Page 267 of 1771
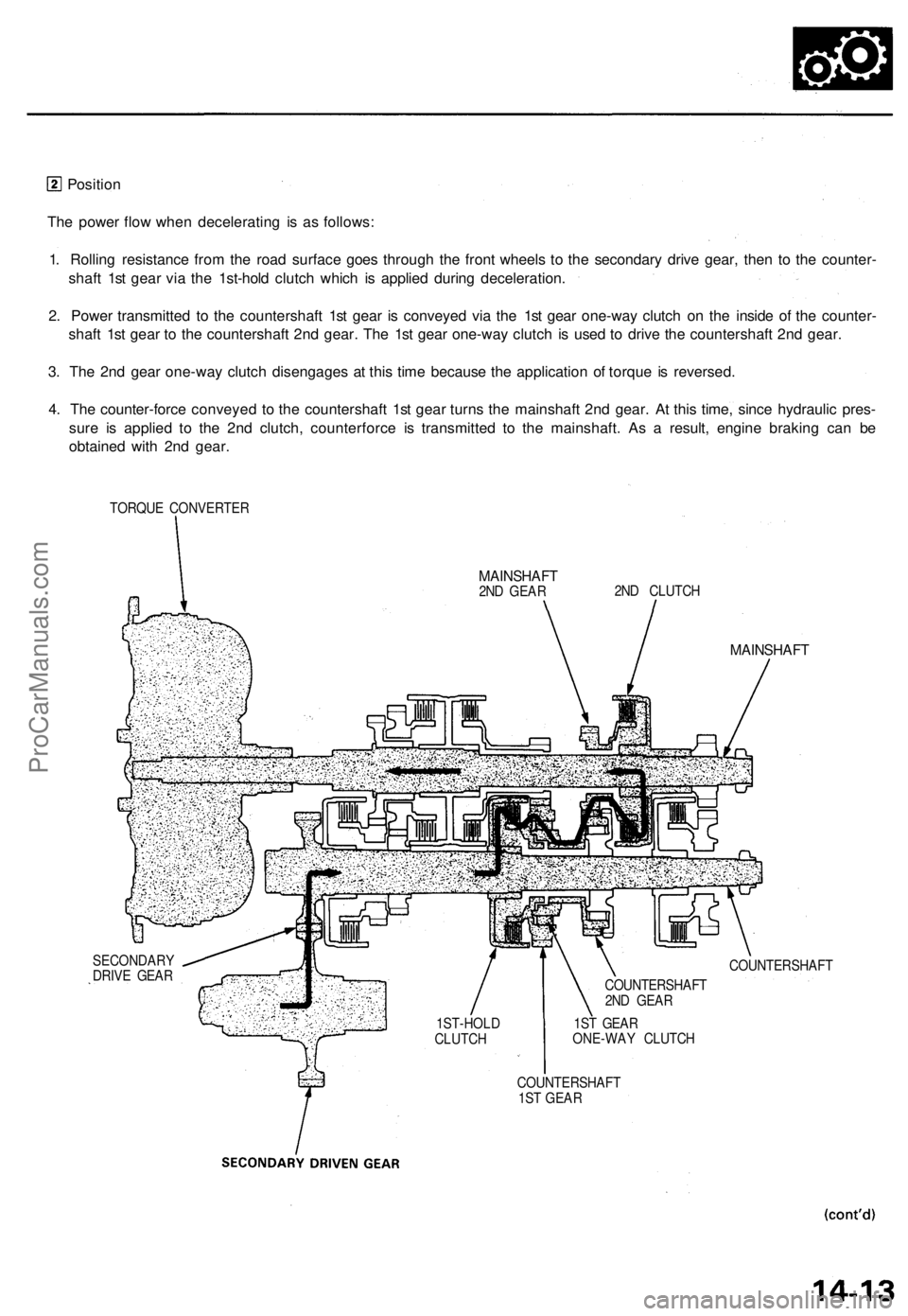
Position
The power flow when decelerating is as follows:
1. Rolling resistance from the road surface goes through the front wheels to the secondary drive gear, then to the counter-
shaft 1st gear via the 1st-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
2. Power transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear is conveyed via the 1st gear one-way clutch on the inside of the counter-
shaft 1st gear to the countershaft 2nd gear. The 1st gear one-way clutch is used to drive the countershaft 2nd gear.
3. The 2nd gear one-way clutch disengages at this time because the application of torque is reversed.
4. The counter-force conveyed to the countershaft 1st gear turns the mainshaft 2nd gear. At this time, since hydraulic pres-
sure is applied to the 2nd clutch, counterforce is transmitted to the mainshaft. As a result, engine braking can be
obtained with 2nd gear.
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEAR
1ST-HOLD
CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
1ST GEAR
1ST GEAR
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
2ND GEARProCarManuals.com
Page 268 of 1771
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the 1st clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 1st
gear rotates.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear, which drives the countershaft via the one-way clutches.
3. Power is transmitted to the secondary drive gear, which drives the secondary driven gear.
Position, 1st gear
position, the optimum gear is automatically selected from 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th gears, according to conditions
balance between throttle opening (engine load) and vehicle speed.
or
such as the
or
In
TORQUE CONVERTER
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEAR
SECONDARY DRIVEN
GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
1ST GEAR
1ST GEAR
ONE-WAY
CLUTCH
2ND GEAR
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
PARKING GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
MAINSHAFT
1ST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
1ST GEAR
NOTE: In
position, hydraulic pressure is not applied to the 1st-hold clutch.
orProCarManuals.com
Page 269 of 1771
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the 2nd clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 2nd
gear rotates.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 2nd gear, which drives the countershaft via the 2nd gear one-way clutch.
3. Power is transmitted to the secondary drive gear, which drives the secondary driven gear.
or
Position, 2nd gear
NOTE: In
or
position, 2nd gear, hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed
of 2nd gear exceeds that of 1st gear, power from 1st gear is cut off at the 1st gear one-way clutch.
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
1ST GEAR
ONE-WAY
CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND GEAR
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
PARKING GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
SECONDARY DRIVEN GEAR
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEARProCarManuals.com
Page 271 of 1771
Position, 4th gear
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 4th
gear rotates.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear, which drives the countershaft.
3. Power is transmitted to the secondary drive gear, which drives the secondary driven gear.
NOTE: In
position, 4th gear, hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch and to the 2nd clutch, but since the
rotation speed of 4th gear exceeds that of 2nd gear, power from 2nd gear is cut off at the 2nd gear one-way clutch.
MAINSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT
4TH GEAR
1ST CLUTCH
4TH CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
4TH GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND GEAR
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEAR
SECONDARY DRIVEN GEAR
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com
Page 272 of 1771
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
Position
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the reverse clutch. Power is transmitted from the mainshaft reverse gear via the
reverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
2. The rotation direction of the countershaft reverse gear is changed via the reverse idler gear in the rear cover.
3. Power is transmitted to the secondary drive gear, which drives the secondary driven gear.
REVERSE IDLER
GEAR
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT REVERSE
GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
REVERSE GEAR
MAINSHAFT
REVERSE GEAR
REVERSE
IDLER GEAR
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
REVERSE GEAR
REVERSE CLUTCH
SECONDARY DRIVEN GEAR
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEARProCarManuals.com
Page 277 of 1771
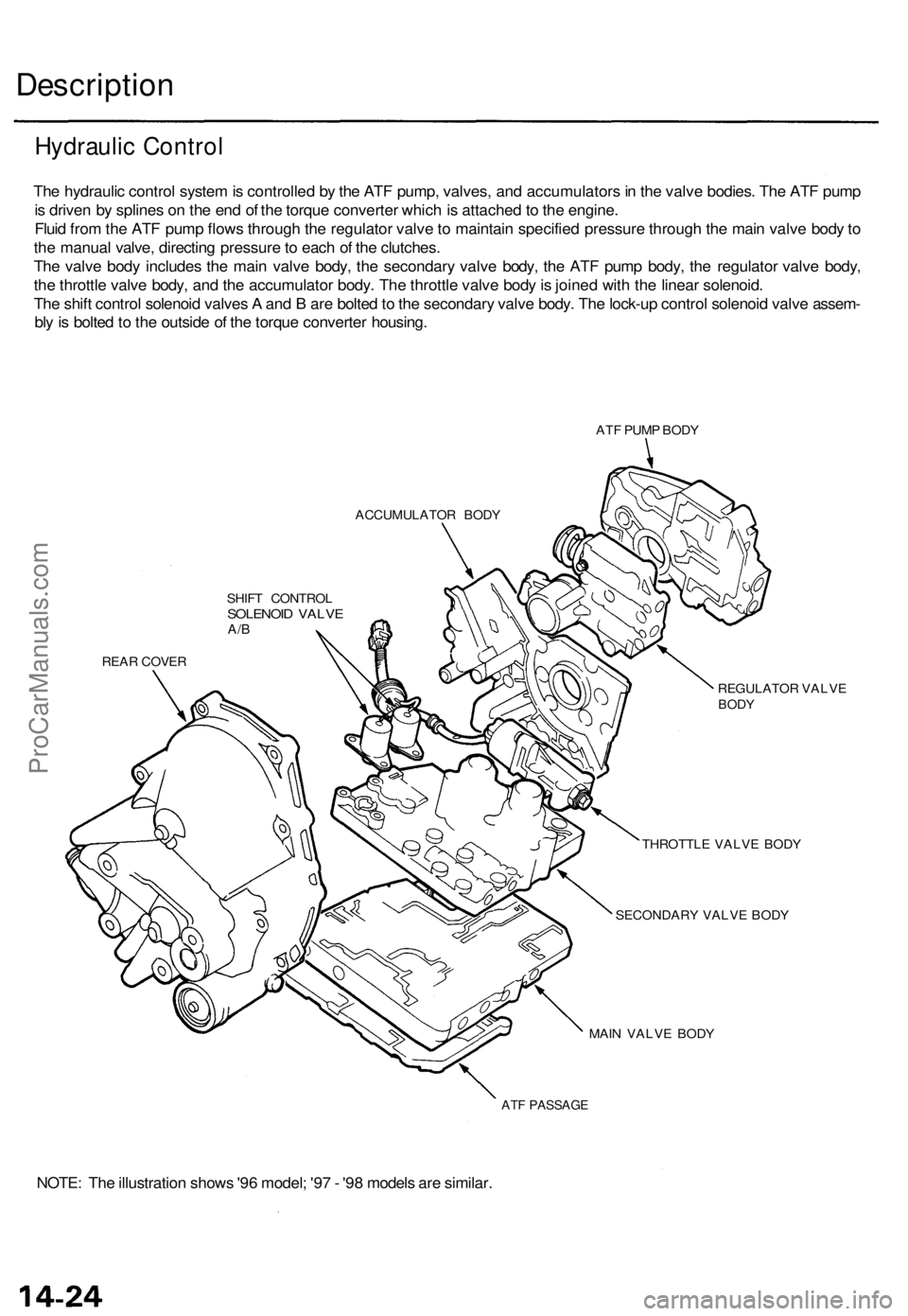
Description
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, and accumulators in the valve bodies. The ATF pump
is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is attached to the engine.
Fluid from the ATF pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure through the main valve body to
the manual valve, directing pressure to each of the clutches.
The valve body includes the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the ATF pump body, the regulator valve body,
the throttle valve body, and the accumulator body. The throttle valve body is joined with the linear solenoid.
The shift control solenoid valves A and B are bolted to the secondary valve body. The lock-up control solenoid valve assem-
bly is bolted to the outside of the torque converter housing.
ATF PUMP BODY
ACCUMULATOR BODY
SHIFT CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
A/B
REAR COVER
REGULATOR VALVE
BODY
THROTTLE VALVE BODY
SECONDARY VALVE BODY
MAIN VALVE BODY
ATF PASSAGE
NOTE: The illustration shows '96 model; '97 - '98 models are similar.
Hydraulic ControlProCarManuals.com
Page 280 of 1771
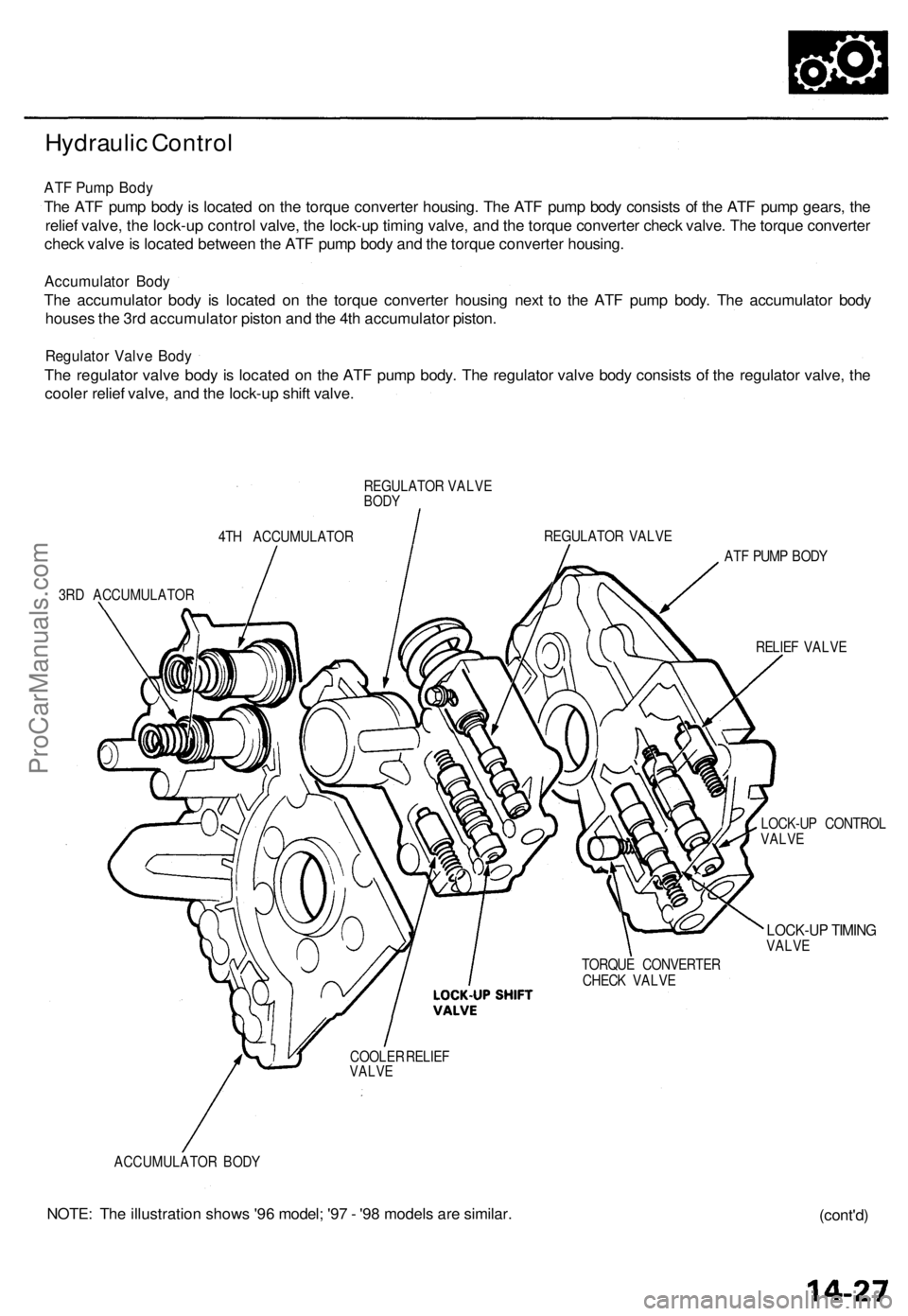
Hydraulic Control
ATF Pump Body
The ATF pump body is located on the torque converter housing. The ATF pump body consists of the ATF pump gears, the
relief valve, the lock-up control valve, the lock-up timing valve, and the torque converter check valve. The torque converter
check valve is located between the ATF pump body and the torque converter housing.
Accumulator Body
The accumulator body is located on the torque converter housing next to the ATF pump body. The accumulator body
houses the 3rd accumulator piston and the 4th accumulator piston.
Regulator Valve Body
The regulator valve body is located on the ATF pump body. The regulator valve body consists of the regulator valve, the
cooler relief valve, and the lock-up shift valve.
REGULATOR VALVE
BODY
4TH ACCUMULATOR
REGULATOR VALVE
3RD ACCUMULATOR
ATF PUMP BODY
RELIEF VALVE
TORQUE CONVERTER
CHECK VALVE
LOCK-UP CONTROL
VALVE
LOCK-UP TIMING
VALVE
COOLER RELIEF
VALVE
ACCUMULATOR BODY
NOTE: The illustration shows '96 model; '97 - '98 models are similar.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com
Page 282 of 1771
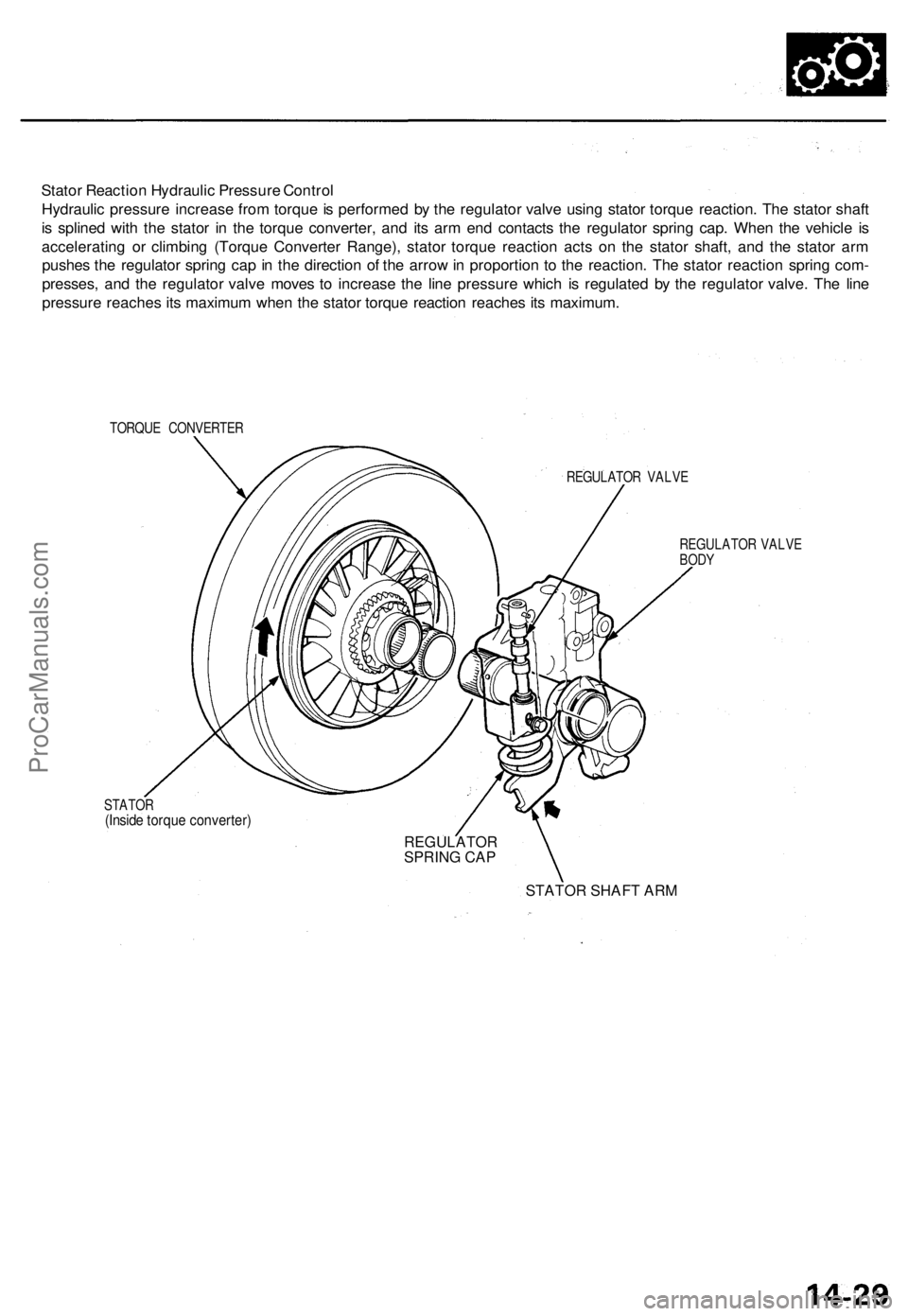
Stator Reactio n Hydrauli c Pressur e Contro l
Hydrauli c pressur e increas e fro m torqu e is performe d b y th e regulato r valv e usin g stato r torqu e reaction . Th e stato r shaf t
i s spline d wit h th e stato r i n th e torqu e converter , an d it s ar m en d contact s th e regulato r sprin g cap . Whe n th e vehicl e i s
acceleratin g o r climbin g (Torqu e Converte r Range) , stato r torqu e reactio n act s o n th e stato r shaft , an d th e stato r ar m
pushe s th e regulato r sprin g ca p in th e directio n o f th e arro w in proportio n t o th e reaction . Th e stato r reactio n sprin g com -
presses , an d th e regulato r valv e move s t o increas e th e lin e pressur e whic h i s regulate d b y th e regulato r valve . Th e lin e
pressur e reache s it s maximu m whe n th e stato r torqu e reactio n reache s it s maximum .
TORQUE CONVERTE R
REGULATOR VALV E
REGULATO R VALV E
BOD Y
STATO R
(Inside torqu e converter )
REGULATOR
SPRING CAP
STATOR SHAFT ARM
ProCarManuals.com