1998 OPEL FRONTERA ad blue
[x] Cancel search: ad bluePage 4251 of 6000
4C–45 DRIVE SHAFT SYSTEM
Universal Joint Reassembly
1. Install spider to flange yoke. Be sure to install the
spider by aligning the setting marks made during
disassembly.
2. Apply a molybdenum–disulfide grease or a
multi–purpose type grease NLGI No. 2 to inside of the
bearing cap.
Grease Amount: Approx. 1.2 g (0.042 oz)
401RS011
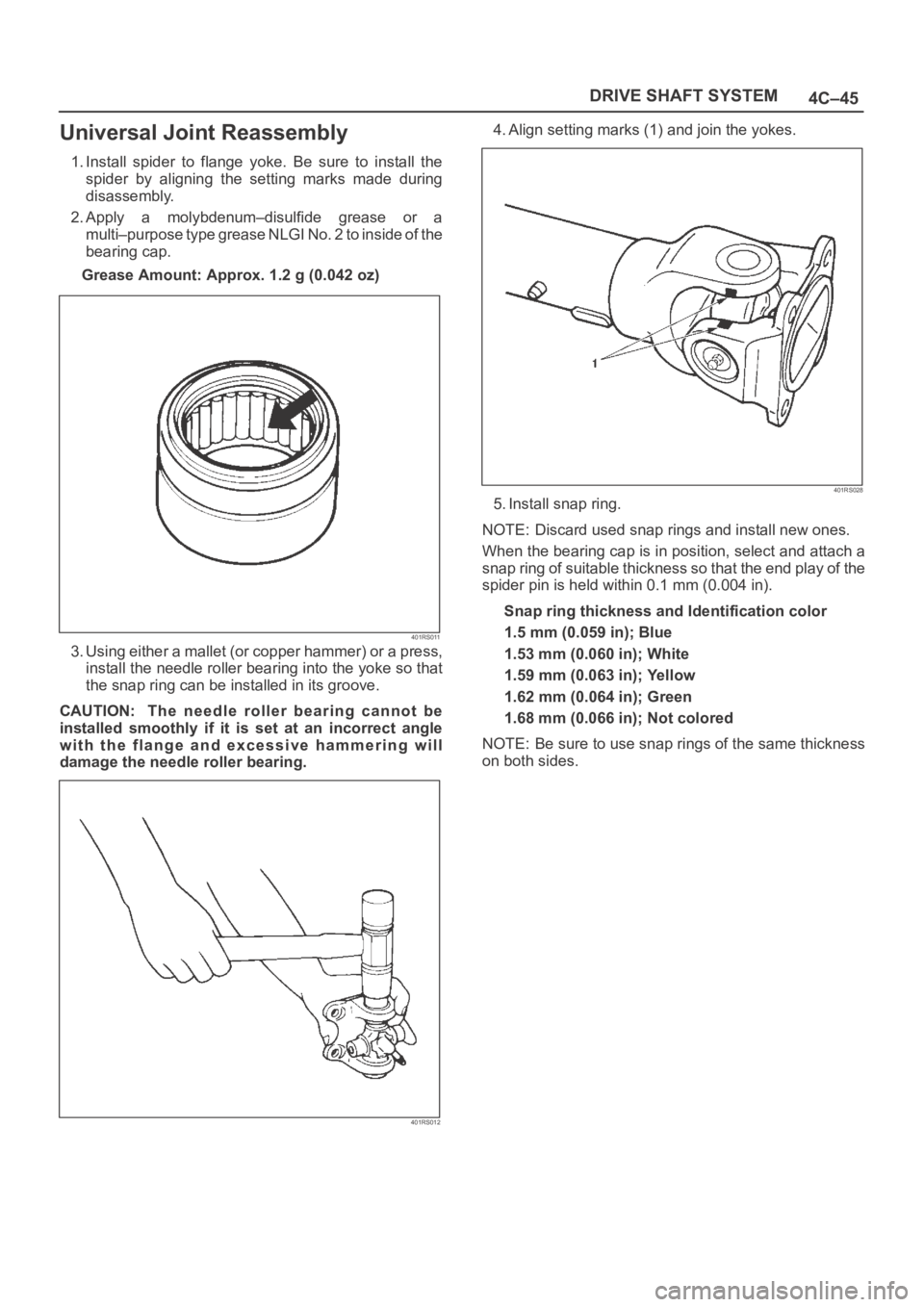
3. Using either a mallet (or copper hammer) or a press,
install the needle roller bearing into the yoke so that
the snap ring can be installed in its groove.
CAUTION: The needle roller bearing cannot be
installed smoothly if it is set at an incorrect angle
with the flange and excessive hammering will
damage the needle roller bearing.
401RS012
4. Align setting marks (1) and join the yokes.
401RS028
5. Install snap ring.
NOTE: Discard used snap rings and install new ones.
When the bearing cap is in position, select and attach a
snap ring of suitable thickness so that the end play of the
spider pin is held within 0.1 mm (0.004 in).
Snap ring thickness and Identification color
1.5 mm (0.059 in); Blue
1.53 mm (0.060 in); White
1.59 mm (0.063 in); Yellow
1.62 mm (0.064 in); Green
1.68 mm (0.066 in); Not colored
NOTE: Be sure to use snap rings of the same thickness
on both sides.
Page 4259 of 6000
4C–53 DRIVE SHAFT SYSTEM
Play in Universal Joint
Limit: Less than 0.1 mm (0.004 in)
401RS010
Universal Joint Reassembly
1. Install spider to flange yoke. Be sure to install the
spider by aligning the setting marks made during
disassembly.
2. Before installing needle roller bearing, apply a
molybdenum–disulfide grease or a multi–purpose
type grease NLGI No. 2 to inside of the bearing cap.
Grease Amount: Approx. 1.2 g (0.042 oz)
401RS011
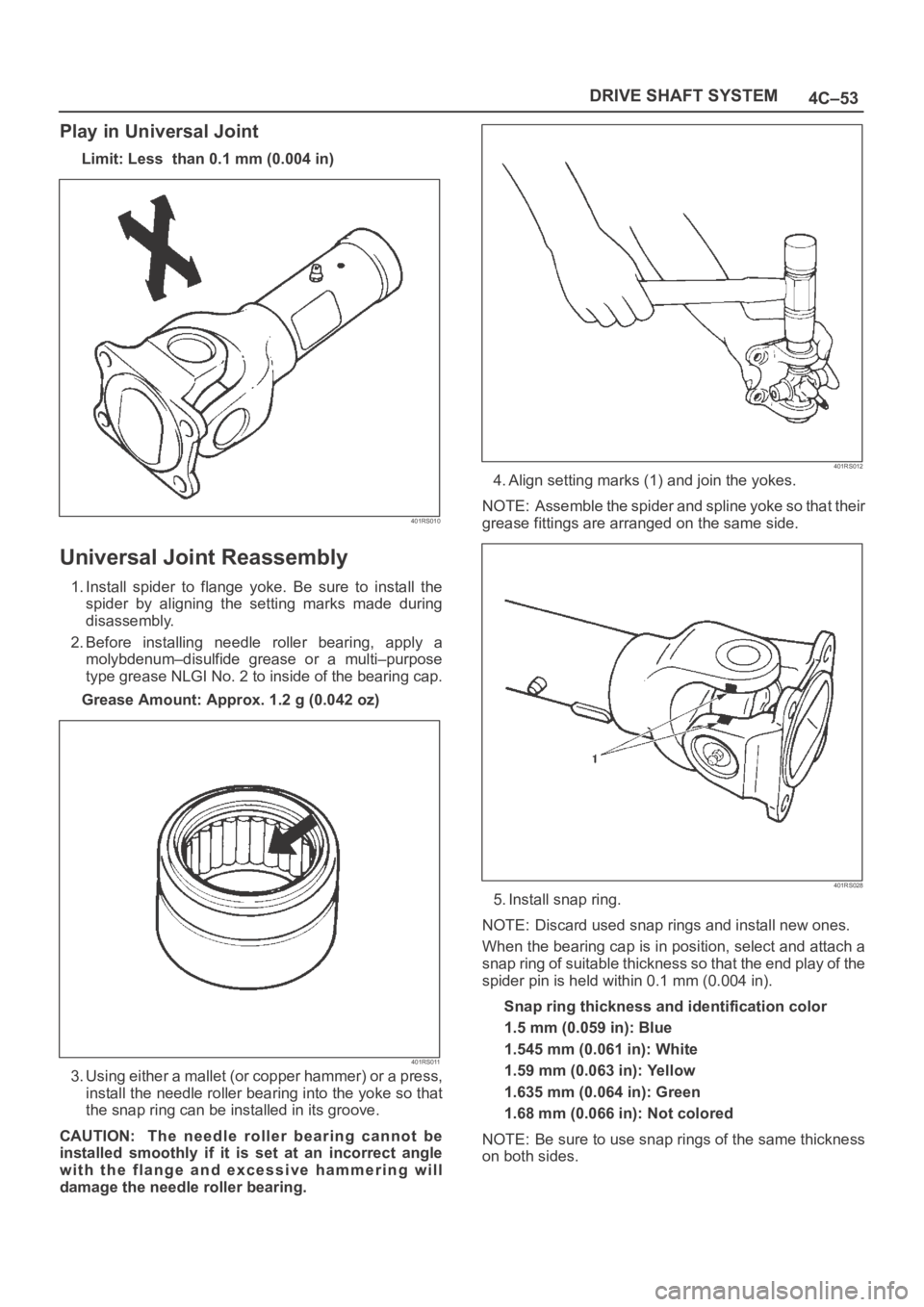
3. Using either a mallet (or copper hammer) or a press,
install the needle roller bearing into the yoke so that
the snap ring can be installed in its groove.
CAUTION: The needle roller bearing cannot be
installed smoothly if it is set at an incorrect angle
with the flange and excessive hammering will
damage the needle roller bearing.
401RS012
4. Align setting marks (1) and join the yokes.
NOTE: Assemble the spider and spline yoke so that their
grease fittings are arranged on the same side.
401RS028
5. Install snap ring.
NOTE: Discard used snap rings and install new ones.
When the bearing cap is in position, select and attach a
snap ring of suitable thickness so that the end play of the
spider pin is held within 0.1 mm (0.004 in).
Snap ring thickness and identification color
1.5 mm (0.059 in): Blue
1.545 mm (0.061 in): White
1.59 mm (0.063 in): Yellow
1.635 mm (0.064 in): Green
1.68 mm (0.066 in): Not colored
NOTE: Be sure to use snap rings of the same thickness
on both sides.
Page 4299 of 6000
4D1–38
TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
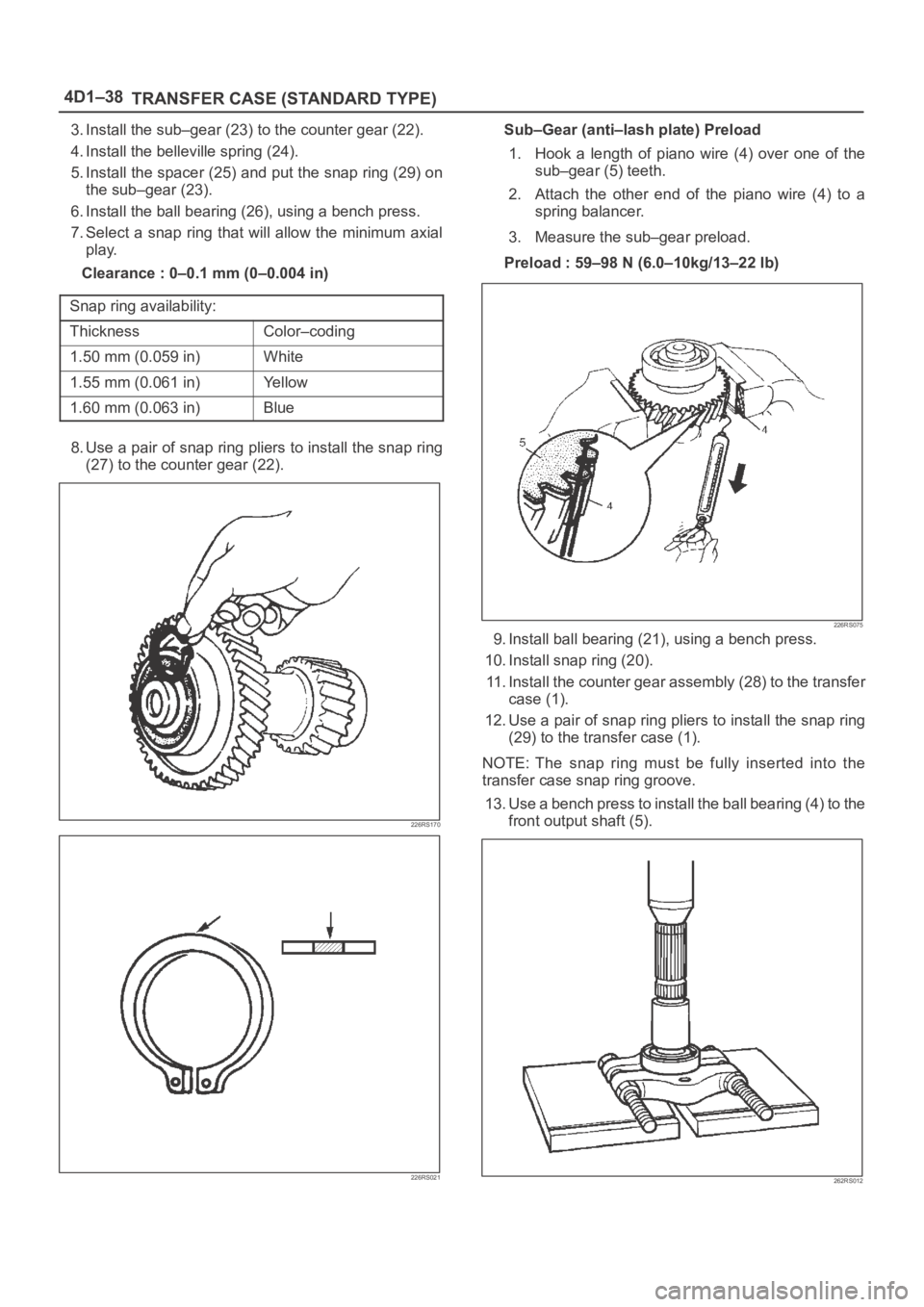
3. Install the sub–gear (23) to the counter gear (22).
4. Install the belleville spring (24).
5. Install the spacer (25) and put the snap ring (29) on
the sub–gear (23).
6. Install the ball bearing (26), using a bench press.
7. Select a snap ring that will allow the minimum axial
play.
Clearance : 0–0.1 mm (0–0.004 in)
Snap ring availability:
ThicknessColor–coding
1.50 mm (0.059 in)White
1.55 mm (0.061 in)Yellow
1.60 mm (0.063 in)Blue
8. Use a pair of snap ring pliers to install the snap ring
(27) to the counter gear (22).
226RS170
226RS021
Sub–Gear (anti–lash plate) Preload
1. Hook a length of piano wire (4) over one of the
sub–gear (5) teeth.
2. Attach the other end of the piano wire (4) to a
spring balancer.
3. Measure the sub–gear preload.
Preload : 59–98 N (6.0–10kg/13–22 lb)
226RS075
9. Install ball bearing (21), using a bench press.
10. Install snap ring (20).
11. Install the counter gear assembly (28) to the transfer
case (1).
12. Use a pair of snap ring pliers to install the snap ring
(29) to the transfer case (1).
NOTE: The snap ring must be fully inserted into the
transfer case snap ring groove.
13. Use a bench press to install the ball bearing (4) to the
front output shaft (5).
262RS012
Page 4301 of 6000
4D1–40
TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
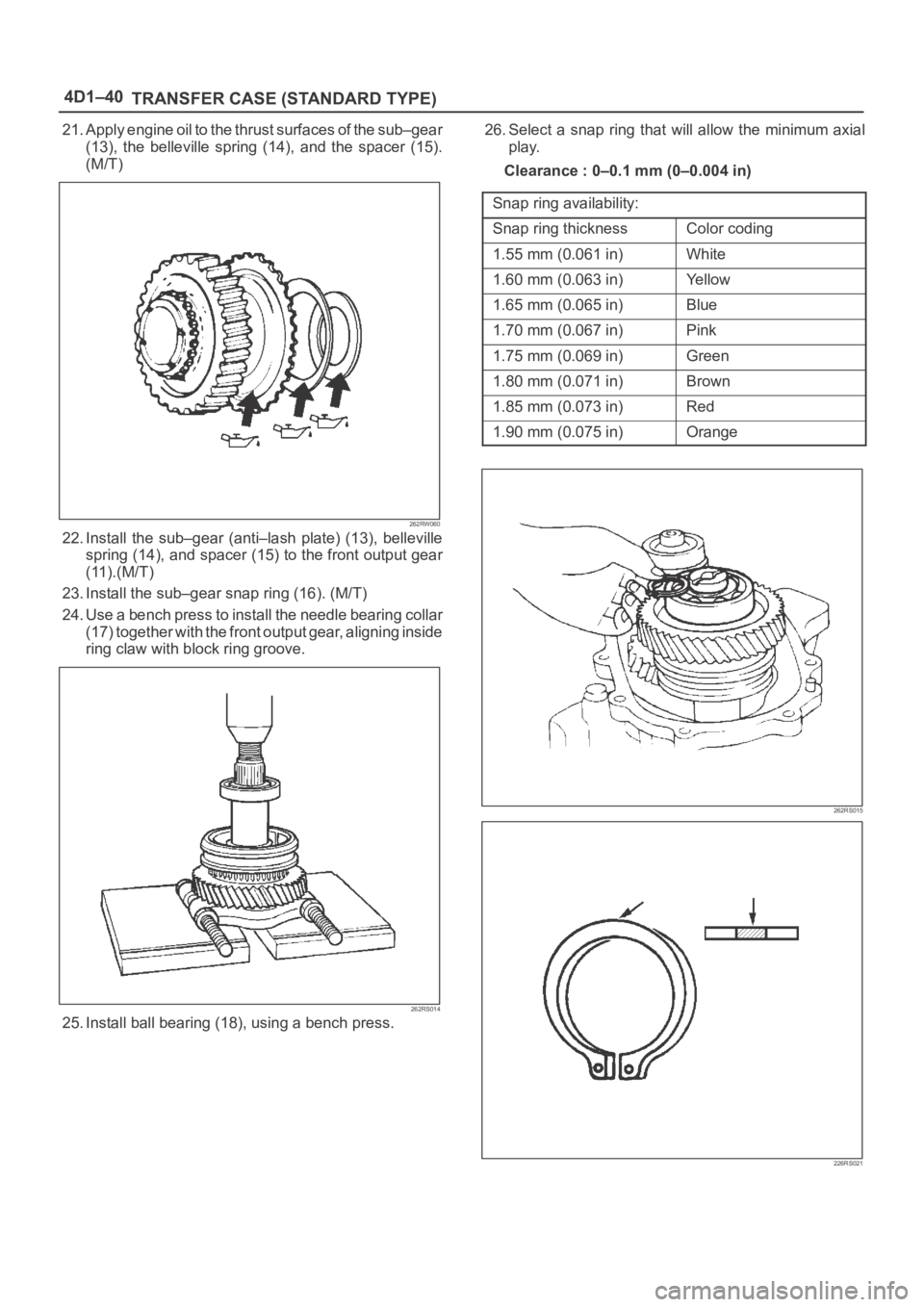
21. Apply engine oil to the thrust surfaces of the sub–gear
(13), the belleville spring (14), and the spacer (15).
(M/T)
262RW060
22. Install the sub–gear (anti–lash plate) (13), belleville
spring (14), and spacer (15) to the front output gear
(11).(M/T)
23. Install the sub–gear snap ring (16). (M/T)
24. Use a bench press to install the needle bearing collar
(17) together with the front output gear, aligning inside
ring claw with block ring groove.
262RS014
25. Install ball bearing (18), using a bench press.26. Select a snap ring that will allow the minimum axial
play.
Clearance : 0–0.1 mm (0–0.004 in)
Snap ring availability:
Snap ring thicknessColor coding
1.55 mm (0.061 in)White
1.60 mm (0.063 in)Ye l l o w
1.65 mm (0.065 in)Blue
1.70 mm (0.067 in)Pink
1.75 mm (0.069 in)Green
1.80 mm (0.071 in)Brown
1.85 mm (0.073 in)Red
1.90 mm (0.075 in)Orange
262RS015
226RS021
Page 4569 of 6000
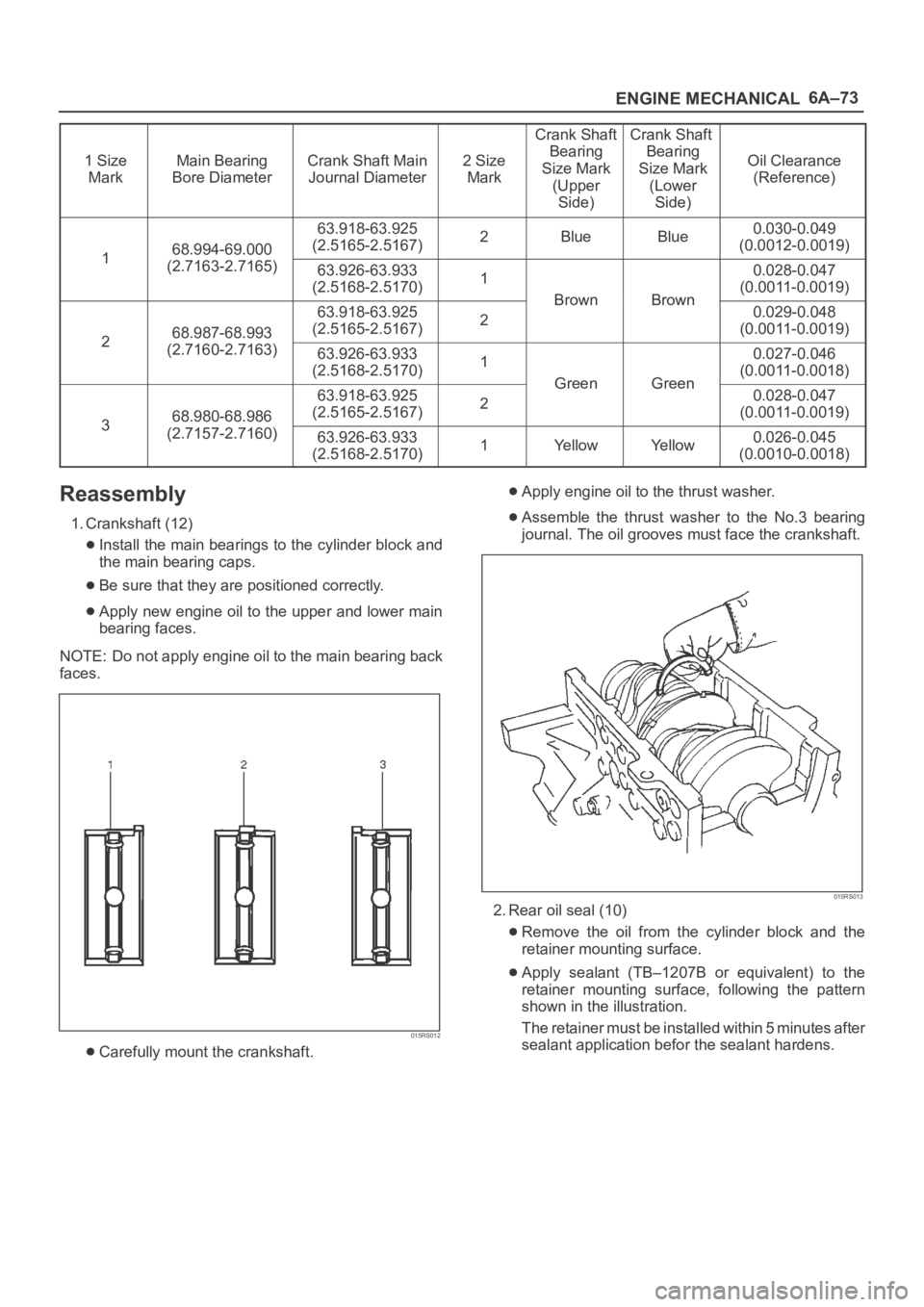
6A–73
ENGINE MECHANICAL
1 Size
MarkMain Bearing
Bore DiameterCrank Shaft Main
Journal Diameter2 Size
Mark
Crank Shaft
Bearing
Size Mark
(Upper
Side)Crank Shaft
Bearing
Size Mark
(Lower
Side)
Oil Clearance
(Reference)
168.994-69.000
63.918-63.925
(2.5165-2.5167)2BlueBlue0.030-0.049
(0.0012-0.0019)
1(2.7163-2.7165)63.926-63.933
(2.5168-2.5170)1
BrownBrown
0.028-0.047
(0.0011-0.0019)
268.987-68.993
63.918-63.925
(2.5165-2.5167)2
BrownBrown0.029-0.048
(0.0011-0.0019)
2(2.7160-2.7163)63.926-63.933
(2.5168-2.5170)1
GreenGreen
0.027-0.046
(0.0011-0.0018)
368.980-68.986
63.918-63.925
(2.5165-2.5167)2
GreenGreen0.028-0.047
(0.0011-0.0019)
3(2.7157-2.7160)63.926-63.933
(2.5168-2.5170)1Ye l l o wYe l l o w0.026-0.045
(0.0010-0.0018)
Reassembly
1. Crankshaft (12)
Install the main bearings to the cylinder block and
the main bearing caps.
Be sure that they are positioned correctly.
Apply new engine oil to the upper and lower main
bearing faces.
NOTE: Do not apply engine oil to the main bearing back
faces.
015RS012
Carefully mount the crankshaft.
Apply engine oil to the thrust washer.
Assemble the thrust washer to the No.3 bearing
journal. The oil grooves must face the crankshaft.
015RS013
2. Rear oil seal (10)
Remove the oil from the cylinder block and the
retainer mounting surface.
Apply sealant (TB–1207B or equivalent) to the
retainer mounting surface, following the pattern
shown in the illustration.
The retainer must be installed within 5 minutes after
sealant application befor the sealant hardens.
Page 4621 of 6000
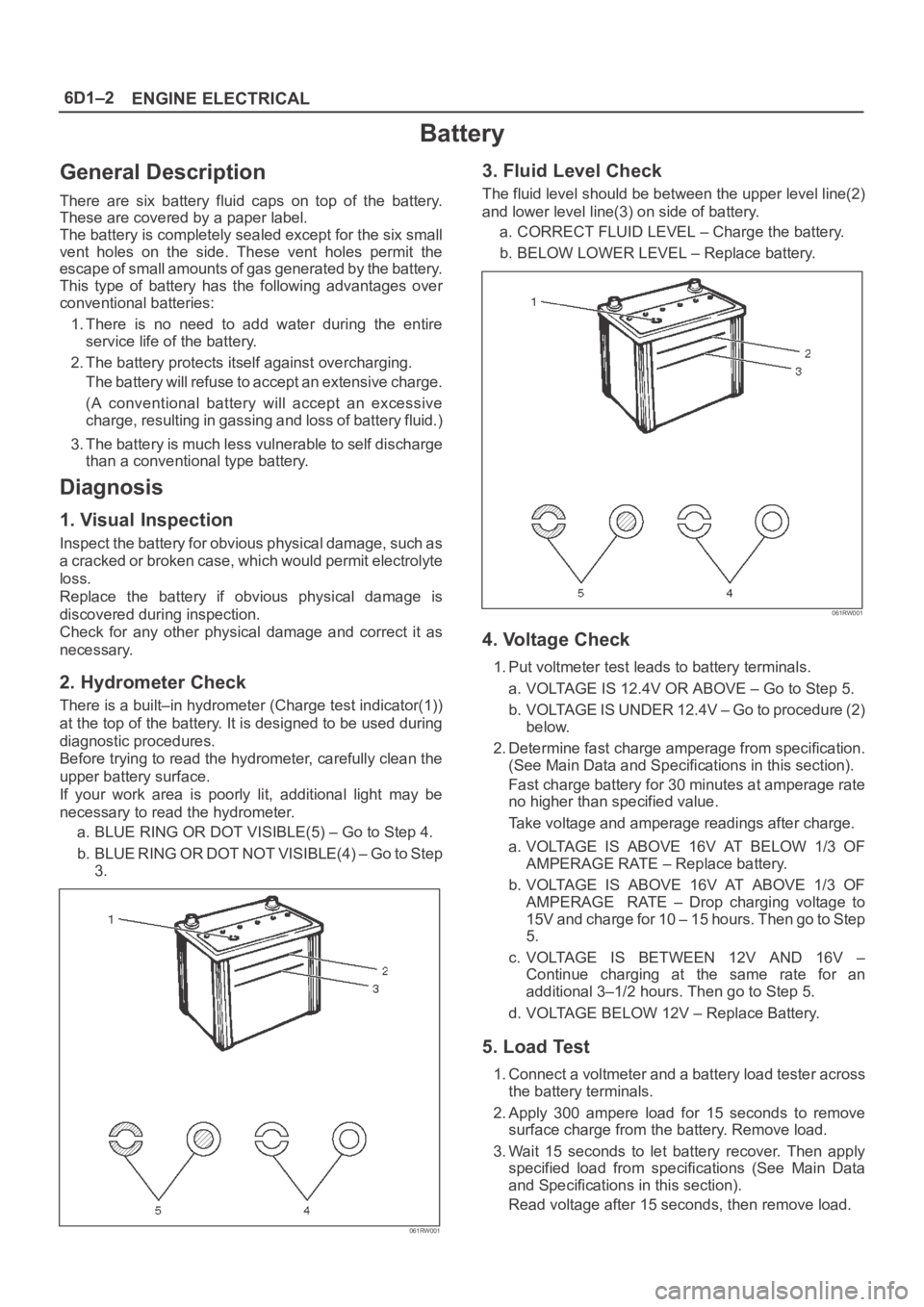
6D1–2
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
Battery
General Description
There are six battery fluid caps on top of the battery.
These are covered by a paper label.
The battery is completely sealed except for the six small
vent holes on the side. These vent holes permit the
escape of small amounts of gas generated by the battery.
This type of battery has the following advantages over
conventional batteries:
1. There is no need to add water during the entire
service life of the battery.
2. The battery protects itself against overcharging.
The battery will refuse to accept an extensive charge.
(A conventional battery will accept an excessive
charge, resulting in gassing and loss of battery fluid.)
3. The battery is much less vulnerable to self discharge
than a conventional type battery.
Diagnosis
1. Visual Inspection
Inspect the battery for obvious physical damage, such as
a cracked or broken case, which would permit electrolyte
loss.
Replace the battery if obvious physical damage is
discovered during inspection.
Check for any other physical damage and correct it as
necessary.
2. Hydrometer Check
There is a built–in hydrometer (Charge test indicator(1))
at the top of the battery. It is designed to be used during
diagnostic procedures.
Before trying to read the hydrometer, carefully clean the
upper battery surface.
If your work area is poorly lit, additional light may be
necessary to read the hydrometer.
a. BLUE RING OR DOT VISIBLE(5) – Go to Step 4.
b . B L U E R I N G O R D O T N O T V I S I B L E ( 4 ) – G o t o S t e p
3.
061RW001
3. Fluid Level Check
The fluid level should be between the upper level line(2)
and lower level line(3) on side of battery.
a. CORRECT FLUID LEVEL – Charge the battery.
b. BELOW LOWER LEVEL – Replace battery.
061RW001
4. Voltage Check
1. Put voltmeter test leads to battery terminals.
a. VOLTAGE IS 12.4V OR ABOVE – Go to Step 5.
b. VOLTAGE IS UNDER 12.4V – Go to procedure (2)
below.
2. Determine fast charge amperage from specification.
(See Main Data and Specifications in this section).
Fast charge battery for 30 minutes at amperage rate
no higher than specified value.
Take voltage and amperage readings after charge.
a. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT BELOW 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Replace battery.
b. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT ABOVE 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Drop charging voltage to
15V and charge for 10 – 15 hours. Then go to Step
5.
c. VOLTAGE IS BETWEEN 12V AND 16V –
Continue charging at the same rate for an
additional 3–1/2 hours. Then go to Step 5.
d. VOLTAGE BELOW 12V – Replace Battery.
5. Load Test
1. Connect a voltmeter and a battery load tester across
the battery terminals.
2. Apply 300 ampere load for 15 seconds to remove
surface charge from the battery. Remove load.
3. Wait 15 seconds to let battery recover. Then apply
specified load from specifications (See Main Data
and Specifications in this section).
Read voltage after 15 seconds, then remove load.
Page 4622 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL6D1–3
a. VOLTAGE DOES NOT DROP BELOW THE
MINIMUM LISTED IN THE TABLE – The battery is
good and should be returned to service.
b. VOLTAGE IS LESS THAN MINIMUM LISTED –
Replace battery.
ESTIMATED TEMPERATURE
MINIMUM
VOLTAGE
FCV
70219.6
60169.5
50109.4
4049.3
30–19.1
20–78.9
10–128.7
0–188.5
The battery temperature must be estimated by feel
and by the temperature the battery has been
exposed to for the preceding few hours.
Battery Charging
Observe the following safety precautions when charging
the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the fluid
level is below the lower level line on the side of the
battery. In this case, the battery must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during charging
procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery feels hot to the touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery begins to gas or spew
electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer blue dot
or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or tilt the battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be either
quick charged or slow charged in the same manner as
other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure that
you completely charge the battery. Never partially
charge the battery.
Jump Starting
Jump Starting with an Auxiliary (Booster)
Battery
CAUTION: Never push or tow the vehicle in an
attempt to start it. Serious damage to the emission
system as well as other vehicle parts will result.Treat both the discharged battery and the booster
battery with great care when using jumper cables.
Carefully follow the jump starting procedure, being
careful at all times to avoid sparking.
WARNING: FAILURE TO CAREFULLY FOLLOW THE
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE COULD RESULT IN
THE FOLLOWING:
1. Serious personal injury, particularly to your eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explosion, battery
acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of one or both
vehicles particularly.
Never expose the battery to an open flame or electrical
spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch fire or
explode.
Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry before
working around the battery. Protect your eyes by wearing
an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with your eyes
or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with fabrics or
painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.
Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes, skin,
fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and thoroughly
rinse the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in
contact with the positive battery terminal, or any other
metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect against a
short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of reach of young children.
Jump Starting Procedure
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector level in the “PARK”
position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission,
place the shift lever in the “NEUTRAL” position.
Turn “OFF” the ignition.
Turn “OFF” all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built–in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built–in hydrometer is
completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive
terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other. This will
cause a ground connection, effectively neutralizing
the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
Page 4658 of 6000

6E–1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ENGINE
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONTENTS
Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tightening Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Type Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagrams and Schematics 6E–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (1 of 11) 6E–6. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (2 of 11) For EC,
THAILAND, SOUTH EAST ASIA, LATIN
AMERICA, GULF, SAUDI, CHINA. 6E–7. . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (3 of 11) For SOUTH
AFRICA and EXP. 6E–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (4 of 11) 6E–9. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (5 of 11) 6E–10. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (6 of 11) For
AUSTRALIA, THAILAND, SOUTH EAST
ASIA, LATIN AMERICA, GULF, SAUDI,
LATIN AMERICA. 6E–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (7 of 11) For EC. 6E–12. . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (8 of 11) For EXPORT
and SOUTH AFRICA. 6E–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (9 of 11) Except EXP
and SOUTH AFRICA 6E–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (10 of 11) For
EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA 6E–15. . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (11 of 11) 6E–16. . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinouts 6E–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red
Connector – Row “A” 6E–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red
Connector – Row “B” 6E–19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “C” (For EC) 6E–20. . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “C” (For except EC) 6E–21. . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “D”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH
AFRICA) 6E–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “D”
(For EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–23. . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “E”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH
AFRICA) 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “E”
(For EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–26. . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “F” 6E–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Component Locators 6E–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Component Locator (This illustration
is based on RHD model.) 6E–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . Engine Component Locator Table 6E–29. . . . . . . .
Engine Component Locator Table 6E–31. . . . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator 6E–32. . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
(Automatic Transmission) 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
(Manual Transmission) 6E–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuse and Relay Panel (Underhood
Electrical Center) 6E–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sensors and Miscellaneous Component
Locators 6E–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Stored 6E–37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No DTC 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Matching Symptom 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittents 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Trouble Found 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Service Information 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OBD Serviceablity Issues 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maintenance Schedule 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Visual / Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required 6E–38. . . . . .
Serial Data Communications 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class II Serial Data Communications 6E–38. . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic Tests 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common OBD Terms 6E–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The Diagnostic Executive 6E–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Types 6E–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2 6E–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Tech 2 6E–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Features 6E–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Getting Started 6E–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Procedure (For Example) 6E–44. . . . .
DTC Modes 6E–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Information Mode 6E–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Injector Balance Test 6E–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Control Test 6E–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control System Test 6E–48. . . . . . . . . . . . .