1994 JEEP CHEROKEE oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 260 of 1784

speed of the fan to a predetermined maximum level
at higher engine speeds. A bimetallic spring coil is
located on the front face. This spring coil reacts to
the temperature of the radiator discharge air. It en-
gages the viscous fan drive for higher fan speed if
the air temperature from the radiator rises above a
certain point. Until additional engine cooling is nec-
essary, the fan will remain at a reduced rpm regard-
less of engine speed.
Only when sufficient heat is present, will the vis-
cous fan drive engage. This is when the air flowing
through the radiator core causes a reaction from the
bimetallic coil. It then increases fan speed to provide
the necessary additional engine cooling.
Once the engine has cooled, the radiator discharge
temperature will drop. The bimetallic coil again re-
acts and the fan speed is reduced to the previous dis-
engaged speed.
CAUTION: Engines equipped with serpentine drive
belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous fan
drives. They are marked with the word REVERSE to
designate their usage. Installation of the wrong fan
or viscous fan drive can result in engine overheat-
ing.
VISCOUS FAN DRIVE TEST
The cooling system must be in good condition. This
is checked prior to performing the following test. It
also will ensure against excessively high coolant
temperature.
CAUTION: Be sure that there is adequate fan blade
clearance before drilling.(1) Drill a 3.18-mm (1/8-in) diameter hole in the
top center of the fan shroud.
(2) Obtain a dial thermometer with an 8 inch stem
(or equivalent). It should have a range of -18É-to-
105ÉC (0É-to-220É F). Insert thermometer through the
hole in the shroud. Be sure that there is adequate
clearance from the fan blades.
(3) Connect a tachometer and an engine ignition
timing light (timing light is to be used as a strobe
light).
(4) Block the air flow through the radiator. Secure
a sheet of plastic in front of the radiator (or air con-
ditioner condenser). Use tape at the top to secure the
plastic and be sure that the air flow is blocked.
(5) Be sure that the air conditioner (if equipped) is
turned off.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A DI-
RECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(6) Start the engine and operate at 2400 rpm with
the timing light (strobe light) aimed at the fan
blades. Within ten minutes the air temperature (in-
dicated on the dial thermometer) should be 88É C
(190É F). Satisfactory operation of the fan drive re-
quires that it engage before or at 88É C (190É F). En-
gagement is distinguishable by a definite increase in
flow noise. The timing light also will indicate an in-
crease in the speed of the fan.
(7) When the air temperature reaches 88É C (190É
F), remove the plastic sheet. Satisfactory operation of
the viscous fan requires the air temperature to drop
20É F (11É C) or more. A definite decrease of audible-
fan-air-flow-noise should be noticed. Replace defec-
tive fan assemblies.
VISCOUS FAN DRIVE REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
Some engines have the mechanical fan/viscous fan
drive assembly mounted directly to the water pump
hub (Fig. 38). It may also be mounted to a hub/bear-
ing attached to an aluminum bracket on the right
front side of engine (Fig. 39).
(1) Loosen but do not remove at this time, the four
fan hub mounting nuts (Figs. 38 or 39).
(2) Remove accessory serpentine drive belt. Refer
to Belt Service in the Engine Accessory Drive Belt
section of this group.
(3) Some models with certain engines may require
the removal of the fan shroud to remove the viscous
fan drive. The fan shroud and fan blade/viscous fan
drive should be removed from the vehicle as one as-
sembly.
Fig. 37 Viscous Fan DriveÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 27
Page 262 of 1784

through the relay. When coolant temperature is be-
low 88ÉC (190ÉF), the PCM opens the ground path to
the relay. This will prevent the cooling fan from be-
ing energized.
Whenever the air conditioning is used, the PCM
engages the auxiliary cooling fan. It provides a
ground path to the cooling fan relay.
DIAGNOSIS
The powertrain control module (PCM) will enter a
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) number 35 in memory
if it detects a problem in the auxiliary cooling fan re-
lay or circuit. This will be read as a flashing signal
at the instrument panel mounted Malfunction Indica-
tor Lamp (formerly referred to as the Check Engine
Lamp). Refer to On-Board Diagnostics in Group 14,
Fuel Systems for information on accessing a DTC.
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for diagnostic information
and operation of the DRB scan tool.
REMOVAL
The auxiliary fan is attached to the radiator upper
crossmember behind the radiator.
(1) Remove the fan retaining bolts from radiator
upper crossmember (Fig. 41).
(2) Disconnect the electric fan connector.
(3) Lift fan straight up and out of vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align lower retaining tabs of fan shroud with
slots in bracket at bottom of radiator. Push fan down
into position.
(2) Tighten the mounting bolts to 4 Nzm (31 in.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect auxiliary cooling fan electrical connec-
tor.
TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERS
WATER-TO-OIL COOLER
All models equipped with an automatic transmis-
sion are equipped with a transmission oil cooler
mounted internally within the radiator tank. This in-
ternal cooler is supplied as standard equipment on
all models equipped with an automatic transmission.
Transmission oil is cooled when it passes through
this separate cooler. In case of a leak in the internal
radiator mounted transmission oil cooler, engine
coolant may become mixed with transmission fluid or
transmission fluid may enter engine cooling system.
Both cooling system and transmission should be
drained and inspected if the internal radiator
mounted transmission cooler is leaking.
Also refer to the section on Transmission Air-to-Oil
Coolers. This auxiliary air-to-oil cooler is an option
on most engine packages.
REPLACING WATER-TO-OIL COOLER IN
RADIATOR SIDE TANK
The internal transmission oil cooler located within
the radiator is not serviceable. If it requires service,
the radiator must be replaced.
Once the repaired or replacement radiator has been
installed, fill the cooling system and inspect for
leaks. Refer to the Refilling Cooling System and
Testing Cooling System For Leaks sections in this
group. If the transmission operates properly after re-
pairing the leak, drain the transmission and remove
the transmission oil pan. Inspect for sludge and/or
rust. Inspect for a dirty or plugged inlet filter. If
none of these conditions are found, the transmission
Fig. 40 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 41 Auxiliary FanÐRemove/Install
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 29
Page 263 of 1784
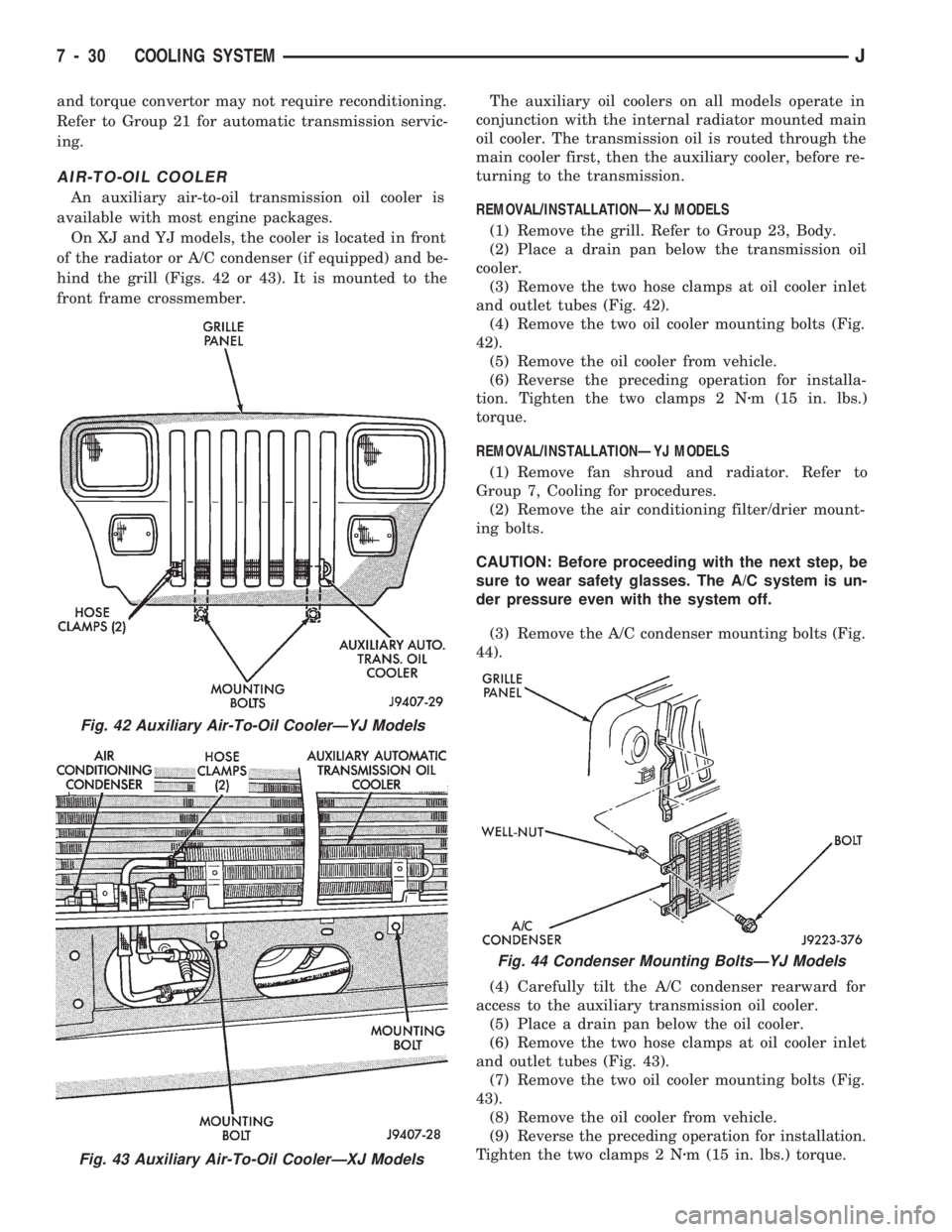
and torque convertor may not require reconditioning.
Refer to Group 21 for automatic transmission servic-
ing.
AIR-TO-OIL COOLER
An auxiliary air-to-oil transmission oil cooler is
available with most engine packages.
On XJ and YJ models, the cooler is located in front
of the radiator or A/C condenser (if equipped) and be-
hind the grill (Figs. 42 or 43). It is mounted to the
front frame crossmember.The auxiliary oil coolers on all models operate in
conjunction with the internal radiator mounted main
oil cooler. The transmission oil is routed through the
main cooler first, then the auxiliary cooler, before re-
turning to the transmission.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONÐXJ MODELS
(1) Remove the grill. Refer to Group 23, Body.
(2) Place a drain pan below the transmission oil
cooler.
(3) Remove the two hose clamps at oil cooler inlet
and outlet tubes (Fig. 42).
(4) Remove the two oil cooler mounting bolts (Fig.
42).
(5) Remove the oil cooler from vehicle.
(6) Reverse the preceding operation for installa-
tion. Tighten the two clamps 2 Nzm (15 in. lbs.)
torque.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS
(1) Remove fan shroud and radiator. Refer to
Group 7, Cooling for procedures.
(2) Remove the air conditioning filter/drier mount-
ing bolts.
CAUTION: Before proceeding with the next step, be
sure to wear safety glasses. The A/C system is un-
der pressure even with the system off.
(3) Remove the A/C condenser mounting bolts (Fig.
44).
(4) Carefully tilt the A/C condenser rearward for
access to the auxiliary transmission oil cooler.
(5) Place a drain pan below the oil cooler.
(6) Remove the two hose clamps at oil cooler inlet
and outlet tubes (Fig. 43).
(7) Remove the two oil cooler mounting bolts (Fig.
43).
(8) Remove the oil cooler from vehicle.
(9) Reverse the preceding operation for installation.
Tighten the two clamps 2 Nzm (15 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 42 Auxiliary Air-To-Oil CoolerÐYJ Models
Fig. 43 Auxiliary Air-To-Oil CoolerÐXJ Models
Fig. 44 Condenser Mounting BoltsÐYJ Models
7 - 30 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 278 of 1784

(7) If the voltmeter reading fell below 9.6 volts,
with the battery temperature at a minimum of 70ÉF
(21ÉC), replace the battery.
BATTERY CHARGING
A battery is completely charged when it has:
²an open circuit voltage of 12.4 volts or more.
²has enough cranking capacity (minimum 9.6 volts
when loaded for 15 seconds to 50% of cold crank am-
perage rating at 21ÉC (70ÉF).
An open circuit voltage of 12.4 volts or greater, in-dicates battery is charged enough for further testing
and possible return to use.
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE A BATTERY THAT
HAS LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL. BATTERY MAY
ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE GASES FORM OVER BAT-
TERY, DO NOT SMOKE, USE FLAME, OR CREATE
SPARKS NEAR BATTERY.
WARNING: DO NOT ASSIST BOOST OR CHARGE A
FROZEN BATTERY, CASING MAY FRACTURE.
WARNING: POISON, CAUSES SEVERE BURNS.
BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC ACID, AVOID CON-
TACT WITH SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING. IN EVENT
OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER AND CALL
PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT OF REACH
OF CHILDREN.
CAUTION: Always disconnect the battery negative
cable before charging battery to avoid damage to
electrical systems. Do not exceed 16.0 volts while
charging battery.
Battery electrolyte will bubble inside case while
being charged properly. If the electrolyte boils or is
discharged from the vent holes while charging, im-
mediately reduce charging rate or turn OFF charger
and evaluate battery condition.
Battery should not be hot to touch.
If the battery feels hot to the touch, turn OFF
charger and let cool before restarting.
Some battery chargers are equipped with polarity
(+ to +/- to -) sensing devices to protect the charger
or battery from being damaged if improperly con-
nected. If the battery state of charge is too low for
the polarity sensor to detect, the sensor must be by-
passed for charger to operate. Refer to operating in-
structions provided with battery charger being used.
Fig. 6 Remove Surface Charge from Battery
Fig. 7 Load 50% Cold Crank Rating Note Voltage
BATTERY CHARGING TIME TABLE
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 5
Page 282 of 1784

ENGINE STARTER MOTOR TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE
INDEX
page page
2.5L Starter Motor Noise Diagnosis........... 13
General Information........................ 9
Starter Control Circuit Tests................ 11
Starter Feed Circuit Tests - (Voltage Drop Method).9
Starter System Diagnostic Inspections.......... 9
Starting System Cold Cranking Test........... 9
GENERAL INFORMATION
The starting system consists of an:
²ignition switch
²starter relay
²park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis-
sion)
²wiring harness
²battery
²starter motor with an integral solenoid.
These components form 2 separate circuits. A high
amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up to
300+ amps, and a control circuit that operates on
less than 20 amps.
STARTER SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC INSPECTIONS
Before removing any unit from the starter motor
system for repair, perform the following inspections:
BATTERY INSPECTION
To determine condition of the battery, perform the
testing procedure outlined in Battery Test Proce-
dures.
WIRING INSPECTION
Inspect wiring for damage. Inspect all connections
at the starter motor solenoid, park/neutral position
switch (if equipped), back-up lamp switch connector,
ignition switch, starter relay, and battery (including
all ground connections). Clean and tighten all con-
nections as required.
SOLENOID, RELAY AND IGNITION SWITCH
INSPECTION
Inspect the solenoid, relay and switch to determine
their condition. Also, if equipped with automatic
transmission, inspect condition of the park/neutral
position switch. Testing information can be found in
the following pages.
STARTING SYSTEM COLD CRANKING TEST
(1) Battery must first pass load and voltage drop
tests and be fully charged before proceeding. Refer to
Battery Test Procedures.(2) Connect a suitable volt-ampere tester to the
battery terminals (Fig. 1). Refer to the operating in-
structions provided with the tester being used.
(3) Fully engage parking brake, place manual
transmission in NEUTRAL, automatic transmission
in PARK.
(4) Verify that all lamps and accessories are OFF.
(5) Remove coil secondary cable from distributor
and connect to ground.
(6) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Note cranking voltage and amper-
age.
(a) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and amperage
draw reads above specifications, go to Starter Feed
Circuit Tests.
(b) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and am-
perage reads below specifications, go to Starter
Control Circuit Tests.
A cold engine will increase starter motor cur-
rent and reduce battery voltage.
STARTER FEED CIRCUIT TESTS - (VOLTAGE DROP
METHOD)
The voltage drop tests will determine if there is ex-
cessive resistance in the high current circuit. When
performing these tests, it is important that the volt-
meter be connected to the terminals that the cables
are connected to, instead of to the cables themselves.
For example, when testing between the battery and
solenoid, touch the voltmeter test probes to the bat-
tery post and the solenoid threaded stud. The follow-
ing operation will require a voltmeter, accurate to
1/10 of a volt.
Before performing the tests, assure the following
procedures are accomplished:
²remove coil secondary cable from distributor and
connect to ground
²transmission in NEUTRAL (manual transmission)
or PARK (automatic transmission)
²parking brake applied
²battery is fully charged (refer to Battery Test Pro-
cedures).
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 9
Page 283 of 1784

(1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
negative post. Connect negative voltmeter lead to
battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and
hold ignition switch in the START position. Observe
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor contact
between cable clamp and post.
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
positive post. Connect negative lead to battery cable
positive clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and hold ignition
switch in the START position. Observe voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct poor contact between ca-
ble clamp and post.
(3) Connect a voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive post and the center of the B+ starter
solenoid stud (Fig. 3).
(4) Rotate and hold ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
TEST CONDITIONS
²PLACE GEAR SELECTOR IN PARK OR NEUTRAL AND SET PARK BRAKE OR EQUIVALENT.
²VERIFY BATTERY STATE-OF-CHARGE AND CRANKING CAPACITY, SEE BATTERY SECTION.
²CLEAN BATTERY TOP, POSTS, AND TERMINALS.
²VERIFY GENERATOR DRIVE BELT TENSION.
²DISCONNECT AND GROUND COIL CABLE.
Fig. 1 Volt-Amps Tester Connections (Typical)
8A - 10 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 284 of 1784

contact at battery cable to solenoid connection. If
reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace positive bat-
tery cable.
(5) Connect voltmeter to measure between the bat-
tery negative post and the engine block (Fig. 4).
(6) Rotate and hold ignition switch in the START po-
sition. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor con-tact at ground cable attaching point. Voltage reading
still above 0.2 volt, replace ground cable.
(7) Connect positive voltmeter lead to starter mo-
tor housing. Connect negative lead to battery nega-
tive terminal (Fig. 5).
(8) Rotate and hold ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor
starter to engine ground.
If resistance tests detect no feed circuit failures, re-
move the starter motor and go to Solenoid Testing.
STARTER CONTROL CIRCUIT TESTS
The starter control circuit consists of a starter so-
lenoid, starter relay, ignition switch, park/neutral po-
sition switch (automatic transmission), and all their
wiring and connections.
Testing procedures for these components are as fol-
lows and should be followed in order as described.
CAUTION: Before performing any test, disconnect dis-
tributor connector to prevent engine from starting.
SOLENOID TESTING
Refer to Group 8B - Battery/Starter/Generator Ser-
vice for starter removal procedures.
(1) Disconnect field coil wire from field coil terminal.
(2) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and field coil terminal with a continuity tester.
There should be continuity (Fig. 6).
Fig. 2 Test Battery Connection Resistance
Fig. 3 Test Positive Battery Cable Resistance
(Typical)
Fig. 4 Test Ground Circuit Resistance
Fig. 5 Test Starter Motor Ground (Typical)
Fig. 6 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Field Coil Terminal
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 11
Page 285 of 1784
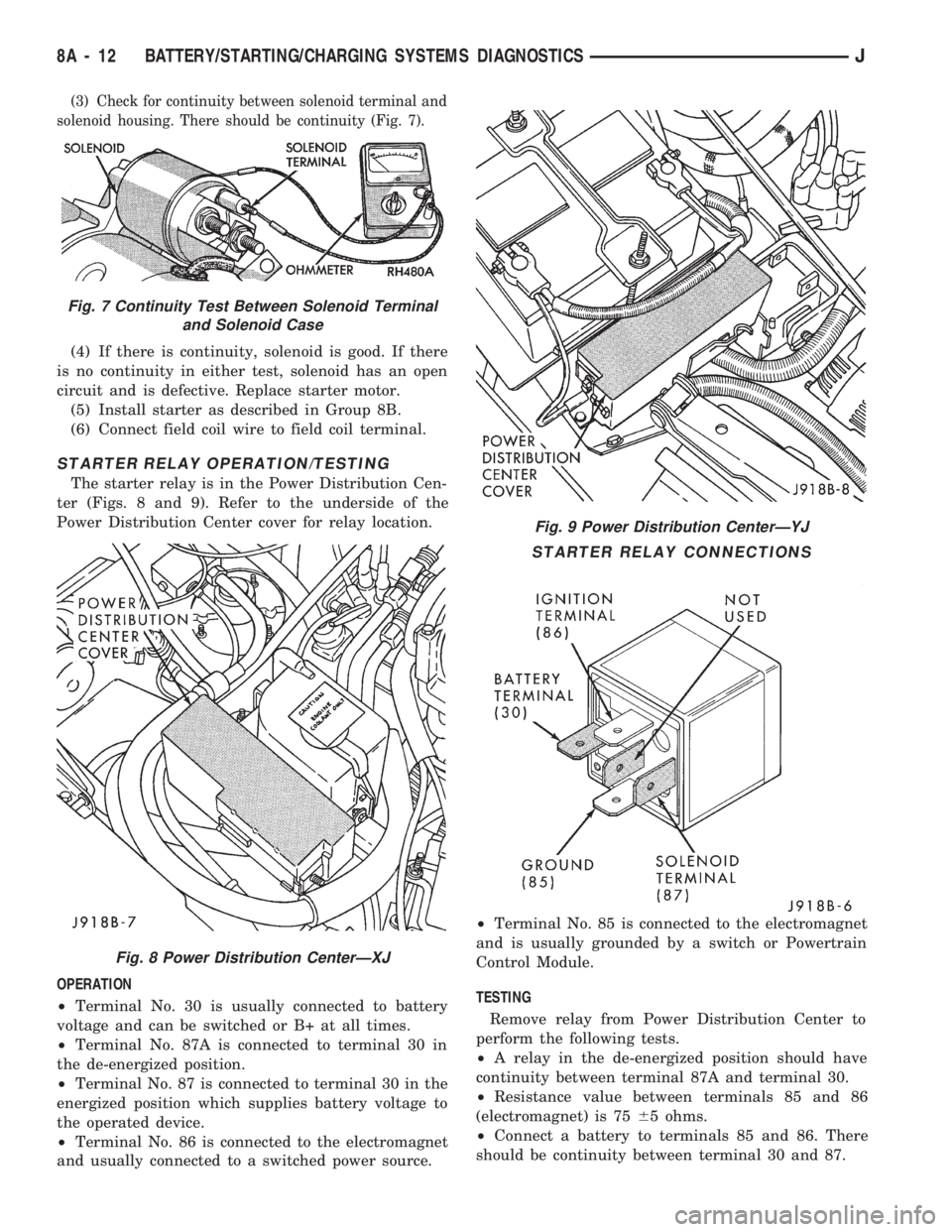
(3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal and
solenoid housing. There should be continuity (Fig. 7).
(4) If there is continuity, solenoid is good. If there
is no continuity in either test, solenoid has an open
circuit and is defective. Replace starter motor.
(5) Install starter as described in Group 8B.
(6) Connect field coil wire to field coil terminal.
STARTER RELAY OPERATION/TESTING
The starter relay is in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (Figs. 8 and 9). Refer to the underside of the
Power Distribution Center cover for relay location.
OPERATION
²Terminal No. 30 is usually connected to battery
voltage and can be switched or B+ at all times.
²Terminal No. 87A is connected to terminal 30 in
the de-energized position.
²Terminal No. 87 is connected to terminal 30 in the
energized position which supplies battery voltage to
the operated device.
²Terminal No. 86 is connected to the electromagnet
and usually connected to a switched power source.²Terminal No. 85 is connected to the electromagnet
and is usually grounded by a switch or Powertrain
Control Module.
TESTING
Remove relay from Power Distribution Center to
perform the following tests.
²A relay in the de-energized position should have
continuity between terminal 87A and terminal 30.
²Resistance value between terminals 85 and 86
(electromagnet) is 7565 ohms.
²Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86. There
should be continuity between terminal 30 and 87.
Fig. 9 Power Distribution CenterÐYJ
STARTER RELAY CONNECTIONS
Fig. 7 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Solenoid Case
Fig. 8 Power Distribution CenterÐXJ
8A - 12 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ