1999 DODGE NEON ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 97 of 1200

PROPORTIONING VALVES
PROPORTIONING VALVE TESTING SPECIAL
TOOLS
The in-line proportioning valves used on this vehi-
cle require special pressure fittings to test the pro-
portioning valves for proper proportioning valve
function. The pressure fittings are installed before
and after the proportioning valve being tested to ver-
ify proportioning valve is maintaining the required
hydraulic pressure to the rear wheel brake which it
controls.
If a condition of premature rear wheel skid occurs
on a vehicle, the proportioning valve should always
be tested prior to it being replaced. This is due to the
fact that there are conditions other then a faulty pro-
portioning valve which can cause a premature rear
wheel skid.
Testing proportioning valve pressures on a vehicle
with or without ABS requires using the same special
tools.
There are 4 Pressure Fittings, Special Tool 6805
(Fig. 24) which are used for testing both rear propor-
tioning valves mounted in the master cylinder.
The pressure gauges used for testing the new in-
line proportioning valves on both non-ABS and ABS
brakes, is Pressure Gauge Set, Special Tool C-4007-A
currently used for testing the combination valve (Fig.
25).
PROPORTIONING VALVE TESTING NON ABS
BRAKE
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on hard brake
application, it could be an indication that a malfunc-
tion has occurred with one of the proportioning
valves.
One proportioning valve controls the right rear
brake, and the other proportioning valve controls the
left rear brake (Fig. 26). Therefore, a road test todetermine which rear brake slides first is essential.
Once the wheel which slides first is determined, use
the following procedure to diagnose the proportioning
valve.
The test procedure for a premature rear wheel skid
is the same for both rear wheel proportioning valves.
The pressure test fittings used for each proportioning
valve though are different due to proportioning valve
and brake tube nut thread sizes being unique for
each rear wheel. After road testing vehicle to deter-
mine which wheel skids first, the proper test fittings
required will have to be determined. Then follow the
procedure below for testing the required proportion-
ing valve.
(1) After road testing vehicle to determine which
rear wheel exhibits premature rear wheel skid, refer
to (Fig. 26) to determine which proportioning valve
needs to be tested.
Fig. 24 Proportioning Valve Pressure Test Fittings
Fig. 25 Proportioning Valve Pressure Test Gauge
Set
Fig. 26 Non-ABS Brakes Proportioning Valve
Location On Master Cylinder
5 - 16 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 99 of 1200
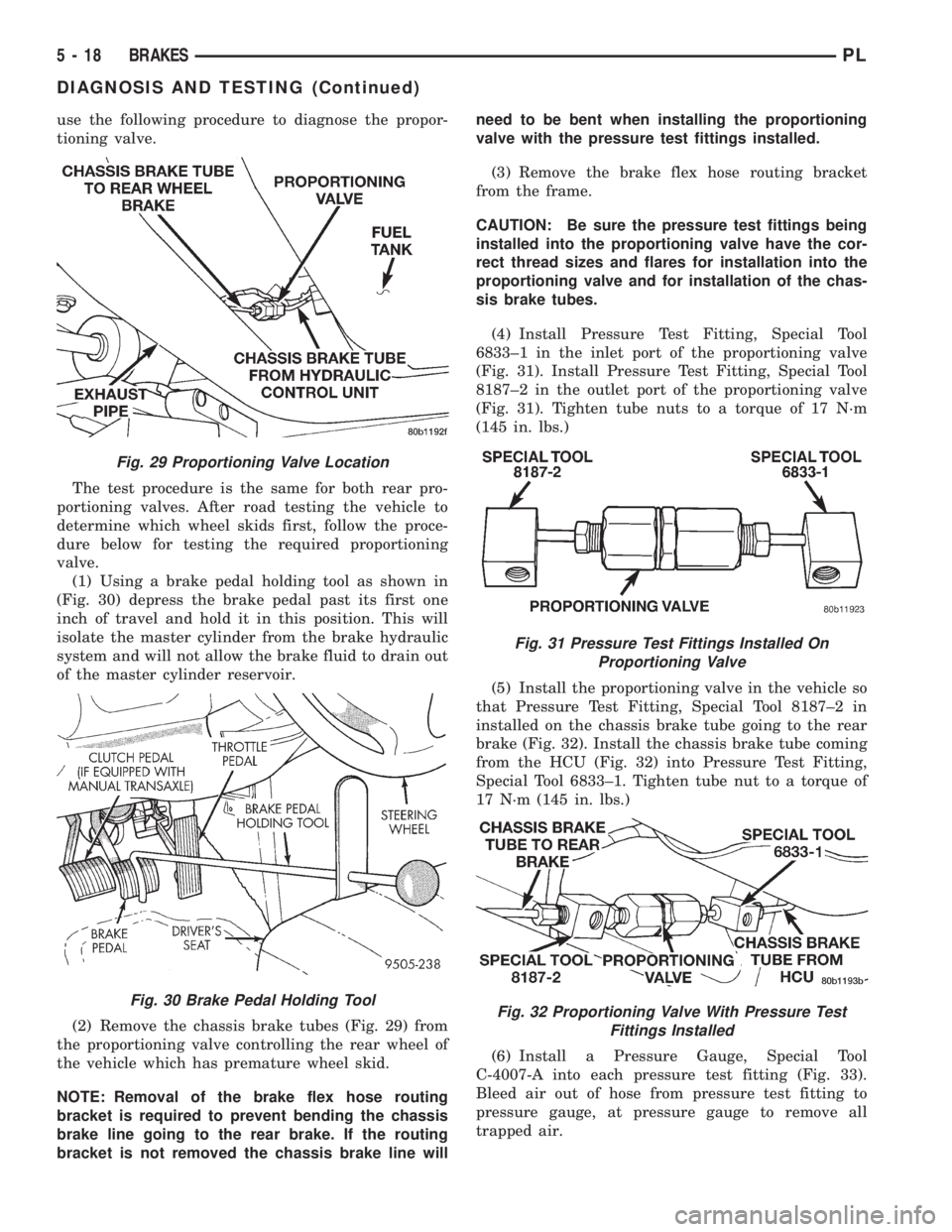
use the following procedure to diagnose the propor-
tioning valve.
The test procedure is the same for both rear pro-
portioning valves. After road testing the vehicle to
determine which wheel skids first, follow the proce-
dure below for testing the required proportioning
valve.
(1) Using a brake pedal holding tool as shown in
(Fig. 30) depress the brake pedal past its first one
inch of travel and hold it in this position. This will
isolate the master cylinder from the brake hydraulic
system and will not allow the brake fluid to drain out
of the master cylinder reservoir.
(2) Remove the chassis brake tubes (Fig. 29) from
the proportioning valve controlling the rear wheel of
the vehicle which has premature wheel skid.
NOTE: Removal of the brake flex hose routing
bracket is required to prevent bending the chassis
brake line going to the rear brake. If the routing
bracket is not removed the chassis brake line willneed to be bent when installing the proportioning
valve with the pressure test fittings installed.
(3) Remove the brake flex hose routing bracket
from the frame.
CAUTION: Be sure the pressure test fittings being
installed into the proportioning valve have the cor-
rect thread sizes and flares for installation into the
proportioning valve and for installation of the chas-
sis brake tubes.
(4) Install Pressure Test Fitting, Special Tool
6833±1 in the inlet port of the proportioning valve
(Fig. 31). Install Pressure Test Fitting, Special Tool
8187±2 in the outlet port of the proportioning valve
(Fig. 31). Tighten tube nuts to a torque of 17 N´m
(145 in. lbs.)
(5) Install the proportioning valve in the vehicle so
that Pressure Test Fitting, Special Tool 8187±2 in
installed on the chassis brake tube going to the rear
brake (Fig. 32). Install the chassis brake tube coming
from the HCU (Fig. 32) into Pressure Test Fitting,
Special Tool 6833±1. Tighten tube nut to a torque of
17 N´m (145 in. lbs.)
(6) Install a Pressure Gauge, Special Tool
C-4007-A into each pressure test fitting (Fig. 33).
Bleed air out of hose from pressure test fitting to
pressure gauge, at pressure gauge to remove all
trapped air.
Fig. 29 Proportioning Valve Location
Fig. 30 Brake Pedal Holding Tool
Fig. 31 Pressure Test Fittings Installed On
Proportioning Valve
Fig. 32 Proportioning Valve With Pressure Test
Fittings Installed
5 - 18 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 100 of 1200

(7) With the aid of a helper, apply pressure to the
brake pedal until reading on proportioning valve
inlet gauge, is at the pressure shown on the following
chart. Then check the pressure reading on the pro-
portioning valve outlet gauge. If proportioning valve
outlet pressure does not agree with value shown on
the following chart, when inlet pressure shown on
chart is obtained, replace the proportioning valve. If
proportioning valve is within pressure specifications
do not replace proportioning valve.
(8) Check rear wheel brake shoe linings for con-
tamination or for replacement brake shoes not meet-
ing OEM brake lining material specifications. These
conditions can also be a possible cause for a prema-
ture rear wheel skid.
(9) Install proportioning valve in chassis brake
tube (Fig. 29). Tighten the proportioning valve to a
torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).
(10) Bleed the affected brake line. See Bleeding
Brake System in the Service Adjustments section of
the manual for proper bleeding procedure.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP TEST
For diagnosis of specific problems with the red
brake warning lamp system, refer to Brake System
Diagnostics Chart 2, located in the Diagnosis And
Testing section in this group of the service manual.
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST PROCEDURE
The required procedure for testing the stop lamp
switch is covered in Group 8H, Vehicle Speed Control
System in this service manual. The electrical circuit
tests for stop lamps is covered in Group 8W Rear
Lighting in this service manual.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Check master cylinder reservoir brake fluid level a
minimum of twice a year.
Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
wordsFULL AND MINindicating proper range of
the master cylinder fluid level (Fig. 34).
Fig. 33 Pressure Gauges Installed On Pressure Test
Fittings
BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE APPLICATIONS AND PRESSURE SPECIFICATIONS
Sales CodeBrake
System
TypeSplit
PointSlopeIdentifi-
cationInlet
PressureOutlet
Pressure
BRA 149
Disc/Drum400 psi 0.43 Black
Band1000 psi 600-700
psi
BRD 149
Disc/Disc300 psi 0.34 Bar Code
Band1000 psi 550-650
psi
BRF 149
Disc/Disc
W/ABS300 psi 0.34 Bar Code
Band1000 psi 550-650
psi
PLBRAKES 5 - 19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 101 of 1200

CAUTION: Use only MoparTbrake fluid or an
equivalent from a tightly sealed container. Brake
fluid must conform to DOT 3 specifications. Do not
use petroleum-based fluid because seal damage in
the brake system will result.
If necessary, add specified brake fluid bringing
level to theFULLmark on the side of the master
cylinder brake fluid reservoir (Fig. 34).
BRAKE BLEEDING
NOTE: For bleeding the ABS hydraulic system, see
Bleeding Teves Mark 20 Hydraulic System in the
Service Procedures Section of the ABS Brake Sec-
tion in this group of the service manual.
CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, wipe it clean to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder.
PRESSURE BLEEDING
CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
with required adapter for the master cylinder reser-
voir to pressurize the hydraulic system for bleed-
ing.
NOTE: Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's
instructions for use of pressure bleeding equip-
ment.
When bleeding the brake system, some air may be
trapped in the brake lines or valves far upstream, as
much as ten feet from the bleeder screw (Fig. 35).
Therefore, it is essential to have a fast flow of a large
volume of brake fluid when bleeding the brakes to
ensure all the air gets out.The following wheel sequence for bleeding the
brake hydraulic system should be used to ensure
adequate removal of all trapped air from the hydrau-
lic system.
²Left rear wheel
²Right front wheel
²Right rear wheel
²Left front wheel
(1) Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleeder screw
starting at the right rear wheel and feed the hose
into a clear jar containing enough fresh brake fluid
to submerge the end of the hose (Fig. 36).
(2) Open the bleeder screw at leastone full turn
or more to obtain an steady stream of brake fluid
(Fig. 37).
(3) After 4 to 8 ounces of fluid has been bled
through the brake and an air-free flow is maintained
in the clear plastic hose and jar, close the bleeder
screw.
(4) Repeat the procedure at all the other remain-
ing bleeder screws. Then check the pedal for travel.
If pedal travel is excessive or has not been improved,
Fig. 34 Master Cylinder Fluid Level
Fig. 35 Trapped Air in Brake Line
Fig. 36 Proper Method for Purging Air From Brake
System (Typical)
5 - 20 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 103 of 1200

(5) Remove master cylinder from vise.
NOTE: Note: It is not necessary to bleed the entire
hydraulic system after replacing the master cylin-
der. But the master cylinder must have been bled
and filled upon installation.
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING PROCEDURES
Any servicing of the rotor requires extreme care to
maintain the rotor to within service tolerances to
ensure proper brake action.
If the rotor surface is deeply scored or warped, or
there is a complaint of brake roughness or pulsation,
the rotor should be resurfaced, refaced (Fig. 41) or
(Fig. 42) or replaced.
The following chart shows the location of measure-
ments and specifications when servicing the rotor.
NOTE: All rotors have markings for minimum
allowable thickness cast on an un-machined sur-
face of the rotor (Fig. 43).
This marking includes 0.76 mm (0.030 inch) allow-
able rotor wear beyond the recommended 0.76 mm
(0.030 inch) of rotor refacing.
The collets, shafts and adapters used on the brake
lathe and the bearing cups in the rotor MUST be
clean and free from any chips or contamination.
When mounting the rotor on the brake lathe, strict
attention to the brake lathe manufacturer's operating
instructions is required.
If the rotor is not mounted properly, the lateral
runout will be worse after refacing or resurfacing
than before.REFACING BRAKE ROTOR
Refacing of the rotor is not required each time the
brake pads are replaced.
When refacing a rotor the required 0.8 mm (0.003
inch) TIR (Total Indicator Reading) and 0.013 mm
(0.0005 inch) thickness variation limits MUST BE
MAINTAINED.Extreme carein the operation of
rotor turning equipment is required.
Fig. 40 Bleeding Master Cylinder
Fig. 41 Refacing Brake Rotor
Fig. 42 Resurfacing Brake Rotor (Final Finish)
5 - 22 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 105 of 1200

(1) Remove screws attaching rear of center console
assembly to console bracket (Fig. 45) or (Fig. 46).
(2) Remove the 2 screws located in cup holders
(Fig. 47), attaching front of center console assembly
to console bracket.
(3) Raise park brake hand lever assembly as high
as it will go for required clearance to remove center
console.
(4) Remove center console assembly from vehicle.
(5) Lower park brake lever handle.
(6) Grasp park brake lever output cable by hand
and pull upward (Fig. 48). Continue pulling on cable
until a 3/16 in. drill bit can be inserted into handle
and sector gear of park brake mechanism (Fig. 48).
This will lock the park brake mechanism and take
tension off park brake cables.
RELEASING PARK BRAKE AUTO ADJUSTER
NOTE: The park brake lever can be in any position
when releasing the auto adjuster. To ease installa-
tion of center console, it is advisable to pull park
brake lever handle all the way up before removing
lockout pin
(1) Be sure rear park brake cables are properly
installed in the equalizer (Fig. 49).
(2) Pull park brake lever handle all the way up.
(3) Firmly grasp park brake lever locking pin (Fig.
50), and quickly remove it from the park brake lever
mechanism. This will allow the park brake lever
mechanism to correctly adjust the park brake cables.
(4) Install center console.
(5) Install the 4 console assembly attaching screws
(Fig. 45) or (Fig. 46).
(6) Cycle park brake lever once to position park
brake cables. Then return the park brake lever its
Fig. 45 Attaching Screws At Rear Of Center Console
W/O Arm Rest
Fig. 46 Attaching Screws At Rear Of Center Console
With Arm Rest
Fig. 47 Attaching Screws At Front Of Center
Console
Fig. 48 Locking Pin Installed In Park Brake
Mechanism
5 - 24 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 107 of 1200
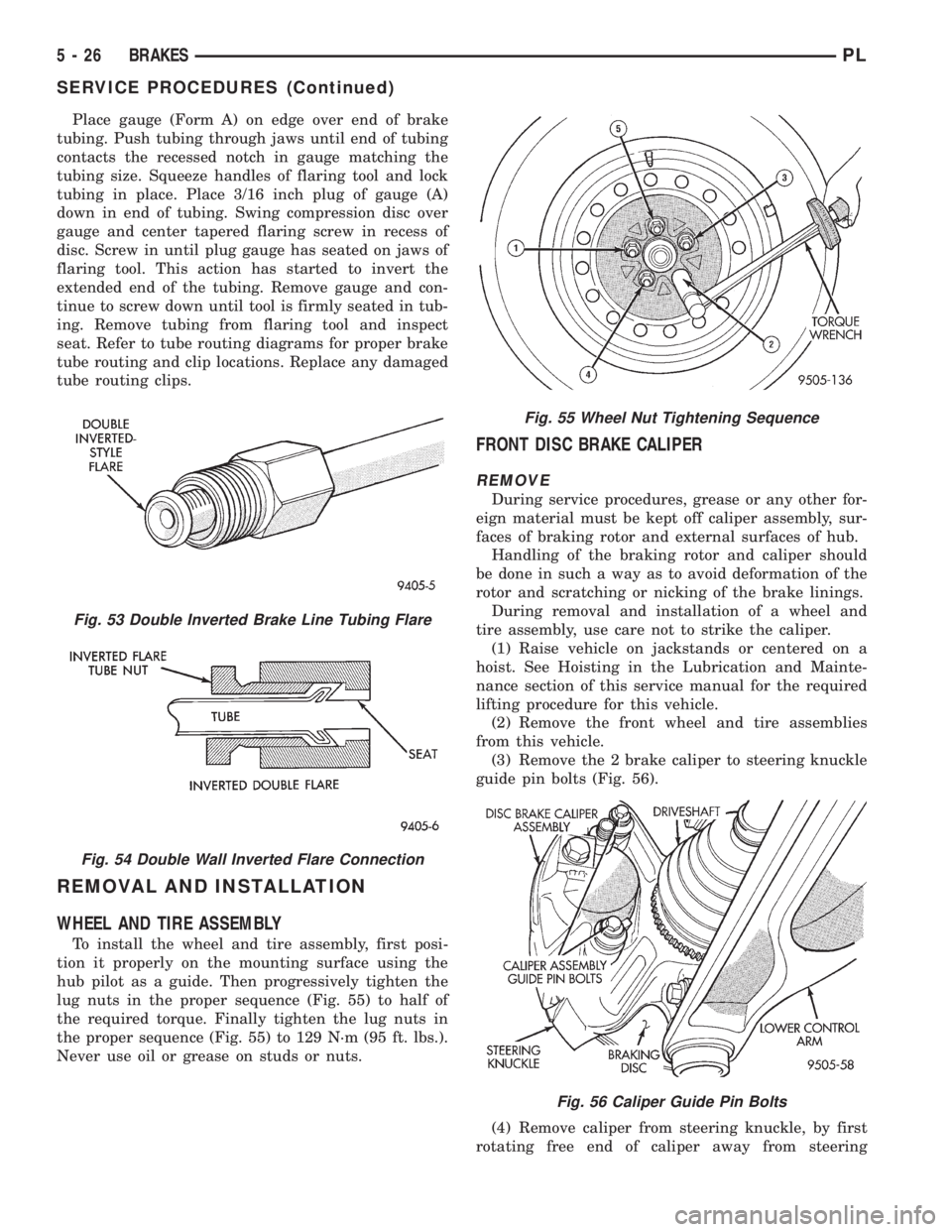
Place gauge (Form A) on edge over end of brake
tubing. Push tubing through jaws until end of tubing
contacts the recessed notch in gauge matching the
tubing size. Squeeze handles of flaring tool and lock
tubing in place. Place 3/16 inch plug of gauge (A)
down in end of tubing. Swing compression disc over
gauge and center tapered flaring screw in recess of
disc. Screw in until plug gauge has seated on jaws of
flaring tool. This action has started to invert the
extended end of the tubing. Remove gauge and con-
tinue to screw down until tool is firmly seated in tub-
ing. Remove tubing from flaring tool and inspect
seat. Refer to tube routing diagrams for proper brake
tube routing and clip locations. Replace any damaged
tube routing clips.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WHEEL AND TIRE ASSEMBLY
To install the wheel and tire assembly, first posi-
tion it properly on the mounting surface using the
hub pilot as a guide. Then progressively tighten the
lug nuts in the proper sequence (Fig. 55) to half of
the required torque. Finally tighten the lug nuts in
the proper sequence (Fig. 55) to 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.).
Never use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
REMOVE
During service procedures, grease or any other for-
eign material must be kept off caliper assembly, sur-
faces of braking rotor and external surfaces of hub.
Handling of the braking rotor and caliper should
be done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the
rotor and scratching or nicking of the brake linings.
During removal and installation of a wheel and
tire assembly, use care not to strike the caliper.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance section of this service manual for the required
lifting procedure for this vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assemblies
from this vehicle.
(3) Remove the 2 brake caliper to steering knuckle
guide pin bolts (Fig. 56).
(4) Remove caliper from steering knuckle, by first
rotating free end of caliper away from steering
Fig. 53 Double Inverted Brake Line Tubing Flare
Fig. 54 Double Wall Inverted Flare Connection
Fig. 55 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 56 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
5 - 26 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 109 of 1200

FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: ALTHOUGH FACTORY INSTALLED
BRAKELININGS ARE MADE FROM ASBESTOS
FREE MATERIALS, SOME AFTER MARKET BRAKE-
LINING MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS. THIS SHOULD
BE TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT WHEN SERVICING A
VEHICLE'S BRAKE SYSTEM, WHEN AFTERMARKET
BRAKELININGS MAY HAVE BEEN INSTALLED ON
THE VEHICLE. ALWAYS WEAR A RESPIRATOR
WHEN CLEANING BRAKE COMPONENTS AS
ASBESTOS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM
SUCH AS ASBESTOSIS AND OR CANCER. NEVER
CLEAN BRAKE COMPONENTS BY USING COM-
PRESSED AIR, USE ONLY A VACUUM CLEANER
SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE REMOVAL OF
BRAKE DUST. IF A VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT
AVAILABLE, CLEAN BRAKE PARTS USING ONLY
WATER DAMPENED SHOP TOWELS. DO NOT CRE-
ATE BRAKELINING DUST BY SANDING BRAKE LIN-
INGS WHEN SERVICING A VEHICLE. DISPOSE OF
ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED OF CONTAINING
ASBESTOS FIBERS USING ONLY SEALED AIR-
TIGHT BAGS OR CONTAINERS. FOLLOW ALL REC-
OMMENDED SAFETY PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY
THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMIN-
ISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA), FOR HANDLING AND
DISPOSAL OF PRODUCTS CONTAINING ASBES-
TOS.
During service procedures, grease or any other for-
eign material must be kept off caliper assembly, sur-
faces of braking rotor and external surfaces of hub.
Handling of the brake rotor and caliper should be
done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the
rotor and scratching or nicking of the brake linings.
If inspection reveals that the square sectioned cal-
iper piston seal is worn or damaged, it should be
replaced immediately.
During removal and installation of a wheel and
tire, use care not to strike the caliper.
NOTE: Before vehicle is moved after any brake
service work, pump the brake pedal several times
to insure the vehicle has a firm brake pedal.
NOTE: Starting with the 1998 model year, different
lining material is used on the disc brake shoes
depending on the type of brake system the vehicle
is equipped with. Vehicles equipped with standard
front disc and rear drum brakes use a new lining
material on the front disc brake shoes. Vehicles that
are equipped with optional 4 wheel disc brakes use
a new lining material on both the front and rear disc
brake shoes. When new brake shoes are installed,be sure brake shoes for the correct model year and
type of brake system the vehicle is equipped with
are used.
REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance section of this manual.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assemblies
from vehicle.
(3) Remove the 2 guide pin bolts (Fig. 60) mount-
ing the caliper to the steering knuckle.
(4) Remove brake caliper from steering knuckle, by
first rotating free end of caliper away from steering
knuckle. Then slide opposite end of caliper out from
under machined abutment on steering knuckle (Fig.
61).
(5) Support caliper firmly to prevent weight of cal-
iper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig. 62).
Fig. 60 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
Fig. 61 Removing Caliper From Steering Knuckle
5 - 28 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)