1994 JEEP CHEROKEE steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 188 of 1784

4). The engine intake manifold serves as the vacuum
source for booster operation.
The booster is mounted on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. The master cylinder is
mounted on attaching studs at the front of the
booster. The master cylinder central valves are di-
rectly actuated by the booster push rod.
The pedal travel sensor is mounted in the forward
face of the booster shell. The sensor plunger is actu-
ated by the booster diaphragm plate.
PEDAL TRAVEL SENSOR
The pedal travel sensor signals brake pedal posi-
tion to the antilock ECU. The sensor signal is based
on changes in electrical resistance. The resistance
changes occur in steps that are generated by changes
in brake pedal position. A resistance signal gener-
ated by changing brake pedal position, will cause the
ECU to run the antilock pump when necessary.
The sensor is a plunger-type, electrical switch
mounted in the forward housing of the power brake
booster (Fig. 5). The sensor plunger is actuated by
movement of the booster diaphragm plate.
The tip on the sensor plunger is color coded. The
tip must be matched to the color dot on the face of
the brake booster front shell (Fig. 5).
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
A sensor is used at each wheel. The sensors convert
wheel speed into an electrical signal. This signal is trans-
mitted to the antilock electronic control unit (ECU).
A gear-type tone ring serves as the trigger mecha-
nism for each sensor. The tone rings are mounted at
the outboard ends of the front and rear axle shafts.
Different sensors are used at the front and rear
wheels (Fig. 6). The front/rear sensors have the same
electrical values but are not interchangeable.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
A separate electronic control unit (ECU) monitors,
operates and controls the antilock system (Fig. 7).
The ECU contains dual microprocessors. The logic
block in each microprocessor receives identical sensor
signals. These signals are processed and compared si-
multaneously (Fig. 8).
The ECU is located under the instrument panel. It
is located at the right side of the steering column.
The power up voltage source for the ECU is through
the ignition switch in the On and Run positions.
The antilock ECU is separate from the other vehi-
cle electronic control units. It contains a self check
program that illuminates the amber warning light
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory and are accessible
with the DRB II scan tool.
ABS faults remain in memory until cleared, or until af-
ter the vehicle is started approximately 50 times. Stored
faults arenoterased if the battery is disconnected.
ACCELERATION SWITCH
An acceleration switch (Fig. 9), provides an addi-
tional vehicle deceleration reference during 4-wheel
drive operation. The switch is monitored by the anti-
lock ECU at all times.
The switch reference signal is utilized by the ECU
when all wheels are decelerating at the same speed.
Equal wheel speeds occur during braking in undiffer-
entiated 4-wheel ranges.
Fig. 5 Pedal Travel Sensor Location
Fig. 6 Wheel Speed Sensors
JBRAKES 5 - 41
Page 190 of 1784

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
ABS Operation in Antilock Braking Mode....... 43
ABS Operation in Normal Braking Mode....... 43
Acceleration Switch Operation............... 45
ECY Operation.......................... 46HCU Pump and Pedal Travel Sensor Operation . 44
HCU Solenoid Valve Operation.............. 43
System Power-Up and Initialization........... 43
Wheel Speed Sensor Operation............. 45
SYSTEM POWER-UP AND INITIALIZATION
The antilock system is in standby mode with the
ignition switch in Off or Accessory position. The an-
tilock electrical components are not operational.
Turning the ignition switch to On or Run position
allows battery voltage to flow through the switch to
the ECU ignition terminal.
The ABS system is activated when battery voltage
is supplied to the ECU. The ECU performs a system
initialization procedure at this point. Initialization
consists of a static and dynamic self check of system
electrical components.
The static check occurs immediately after the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position. The dynamic
check occurs when vehicle road speed reaches ap-
proximately 10 kph (6 mph). During the dynamic
check, the ECU briefly cycles the pump to verify op-
eration. The HCU solenoids are checked continu-
ously.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the ECU illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ABS OPERATION IN NORMAL BRAKING MODE
The ECU monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the ECU will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs and the acceleration switch in-
dicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
ABS OPERATION IN ANTILOCK BRAKING MODE
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock ECU activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching zero (or lockup)
during braking. Periods of high wheel slip occur
when brake stops involve high pedal pressure and
rate of vehicle deceleration.The antilock system retards lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the ECU for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The Jeep ABS system has three fluid pressure con-
trol channels. The front brakes are controlled sepa-
rately and the rear brakes in tandem (Fig. 10). A
speed sensor input signal indicating high slip condi-
tions activates the ECU antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel (Fig. 11). The valves are all located
within the HCU valve body and work in pairs to ei-
ther increase, hold, or decrease apply pressure as
needed in the individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
HCU SOLENOID VALVE OPERATION
Normal Braking
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
Antilock Pressure Modulation
Solenoid valve pressure modulation occurs in three
stages which are: pressure increase, pressure hold,
and pressure decrease. The valves are all contained
in the valve body portion of the HCU.
Pressure Decrease
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle (Fig. 11).
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the ECU opens the outlet
valve. Opening the outlet valve also opens the hy-
draulic return circuit to the master cylinder reser-
JANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION 5 - 43
Page 192 of 1784

At the start of antilock braking, pedal height will
decrease as the volume of fluid in the master cylin-
der is used up. When pedal height drops a predeter-
mined amount, the pedal travel sensor will signal
the ECU to run the pump. At this point, the pump is
activated to supply the extra fluid volume and re-
store pedal height at the same time.
The pump does not run continuously. It cycles on/
off according to signals from the travel sensor and
ECU. The pump is connected directly to the mastercylinder reservoir by hoses. During antilock braking,
the additional volume of fluid needed is drawn by the
pump from the reservoir.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OPERATION
Wheel speed input signals are generated by a sen-
sor and tone ring at each wheel. The sensors, which
are connected directly to the ECU, are mounted on
brackets attached to the front steering knuckles and
rear brake support plates.
The sensor triggering devices are the tone rings
which are similar in appearance to gears. The tone
rings are located on the outboard end of each front/
rear axle shaft. The speed sensors generate a signal
whenever a tone ring tooth rotates past the sensor
pickup face.
The wheel speed sensors provide the input signal to
the ECU. If input signals indicate ABS mode brak-
ing, the ECU causes the HCU solenoids to decrease,
hold, or increase fluid apply pressure as needed.
The HCU solenoid valves are activated only when
wheel speed input signals indicate that a wheel is
approaching a high slip, or lockup condition. At this
point, the ECU will cycle the appropriate wheel con-
trol channel solenoid valves to prevent slip or lockup.
The wheel sensors provide speed signals whenever
the vehicle wheels are rotating. The ECU examines
these signals for degree of deceleration and wheel
slip. If signals indicate normal braking, the solenoid
valves are not activated. However, when incoming
signals indicate the approach of wheel slip, or lockup,
the ECU cycles the solenoid valves as needed.
ACCELERATION SWITCH OPERATION
The ECU monitors the acceleration switch at all
times. The switch assembly contains three mercury
switches that monitor vehicle ride height and decel-
eration rates (G-force). Sudden, rapid changes in ve-
hicle and wheel deceleration rate, triggers the switch
sending a signal to the ECU. The switch assembly
provides three deceleration rates; two for forward
braking and one for rearward braking.
Fig. 12 Solenoid Valves In Pressure Hold Cycle
Fig. 13 Solenoid Valves In Pressure Increase Cycle
Fig. 14 Pedal Travel Sensor Actuation
JANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION 5 - 45
Page 196 of 1784

Clean the reservoir and caps thoroughly before
checking level or adding fluid. Cap open lines and
hoses during service to prevent dirt entry.
Dirt or foreign material entering the ABS hydrau-
lic system through the reservoir opening will circu-
late within the system. The result will be poor brake
performance and possible component failure. Use
clean, fresh fluid only to top off, or refill the system.
WHEEL SENSOR AIR GAP ADJUSTMENT
Only rear sensor air gap is adjustable. The front
sensors are fixed and cannot be adjusted.
A rear sensor air gap adjustment is only
needed when reinstalling an original sensor. Re-
placement sensors have an air gap spacer at-
tached to the sensor pickup face. The spacer
establishes correct air gap when pressed against
the tone ring during installation. As the tone
ring rotates, it peels the spacer off the sensor to
create the required air gap.
Preferred rear sensor air gap is 1.1 mm (0.043 in.).
Acceptable air gap range is 0.92 to 1.275 mm (0.036
to 0.050 in.).
Front sensor air gap is not adjustable. The front
sensors are fixed in position and cannot be adjusted.
Front sensor air gap can only be checked. Air gap
should be 0.040 to 1.3 mm (0.0157 to 0.051 in.). If
front sensor air gap is incorrect, the sensor is either
loose, or damaged.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and turn wheel outward for eas-
ier access to sensor.
(2) Remove sensor wire from mounting brackets.
(3) Clean sensor and surrounding area before removal.
(4) Remove bolt attaching sensor to steering
knuckle and remove sensor.
(5) Unseat grommet retaining sensor wire in wheel
house panel.
(6) In engine compartment, disconnect sensor wire con-
nector at harness plug. Then remove sensor and wire.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION
(1) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to
bolt that attaches sensor to steering knuckle. Use
new sensor bolt if original bolt is worn or damaged.
(2) Position sensor on steering knuckle. Seat sen-
sor locating tab in hole in knuckle and install sensor
attaching bolt finger tight.
(3) Tighten sensor bolt to 14 NIm (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Attach sensor wire to steering knuckle bracket
with grommets on sensor wire.
(5) Route sensor wire forward and behind shock
absorber. Then attach sensor wire to spring seat
bracket with grommets on sensor wire.
(6) Route sensor wire to outer sill bracket. Remove
all twists or kinks from wire.(7) Attach sensor wire to sill bracket with grom-
met. Be sure wire is free of twists and kinks.
(8) Verify sensor wire routing. Wire should loop
forward and above sill bracket. Loose end of wire
should be below sill bracket and towards brake hose.
(9) Seat sensor wire grommet in body panel and
clip wire to brake line at grommet location.
(10) Connect sensor wire to harness in engine com-
partment.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) On XJ models, if separate connectors are not
used to attach sensor harness to each sensor wire,
proceed as follows:
(a) Raise and fold rear seat forward for access to
rear sensor connectors (Figs. 4 and 5).
(b) Disconnect sensors at rear harness connectors.
(c) Push sensor grommets and sensor wires
through floorpan.
Fig. 4 Acceleration Switch And Rear Sensor
Connections (XJ)
Fig. 5 Rear Sensor Connections (XJ)
JABS COMPONENT SERVICE 5 - 49
Page 344 of 1784
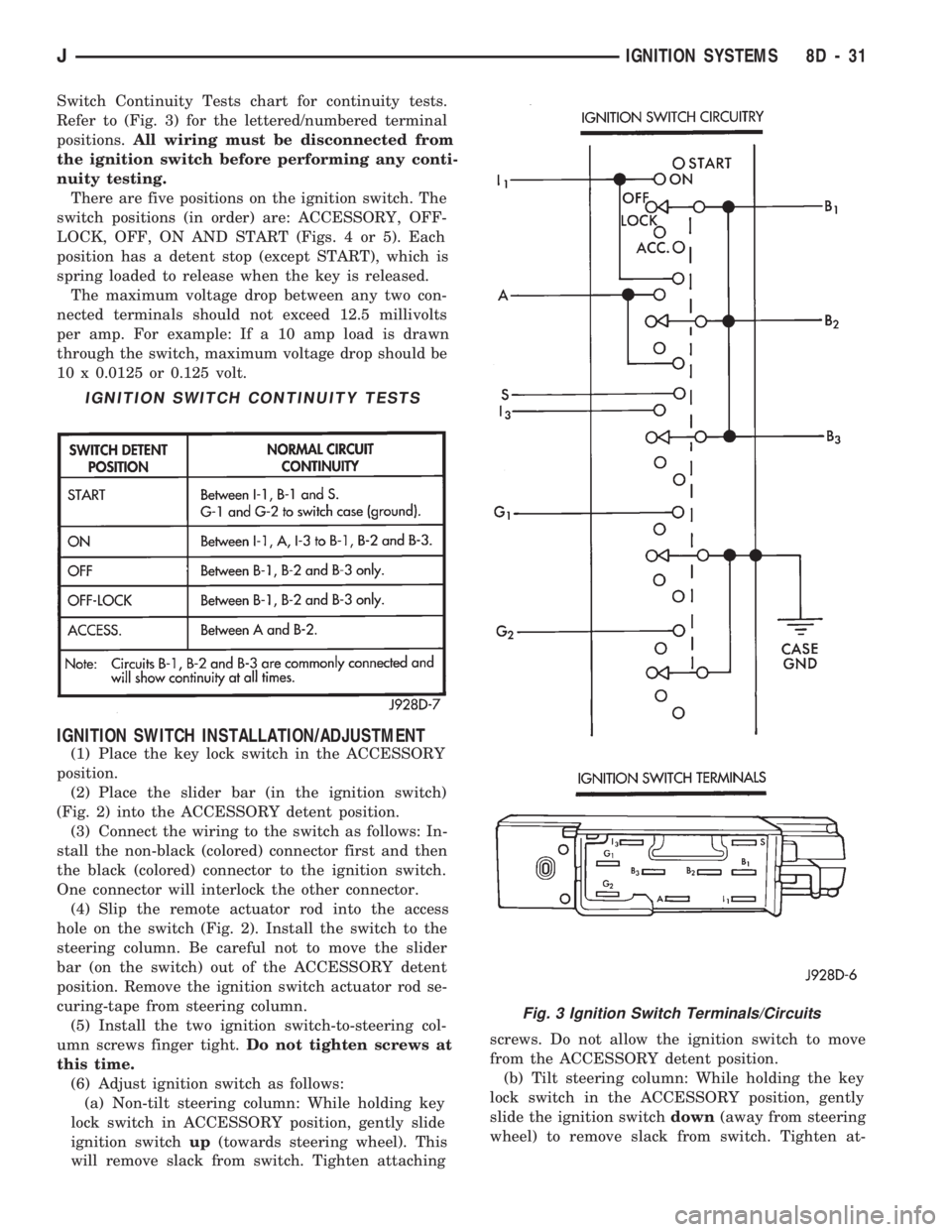
Switch Continuity Tests chart for continuity tests.
Refer to (Fig. 3) for the lettered/numbered terminal
positions.All wiring must be disconnected from
the ignition switch before performing any conti-
nuity testing.
There are five positions on the ignition switch. The
switch positions (in order) are: ACCESSORY, OFF-
LOCK, OFF, ON AND START (Figs. 4 or 5). Each
position has a detent stop (except START), which is
spring loaded to release when the key is released.
The maximum voltage drop between any two con-
nected terminals should not exceed 12.5 millivolts
per amp. For example: If a 10 amp load is drawn
through the switch, maximum voltage drop should be
10 x 0.0125 or 0.125 volt.
IGNITION SWITCH INSTALLATION/ADJUSTMENT
(1) Place the key lock switch in the ACCESSORY
position.
(2) Place the slider bar (in the ignition switch)
(Fig. 2) into the ACCESSORY detent position.
(3) Connect the wiring to the switch as follows: In-
stall the non-black (colored) connector first and then
the black (colored) connector to the ignition switch.
One connector will interlock the other connector.
(4) Slip the remote actuator rod into the access
hole on the switch (Fig. 2). Install the switch to the
steering column. Be careful not to move the slider
bar (on the switch) out of the ACCESSORY detent
position. Remove the ignition switch actuator rod se-
curing-tape from steering column.
(5) Install the two ignition switch-to-steering col-
umn screws finger tight.Do not tighten screws at
this time.
(6) Adjust ignition switch as follows:
(a) Non-tilt steering column: While holding key
lock switch in ACCESSORY position, gently slide
ignition switchup(towards steering wheel). This
will remove slack from switch. Tighten attachingscrews. Do not allow the ignition switch to move
from the ACCESSORY detent position.
(b) Tilt steering column: While holding the key
lock switch in the ACCESSORY position, gently
slide the ignition switchdown(away from steering
wheel) to remove slack from switch. Tighten at-
IGNITION SWITCH CONTINUITY TESTS
Fig. 3 Ignition Switch Terminals/Circuits
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 31
Page 345 of 1784

taching screws. Do not allow the ignition switch to
move from the ACCESSORY detent position.
Because the ignition switch and the headlamp dim-
mer switch share the same two mounting screws, one
of the screws must be removed from the ignition
switch. This must be doneafterthe ignition switch
has been adjusted andbeforethe dimmer switch has
been installed. Remove one screw.Do notremove
the stud/nut.
(7) Install the headlamp dimmer switch as follows:
Slip switch into actuator rod and position over the ig-
nition switch. Install screws finger tight. Remove the
dimmer switch actuator rod securing-tape from steer-
ing column.
(8) Adjust dimmer switch as follows: Depress the
switch slightly and insert a 3/32-inch drill bit into
the adjustment hole (Fig. 1). This is done to prevent
horizontal switch movement.
(9) Move switch toward steering wheel to remove
any lash from switch actuator rod. Tighten dimmer
and ignition switch fasteners to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(10) XJ models: Install the lower instrument panel
trim assembly. YJ models: Install the windshield
wiper intermittent control module and its bracket (if
equipped).
(11) Install the negative battery cable.
Test dimmer switch. Test ignition switch operation
in all switch positions. If equipped with a tilt steer-
ing column, test operation of dimmer switch and ig-
nition switch in all tilt positions.
Fig. 4 Detent PositionsÐNon-Tilt Steering Column
Fig. 5 Detent PositionsÐTilt Steering Column
8D - 32 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 364 of 1784

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Headlamp Switch/Illumination Rheostat........ 21
Indicator Bezel Replacement................ 17
Instrument Cluster Bulb Replacement......... 19
Instrument Cluster Replacement............. 17Printed Circuit Replacement................ 19
Rear Defogger/Fog Lamp/Rear Wiper Switches . . 21
Speedometer Replacement................. 17
Tachometer Replacement.................. 17
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove 6 shroud screws (Fig. 1).
(2) Slide shroud toward steering wheel.
(3) Remove 3 screws holding right side switch
panel (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove 3 screws holding left side switch bezel.(5) Remove 2 screws holding cluster in place.
(6) Lift up top of cluster. Roll cluster out between
steering column and instrument panel far enough to
reach connector located behind tachometer.
(7) Disconnect cluster connector and remove clus-
ter (Fig. 3).
(8) To install cluster, reverse the removal proce-
dures.
TACHOMETER REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove instrumentation shroud (Fig. 1). Refer
to Instrument Cluster Replacement.
(3) Remove cluster as described in Instrument
Cluster replacement.
(4) Remove 3 screws and tachometer lens (Fig. 4).
(5) Gently pry up clip to release lens from bezel
(Fig. 5).
(6) Remove 3 screws from rear of housing (Fig. 6).
Remove tachometer.
(7) Install tachometer with 3 screws.
(8) Snap lens into place.
(9) Install lens with 3 screws.
(10) To install the cluster, reverse the removal pro-
cedures.
SPEEDOMETER REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove instrument shroud (Fig. 1). Refer to In-
strument Cluster Replacement.
(3) Remove cluster as described in Instrument
Cluster Replacement.
(4) Remove 3 screws and speedometer lens (Fig. 7).
(5) Gently pry up clip to release lens from bezel
(Fig. 5).
(6) Remove 3 screws from rear of housing (Fig. 8).
Remove speedometer.
(7) Install speedometer with 3 screws.
(8) Snap lens into place.
(9) Install lens with 3 screws.
(10) To install the cluster, reverse the removal pro-
cedures.
INDICATOR BEZEL REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove instrumentation shroud (Fig. 1).
(3) Remove 3 screws and tachometer lens (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 Cluster Removal
Fig. 1 Instrument Shroud Removal/Installation
JYJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES 8E - 17
Page 386 of 1784

HORNS
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
HORN SWITCH (HORN PAD) REPLACEMENT . . 3
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS................. 3XJ ..................................... 1
YJ ..................................... 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
For XJ/YJ vehicles battery voltage is applied to the
horn relay through a fuse.
When the horn switch is depressed, the horn relay
is grounded, pulling the contact closed and providing
battery voltage to the horns.
A slip ring and brush arrangement in the steering
wheel allows the switch circuit to maintain contact
while allowing rotation of the steering wheel.On XJ models, a cadmium-plated ground
screw is used to attach the horn(s) to the body.
Do not substitute other types of ground screws
as they may become corroded and cause a loss
of ground.
XJ
REPLACEMENT
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the splash shield.
(3) Remove horn mounting bolt and horn mounted
on the drivers side (Fig. 1).
(4) Remove wire from horn.
(5) To install horn, reverse the removal proce-
dures.
DIAGNOSIS AND REPAIR
Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for a com-
plete circuit diagram.
HORN RELAY
²Inspect 25 amp, #11 fuse. Replace fuse as re-
quired.
²Depress horn switch. The relay contacts should
click. If OK, go to HORNS. If not, go to next step.
²Remove the horn relay located in the relay center.
The relay center is on the lower instrument panel
trim cover just right of the steering column (Fig. 2).
There should be 12 volts at relay connector pins 1
and 2. If not, repair open in circuit to relay.
²Depress horn switch. Measure resistance between
relay connector pin 5 and ground. The meter should
read zero ohms. If not, repair open to horn switch
ground.
²Measure resistance between relay connector pin 4
and ground. The meter should read almost zero ohms
(horn resistance) If OK, replace relay. If not, repair
open in circuit between relay and horns.
Fig. 1 Drivers Side Horn
JHORNS 8G - 1