1999 DODGE NEON coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 1160 of 1200

INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
SUCTION LINE
WARNING: THE REFRIGERANT MUST BE RECOV-
ERED BEFORE SERVICING ANY PART OF THE
REFRIGERANT SYSTEMS.
REMOVAL
(1) Using a R-134a refrigerant recovery machine,
remove the refrigerant from A/C system.
(2) Remove retaining bolt at expansion valve (Fig.
40).
(3) Remove line at drier.
(4) Remove line at compressor.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE
The Control Cable can be removed and installed
without having to remove the instrument panel from
the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove instrument panel upper cowl panel.
(2) Remove right side upper instrument panel
bezel (Fig. 35).
(3) Remove center vent duct (Fig. 36).
(4) Remove upper defrost duct (Fig. 37).
(5) Remove inner defrost duct (Fig. 38).
(6) Disconnect cable at heater unit.
(7) Disconnect cable at control panel. Remove con-
trol from instrument panel.
(8) Remove cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures,
adjust cable and test. See Temperature Control Cable
Adjustment in this section.
UNIT HOUSING
The instrument panel must be removed in order to
remove the Unit Housing. Refer to group 8E Instru-
ment Panel and Gauges for detailed procedure.
WARNING: THE R-134a REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
MUST BE RECOVERED BEFORE SERVICING ANY
PART OF THE REFRIGERANT SYSTEM.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove instrument panel from vehicle. Refer
to group 8E Instrument Panel and Gauges for
detailed procedure.
(2) Drain cooling system and remove heater hoses
at the dash panel. Place plugs in the heater core out-
lets to prevent coolant spillage during unit housing
removal.
Fig. 40 Bolt RemovalFig. 38 Instrument Panel Inner Defrost Duct
Fig. 39 Recirculation Door Actuator
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 27
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1166 of 1200
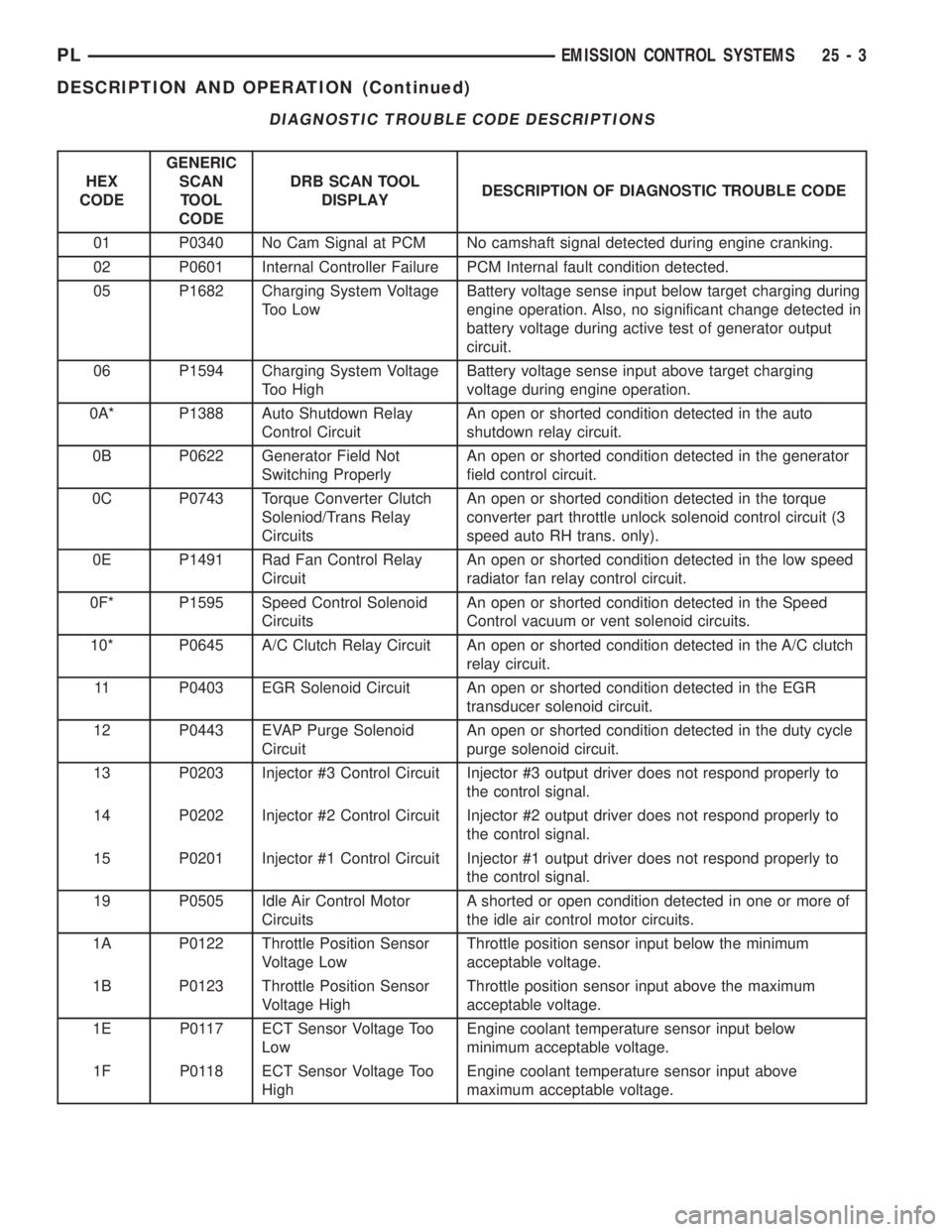
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONS
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
01 P0340 No Cam Signal at PCM No camshaft signal detected during engine cranking.
02 P0601 Internal Controller Failure PCM Internal fault condition detected.
05 P1682 Charging System Voltage
Too LowBattery voltage sense input below target charging during
engine operation. Also, no significant change detected in
battery voltage during active test of generator output
circuit.
06 P1594 Charging System Voltage
Too HighBattery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
0A* P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay
Control CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
0B P0622 Generator Field Not
Switching ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator
field control circuit.
0C P0743 Torque Converter Clutch
Soleniod/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter part throttle unlock solenoid control circuit (3
speed auto RH trans. only).
0E P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the low speed
radiator fan relay control circuit.
0F* P1595 Speed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed
Control vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
10* P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch
relay circuit.
11 P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
transducer solenoid circuit.
12 P0443 EVAP Purge Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the duty cycle
purge solenoid circuit.
13 P0203 Injector #3 Control Circuit Injector #3 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
14 P0202 Injector #2 Control Circuit Injector #2 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
15 P0201 Injector #1 Control Circuit Injector #1 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
19 P0505 Idle Air Control Motor
CircuitsA shorted or open condition detected in one or more of
the idle air control motor circuits.
1A P0122 Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage LowThrottle position sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
1B P0123 Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
1E P0117 ECT Sensor Voltage Too
LowEngine coolant temperature sensor input below
minimum acceptable voltage.
1F P0118 ECT Sensor Voltage Too
HighEngine coolant temperature sensor input above
maximum acceptable voltage.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1172 of 1200

system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .020º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
TRIP DEFINITION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.
Any component that has an associated limp in will
set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunction present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)