Page 728 of 1954
Electronic Control System
The electronic control system consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a A/T clutch pressure control
solenoid and four solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all con-
ditions. The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side.
PCM
Throttle Position Sensor
Signal
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor Signal
Indicator Light
Self-Diagnosis Signal
PGM-FI
Control System
Shift Control
Lock-up Control
A/T Control System
Self-Diagnosis
Function
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Signal
Service Check Connector
Shift Solenoid
Valve A
Shift Solenoid
Valve B
A/T Clutch Pressure Control
Solenoid Valve
Torque Converter Clutch
(Lock-up Control)
Solenoid Valve A
Torque Converter Clutch
(Lock-up Control)
Solenoid Valve B
Mainshaft Speed Sensor
Signal
Countershaft Speed
Sensor Signal
Interlock SystemProCarManuals.com
Page 729 of 1954
Description
Electronic Contro l Syste m (cont'd )
Shift Contro l
Th e PC M instantl y determine s whic h gea r shoul d b e selecte d b y variou s signal s sen t fro m sensors , an d i t actuate s th e
shif t solenoi d valve s A an d B to contro l shifting . Also , a Grad e Logi c Contro l Syste m control s shiftin g i n positio n whil e
th e vehicl e is ascendin g o r descendin g a slope , o r reducin g speed .
* : Se e pag e 14-3 6 fo r revers e inhibito r contro l description .
Lock-u p Contro l
Fro m senso r inpu t signals , th e PC M determine s whethe r t o tur n th e lock-u p O N o r OF F an d activate s torqu e converte r
clutc h (lock-u p control ) solenoi d valv e A and/o r B accordingly . Th e combinatio n o f drivin g signal s t o torqu e converte r
clutc h (lock-u p control ) solenoi d valve s A an d B is show n in th e tabl e below .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 731 of 1954

Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in position, the system extends the engagement area of
3rd gear to prevent the transmission from frequently shifting between 3rd and 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth
and have more power when needed.
NOTE:
• Shift schedules between 3rd and 4th gear stored in the PCM enable the PCM's fuzzy logic to automatically select the
most suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient.
• Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a human
mind would.
Descending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear
when the throttle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.
This, in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is
descending. There are two descending modes with different downshift (4-3) schedules according to the magnitude of a
gradient stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you are
applying the brakes on a steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accelerate, the transmission will
then return to 4th gear.
ASCENDING MODE
DESCENDING MODE
3RD/4TH SHIFTING
CHARACTERISTICS
CONTROL AREA
Flat road
mode
Steep descending
mode
Gradual descending
modeProCarManuals.com
Page 733 of 1954
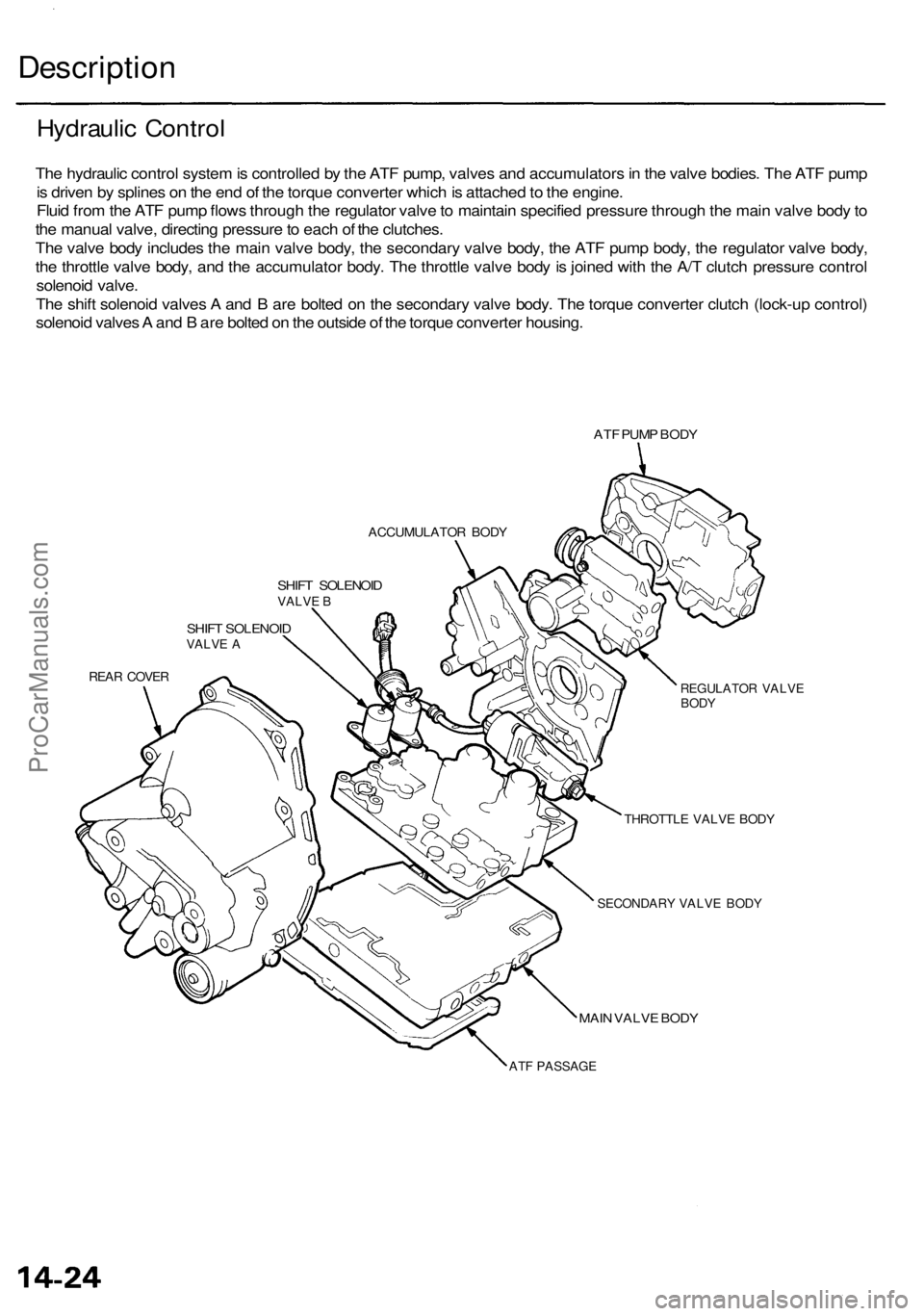
Description
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves and accumulators in the valve bodies. The ATF pump
is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is attached to the engine.
Fluid from the ATF pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure through the main valve body to
the manual valve, directing pressure to each of the clutches.
The valve body includes the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the ATF pump body, the regulator valve body,
the throttle valve body, and the accumulator body. The throttle valve body is joined with the A/T clutch pressure control
solenoid valve.
The shift solenoid valves A and B are bolted on the secondary valve body. The torque converter clutch (lock-up control)
solenoid valves A and B are bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing.
ATF PUMP BODY
ACCUMULATOR BODY
SHIFT SOLENOID
VALVE B
SHIFT SOLENOID
VALVE A
REAR COVER
REGULATOR VALVE
BODY
THROTTLE VALVE BODY
SECONDARY VALVE BODY
ATF PASSAGE
MAIN VALVE BODY
Hydraulic ControlProCarManuals.com
Page 735 of 1954
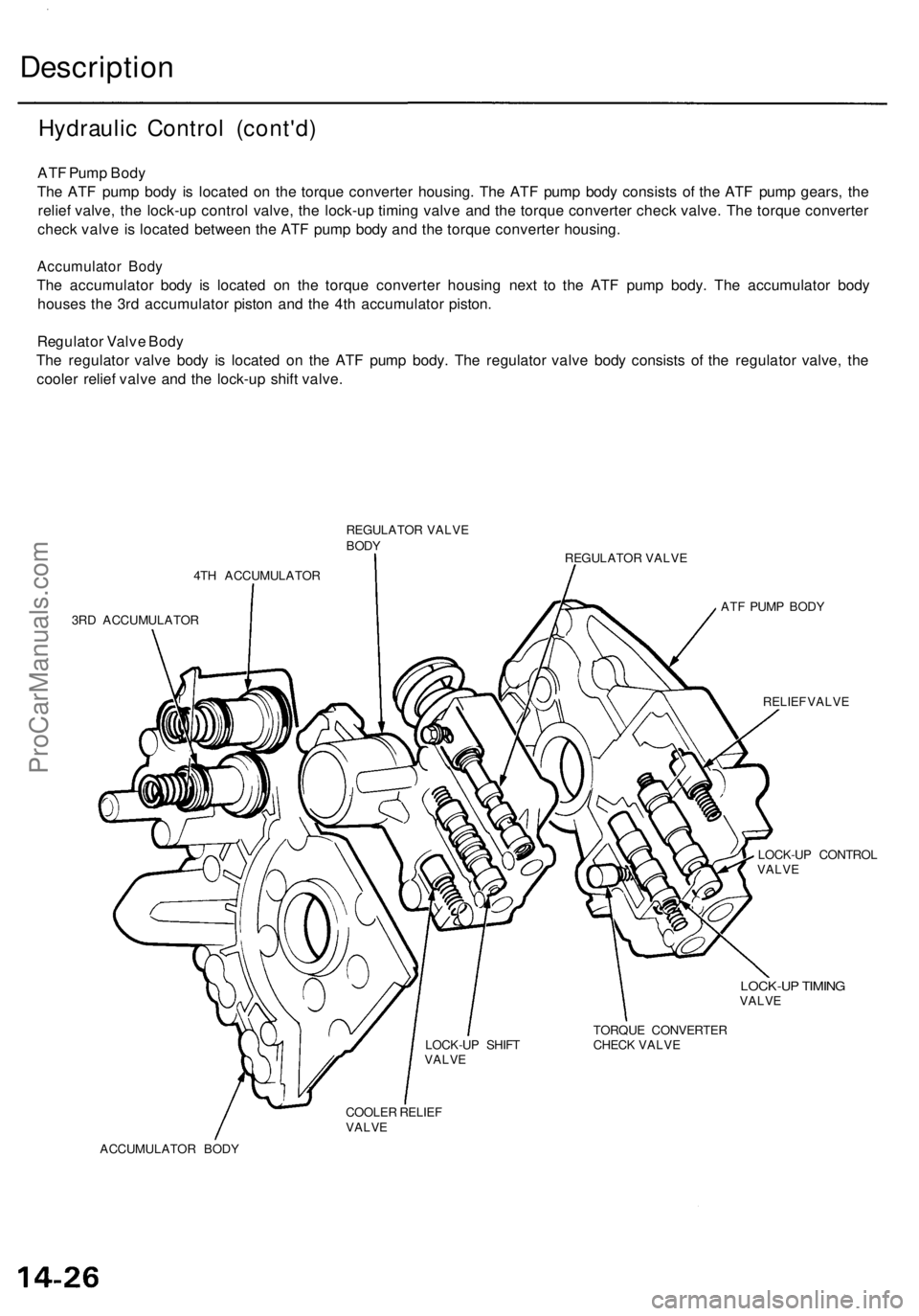
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
ATF Pump Body
The ATF pump body is located on the torque converter housing. The ATF pump body consists of the ATF pump gears, the
relief valve, the lock-up control valve, the lock-up timing valve and the torque converter check valve. The torque converter
check valve is located between the ATF pump body and the torque converter housing.
Accumulator Body
The accumulator body is located on the torque converter housing next to the ATF pump body. The accumulator body
houses the 3rd accumulator piston and the 4th accumulator piston.
Regulator Valve Body
The regulator valve body is located on the ATF pump body. The regulator valve body consists of the regulator valve, the
cooler relief valve and the lock-up shift valve.
REGULATOR VALVE
BODY
REGULATOR VALVE
4TH ACCUMULATOR
3RD ACCUMULATOR
ATF PUMP BODY
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK-UP CONTROL
VALVE
LOCK-UP TIMING
VALVE
TORQUE CONVERTER
CHECK VALVE
COOLER RELIEF
VALVE
ACCUMULATOR BODY
LOCK-UP SHIFT
VALVE
DescriptionProCarManuals.com
Page 737 of 1954
Description
Hydraulic Flo w
Genera l Char t o f Hydrauli c Pressur e
Line Pressur e Modulato
r Pressur e
Throttl e B Pressur e
Clutc h Pressur e
Lin e Pressur e Contro l Pressur e
Torqu e Converte r Pressur e
Lubricatio n Pressur e
Distributio n o f Hydrauli c Pressur e
Regulato r Valv e
Manua l Valv e - Torqu
e Converte r Pressur e
• Lubricatio n Pressur e
T o Regulat e Lin e Pressur e
Modulato r Valv e
To Selec t Lin e Pressur e
Clutc h Pressur e Clutc
h Pressur e
Shift Solenoi d Valve s
Torque Converte r Clutc h (Lock-u p Control )
Solenoi d Valve s
Regulato r Valv e
Throttl e B Pressur e
Line Pressur e Contro l Pressur e
Lin e Pressur e Contro l Valv e
Throttl e Valv e
1-2 Shif t Valv e
2- 3 Shif t Valv e
3- 4 Shif t Valv e
Modulato r Pressur e
ATF Pum p Regulator Valv e
ProCarManuals.com
Page 738 of 1954
Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump also starts to operate. Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-
charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes the line pressure (1). The line pressure (1) is regulated
by the regulator valve. The torque converter inlet pressure (92) enters (94) of the torque converter through the lock-up
shift valve and discharges into (90). The torque converter check valve prevents the torque converter pressure from rising.
Under this condition, the hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches as the manual valve stops line pressure (1).
NOTE:
• When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
• The hydraulic circuit is for '96 - '98 models. On '99 - 01 models, the 2nd accumulator is different.ProCarManuals.com
Page 747 of 1954
Lock-up System
Lock-up Clutch
1. Operation (clutch on)
With the lock-up clutch on, the fluid in the chamber between the torque converter cover and the lock-up piston is drained
off, and the converter fluid exerts pressure through the piston against the torque converter cover. As a result, the converter
turbine is locked to the converter cover. The effect is to bypass the converter, thereby placing the vehicle in direct drive.
LOCK-UP PISTON
TORQUE CONVERTER
COVER
DAMPER SPRING
TURBINE
2. Operation (clutch off)
With the lock-up clutch off, the fluid flows in the reverse of CLUTCH ON. As a result, the lock-up piston moves away from
the converter cover, and the torque converter lock-up is released.
TORQUE CONVERTER
COVER
MAINSHAFT
DescriptionProCarManuals.com