1993 FORD MONDEO air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 69 of 279

How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to
engine/transmission removal and refitting, to
those repair procedures requiring the removal
of the engine/transmission from the vehicle,
and to the overhaul of engine components. It
includes only the Specifications relevant to
those procedures. Refer to Part A for
additional Specifications, if required.
General information
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts, to detailed
step-by-step procedures covering removal
and installation of internal engine components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and installation of
the external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Part A of this Chapter and
Section 5 of this Part.
When overhauling this engine, it is essential
to establish first exactly what replacement
parts are available. At the time of writing,
components such as the piston rings are not
available separately from the
piston/connecting rod assemblies; pistons,
gudgeon pins and valve guides are not
available separately, and very few under- or
oversized components are available for
engine reconditioning. In most cases, it would
appear that the easiest and most
economically-sensible course of action is to
replace a worn or damaged engine with an
exchange unit.
It’s not always easy to determine when, or
if, an engine should be completely
overhauled, as a number of factors must be
considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an
indication that an overhaul is needed, while
low mileage doesn’t preclude the need for an
overhaul. Frequency of servicing is probably
the most important consideration. An engine
that’s had regular and frequent oil and filter
changes, as well as other required
maintenance, will most likely give many
thousands of miles of reliable service.
Conversely, a neglected engine may require
an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make surethat oil leaks aren’t responsible before
deciding that the rings and/or guides are
worn. Perform a cylinder compression check
(Part A of this Chapter, Section 3) to
determine the extent of the work required.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption rates may
also point to the need for an overhaul,
especially if they’re all present at the same
time. If a full service doesn’t remedy the
situation, major mechanical work is the only
solution.
An engine overhaul involves restoring all
internal parts to the specification of a new
engine. Note:Always check first what
replacement parts are available before
planning any overhaul operation; refer to
Section 1 of this Part. Ford dealers, or a good
engine reconditioning specialist/automotive
parts supplier may be able to suggest
alternatives which will enable you to overcome
the lack of replacement parts.
During an overhaul, it is usual to renew the
piston rings, and to rebore and/or hone the
cylinder bores; where the rebore is done by an
automotive machine shop, new oversize
pistons and rings will also be installed - all
these operations, of course, assume the
availability of suitable replacement parts. The
main and big-end bearings are generally
renewed and, if necessary, the crankshaft
may be reground to restore the journals.
Generally, the valves are serviced as well,
since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the starter and alternator, can be renewed as
well, or rebuilt, if the necessary parts can be
found. The end result should be an as-new
engine that will give many trouble-free miles.
Note:Critical cooling system components
such as the hoses, drivebelt, thermostat and
water pump MUST be replaced with new
parts when an engine is overhauled. The
radiator should be checked carefully, to
ensure that it isn’t clogged or leaking (see
Chapter 3). Also, as a general rule, the oil
pump should be renewed when an engine is
rebuilt.
Before beginning the engine overhaul, read
through the entire procedure to familiarise
yourself with the scope and requirements of
the job. Overhauling an engine isn’t difficult,
but it is time-consuming. Plan on the vehicle
being off the road for a minimum of two
weeks, especially if parts must be taken to an
automotive machine shop for repair or
reconditioning. Check on availability of parts,
and make sure that any necessary special
tools and equipment are obtained in advance.
Most work can be done with typical hand
tools, although a number of precision
measuring tools are required, for inspecting
parts to determine if they must be replaced.
Often, an automotive machine shop will
handle the inspection of parts, and will offer
advice concerning reconditioning andreplacement. Note:Always wait until the
engine has been completely dismantled, and
all components, especially the cylinder
block/crankcase, have been inspected, before
deciding what service and repair operations
must be performed by an automotive machine
shop. Since the block’s condition will be the
major factor to consider when determining
whether to overhaul the original engine or buy
a rebuilt one, never purchase parts or have
machine work done on other components
until the cylinder block/crankcase has been
thoroughly inspected.As a general rule, time
is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it
doesn’t pay to install worn or sub-standard
parts.
As a final note, to ensure maximum life and
minimum trouble from a rebuilt engine,
everything must be assembled with care, in a
spotlessly-clean environment.
If you’ve decided that an engine must be
removed for overhaul or major repair work,
several preliminary steps should be taken.
Locating a suitable place to work is
extremely important. Adequate work space,
along with storage space for the vehicle, will
be needed. If a workshop or garage isn’t
available, at the very least, a flat, level, clean
work surface made of concrete or asphalt is
required.
Cleaning the engine compartment and
engine/transmission before beginning the
removal procedure will help keep tools clean
and organized.
The engine can only be withdrawn by
removing it complete with the transmission;
the vehicle’s body must be raised and
supported securely, sufficiently high that the
engine/transmission can be unbolted as a
single unit and lowered to the ground; the
engine/transmission unit can then be
withdrawn from under the vehicle and
separated. An engine hoist or A-frame will
therefore be necessary. Make sure the
equipment is rated in excess of the combined
weight of the engine and transmission. Safety
is of primary importance, considering the
potential hazards involved in removing the
engine/transmission from the vehicle.
If this is the first time you have removed an
engine, a helper should ideally be available.
Advice and aid from someone more
experienced would also be helpful. There are
many instances when one person cannot
simultaneously perform all of the operations
required when removing the engine/
transmission from the vehicle.
Plan the operation ahead of time. Arrange for,
or obtain, all of the tools and equipment you’ll
need prior to beginning the job. Some of the
equipment necessary to perform
engine/transmission removal and installation
3 Engine/transmission removal -
methods and precautions
2 Engine overhaul -
general information
1 General information
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•3
2B
procarmanuals.com
Page 71 of 279

(a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator) (see
illustration).
(b) One from the union on the inlet manifold’s
left-hand end (see illustration).
(c) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose - from the inlet manifold (see
Chapter 9 for details).
(d) Also disconnect the vacuum hoses from
the Exhaust Gas Recirculation system
components - one from the EGR valve,
two from the EGR pipe (note that these
last two are of different sizes, as are their
pipe stubs, so that they can only be
connected the correct way round).
(e) While you are there, trace the vacuum line
from the pulse-air filter housing over the
top of the transmission, and disconnect it
by pulling the plastic pipe out of the
rubber hose just beneath the bulkhead-
mounted pulse-air solenoid valve (see
illustration).
(f) Secure all these hoses so that they won’t
get damaged as the engine/transmission
is removed.
11Unbolt the engine/transmission-to-body
earth lead from the transmission’s top surface
(see illustration). Disconnect the speed-
ometer drive cable (see Chapter 12) and
secure it clear of the engine/transmission.
12Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, disconnect the clutch cable (seeChapter 8). Where automatic transmission is
fitted, disconnect the selector cable (see
Chapter 7, Part B). Secure the cable clear of
the engine/transmission.
13Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above), disconnect the engine wiring loom
from the body as follows:
(a) Starting at the left-hand side of the engine
compartment, release and unplug the
three large electrical connectors clipped
to the suspension mounting - note the
wire clips fitted to some connectors (see
illustration).
(b) Disconnect and/or release the battery-to-
starter motor wiring, noting the single
connector which must be unplugged.
(c) Unplug the electrical connector(s) to
disconnect the vehicle speed sensor,
oxygen sensor and, where fitted, the oil
level sensor wiring - unclip the connectors
to release the wiring where necessary.
(d) Work along the loom to the bulkhead,
unclipping the loom and unplugging the
various bulkhead-mounted components
connected into it, until you reach the
right-hand side of the engine
compartment (see illustration).
(e) Carefully prise the power steering fluid
reservoir upwards out of its clip on the
suspension mounting, then unscrew the
ECU connector’s retaining bolt and
unplug the connector (see illustration).
(f) Unbolt the earth lead from the right-hand
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•5
2B
4.13A Unplug three large electrical
connectors (arrowed) . . .4.13B . . . unplug engine wiring loom from
battery wiring and bulkhead components
(arrowed) . . .4.13C . . . and disconnect ECU wiring and
earth lead (arrowed) to release engine
wiring loom from vehicle body
4.9C . . . and the earth lead from the
cylinder head rear support plate/engine
lifting eye4.10A Disconnect vacuum hose shown
from rear of throttle housing . . .4.10B . . . vacuum hose (arrowed) from
union on left-hand end on inlet manifold . . .
4.10C . . . also brake servo hose (A), EGR
valve hose (B), EGR pipe hoses (C) - noting
their different sizes - and pulse-air filter
vacuum line (D)
4.11 Unbolt the engine/transmission-to-
body earth lead - hidden behind wiring
loom guide - from location (arrowed) on
the transmission’s top surface
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 279

inner wing panel, release the engine
wiring loom and refit the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(g) Secure the engine wiring loom neatly to
the engine/transmission so that it cannot
be damaged as the unit is removed from
the vehicle.
14Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow
the upper part to be withdrawn.
15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the power steering pump (see
Chapter 10); secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
17Raise the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands, then remove the front
roadwheels. Drain the cooling system and (if
the engine is to be dismantled) drain the
engine oil and remove the oil filter (see
Chapter 1). Also drain the transmission as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 7.
18Withdraw the lower part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield.
19Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then unhook all the system’s rubber
mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle (see
Chapter 4 for details).
20Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, mark their positions, then
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
transmission support rods from the rear of the
transmission. Unscrew the retaining nuts, and
withdraw the gear linkage heat shield from the
underbody. Unbolt the rear end of the linkage
from the underbody, swivel the linkage around
to the rear, and tie it to the underbody (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
21Disconnect both anti-roll bar links from
their respective suspension strut - note the
flexible brake hose bracket attached to each
link stud - and both track rod ends from their
steering knuckles. Unfasten the clamp bolt
securing each front suspension lower arm
balljoint to its steering knuckle (see Chap-
ter 10 for details). Check that both balljoints
can be released from the knuckle assemblies
when required, but leave them in place for thetime being, secured by the clamp bolts if
necessary.
22Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unbolt the accumulator/
dehydrator from the subframe; secure it as far
as possible (without disconnecting the
system’s hoses) clear of the engine/
transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
23Unbolt the steering gear from the
subframe; if the bolts are not accessible from
above, a Ford service tool will be required to
reach them from underneath the vehicle (see
Chapter 10 for details).
24Unscrew the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
25Hold the radiator in its raised position, by
inserting split pins through the holes in the
rear of the engine compartment front
crossmember and into the radiator’s upper
mounting extensions. Unbolt the radiator
mounting brackets from the subframe; note
that they are handed, and are marked to
ensure correct refitting (see illustrations).
Collect and store the bottom mounting
rubbers for safekeeping, noting which way up
they are fitted.
26Unbolt the engine/transmission rear
mounting from the subframe - where the
vehicle is fitted with automatic transmission, a
separate damper may be fitted beneath the
subframe, which must be unbolted to reach
the mounting’s fasteners. Where the vehicle is
fitted with manual transmission, also unscrew
the mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting bracket from the transmission.
27Unscrew the engine/transmission front
mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting from the subframe, noting the
location of the wiring connector bracket.
28Use white paint or similar (do not use a
sharp-pointed scriber, which might break the
underbody protective coating and cause
rusting) to mark the exact relationship of the
subframe to the underbody. Unscrew the four
mounting bolts from the subframe (note their
different-sized washers - see also illus-tration 4.47A) and allow the subframe to hang
down on the suspension lower arm balljoints.
Disconnect the balljoints one at a time from
the steering knuckle assemblies (see Chap-
ter 10) and lower the subframe to the ground;
withdraw the subframe from under the
vehicle.
29Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above) and catching as much as possible of
the escaping coolant in the drain tray,
disconnect the cooling system hoses and
pipes as follows - refer to Chapter 3 for further
details, if required:
(a) Remove the radiator top hose.
(b) Remove the (heater) hose running from
the thermostat to the engine
compartment bulkhead union.
(c) Disconnect from the thermostat the hose
running to the expansion tank - secure the
hose clear of the working area.
(d) Disconnect from the thermostat the
coolant hose/pipe which runs to the
radiator bottom hose.
(e) Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union, from the (sump) heater
coolant pipe and from the water pump
union - secure the hose clear of the
working area.
(f) Unbolt the (heater) coolant pipe from the
sump, trace the pipe/hose round to the
engine compartment bulkhead union,
disconnecting (where fitted) the oil cooler
hoses from the cooler unions, then
remove it.
(g) Unless the vehicle has air conditioning
fitted, secure the radiator as far forwards
as possible while it is in its raised position;
if air conditioning is fitted, remove the
radiator completely (see Chapter 3).
30Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unplug the compressor’s
electrical connector, and unbolt the
compressor from the engine (see
illustration). Secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
2B•6 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.25A Use split pins as shown to secure
radiator in its raised position . . .
4.25B . . . while you unbolt the bottom
mountings (arrowed) - note that the
mountings are handed, and do not lose the
mounting rubbers
4.30 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to release
air conditioning compressor from engine
procarmanuals.com
Page 84 of 279

Note:Always check first what replacement
parts are available before planning any
overhaul operation; refer to Section 1 of this
Part. A Ford dealer, or a good engine
reconditioning specialist/automotive parts
supplier, may be able to suggest alternatives
which will enable you to overcome the lack of
replacement parts.
1Clean the crankshaft, and dry it with
compressed air if available.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air! Be
sure to clean the oil holes with a
pipe cleaner or similar probe.
2Check the main and crankpin (big-end)
bearing journals for uneven wear, scoring,
pitting and cracking.
3Rub a penny across each journal several
times (see illustration). If a journal picks up
copper from the penny, it is too rough.
4Remove all burrs from the crankshaft oil
holes with a stone, file or scraper.
5Using a micrometer, measure the diameter
of the main bearing and crankpin (big-end)
journals, and compare the results with the
Specifications at the beginning of this Chapter
(see illustration).
6By measuring the diameter at a number of
points around each journal’s circumference,
you will be able to determine whether or not
the journal is out-of-round. Take the
measurement at each end of the journal, near
the webs, to determine if the journal is
tapered.
7If the crankshaft journals are damaged,
tapered, out-of-round, or worn beyond the
limits specified in this Chapter, the crankshaft
must be taken to an engine overhaul
specialist, who will regrind it, and who can
supply the necessary undersize bearing
shells.
8Check the oil seal journals at each end of
the crankshaft for wear and damage. If either
seal has worn an excessive groove in itsjournal, consult an engine overhaul specialist,
who will be able to advise whether a repair is
possible, or whether a new crankshaft is
necessary.
Note:Always check first what replacement
parts are available before planning any
overhaul operation; refer to Section 1 of this
Part. A Ford dealer, or a good engine
reconditioning specialist/automotive parts
supplier, may be able to suggest alternatives
which will enable you to overcome the lack of
replacement parts.
1Even though the main and big-end bearing
shells should be renewed during the engine
overhaul, the old shells should be retained for
close examination, as they may reveal
valuable information about the condition of
the engine (see illustration).
2Bearing failure occurs because of lack of
lubrication, the presence of dirt or other
foreign particles, overloading the engine, and
corrosion. Regardless of the cause of bearing
failure, it must be corrected before the engine
is reassembled, to prevent it from happening
again.
3When examining the bearing shells, remove
them from the cylinder block/crankcase and
main bearing caps, and from the connecting
rods and the big-end bearing caps, then lay
them out on a clean surface in the same
general position as their location in the
engine. This will enable you to match any
bearing problems with the corresponding
crankshaft journal. Do nottouch any shell’s
bearing surface with your fingers while
checking it, or the delicate surface may be
scratched.
4Dirt or other foreign matter gets into the
engine in a variety of ways. It may be left in
the engine during assembly, or it may pass
through filters or the crankcase ventilation
system. It may get into the oil, and from there
into the bearings. Metal chips from machining
operations and normal engine wear are often
present. Abrasives are sometimes left in
engine components after reconditioning,especially when parts are not thoroughly
cleaned using the proper cleaning methods.
Whatever the source, these foreign objects
often end up embedded in the soft bearing
material, and are easily recognized. Large
particles will not embed in the material, and
will score or gouge the shell and journal. The
best prevention for this cause of bearing
failure is to clean all parts thoroughly, and to
keep everything spotlessly-clean during
engine assembly. Frequent and regular engine
oil and filter changes are also recommended.
5Lack of lubrication (or lubrication
breakdown) has a number of inter-related
causes. Excessive heat (which thins the oil),
overloading (which squeezes the oil from the
bearing face) and oil leakage (from excessive
bearing clearances, worn oil pump or high
engine speeds) all contribute to lubrication
breakdown. Blocked oil passages, which
usually are the result of misaligned oil holes in
a bearing shell, will also starve a bearing of oil,
and destroy it. When lack of lubrication is the
cause of bearing failure, the bearing material
is wiped or extruded from the shell’s steel
backing. Temperatures may increase to the
point where the steel backing turns blue from
overheating.
6Driving habits can have a definite effect on
bearing life. Full-throttle, low-speed operation
(labouring the engine) puts very high loads on
bearings, which tends to squeeze out the oil
film. These loads cause the shells to flex,
which produces fine cracks in the bearing
face (fatigue failure). Eventually, the bearing
material will loosen in pieces, and tear away
from the steel backing. Short-distance driving
leads to corrosion of bearings, because
insufficient engine heat is produced to drive
off condensed water and corrosive gases.
These products collect in the engine oil,
forming acid and sludge. As the oil is carried
14 Main and big-end bearings-
inspection
13 Crankshaft - inspection
2B•18 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
13.3 Rubbing a penny lengthwise along
each journal will reveal its condition - if
copper rubs off and is embedded in the
crankshaft, the journals should be
reground13.5 Measure the diameter of each
crankshaft journal at several points, to
detect taper and out-of-round conditions
14.1 When inspecting the main and big-
end bearings, look for these problems
procarmanuals.com
Page 89 of 279

Chapter 3
Cooling, heating, and air conditioning systems
Air conditioning system - general information
and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Air conditioning system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system checks (coolant leaks,
hose condition) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system electrical switches and sensors -
testing, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Cooling system hoses - disconnection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . 3Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing
and refilling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater/air conditioning controls - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 10
Heater/ventilation components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Pollen filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Radiator and expansion tank - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Radiator electric cooling fan(s) - testing, removal and refitting . . . . . 5
Thermostat - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Water pump - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Coolant
Mixture type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
System pressure
Pressure test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 bars - should hold this pressure for at least 10 seconds
Expansion tank filler cap
Pressure rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 bars approximately - see cap for actual value
Thermostat
Starts to open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88°C
Radiator electric cooling fan
Switches on at:
Single-speed fans, two-speed fans - first stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C
Two-speed fans - second stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103°C
Switches off at:
Single-speed fans, two-speed fans - first stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93°C
Two-speed fans - second stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C
Coolant temperature sensor
Resistance:
At -40°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 860.0 to 900.0 kilohms
At 20°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35.0 to 40.0 kilohms
At 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 to 2.5 kilohms
At 120°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.3 kilohms
Air conditioning system
Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . R134a
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
3
procarmanuals.com
Page 96 of 279
duct is lowered from the air distributor and
secured with its screw.
16Refill the cooling system with the proper
mixture of antifreeze and water (see Chapter
1). Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature, indicated by
the radiator top hose becoming hot. Recheck
the coolant level and add more if required,
then check for leaks. Check the operation of
the heater.
Pollen filter
17Refer to Chapter 1.
Blower/air conditioning control
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Remove the ashtray. Referring to the
relevant Sections of Chapter 11, undo the two
upper screws from the centre console and
pull out the cassette storage compartment,
then remove the radio/cassette player.
3Pull the heater control/radio bezel out of the
three clips securing its top edge, pull it
forwards and unplug the switch electrical
connector (where fitted).
4Pull off the heater control knobs, and
remove the screw securing each end of the
heater control unit (see illustration). Pull the
control unit out of the facia.
5Unplug the two electrical connectors from
the blower/air conditioning control. Remove
the retaining screw and withdraw the control,
twisting it to release it from the panel.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Check the operation of the control
on completion.
Temperature control
Removal
7Remove the heater control unit as
described in paragraphs 1 to 4 above.
8On vehicles without air conditioning,unhook the operating cable from the
temperature control (see illustration); where
air conditioning is fitted, unplug the control’s
electrical connector. Undo the retaining
screw, and withdraw the control.
Refitting
9Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; check the operation of the control
on completion.
Air distribution control
Removal
10Remove the heater control unit as
described in paragraphs 1 to 4 above. Unplug
the electrical connectors, and unhook the
operating cable (where fitted) to withdraw the
unit (see illustration).
11Use a pair of slim screwdrivers to release
the clips on each side of the control, then
withdraw the control from the unit.
Refitting
12Refitting is the reverse of the removalprocedure. Check the operation of the
controls on completion.
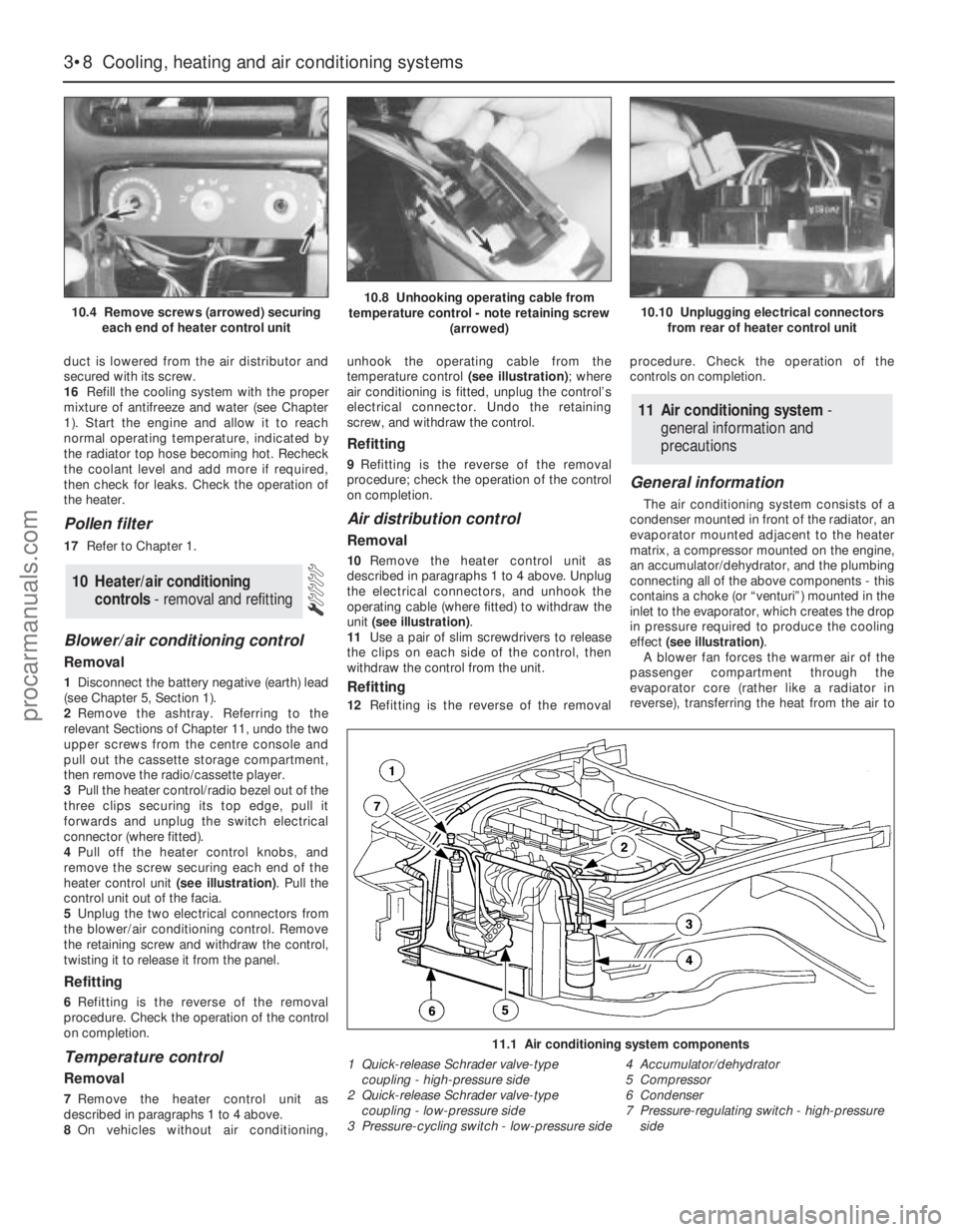
General information
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
an accumulator/dehydrator, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components - this
contains a choke (or “venturi”) mounted in the
inlet to the evaporator, which creates the drop
in pressure required to produce the cooling
effect (see illustration).
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator core (rather like a radiator in
reverse), transferring the heat from the air to
11 Air conditioning system -
general information and
precautions
10 Heater/air conditioning
controls- removal and refitting
3•8 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
10.4 Remove screws (arrowed) securing
each end of heater control unit10.8 Unhooking operating cable from
temperature control - note retaining screw
(arrowed)10.10 Unplugging electrical connectors
from rear of heater control unit
11.1 Air conditioning system components
1 Quick-release Schrader valve-type
coupling - high-pressure side
2 Quick-release Schrader valve-type
coupling - low-pressure side
3 Pressure-cycling switch - low-pressure side4 Accumulator/dehydrator
5 Compressor
6 Condenser
7 Pressure-regulating switch - high-pressure
side
procarmanuals.com
Page 97 of 279

the refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off
into low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with
it when it leaves the evaporator.
Precautions
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
When an air conditioning system is fitted, it
is necessary to observe the following special
precautions whenever dealing with any part of
the system, its associated components, and
any items which necessitate disconnection of
the system:
(a) While the refrigerant used - R134a - is
less damaging to the environment than
the previously-used R12, it is still a very
dangerous substance. It must not be
allowed into contact with the skin or eyes,
or there is a risk of frostbite. It must also
not be discharged in an enclosed space -
while it is not toxic, there is a risk of
suffocation. The refrigerant is heavier than
air, and so must never be discharged over
a pit.
(b) The refrigerant must not be allowed to
come in contact with a naked flame,
otherwise a poisonous gas will be created
- under certain circumstances, this can
form an explosive mixture with air. For
similar reasons, smoking in the presence
of refrigerant is highly dangerous,
particularly if the vapour is inhaled
through a lighted cigarette.
(c) Never discharge the system to the
atmosphere - R134a is not an ozone-
depleting ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC) as is
R12, but is instead a hydrofluorocarbon,
which causes environmental damage by
contributing to the “greenhouse effect” if
released into the atmosphere.
(d) R134a refrigerant must notbe mixed with
R12; the system uses different seals (now
green-coloured, previously black) and has
different fittings requiring different tools,
so that there is no chance of the two
types of refrigerant becoming mixed
accidentally.
(e) If for any reason the system must be
disconnected, entrust this task to your
Ford dealer or a refrigeration engineer.
(f) It is essential that the system be
professionally discharged prior to using
any form of heat - welding, soldering,
brazing, etc - in the vicinity of the system,
before having the vehicle oven-dried at a
temperature exceeding 70°C after
repainting, and before disconnecting any
part of the system.Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until after the
system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Cap or plug the pipe lines as
soon as they are disconnected, to prevent
the entry of moisture. Always wear eye
protection when disconnecting air
conditioning system fittings.
Note: This Section refers to the components
of the air conditioning system itself - refer to
Sections 9 and 10 for details of components
common to the heating/ventilation system.
Condenser
1Have the refrigerant discharged at a dealer
service department or an automotive air
conditioning repair facility.
2Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
3Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).
4Using the Ford service tool 34-001,
disconnect the refrigerant lines from the
condenser. Immediately cap the open fittings,
to prevent the entry of dirt and moisture.
5Unbolt the condenser (see illustration 7.5)
and lift it out of the vehicle. Store it upright, to
prevent oil loss.
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7If a new condenser was installed, add 20 cc
of refrigerant oil to the system.
8Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist who discharged
it.
Evaporator
9The evaporator is mounted with the heater
matrix. Apart from the need to have the
refrigerant discharged, and to use Ford
service tools 34-001 and 34-003 to
disconnect the lines, the procedure is as
described in Section 9 of this Chapter.
10On reassembly, if a new evaporator was
installed, add 20 cc of refrigerant oil to the
system.
11Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist who discharged
it.
Compressor
12Have the refrigerant discharged at a
dealer service department or an automotive
air conditioning repair facility.
13Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead (see Chapter 5, Section 1).
14Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the compressor from the cylinder
block/crankcase, press it to one side, and
unscrew the clamping bolt to disconnect the
refrigerant lines. Plug the line connections,
swing the compressor upright, unplug its
electrical connector, then withdraw the
compressor from the vehicle. Note:Keep the
compressor level during handling and storage.
If the compressor has seized, or if you find
metal particles in the refrigerant lines, the
system must be flushed out by an air
conditioning technician, and the
accumulator/dehydrator must be renewed.
17Prior to installation, turn the compressor
clutch centre six times, to disperse any oil that
has collected in the head.
18Refit the compressor in the reverse order
of removal; renew all seals disturbed.
19If you are installing a new compressor,
refer to the compressor manufacturer’s
instructions for adding refrigerant oil to the
system.
20Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist that discharged
it.
Accumulator/dehydrator
21Have the refrigerant discharged at a
dealer service department or an automotive
air conditioning repair facility.
22Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead (see Chapter 5, Section 1).
23The accumulator/dehydrator, which acts
as a reservoir and filter for the refrigerant, is
located in the left-hand front corner of the
engine compartment. Using the Ford service
tool 34-003, disconnect the refrigerant line
next to the accumulator/dehydrator from the
compressor. Immediately cap the open
fittings, to prevent the entry of dirt and
moisture, then unplug the pressure-cycling
switch electrical connector (see illustration).
24Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).
25Unbolt the accumulator/dehydrator from
the front suspension subframe.
26Using the Ford service tool 34-003,
disconnect the lower refrigerant line from the
accumulator/dehydrator. It may be necessary
12 Air conditioning system
components -
removal and refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•9
3
12.23 Unplug pressure-cycling switch
electrical connector (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 99 of 279

Chapter 4 Fuel and exhaust systems
Accelerator cable (models with traction control) -
removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Accelerator cable (models without traction control) -
removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Accelerator pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Air cleaner assembly/air intake components - removal and refitting . 4
Air filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 6
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2A
Exhaust system - general information and component renewal . . . . 17
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel cut-off switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel injection system/engine management system - check . . . . . . . 15
Fuel injection system/engine management system - general . . . . . 14Fuel lines and fittings - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 9
Fuel pump/fuel pressure - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Fuel system - depressurisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuel system components - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Fuel tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fuel tank cleaning and repair - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment . . . . . . See Section 14
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2A
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 6
Roll-over valves - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Underbody fuel/brake line check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Underbonnet hose check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
General
Idle speed:
Regulated - nominal (± 50 rpm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830 to 880 rpm*
Unregulated - base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500 rpm*
Idle mixture (CO level) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not available
* Given for reference only - not adjustable.
Rev limiter operation
Fuel injectors shut off at:
Automatic transmission, position “N” selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4100 rpm
Automatic transmission, any other position selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6800 rpm (approximately)
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6800 to 7100 rpm
Fuel pressure
Regulated fuel pressure - engine running at idle speed:
Pressure regulator vacuum hose connected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 ± 0.2 bars
Pressure regulator vacuum hose disconnected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.7 ± 0.2 bars
Note:When the ignition is switched off, the system should hold 1.8 bars for 5 minutes. If the engine is hot, the pressure may rise to maximum of
2.7 bars during this check. Pressure regulator (when reconnected) should prevent any higher pressure being reached.
Fuel injectors
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.7 to 15.2 ohms
Idle speed control valve
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 to 14 ohms
Idle-increase solenoid valve
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 to 120 ohms
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Plenum chamber-to-inlet manifold fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 3
Throttle housing-to-inlet manifold screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Idle speed control valve bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 4
Fuel pressure regulator bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 4
Fuel injector bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 4
Fuel rail-to-inlet manifold bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Fuel feed and return line threaded couplings at fuel rail . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 to 30 17 to 22
All exhaust system nuts and bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 to 45 30 to 33
4•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
4
procarmanuals.com