1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO trouble code connector
[x] Cancel search: trouble code connectorPage 1031 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-48 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 09
LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F160
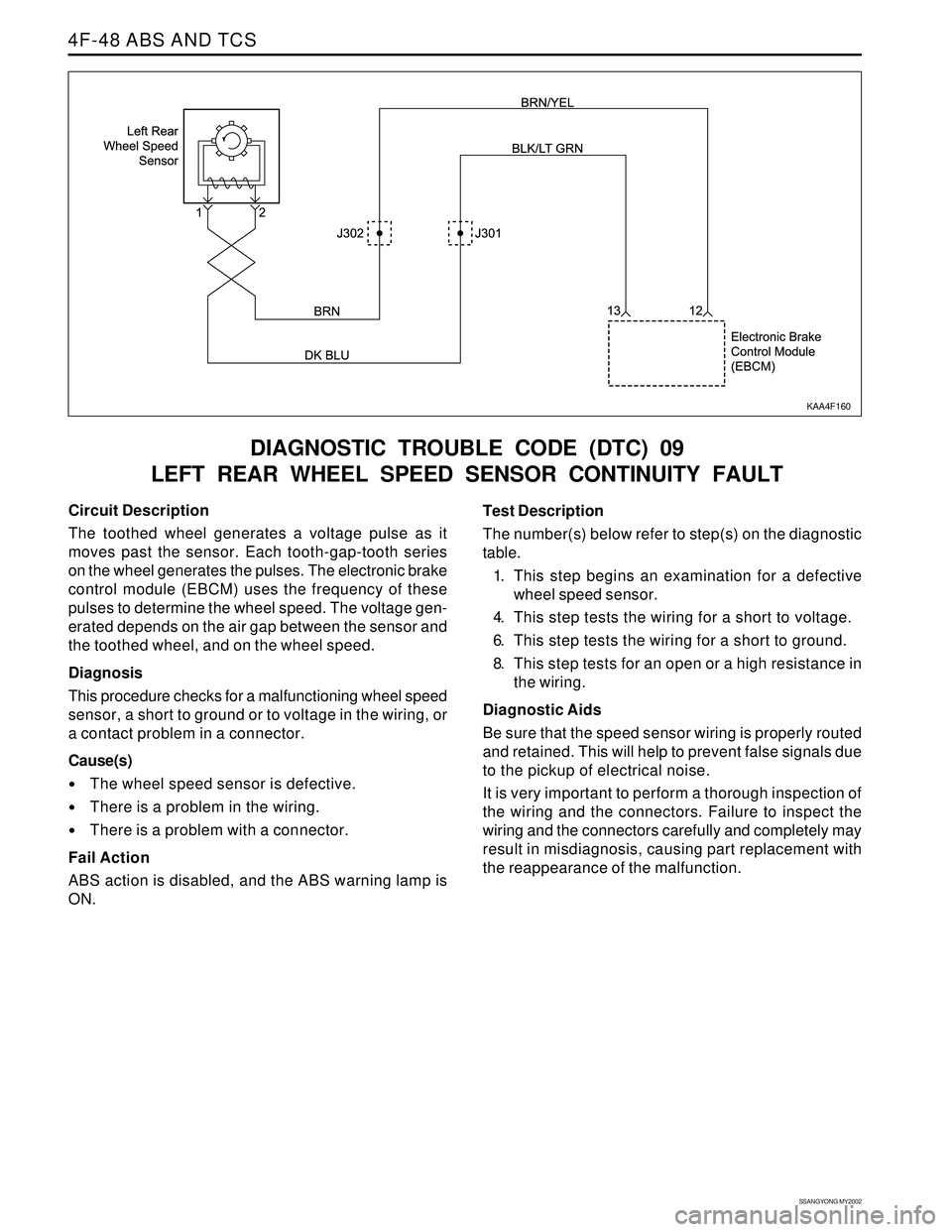
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1033 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-50 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 06
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F170
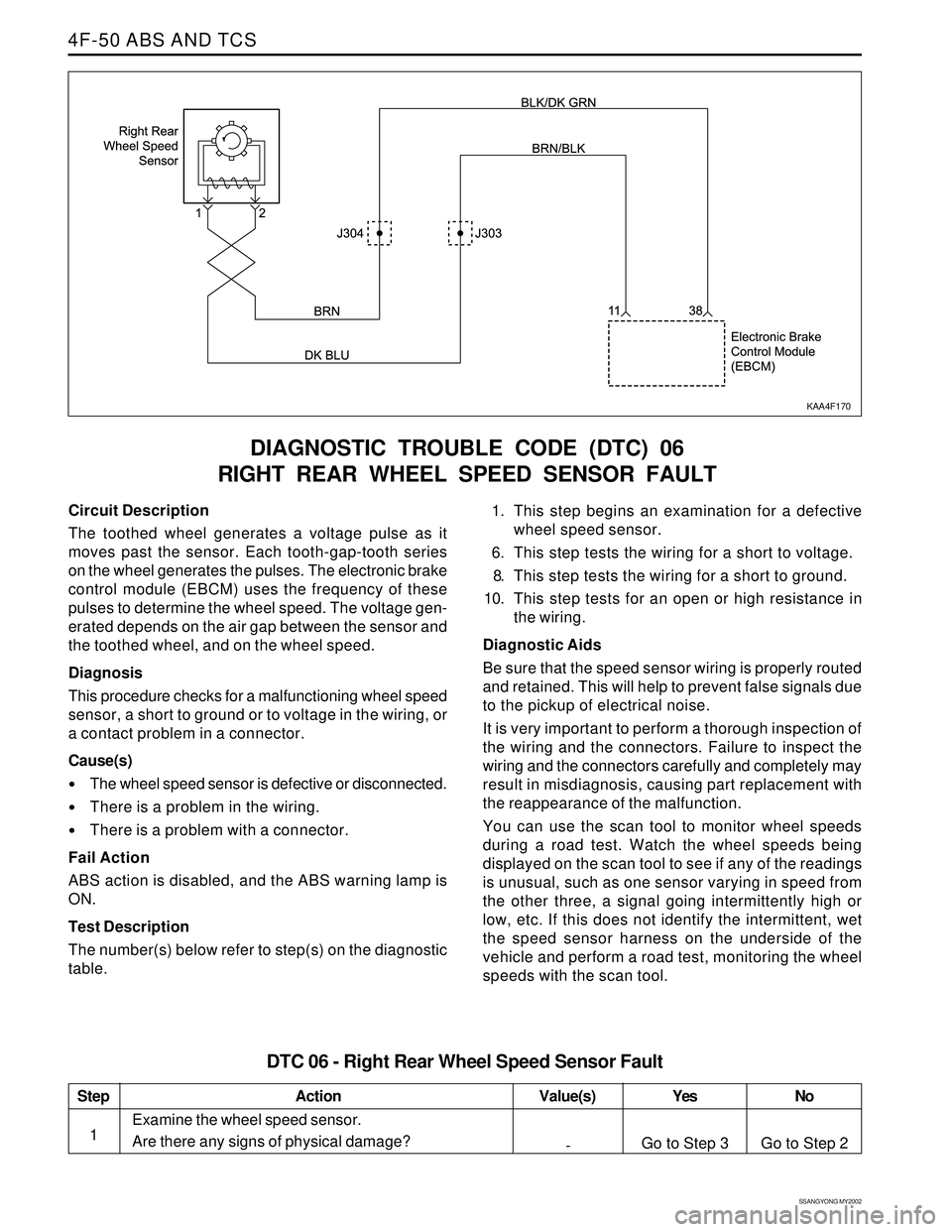
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective or disconnected.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds
during a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being
displayed on the scan tool to see if any of the readings
is unusual, such as one sensor varying in speed from
the other three, a signal going intermittently high or
low, etc. If this does not identify the intermittent, wet
the speed sensor harness on the underside of the
vehicle and perform a road test, monitoring the wheel
speeds with the scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 06 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1035 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-52 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 10
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F170
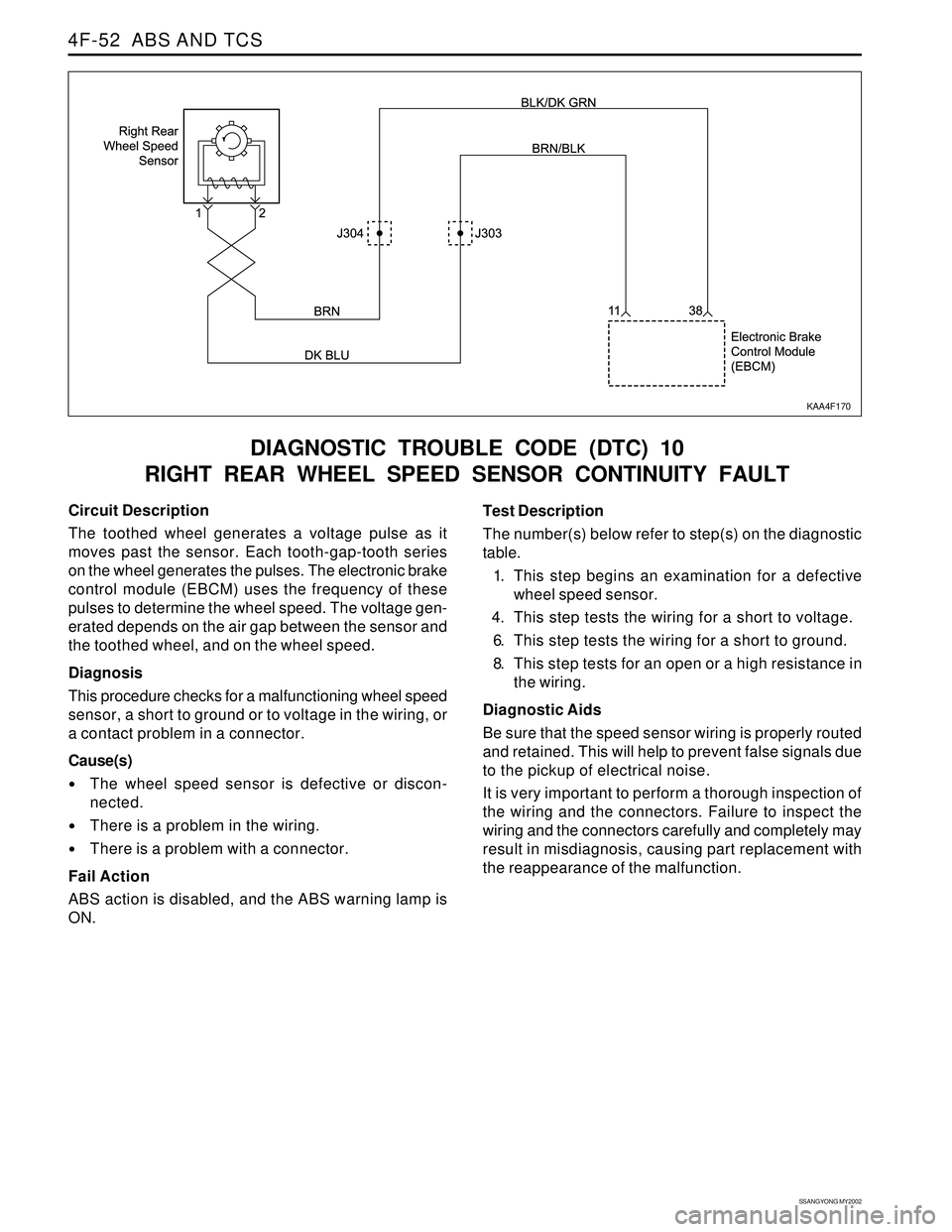
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
•The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1041 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-58 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 42
ACCELERATION SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F190
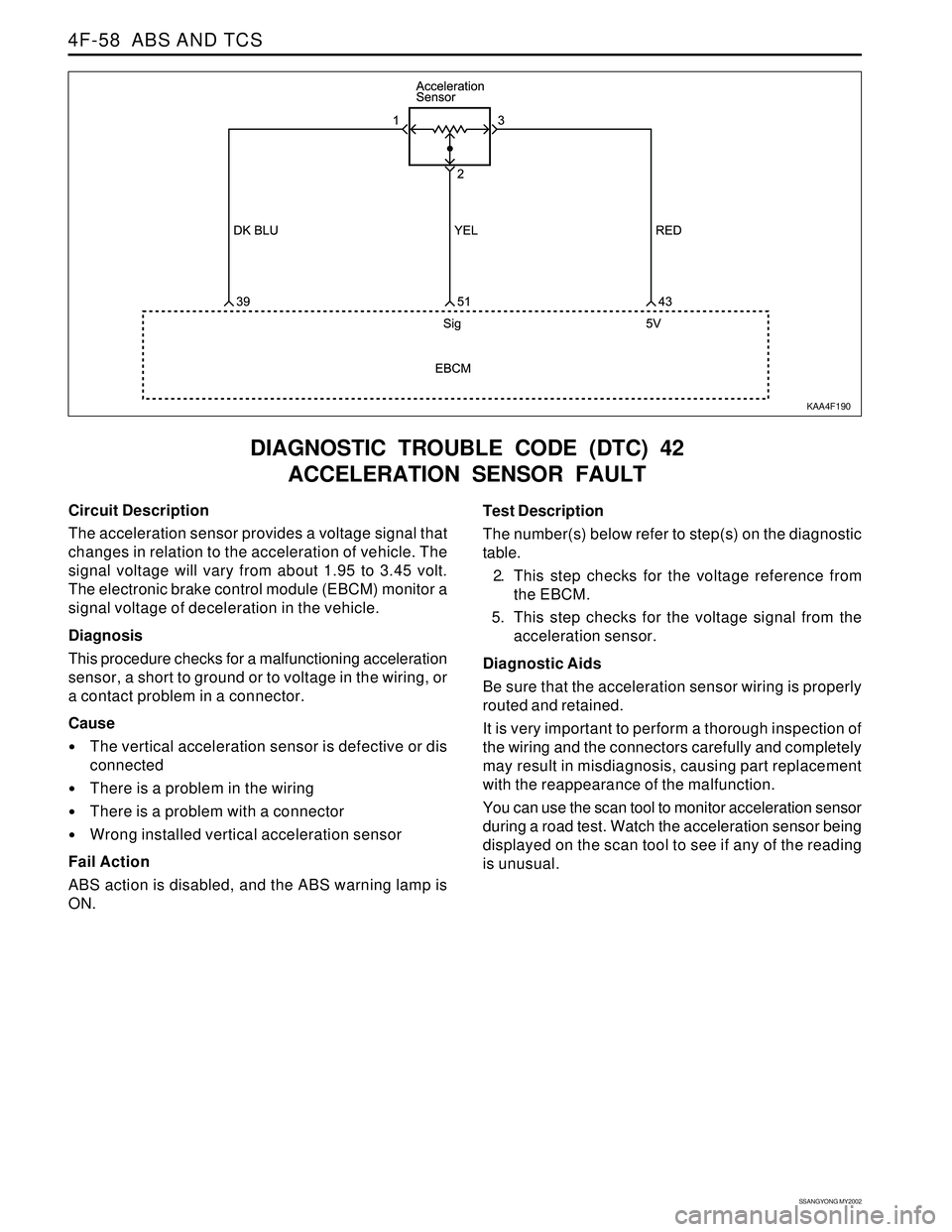
Circuit Description
The acceleration sensor provides a voltage signal that
changes in relation to the acceleration of vehicle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 1.95 to 3.45 volt.
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) monitor a
signal voltage of deceleration in the vehicle.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning acceleration
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause
The vertical acceleration sensor is defective or dis
connected
There is a problem in the wiring
There is a problem with a connector
Wrong installed vertical acceleration sensor
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. This step checks for the voltage reference from
the EBCM.
5. This step checks for the voltage signal from the
acceleration sensor.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the acceleration sensor wiring is properly
routed and retained.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors carefully and completely
may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement
with the reappearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor acceleration sensor
during a road test. Watch the acceleration sensor being
displayed on the scan tool to see if any of the reading
is unusual.
Page 1043 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-60 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 43
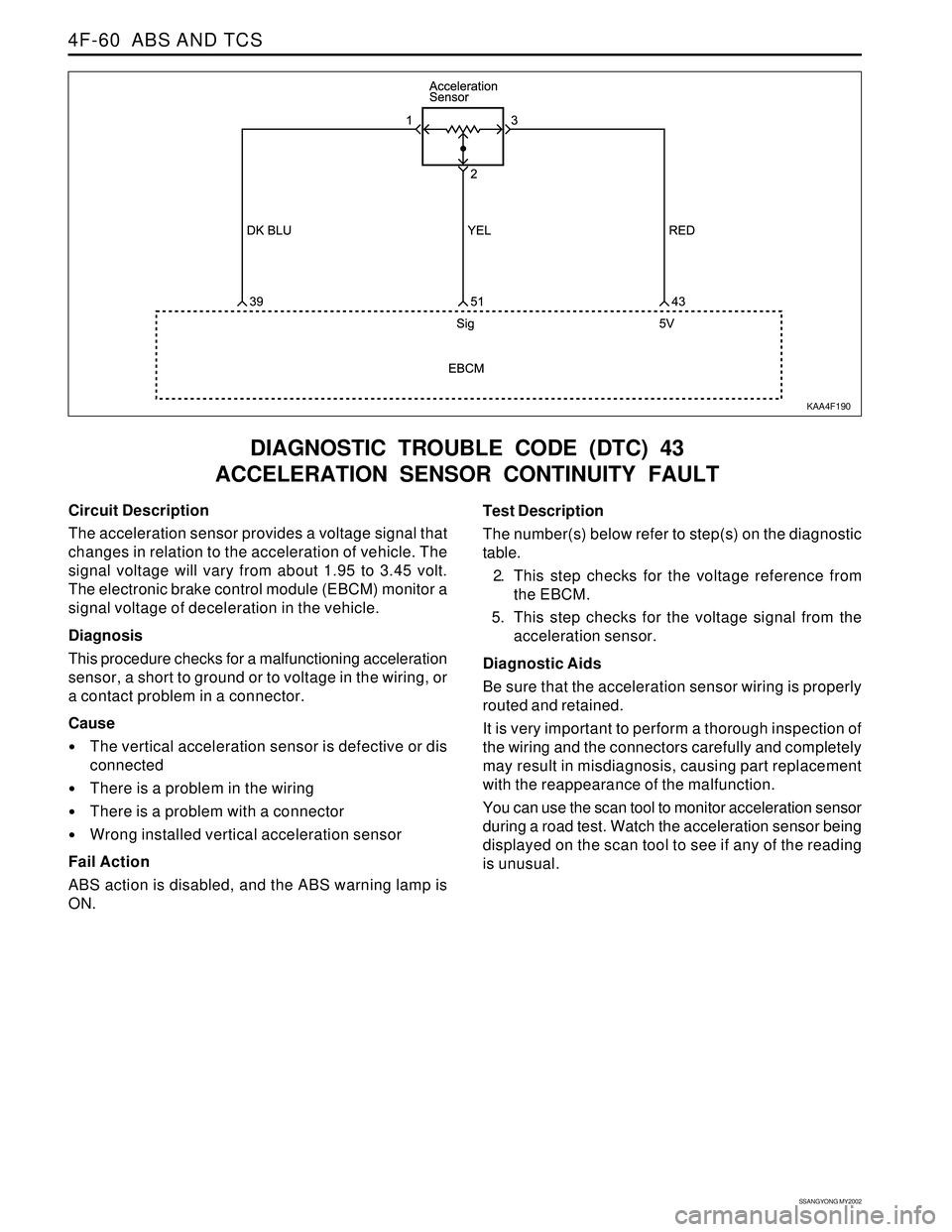
ACCELERATION SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F190
Circuit Description
The acceleration sensor provides a voltage signal that
changes in relation to the acceleration of vehicle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 1.95 to 3.45 volt.
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) monitor a
signal voltage of deceleration in the vehicle.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning acceleration
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause
The vertical acceleration sensor is defective or dis
connected
There is a problem in the wiring
There is a problem with a connector
Wrong installed vertical acceleration sensor
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. This step checks for the voltage reference from
the EBCM.
5. This step checks for the voltage signal from the
acceleration sensor.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the acceleration sensor wiring is properly
routed and retained.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors carefully and completely
may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement
with the reappearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor acceleration sensor
during a road test. Watch the acceleration sensor being
displayed on the scan tool to see if any of the reading
is unusual.
Page 1057 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-74 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 12
VALVE RELAY CIRCUIT FAULT
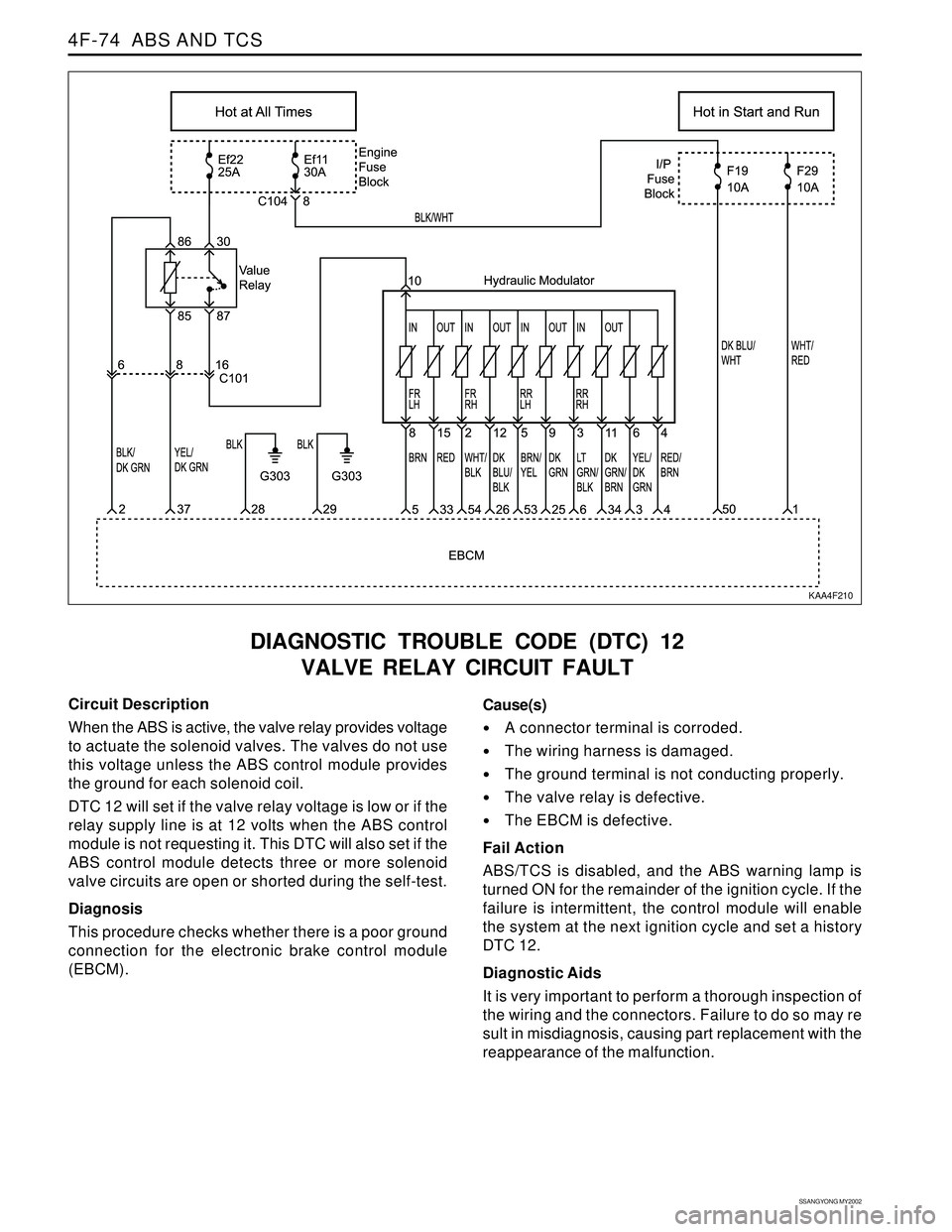
KAA4F210
Circuit Description
When the ABS is active, the valve relay provides voltage
to actuate the solenoid valves. The valves do not use
this voltage unless the ABS control module provides
the ground for each solenoid coil.
DTC 12 will set if the valve relay voltage is low or if the
relay supply line is at 12 volts when the ABS control
module is not requesting it. This DTC will also set if the
ABS control module detects three or more solenoid
valve circuits are open or shorted during the self-test.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks whether there is a poor ground
connection for the electronic brake control module
(EBCM).Cause(s)
A connector terminal is corroded.
The wiring harness is damaged.
The ground terminal is not conducting properly.
The valve relay is defective.
The EBCM is defective.
Fail Action
ABS/TCS is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
turned ON for the remainder of the ignition cycle. If the
failure is intermittent, the control module will enable
the system at the next ignition cycle and set a history
DTC 12.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may re
sult in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the
reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1059 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-76 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 24
PUMP MOTOR OR PUMP MOTOR RELAY FAULT
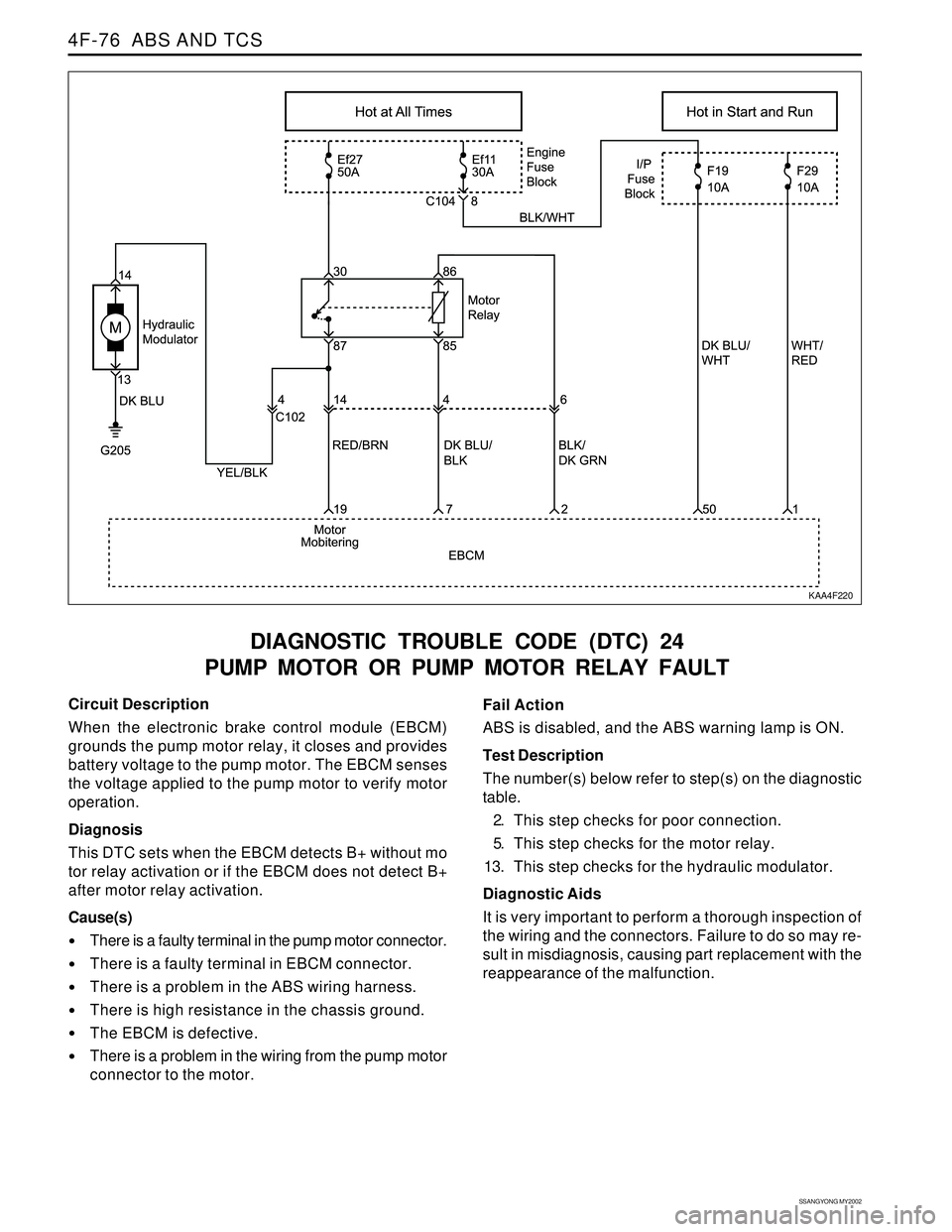
KAA4F220
Circuit Description
When the electronic brake control module (EBCM)
grounds the pump motor relay, it closes and provides
battery voltage to the pump motor. The EBCM senses
the voltage applied to the pump motor to verify motor
operation.
Diagnosis
This DTC sets when the EBCM detects B+ without mo
tor relay activation or if the EBCM does not detect B+
after motor relay activation.
Cause(s)
There is a faulty terminal in the pump motor connector.
There is a faulty terminal in EBCM connector.
There is a problem in the ABS wiring harness.
There is high resistance in the chassis ground.
The EBCM is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring from the pump motor
connector to the motor.Fail Action
ABS is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. This step checks for poor connection.
5. This step checks for the motor relay.
13. This step checks for the hydraulic modulator.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may re-
sult in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the
reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1063 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-80 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 27
STOPLAMP SWITCH FAULT
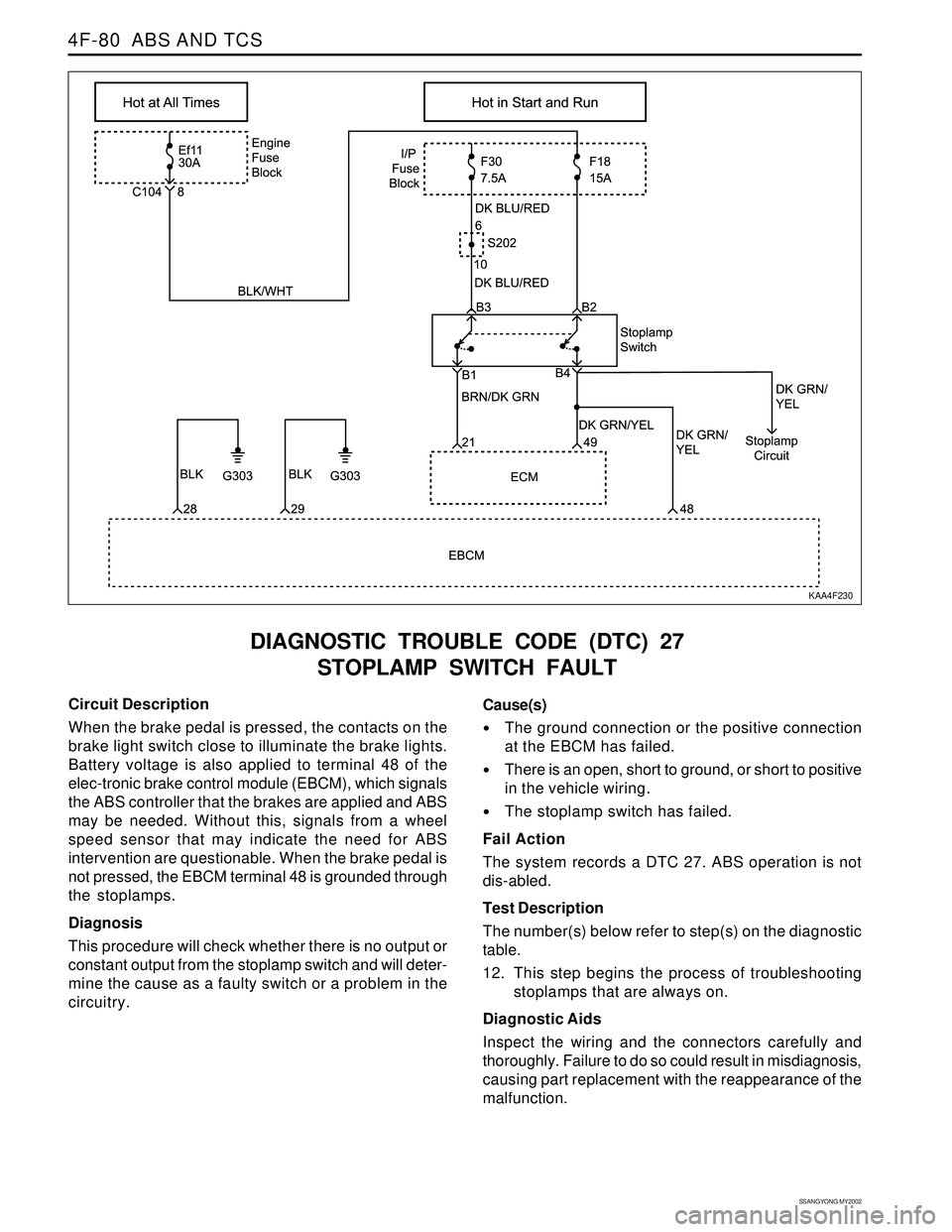
KAA4F230
Circuit Description
When the brake pedal is pressed, the contacts on the
brake light switch close to illuminate the brake lights.
Battery voltage is also applied to terminal 48 of the
elec-tronic brake control module (EBCM), which signals
the ABS controller that the brakes are applied and ABS
may be needed. Without this, signals from a wheel
speed sensor that may indicate the need for ABS
intervention are questionable. When the brake pedal is
not pressed, the EBCM terminal 48 is grounded through
the stoplamps.
Diagnosis
This procedure will check whether there is no output or
constant output from the stoplamp switch and will deter-
mine the cause as a faulty switch or a problem in the
circuitry.Cause(s)
The ground connection or the positive connection
at the EBCM has failed.
There is an open, short to ground, or short to positive
in the vehicle wiring.
The stoplamp switch has failed.
Fail Action
The system records a DTC 27. ABS operation is not
dis-abled.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
12. This step begins the process of troubleshooting
stoplamps that are always on.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring and the connectors carefully and
thoroughly. Failure to do so could result in misdiagnosis,
causing part replacement with the reappearance of the
malfunction.