1999 DODGE NEON ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 390 of 1200

CHIME WARNING/REMINDER SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHIME SYSTEM CONDITIONS.............. 1
FASTEN SEAT BELTS..................... 1
HEADLAMPS LEFT ON.................... 1KEY LEFT IN IGNITION SWITCH............ 1
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CHIME................................. 2
HEADLAMP SWITCH..................... 2
KEY-IN SWITCH......................... 2
SEAT BELT BUCKLE...................... 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AN
AIRBAG, REFER TO THE AIRBAG PORTION OF
THIS SECTION FOR STEERING WHEEL OR SWITCH
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION PROCEDURES.
The seat belt reminder system uses both visual
and audible signals. A combined seat belt and key
reminder chime with a red light on the instrument
panel.
The system will always illuminate the seat belt
reminder lamp for four to eight seconds when the
ignition switch is turned to the ON position. The
CHIME will sound during the same time interval if
the driver's seat belt is not fastened. Passenger belts
are not connected to the system. The chime will acti-
vate if the drivers door is opened and:
²The key is in the ignition switch, with the igni-
tion switch in either the OFF or accessory (ACC)
position
²The head lamps are ON.
The chime is part of the instrument cluster.
NOTE: This group covers both Left-Hand Drive
(LHD) and Right-Hand Drive (RHD) versions of this
model. Whenever required and feasible, the RHD
versions of affected vehicle components have been
constructed as mirror-image of the LHD versions.
While most of the illustrations used in this group
represent only the LHD version, the diagnostic and
service procedures outlined can generally be
applied to either version. Exceptions to this rule
have been clearly identified as LHD, RHD, or Export
if a special illustration or procedure is required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FASTEN SEAT BELTS
To test the fasten seat belts function, turn the igni-
tion switch to the ON position with the driver's seat
belt unbuckled and fully retracted. The seat belt
warning lamp should light for four to eight seconds
and the tone should sound three to five times.
HEADLAMPS LEFT ON
To test the headlamps left on function:
²Turn headlamps
²Driver's door open
²Key removed from the ignition switch
Chime should sound until headlamps are turned
off or driver's door is closed.
KEY LEFT IN IGNITION SWITCH
To test the key left in ignition function, insert key
into the ignition and open driver's door. Chime
should sound until key is removed from ignition or
driver's door is closed.
CHIME SYSTEM CONDITIONS
The cluster harness connector, J1 is car right and
the J2 is car left.
NO TONE WHEN IGNITION SWITCH IS
TURNED ON AND DRIVERS SEAT BELT IS
UNBUCKLED
(1) Using an ohmmeter, with the seat belt fully
retracted, check for continuity to ground at Pin 4 of
the J1 wire harness connector (Fig. 1). If OK, go to
step 2. If not OK, repair as necessary .
(2) Check for continuity to ground at Pin 8 of the
J1 wire harness connector. If OK, go to Step 3. If not
OK, repair as necessary.
(3) Using voltmeter, check for battery feed at Pin 6
of the J1 wire harness connector. Check for ignition
feed at Pin 5 of the J1 wire harness connector. If not
OK, repair as necessary.
PLCHIME WARNING/REMINDER SYSTEM 8U - 1
Page 397 of 1200
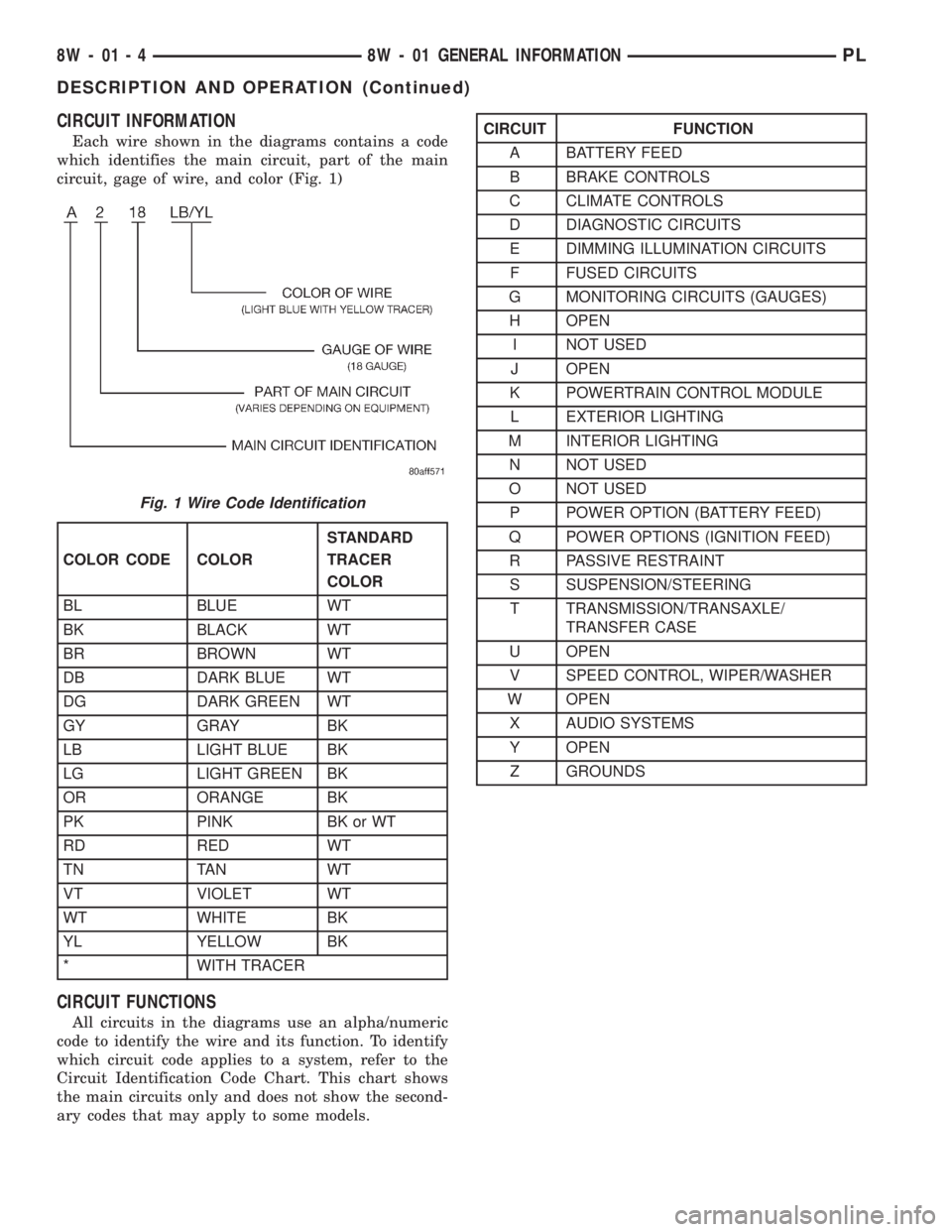
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
Each wire shown in the diagrams contains a code
which identifies the main circuit, part of the main
circuit, gage of wire, and color (Fig. 1)
CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the wire and its function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second-
ary codes that may apply to some models.
Fig. 1 Wire Code Identification
COLOR CODE COLORSTANDARD
TRACER
COLOR
BL BLUE WT
BK BLACK WT
BR BROWN WT
DB DARK BLUE WT
DG DARK GREEN WT
GY GRAY BK
LB LIGHT BLUE BK
LG LIGHT GREEN BK
OR ORANGE BK
PK PINK BK or WT
RD RED WT
TN TAN WT
VT VIOLET WT
WT WHITE BK
YL YELLOW BK
* WITH TRACER
CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A BATTERY FEED
B BRAKE CONTROLS
C CLIMATE CONTROLS
D DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUITS
E DIMMING ILLUMINATION CIRCUITS
F FUSED CIRCUITS
G MONITORING CIRCUITS (GAUGES)
H OPEN
I NOT USED
J OPEN
K POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
L EXTERIOR LIGHTING
M INTERIOR LIGHTING
N NOT USED
O NOT USED
P POWER OPTION (BATTERY FEED)
Q POWER OPTIONS (IGNITION FEED)
R PASSIVE RESTRAINT
S SUSPENSION/STEERING
T TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
TRANSFER CASE
U OPEN
V SPEED CONTROL, WIPER/WASHER
W OPEN
X AUDIO SYSTEMS
Y OPEN
Z GROUNDS
8W - 01 - 4 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 728 of 1200

inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
with the fitting of pistons and rings in order that
specified clearances may be maintained.Refer to
Honing Cylinder Bores outlined in the Stan-
dard Service Procedures for specification and
procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 3). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specifications
Chart.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-
tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 4). Cylinder boresshould be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 3). Refer to Cylinder Bore and Speci-
fications Table. Correct piston to bore clearance must
be established in order to assure quiet and economi-
cal operation.
Chrysler engines use pistons designed specifically
for each engine model. Clearance and sizing locations
vary with respect to engine model.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
Fig. 3 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
Standard Bore Maximum
Out-of-RoundMaximum Taper
87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Standard Piston Size
Federal Emission: 87.463 - 87.481 mm
(3.4434 - 3.4441 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):87.456 - 87.474 mm
(3.4432 - 3.4439 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance
Federal Emission: 0.012 - 0.044 mm (0.0004 - 0.0017 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):0.18 - 0.050 mm (0.0008 - 0.0020 in.)
Measurements Taken at Piston Size Location
Fig. 4 Piston Measurements
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 15
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 774 of 1200
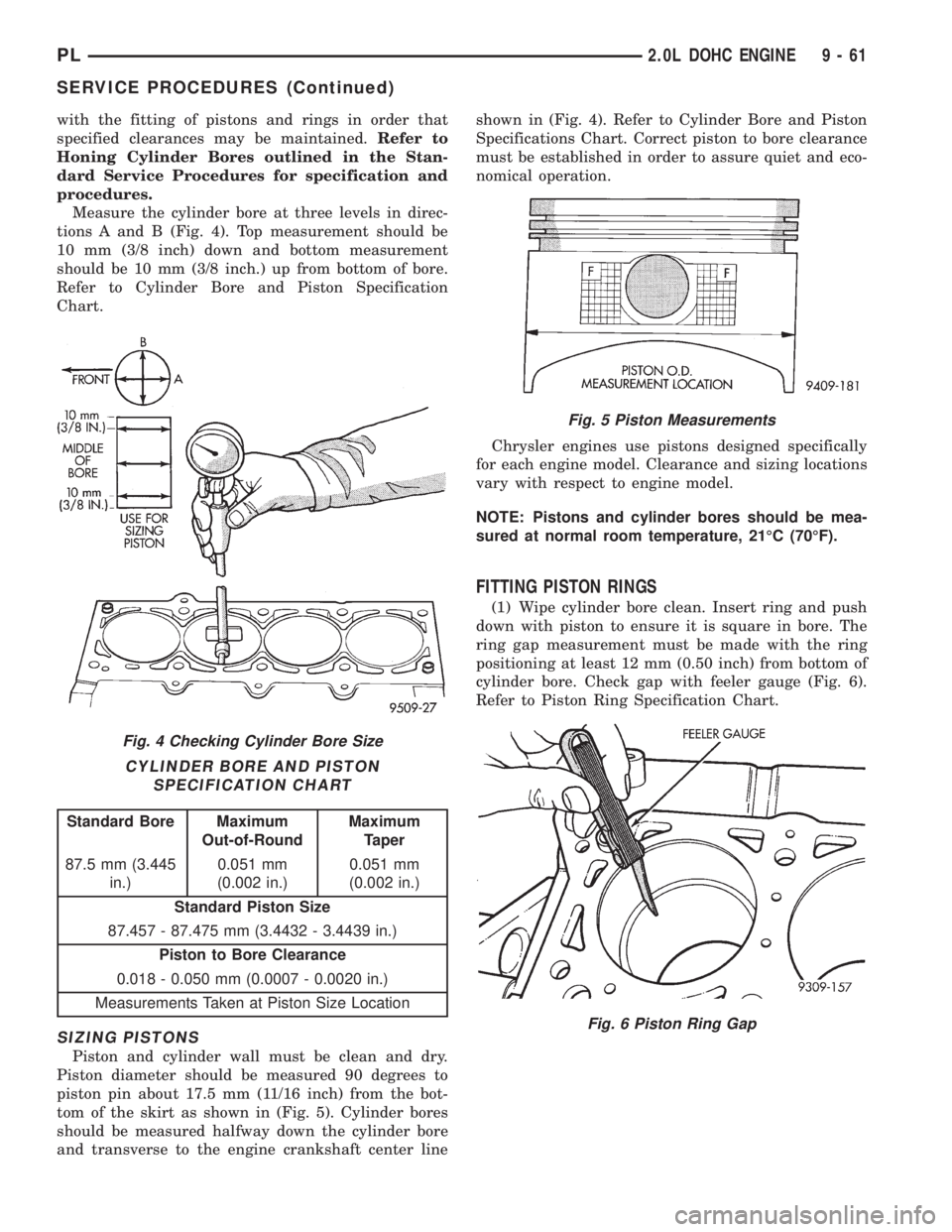
with the fitting of pistons and rings in order that
specified clearances may be maintained.Refer to
Honing Cylinder Bores outlined in the Stan-
dard Service Procedures for specification and
procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 4). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specification
Chart.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-
tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 5). Cylinder bores
should be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center lineshown in (Fig. 4). Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston
Specifications Chart. Correct piston to bore clearance
must be established in order to assure quiet and eco-
nomical operation.
Chrysler engines use pistons designed specifically
for each engine model. Clearance and sizing locations
vary with respect to engine model.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
FITTING PISTON RINGS
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12 mm (0.50 inch) from bottom of
cylinder bore. Check gap with feeler gauge (Fig. 6).
Refer to Piston Ring Specification Chart.
Fig. 4 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
Standard Bore Maximum
Out-of-RoundMaximum
Taper
87.5 mm (3.445
in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Standard Piston Size
87.457 - 87.475 mm (3.4432 - 3.4439 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance
0.018 - 0.050 mm (0.0007 - 0.0020 in.)
Measurements Taken at Piston Size Location
Fig. 5 Piston Measurements
Fig. 6 Piston Ring Gap
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 61
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 862 of 1200

GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than .745
volts or less than .1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 863 of 1200

ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays. If
the PCM does not receive both signals within approx-
imately one second, it will not energize the ASD
relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel pump
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes all four injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference
between the two values, it sets a MAP diagnostic
trouble code into memory.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²Both O2 sensors
²All diagnostics
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Power steering pressure switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to Group 25 for
On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 864 of 1200

below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in respones to MAP
sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information, refer to Group 25, Emission
Control Systems. See On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The power distribution center (PDC) is located next
to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the starter
relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor clutch relay,
auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay and several
fuses.
Fig. 1 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 23
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 875 of 1200

FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
The 2.0L engine uses electrically operated top feed
fuel injectors (Fig. 26). The Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) relay supplies battery voltage to the fuel injec-
tors. The PCM controls the ground path for each
injector in sequence. By switching the ground paths
on and off, the PCM fine-tunes injector pulse width.
Injector pulse width refers to the amount of time an
injector operates.
The PCM determines injector synchronization from
the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position
sensor inputs. The PCM grounds the ASD and fuel
pump relays after receiving the camshaft position
sensor and crankshaft position sensor inputs.
The PCM energizes the injectors in a sequential
order during all engine operating conditions except
start-up. For the first injector pulse width during
start-up, all injectors are energized at the same time.
Once the PCM determines crankshaft position, it
begins energizing the injectors in sequence.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The coil assembly consists of 2 coils molded
together. The coil assembly is mounted over the valve
cover (Fig. 27) or (Fig. 28). High tension leads route
to each cylinder from the coil. The coil fires two
spark plugs every power stroke. One plug is the cyl-
inder under compression, the other cylinder fires on
the exhaust stroke. Coil number one fires cylinders 1
and 4. Coil number two fires cylinders 2 and 3. The
PCM determines which of the coils to charge and fire
at the correct time.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary causing the
spark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor andcamshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output in this section for
relay operation.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the malfunction indicator (check
engine) lamp on/off signal to the instrument panel
through the CCD Bus. The CCD Bus is a communi-
cations port. Various modules use the CCD Bus to
exchange information.
The Check Engine lamp comes on each time the
ignition key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds
as a bulb test.
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) stays on
continuously, when the PCM has entered a Limp-In
mode or identified a failed emission component. Dur-
ing Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The MIL signals the need for
immediate service. In limp-in mode, the PCM com-
pensates for the failure of certain components that
Fig. 26 Fuel Injector
Fig. 27 Ignition Coil PackÐSOHC
Fig. 28 Ignition Coil PackÐDOHC
14 - 34 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)