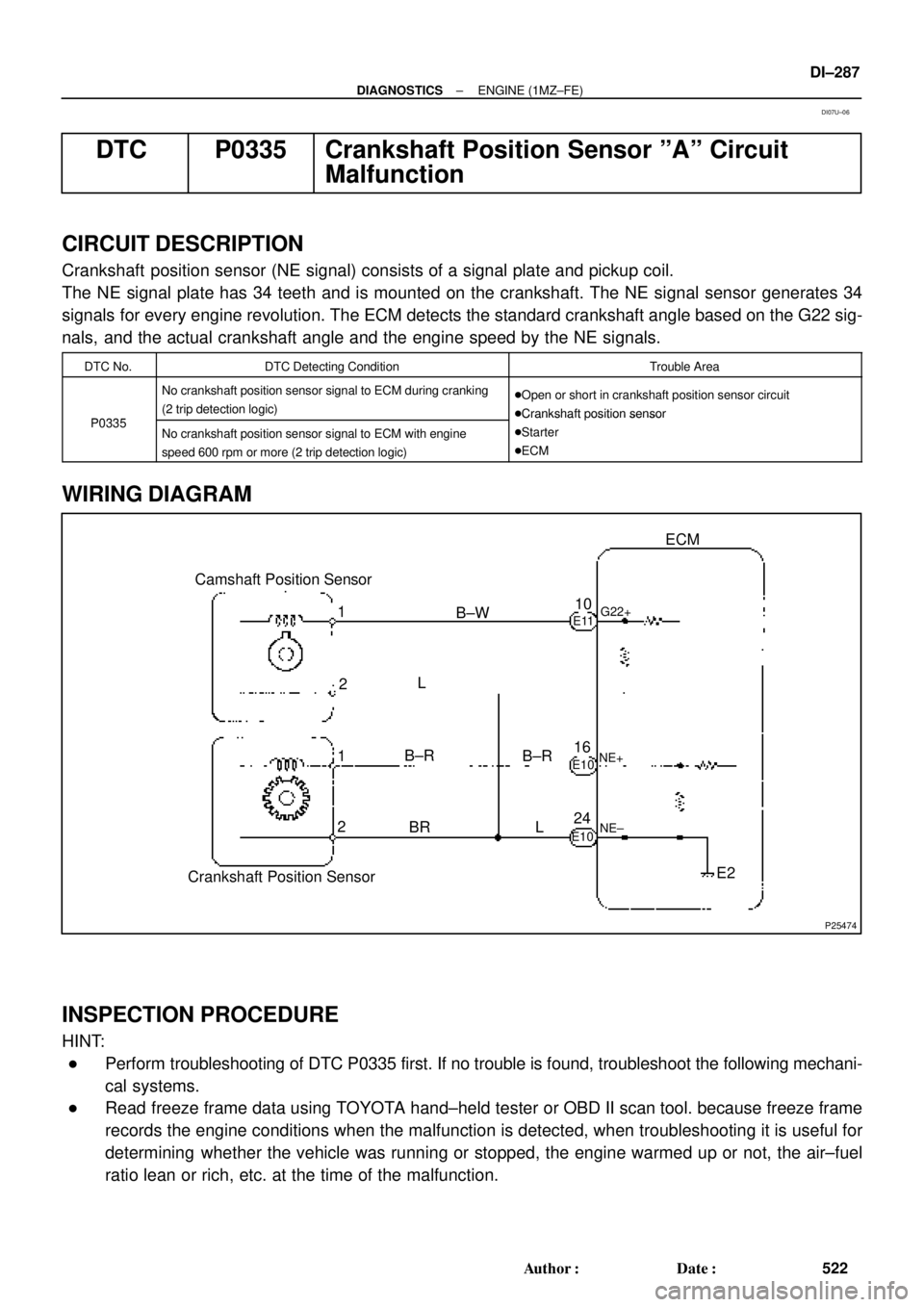
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor ºAº Circuit
Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Crankshaft position sensor (NE signal) consists of a signal plate and pickup coil.
The NE signal plate has 34 teeth and is mounted on the crankshaft. The NE signal sensor generates 34
signals for every engine revolution. The ECM detects the standard crankshaft angle based on the G22 sig-
nals, and the actual crankshaft angle and the engine speed by the NE signals.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0335
No crankshaft position sensor signal to ECM during cranking
(2 trip detection logic)�Open or short in crankshaft position sensor circuit
�Crankshaft position sensor
P0335No crankshaft position sensor signal to ECM with engine
speed 600 rpm or more (2 trip detection logic)
�Crankshaft osition sensor
�Starter
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�Perform troubleshooting of DTC P0335 first. If no trouble is found, troubleshoot the following mechani-
cal systems.
�Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. because freeze frame
records the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected, when troubleshooting it is useful for
determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine warmed up or not, the air±fuel
ratio lean or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
DI07U±06
Page 1502 of 4592

DI±290
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
525 Author�: Date�:
DTC P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Camshaft position sensor (G22 signal) consist of a signal plate and pickup coil.
The G22 signal plate has one tooth, on its outer circumference and is mounted on the left bank camshafts.
When the camshafts rotate, the protrusion on the signal plate and the air gap on the pickup coil change,
causing fluctuations in the magnetic field and generating an electromotive force in the pickup coil.
The NE signal plate has 34 teeth and is mounted on the crankshaft. The NE signal sensor generates 34
signals for every engine revolution. The ECM detects the standard crankshaft angle based on the G22 signal
and the actual crankshaft angle and the engine speed by the NE signals.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0340
No camshaft position sensor signal to ECM during cranking
(2 trip detection logic)�Open or short in camshaft position sensor circuit
�Camshaft position sensor
P0340No camshaft position sensor signal to ECM with engine speed
600 rpm or more
�Camshaft osition sensor
�Starter
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor ºAº Circuit Malfunction) on page DI±287 .
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected, when troubleshooting it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio lean or rich, etc.
at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check resistance of camshaft position sensor (See page IG±1).
Reference INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
Refer to DTC P0335 on page DI±287.
NG Replace camshaft position sensor.
OK
DI07V±06
Page 1563 of 4592
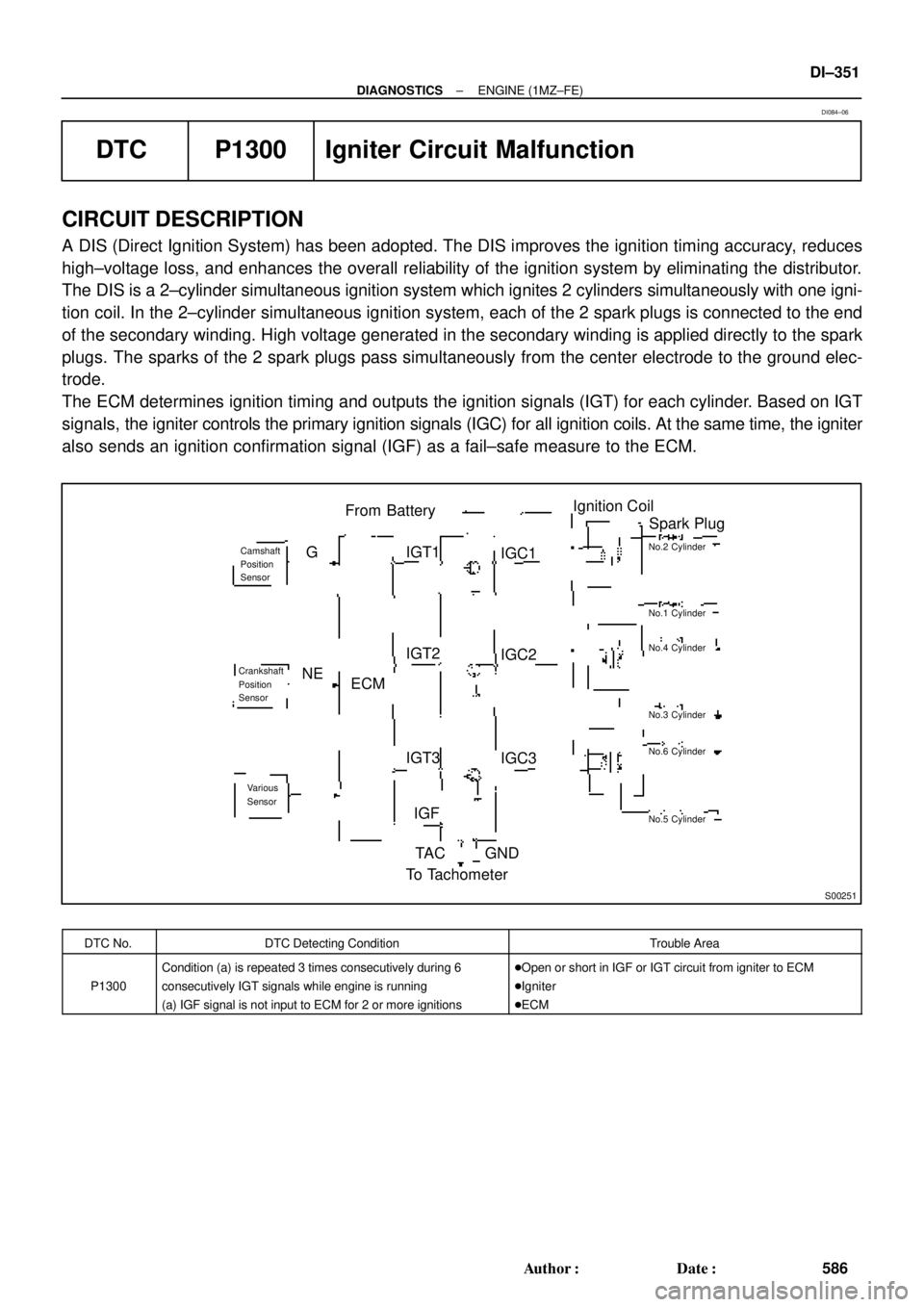
S00251
From BatteryIgnition Coil
Spark Plug
IGC1
IGC2
IGC3
GND TA C IGT1
IGT2
IGT3
IGF
To Tachometer ECM G
NE
Camshaft
Position
Sensor
Crankshaft
Position
Sensor
Various
SensorNo.2 Cylinder
No.1 Cylinder
No.4 Cylinder
No.3 Cylinder
No.6 Cylinder
No.5 Cylinder
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
DI±351
586 Author�: Date�:
DTC P1300 Igniter Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
A DIS (Direct Ignition System) has been adopted. The DIS improves the ignition timing accuracy, reduces
high±voltage loss, and enhances the overall reliability of the ignition system by eliminating the distributor.
The DIS is a 2±cylinder simultaneous ignition system which ignites 2 cylinders simultaneously with one igni-
tion coil. In the 2±cylinder simultaneous ignition system, each of the 2 spark plugs is connected to the end
of the secondary winding. High voltage generated in the secondary winding is applied directly to the spark
plugs. The sparks of the 2 spark plugs pass simultaneously from the center electrode to the ground elec-
trode.
The ECM determines ignition timing and outputs the ignition signals (IGT) for each cylinder. Based on IGT
signals, the igniter controls the primary ignition signals (IGC) for all ignition coils. At the same time, the igniter
also sends an ignition confirmation signal (IGF) as a fail±safe measure to the ECM.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P1300
Condition (a) is repeated 3 times consecutively during 6
consecutively IGT signals while engine is running
(a) IGF signal is not input to ECM for 2 or more ignitions�Open or short in IGF or IGT circuit from igniter to ECM
�Igniter
�ECM
DI084±06
Page 1564 of 4592
S05723
J18
Junction
Connector
A
A A A AII3B±R
B±R B±R W±R128 3
1K 1C
Ignition
Switch
76
1K
1BB±R
G
B±R
B±R Y
LIgnition Coil
Spark Plug
No.1
No.2
No.3
11
12
2
2
ED
BR
3 2 1
10
9
7
6
5
4
W±R LG±B
BR±Y
IgniterECM
IGT1
IGT2
IGT3
IGF5 VInstrument
Panel J/B
E1125
E1113
E1112
E1111GR
B±R
5
5
W±R
Engine Room J/B
2L4
AM2
2A1
B
Fusible
Link
Block 1
1
F6
B±GFL
MAIN
Battery
F4
Instrument
Panel J/B
DI±352
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE (1MZ±FE)
587 Author�: Date�:
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected, when troubleshooting it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine warmed up or not, the air±fuel ratio lean or rich, etc.
at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check spark plug and spark of misfiring cylinder (See page DI±276).
NG Go to step 4.
OK