1994 JEEP CHEROKEE steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 39 of 1784

axle assembly to the frame. The lower arms uses
shims at the frame mount to allow for adjustment of
caster and pinion angle. The suspension arm travel
(jounce or rebound) is limited through the use of rub-
ber bumpers.
Suspension components which use rubber bushings
should be tightened at vehicle ride height. This will
prevent premature failure of the bushing and main-
tain ride comfort. Bushings must never be lubricated.
The coil springs control ride quality and maintain
proper ride height. The coil springs mount up in the
fender shield which is part of the unitized body
bracket. A rubber isolator is located between the top
of the spring and the frame. The bottom of the spring
seats on a axle pad and is retained with a clip.
The shock absorbers dampen jounce and rebound of
the vehicle over various road conditions. The top of
the shock absorbers are bolted to the frame. The bot-
tom of the shocks are bolted to the axle spring
bracket.
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion. The bar extends across the front underside of
the chassis and connects to the frame rails. Links are
connected from the bar to the axle brackets. Stabi-
lizer bar mounts are isolated by rubber bushings.
The track bar is used to minimize front axle side-
to-side movement. The bar is attached to a frame rail
bracket with a ball stud and isolated with a bushing
at the axle bracket.
TUBE AXLE (2WD VEHICLES)
The front axle used on two-wheel drive vehicles is
a one-piece, tubular axle (Fig. 2). The tubular axle
mounts in the same bracketry as does the four-wheel
drive front axle. The steering knuckles and hub bear-
ing assemblies are the same as used on the Model 30
drive axle.
YJ VEHICLES
The Wrangler (YJ) front suspension is leaf spring
design comprised of (Fig. 3);
²Drive axle
²Track bar
²Stabilizer bar
²Leaf springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers
²Jounce bumpers (used to limit the travel of the
suspension)
The front suspension uses semi-elliptic multi-leaf
springs mounted on the drive axle. The rearward end
of the springs are mounted to the frame rail hangers
through rubber bushings. The bushings isolate road
noise as the springs move. The forward end of the
springs are attached to the frame with shackles. The
spring and shackles use rubber bushings to isolate
road noise. The shackles allow the springs to changetheir length as the vehicle moves over various road
conditions. The spring and axle travel (jounce or re-
bound) is limited through use of rubber bumpers
mounted on the frame.
Suspension components which use rubber bushings
should be tightened at vehicle ride height. This will
prevent premature failure of the bushing and main-
tain ride comfort. The bushings should never be lu-
bricated.
Fig. 2 Front AxleÐ 2WD Vehicles
Fig. 3 YJ Front Suspension
2 - 2 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 42 of 1784

FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
INDEX
page page
Alignment Measurements and Adjustments...... 6
General Information........................ 5Pre-Alignment Inspection.................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Front wheel alignment involves the correct posi-
tioning of the wheels in relation to the vehicle. The
positioning is accomplished through suspension and
steering linkage adjustments. An alignment is con-
sidered essential for efficient steering, good direc-
tional stability and to maximize tire wear. The most
important measurements of front end alignment are
caster, camber and toe position.
Routine inspection of the front suspension
and steering components is a good preventative
maintenance practice. Inspection also helps to
ensure safe operation of the vehicle.
²CASTER is the forward or rearward tilt of the
steering knuckle from vertical. Tilting the top of the
knuckle rearward provides positive caster. Tilting the
top of the knuckle forward provides negative caster.
Caster is a directional stability angle whichenables the front wheels to return to a straight
ahead position after turns (Fig. 1).
²CAMBER is the inward or outward tilt of the
wheel relative to the center of the vehicle. Tilting the
top of the wheel inward provides negative camber.
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive
camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on the in-
side or outside edge of the tire (Fig. 1).
²WHEEL TOE POSITION is the difference between
the leading inside edges and trailing inside edges of
the front tires (Fig. 1). Incorrect wheel toe position is
the most common cause of unstable steering and un-
even tire wear. The wheel toe position is thefinal
front wheel alignment adjustment.
²STEERING AXIS INCLINATION ANGLE is mea-
sured in degrees and is the angle that the steering
knuckles are tilted (Fig. 1). The inclination angle has
a fixed relationship with the camber angle. It will
Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 5
Page 43 of 1784

not change except when a spindle or ball stud is
damaged or bent. The angle is not adjustable and the
damaged component(s) must be replaced to correct
mis-alignment.
CAUTION:Do not attempt to modify any suspension
or steering component by heating and bending.
PRE-ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before starting a front wheel alignment, the follow-
ing inspection and necessary corrections must be
completed.
(1) Tires with the same recommended air pressure,
size, and thread wear. Refer to Group 22, Tires And
Wheels for diagnosis information.
(2) Front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Ball studs, steering linkage pivot points and
steering gear for looseness, roughness, binding or
wear. Refer to Group 19, Steering for additional in-
formation.
(4) Front wheels for excessive radial or lateral
runout and unbalance. Refer to Group 22, Tires And
Wheels for diagnosis information.
(5) Suspension components for wear and noise.
Check components for correct torque. Refer to Groups
2 and 3, Suspension and Axle for additional informa-
tion.
ALIGNMENT MEASUREMENTS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Before each alignment reading, the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each bumper
at the center and jounce the vehicle up and down
several times. Always release the bumper in the
down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications with the vehicle at its NOR-
MALLY RIDE HEIGHT.
CAMBER
The wheel camber angle (Fig. 1) is preset at ZERO
DEGREES (0É). The angle is not adjustable and can-
not be altered.
CASTER
The caster angle (Fig. 1) is set at:
²XJ manual transmission, POSITIVE 6.5 DE-
GREES (+6.5É).
²XJ automatic transmission, POSITIVE 8.0 DE-
GREES (+8.0É).
²YJ all transmissions, POSITIVE 6.0 DEGREES
(+6.0É).
Before checking the caster of the front axle for cor-
rect angle. Be sure the axle is not bent or twisted.
Road test the vehicle, and make left and right
turns. If the steering wheel returns to the center po-
sition unassisted, the caster angle is correct. How-ever, if steering wheel does not return toward the
center position unassisted, an incorrect caster angle
is probable.
Caster can be adjusted by installing the appropri-
ate size shims (Fig. 2, 3).Changing caster angle
will also change the front propeller shaft angle.
The propeller shaft angle has priority over
caster. Refer to Group 16, Propeller Shafts for
additional information.
Fig. 2 AdjustmentÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 3 AdjustmentÐXJ Vehicles
2 - 6 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 45 of 1784
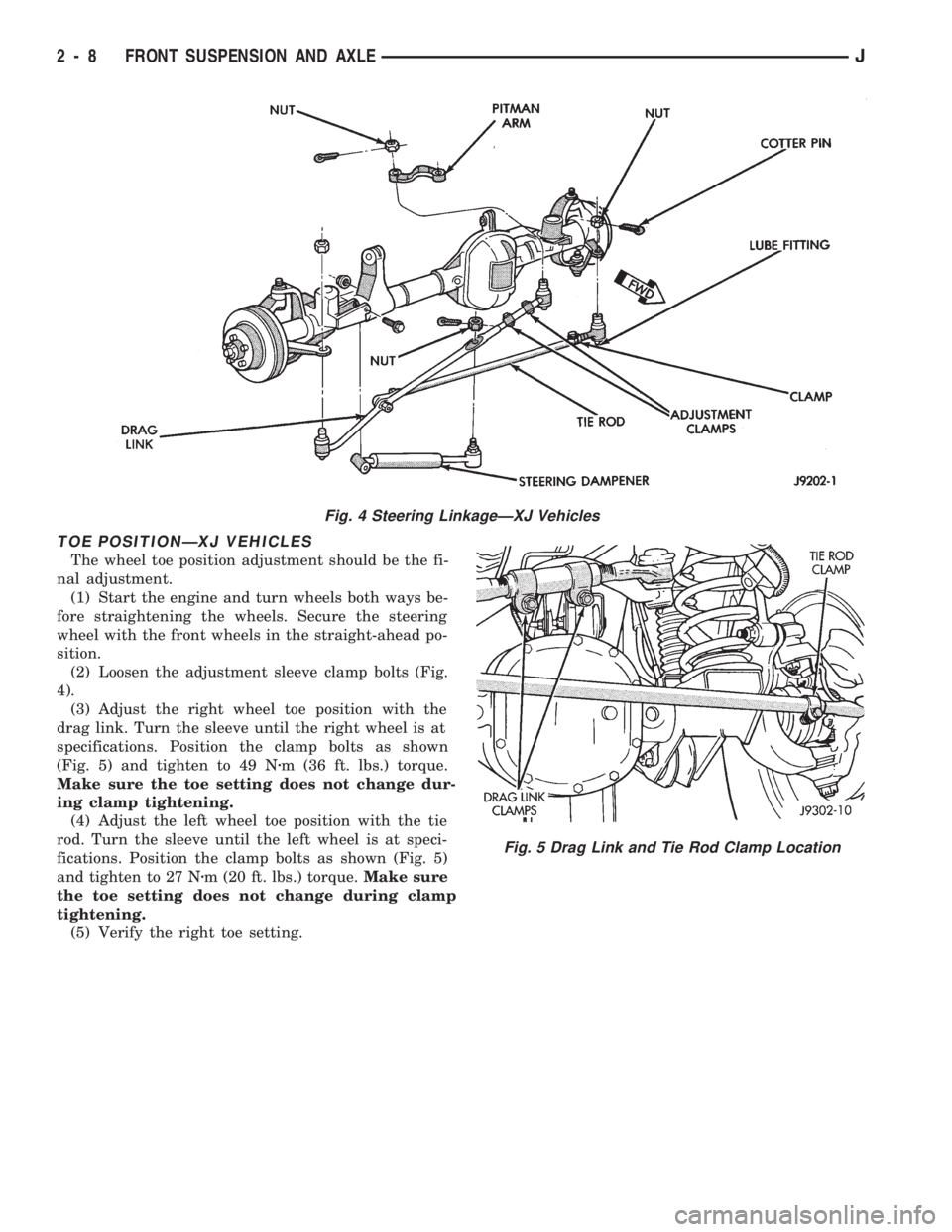
TOE POSITIONÐXJ VEHICLES
The wheel toe position adjustment should be the fi-
nal adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways be-
fore straightening the wheels. Secure the steering
wheel with the front wheels in the straight-ahead po-
sition.
(2) Loosen the adjustment sleeve clamp bolts (Fig.
4).
(3) Adjust the right wheel toe position with the
drag link. Turn the sleeve until the right wheel is at
specifications. Position the clamp bolts as shown
(Fig. 5) and tighten to 49 Nzm (36 ft. lbs.) torque.
Make sure the toe setting does not change dur-
ing clamp tightening.
(4) Adjust the left wheel toe position with the tie
rod. Turn the sleeve until the left wheel is at speci-
fications. Position the clamp bolts as shown (Fig. 5)
and tighten to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.Make sure
the toe setting does not change during clamp
tightening.
(5) Verify the right toe setting.
Fig. 4 Steering LinkageÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 5 Drag Link and Tie Rod Clamp Location
2 - 8 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 46 of 1784
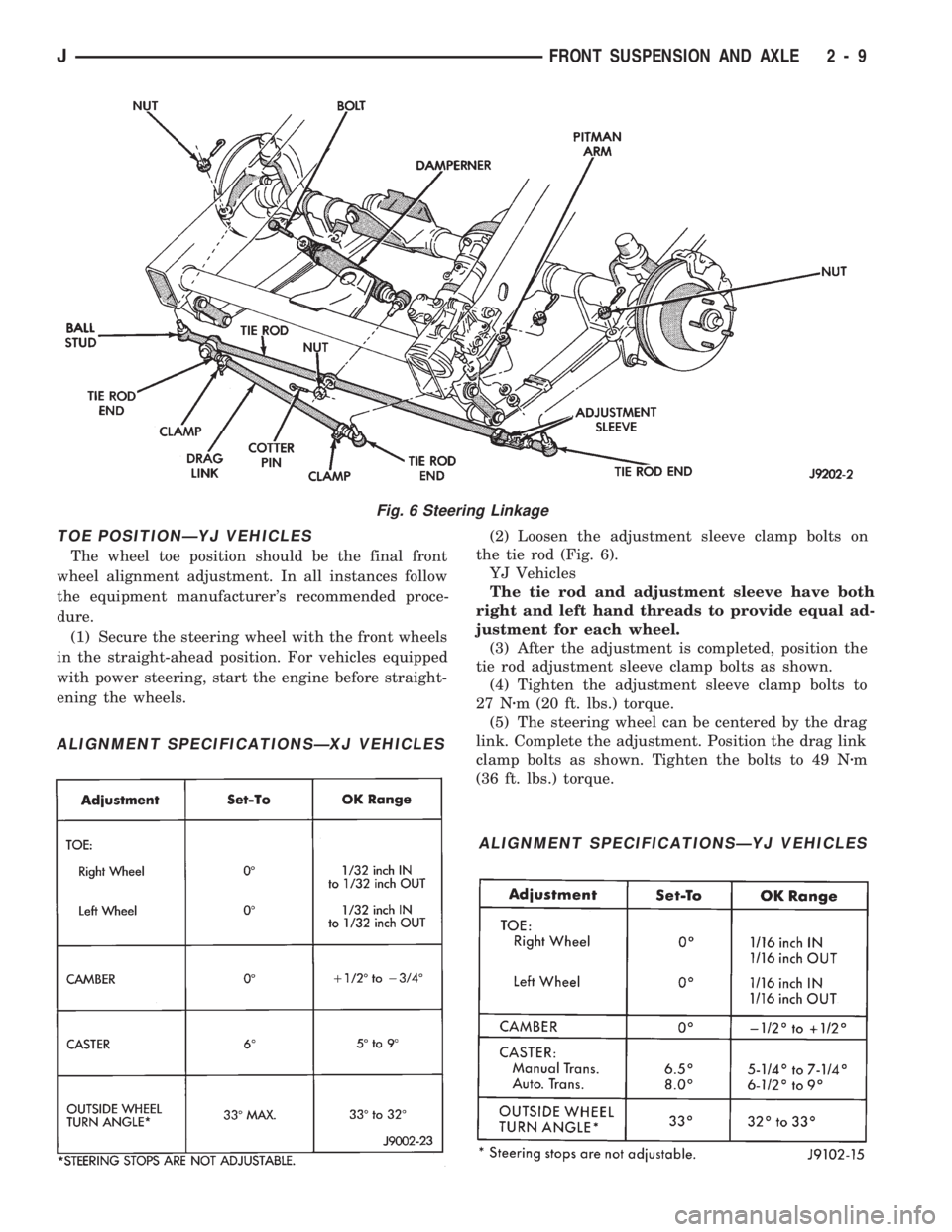
TOE POSITIONÐYJ VEHICLES
The wheel toe position should be the final front
wheel alignment adjustment. In all instances follow
the equipment manufacturer's recommended proce-
dure.
(1) Secure the steering wheel with the front wheels
in the straight-ahead position. For vehicles equipped
with power steering, start the engine before straight-
ening the wheels.(2) Loosen the adjustment sleeve clamp bolts on
the tie rod (Fig. 6).
YJ Vehicles
The tie rod and adjustment sleeve have both
right and left hand threads to provide equal ad-
justment for each wheel.
(3) After the adjustment is completed, position the
tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp bolts as shown.
(4) Tighten the adjustment sleeve clamp bolts to
27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) The steering wheel can be centered by the drag
link. Complete the adjustment. Position the drag link
clamp bolts as shown. Tighten the bolts to 49 Nzm
(36 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 6 Steering Linkage
ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONSÐXJ VEHICLES
ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONSÐYJ VEHICLES
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 9
Page 57 of 1784

MODEL 30 AXLE AND TUBE AXLE (2WD)
INDEX
page page
Axle Bushing Replacement................. 32
Axle Shaft Ð Cardan U-Joint................ 25
Axle Specifications....................... 46
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis........ 44
Cleaning/Inspection....................... 35
Differential and Pinion Measurement.......... 38
Differential Assembly...................... 36
Differential Disassembly.................... 34
Differential Installation..................... 43
Differential Removal...................... 32
Differential Shim Pack Measurement and Adjustment.42
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . 21
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . 21Final Assembly.......................... 44
Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft................ 24
Information............................. 20
Inner Axle Shaft Oil Seal Replacement........ 33
Lubricant Change........................ 22
Lubricant Specifications.................... 20
Pinion Gear Assembly/Installation............ 40
Pinion Gear Depth Information.............. 37
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................ 34
Pinion Seal Replacement.................. 23
Steering Knuckle and Ball Studs............. 30
Vacuum Disconnect Axle Ð YJ Vehicles....... 26
INFORMATION
The housing for Model 30 front axles consists of an
iron center casting (differential housing) with axle
shaft tubes extending from either side. The tubes are
pressed into and welded to the differential housing to
form a one-piece axle housing.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set above the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a fitting for a vent hose used to re-
lieve internal pressure caused by lubricant vaporiza-
tion and internal expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the hub
bearings. The axle shafts are retained by nuts at the
hub bearings. The hub bearings are bolted to the
steering knuckle at the outboard end of the axle tube
yoke. The hub bearings are serviced as an assembly.
The axles are equipped with ABS brake sensors.
The sensors are attached to the knuckle assemblies
and tone rings are pressed on the axle shaft.Use
care when removing axle shafts as NOT to dam-
age the tone wheel or the sensor.
The stamped steel cover provides a means for in-
spection and servicing the differential.
The Model 30 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a roll
pin. Differential bearing preload and ring gear back-
lash is adjusted by the use of shims (select thick-
ness). The shims are located between the differential
bearing cones and case. Pinion bearing preload is set
and maintained by the use of collapsible spacer.
PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT WITH
PINION GAUGE SET 6774, Pinion Block 6733 and
Dial Indicator C-3339 is performed when;²Axle/differential housing is being replaced
²Original pinion depth shim pack is lost or mis-
placed
²Replacing the differential case
²Original differential bearing shim pack is lost or
misplaced
COMMAND-TRACÐYJ VEHICLES
The Command-Trac system is a vacuum disconnect
axle. The system has a two-piece axle shaft coupled
together by a shift collar. For two-wheel drive oper-
ation, the vacuum motor and shift fork disengages
the axle shaft splines. For four-wheel drive opera-
tion, the vacuum motor and shift fork engages the
splines.
SELEC-TRACÐXJ VEHICLES
The Selec-Trac system is a non-disconnect axle.
Shifting from two-wheel to four-wheel drive is at the
transfer case.
For XJ vehicles equipped withSelec-Tracand
ABS brake system, refer to Group 5ÐBrakes for ad-
ditional service information.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 30 axles. The lubricant should have
MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²The factory fill for the Model 30 axle is SAE 75W
gear lubricant.Do not use heavier weight lubri-
cant, this will cause axle engagement difficulties.
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
NON-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 5061 fluid oz..
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
VACUUM-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 5661 fluid
oz..
2 - 20 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 58 of 1784

Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information regarding temperature range,
viscosity and fluid level.
CAUTION: If the axle is submerged in water, the lu-
bricant must be replaced immediately to avoid the
possibility of premature axle failure.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly in behind the lower
suspension arm frame brackets.
(2) Remove the front wheels.
(3) Remove the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(4) On 4WD vehicles, disconnect the axle vent
hose.
(5) On 4WD vehicles, mark the drive shaft yoke
and axle pinion yoke for alignment reference. Discon-
nect the drive shaft from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link at the axle
bracket.
(7) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
bracket.
(8) Disconnect the track bar from the axle bracket.
(9) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckle. Disconnect the steering dampener
from the axle bracket.
(10) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(11) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(12) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
The coil springs will drop with the axle.
(13) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: All suspension components that use rub-
ber bushings should be tightened with the vehicle
at the ride height. It is important to have the
springs supporting the weight of the vehicle when
the fasteners are torqued. If the springs are not at
their normal ride position, vehicle ride comfort
could be affected along with premature rubber
bushing wear. Rubber bushings must never be lu-
bricated.
(1) Install the springs and retainer clip. Tighten
the retainer bolts to 21 Nzm (16 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(3) Raise the axle with a floor jack and align it
with the spring pads.(4) Position the upper and lower suspension arm at
the axle bracket. Install bolts and nuts finger
tighten.
(5) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt.Do not tighten at this time.
It is important that the springs support the
weight of the vehicle when the track bar is con-
nected. If the springs are not at their usual po-
sition, the vehicle ride comfort could be affected.
(6) Install the shock absorber and tighten the bolt
to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 95 Nzm (70 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles and tighten the nuts to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.)
torque. Install the steering dampener to the axle
bracket and tighten the nut to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(9) Install the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(10) On 4WD vehicles, connect the vent hose to the
tube fitting.
(11) On 4WD vehicles, align the reference marks
and connect the drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten
the U-joint clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(13) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(14) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(15) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts to 75
Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower suspension
arm nuts to 115 Nzm (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 100 Nzm (74 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Check the front wheel alignment.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐYJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly behind the spring
frame brackets.
(2) Remove the front wheels.
(3) Remove the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose and axle shift
motor vacuum harness.
(5) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link at the axle
bracket.
(7) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
bracket.
(8) Disconnect the track bar from the axle bracket.
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 21
Page 59 of 1784

(9) Disconnect the tie rod from the steering
knuckle. Disconnect the steering dampener from the
axle bracket.
(10) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential. Raise the axle just enough to relieve
the axle weight from the springs.
(11) Remove the spring U-bolts from the plate
brackets.
(12) Loosen BUT DO NOT REMOVE the bolts that
attach the spring rear pivot at the frame rail brack-
ets. This will allow the springs to pivot without bind-
ing on the bushings.
(13) Disconnect shackle from the springs and lower
the springs to the surface.
(14) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: All suspension components that use rub-
ber bushings should be tightened with the vehicle
at the normal height. It is important to have the
springs supporting the weight of the vehicle when
the fasteners are torqued. If the springs are not at
their normal ride position, vehicle ride comfort
could be affected along with premature rubber
bushing wear. Rubber bushings must never be lu-
bricated.
(1) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Raise the springs and install the spring shackle
bolts.Do not tighten at this time.
(3) Lower the axle and align the spring center
bolts with the locating holes in the axle pads and
plate brackets.
(4) Install the spring U-bolts through the plate
brackets and tighten to 122 Nzm (90 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt.Do not tighten at this time.
It is important that the springs support the
weight of the vehicle when the track bar is con-
nected. If the springs are not at their usual po-
sition, the vehicle ride comfort could be affected.
(6) Install the shock absorber and tighten the nut
to 61 Nzm (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 61 Nzm (45 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Install the tie rod to the steering knuckles and
tighten the nuts to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Install
the steering dampener to the axle bracket and
tighten the bolt to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(10) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting and
axle shift motor vacuum harness.(11) Align the reference marks and connect the
drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten the U-joint
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(13) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(14) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(15) Tighten the spring rear pivot bolt/nut to 142
Nzm (105 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the spring shackle
bolt/nut to 135 Nzm (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Tighten the track bar nut at the axle bracket
to 100 Nzm (74 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Check the front wheel alignment.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the
differential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces. Use solvent to clean the mating surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 1).Allow the sealant
to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the seal-
ant must be removed and another bead applied.
Fig. 1 Typical Housing Cover With Sealant
2 - 22 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ