1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO FUEL PUMP RELAY
[x] Cancel search: FUEL PUMP RELAYPage 164 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1F1
ENGINE CONTROLS
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless other -
wise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Engine and ECM Problem Check Report 1F1 -- 2....
Specifications 1F1 -- 3............................
Engine Data Display Table 1F1 -- 3.................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1F1 -- 4..........
Fuel System Specification 1F1 -- 5.................
Temperature vs Resistance 1F1 -- 5................
Special Tools and Equipment 1F1 -- 6..............
Special Tools Table 1F1 -- 6.......................
Schematic and Routing Diagrams 1F1 -- 7..........
ECM Wiring Diagram
(3.2L DOHC -- MSE 3.62S) 1F1 -- 7..............
Diagnosis 1F1 -- 14................................
Failure Code Diagnosis 1F1 -- 14.....................
Clearing Failure Codes 1F1 -- 14...................
Failure Codes Table 1F1 -- 14.....................
Ignition System 1F1 -- 18...........................
Ignition Coil 1F1 -- 20.............................
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 1F1 -- 22.........
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 1F1 -- 26..........
Camshaft Actuator 1F1 -- 30......................
Knock Sensor (KS) 1F1 -- 32......................
Spark Plug 1F1 -- 34.............................
System Voltage 1F1 -- 38.........................
Ignition Switch 1F1 -- 39..........................
Fuel System 1F1 -- 40..............................
Fuel Pump 1F1 -- 42.............................
Fuel Injector 1F1 -- 46............................
Purge Control Valve 1F1 -- 50.....................
Fuel Rail 1F1 -- 52...............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F1 -- 54.................
Induction System 1F1 -- 56..........................
Throttle Valve Actuator 1F1 -- 56...................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F1 -- 60..........
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 1F1 -- 64.
Accelerator Pedal Module 1F1 -- 68................
Clutch Switch 1F1 -- 71...........................Cooling Fan 1F1 -- 72............................
A/C Compressor Relay 1F1 -- 73...................
Cruise Control Switch 1F1 -- 74....................
Traction Control System (TCS) 1F1 -- 75............
Resonance Flap 1F1 -- 76.........................
Stop Lamp Switch 1F1 -- 77.......................
Engine RPM 1F1 -- 78............................
Exhaust System 1F1 -- 79...........................
Catalytic Converter 1F1 -- 79......................
Oxygen Sensor 1F1 -- 80.........................
Engine Control Module 1F1 -- 86.....................
Serial Data Communication 1F1--88...............
Internal Failure 1F1 -- 90..........................
Electronic Throttle Controller Safety
Malfunction 1F1 -- 92...........................
Immobilizer 1F1 -- 94.............................
Maintenance and Repair 1F1 -- 95..................
On -- Vehicle Service 1F1 -- 95........................
Discharging the Pressure in Fuel System 1F1 -- 95...
Fuel Pump 1F1 -- 95.............................
Fuel Filter 1F1 -- 96..............................
Fuel Tank 1F1 -- 97..............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F1 -- 98.................
Fuel Rail and Injector 1F1 -- 99....................
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 1F1 -- 100......
Throttle Body (Integrated with the
Actuator) 1F1 -- 101............................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F1 -- 102.........
Knock Sensor 1F1 -- 102..........................
Pedal Position Sensor 1F1 -- 103...................
Oxygen Sensor 1F1 -- 103........................
Purge Control Valve 1F1 -- 104....................
Canister 1F1 -- 104...............................
Camshaft Position Sensor 1F1 -- 104...............
Crankshaft Position Sensor 1F1 -- 105..............
Engine Control Module 1F1 -- 105..................
Page 177 of 2053

1F1 -- 14 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
FAILURE CODE DIAGNOSIS
CLEARING FAILURE CODES
Notice:To prevent Engine Control Module (ECM) damage, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting
the power to the ECM (for example battery cable, ECM pigtail connector, ECM fuse, jumper cables, etc.)
Parameters listed in the table may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other
factors. If a failure code is displayed during the “TROUBLE CODE” in scan tool check mode, check the circuit for the
code listed in the table below. For details of each code, turn to the page referred to under the “See Page” for the re-
spective “Failure Code” in the below table.
Failure codes should be cleared after repairs have been completed.
FAILURE CODES TABLE
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
001F1 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor low voltage
011F1 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor high voltage
021F1 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor plausibility
031F1 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor low voltage
041F1 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor high voltage
051F1 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor plausibility
061F1 -- 66Engine coolant temperature insufficient for closed loop fuel control
081F1 -- 38System voltage too low
091F1 -- 62Mass air flow sensor plausibility
101F1 -- 62Mass air flow sensor low voltage
111F1 -- 62Mass air flow sensor high voltage
171F1 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (no engine revolution signal)
181F1 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (rpm > max. value)
191F1 -- 27Camshaft position senosr signal : No.1 cylinder recognition failure
201F1 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (gap recognition failure)
211F1 -- 90Transmission coding failure
231F1 -- 88CAN communication failure : ASR/MSR
241F1 -- 88CAN communication failure : ABS
251F1 -- 94Communication with transponder missing
261F1 -- 88CAN communication failure : TCU (A/T only)
271F1 -- 88CAN communication failure : TOD (E32 only)
291F1 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 200h not plausible
301F1 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 208h not plausible
311F1 -- 89CAN communication failure : communication initialization failure
321F1 -- 78Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to battery
331F1 -- 78Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to ground or open
341F1 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to battery
351F1 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to ground or open
Page 203 of 2053

1F1 -- 40 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL SYSTEM
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating condi-
tions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the individual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near each
cylinder.
The main fuel control sensors are the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and the oxygen (O2) sensors.
The MAF sensor monitors the mass flow of the air being drawn into the engine. An electrically heated element is
mounted in the intake air stream, where it is cooled by the flow of incoming air. Engine Control Module (ECM) modu-
lates the flow of heating current to maintain the temperature differential between the heated film and the intake air at a
constant level. The amount of heating current required to maintain the temperature thus provides an index for the
mass air flow. This concept automatically compensates for variations in air density, as this is one of the factors that
determines the amount of warmth that the surrounding air absorbs from the heated element. MAF sensor is located
between the air filter and the throttle valve.
Under high fuel demands, the MAF sensor reads a high mass flow condition, such as wide open throttle. The ECM
uses this information to enrich the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on-- time, to provide the correct amount of
fuel. When decelerating, the mass flow decreases. This mass flow change is sensed by the MAF sensor and read by
the ECM, which then decreases the fuel injector on-- time due to the low fuel demand conditions.
The O2 sensors are located in the exhaust pipe before catalytic converter. The O2 sensors indicate to the ECM the
amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling the fuel
injectors. The best air/fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which allows the catalytic converter to
operate most efficiently. Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system
is called a “closed loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to determine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions, called ‘‘modes”.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel pump relay on for 1 second. The fuel pump then builds fuel
pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP) sensor
and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at -- 36°C(--33°F) coolant
temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 94°C (201°F) coolant temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by changing how long the fuel injector is turned on and off. This is done by ‘‘pulsing” the fuel injectors for
very short times.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ‘‘open loop” and ‘‘closed loop”.
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 690 rpm, thesystem goes into “open loop” operation. In “open loop”, the
ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and the
MAF sensor. The ECM stays in “open loop” until the following conditions are met:
DThe O2 has a varying voltage output, showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
DThe ECT sensor is above a specified temperature (22.5°C).
DA specific amount of time has elapsed after starting the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with different engines and are stored in the Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read -- Only Memory (EEPROM). When these conditions are met, thesystem goes into “closed loop”
operation. In “closed loop”, the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on-- time) based on the signals from the
O2 sensors. This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and airflow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration is
very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short periods of time.
Page 206 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 43
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F210
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
34Fuel pump relay short
circuit to batteryWhen short circuit to power
sourceDInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 33 about short circuit or
openwithbadcontact
35Fuel pump relay short
circuit to ground or openWhen short circuit to ground
or open
openwithbadcontact
DInspection the fuel pump relay
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the ECM will activate the pump relay and run the in -- tank fuel pump. The fuel
pump willoperate as long as the engine is cranking or running and the ECM is receiving ignition reference pulses.
If there are no reference pulses, the ECM will shut off the fuel pump within 2 seconds after the ignition switch is turned
ON, engine stopped or engine stalled.
Fuel Pump Relay Inspection
Measure the voltage between the ECM terminal No. 33 and Ground.
Ignition Switch : ON
0v(for1~2sec.)
Cranking0v
Page 207 of 2053

1F1 -- 44 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Measure the Fuel Delivery from the Fuel Pump
1. Disconnect the return pipe from fuel distributor and insert the appropriate hose into it.
2. Place the hose end into the beaker with the minimum capacity of 1 Liter
3. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
4. Connect the terminal No. 33 and No. 5 of ECM with a service wire.
5. Measure the fuel delivery from the fuel pump
Specified Value
1 Liter/max. 35 sec.
Notice:Check the fuel filter and fuel line when the fuel delivery is not within specified value.
Measure the Current Consumption of Fuel Pump
1. Remove the fuel pump relay from fuse and relay box in trunk, and turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Using a multimeter, measure the current consumption by connecting the terminal No. 30 and No. 87 of the fuel
pump relay connector.
Specified Value
5~9A
Notice:Replace the fuel pump relay if the measured value is over 9 A.
Page 249 of 2053

1F1 -- 86 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
YAA1F830
The Engine Control Module (ECM), located inside the right side kick panel, is the control center of the fuel injection
system. It constantly looks at the information from various sensors and controls the systems that affect the vehicle’s
performance. Engine rpm and air mass are used to measure the air intake quantity resulting in fuel injection metering.
The ECM also performs the diagnostic functions of the system. It can recognize operational problems, store failure
code(s) which identify the problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs.
There are no serviceable parts in the ECM. The calibrations are stored in the ECM in the Programmable Read Only
Memory (PROM).
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power the sensors or switches. This is done through resistance in the ECM
which are so high in value that a test light will not come ON when connected to the circuit. In some cases, even an
ordinary shop voltmeter will not give and accurate reading because its resistance is too low. You must use a digital
voltmeter with a 10 Mohm input impedance to get accurate voltage readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as
the ignition coils, the fuel injectors, the fuel pump relay, the intake manifold resonance flap, the camshaft actuator, the
canister purge valve, etc., by controlling the ground circuit.
Page 423 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1F2
ENGINE CONTROLS
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless other -
wise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Engine and ECM Problem Check Report 1F2 -- 2....
Specifications 1F2 -- 3............................
Engine Data Display Table 1F2 -- 3.................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1F2 -- 4..........
Fuel System Specification 1F2 -- 5.................
Temperature vs Resistance 1F2 -- 5................
Special Tools and Equipment 1F2 -- 6..............
Special Tools Table 1F2 -- 6.......................
Schematic and Routing Diagrams 1F2 -- 7..........
ECM Wiring Diagram
(2.3L DOHC -- MSE 3.53S) 1F2 -- 7..............
Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14................................
Failure Code Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14.....................
Clearing Failure Codes 1F2 -- 14...................
Failure Codes Table 1F2 -- 14.....................
Ignition System 1F2 -- 18...........................
Ignition Coil 1F2 -- 20.............................
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 1F2 -- 22.........
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 1F2 -- 26..........
Camshaft Actuator 1F2 -- 30......................
Knock Sensor (KS) 1F2 -- 32......................
Spark Plug 1F2 -- 34.............................
System Voltage 1F2 -- 38.........................
Ignition Switch 1F2 -- 39..........................
Fuel System 1F2 -- 40..............................
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 42.............................
Fuel Injector 1F2 -- 46............................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 50.....................
Fuel Rail 1F2 -- 52...............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 54.................
Induction System 1F2 -- 56..........................
Throttle Valve Actuator 1F2 -- 56...................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 60..........
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 1F2 -- 64.
Accelerator Pedal Module 1F2 -- 68................Cooling Fan 1F2 -- 72............................
A/C Compressor Relay 1F2 -- 73...................
Cruise Control Switch 1F2 -- 74....................
Traction Control System (TCS) 1F2 -- 75............
Stop Lamp Switch 1F2 -- 76.......................
Engine RPM 1F2 -- 77............................
Exhaust System 1F2 -- 78...........................
Catalytic Converter 1F2 -- 78......................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 80.........................
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 86.....................
Serial Data Communication 1F2--88...............
Internal Failure 1F2 -- 90..........................
Electronic Throttle Controller Safety
Malfunction 1F2 -- 92...........................
Immobilizer 1F2 -- 94.............................
Maintenance and Repair 1F2 -- 95..................
On -- Vehicle Service 1F2 -- 95........................
Discharging the Pressure in Fuel System 1F2 -- 95...
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 95.............................
Fuel Filter 1F2 -- 96..............................
Fuel Tank 1F2 -- 97..............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 98.................
Fuel Rail and Injector 1F2 -- 99....................
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 1F2 -- 100......
Throttle Body (Integrated with the
Actuator) 1F2 -- 101............................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 102.........
Knock Sensor 1F2 -- 102..........................
Pedal Position Sensor 1F2 -- 103...................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 103........................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 104....................
Canister 1F2 -- 104...............................
Camshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 104...............
Crankshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 105..............
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 105..................
Page 436 of 2053
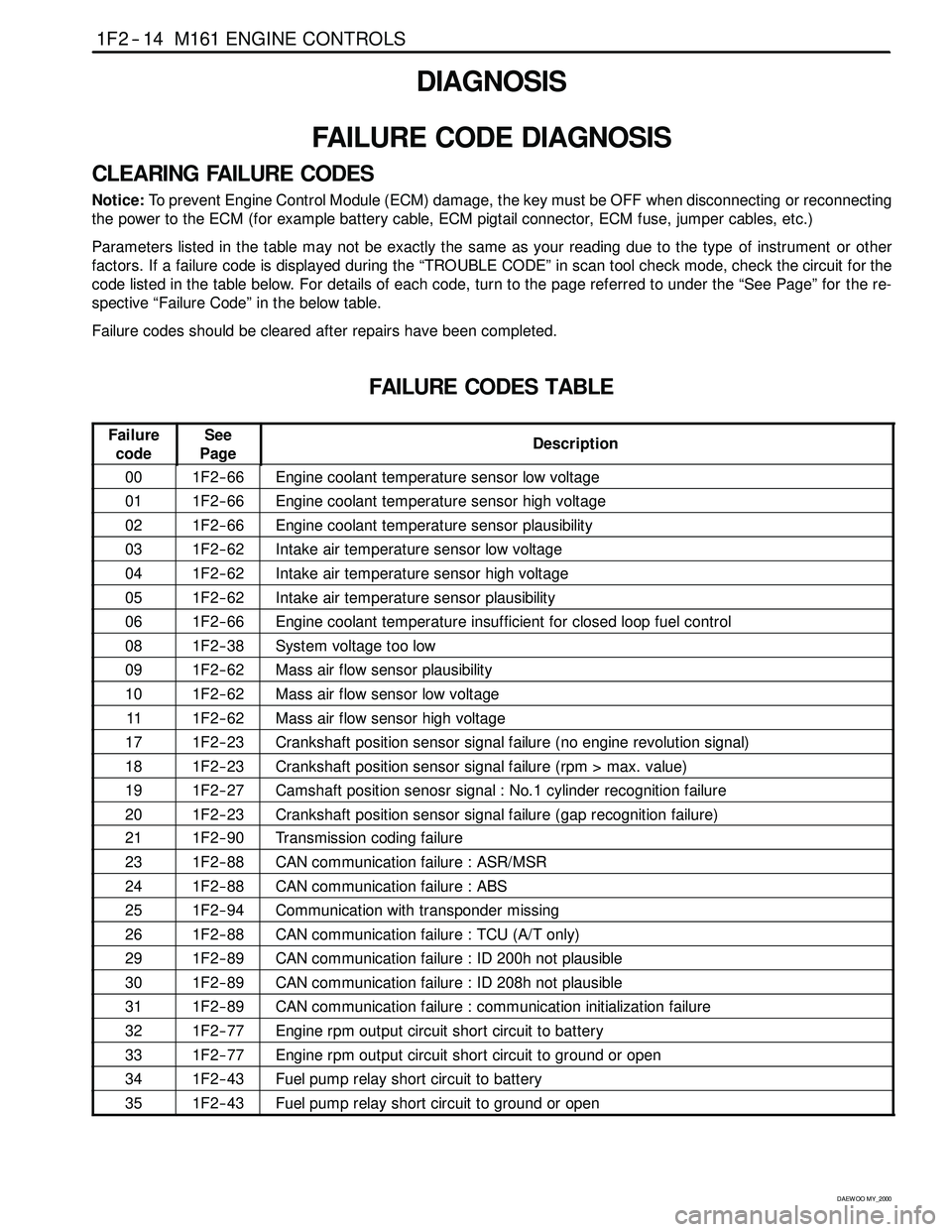
1F2 -- 14 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
FAILURE CODE DIAGNOSIS
CLEARING FAILURE CODES
Notice:To prevent Engine Control Module (ECM) damage, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting
the power to the ECM (for example battery cable, ECM pigtail connector, ECM fuse, jumper cables, etc.)
Parameters listed in the table may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other
factors. If a failure code is displayed during the “TROUBLE CODE” in scan tool check mode, check the circuit for the
code listed in the table below. For details of each code, turn to the page referred to under the “See Page” for the re-
spective “Failure Code” in the below table.
Failure codes should be cleared after repairs have been completed.
FAILURE CODES TABLE
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
001F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor low voltage
011F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor high voltage
021F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor plausibility
031F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor low voltage
041F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor high voltage
051F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor plausibility
061F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature insufficient for closed loop fuel control
081F2 -- 38System voltage too low
091F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor plausibility
101F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor low voltage
111F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor high voltage
171F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (no engine revolution signal)
181F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (rpm > max. value)
191F2 -- 27Camshaft position senosr signal : No.1 cylinder recognition failure
201F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (gap recognition failure)
211F2 -- 90Transmission coding failure
231F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ASR/MSR
241F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ABS
251F2 -- 94Communication with transponder missing
261F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : TCU (A/T only)
291F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 200h not plausible
301F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 208h not plausible
311F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : communication initialization failure
321F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to battery
331F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to ground or open
341F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to battery
351F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to ground or open