1993 FORD MONDEO fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 88 of 279

rod’s big-end onto the crankpin. The piston
rings may try to pop out of the ring
compressor just before entering the cylinder
bore, so keep some pressure on the ring
compressor. Work slowly, and if any
resistance is felt as the piston enters the
cylinder, stop immediately. Find out what’s
binding, and fix it before proceeding. Do not,
for any reason, force the piston into the
cylinder - you might break a ring and/or the
piston.
10To check the big-end bearing running
clearance, cut a piece of the appropriate-size
Plastigage slightly shorter than the width of
the connecting rod bearing, and lay it in place
on the No 1 crankpin (big-end) journal, parallel
with the crankshaft centre-line (see illus-
tration 17.6).
11Clean the connecting rod-to-cap mating
surfaces, and refit the big-end bearing cap.
Make sure the etched number on the cap is
on the same side as that on the rod (see
illustration). Tighten the cap bolts evenly -
first use a torque wrench to tighten the bolts
to the specified (first stage) torque setting,
then use an ordinary socket extension bar
and an angle gauge to tighten the bolts
further through the specified (second stage)
angle. Use a thin-wall socket, to avoid
erroneous torque readings that can result if
the socket is wedged between the cap and
nut. If the socket tends to wedge itself
between the nut and the cap, lift up on it
slightly until it no longer contacts the cap.
Don’t rotate the crankshaft at any time during
this operation!
12Unscrew the bolts and detach the cap,
being very careful not to disturb the
Plastigage.
13Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale printed on the
Plastigage envelope, to obtain the running
clearance (see illustration 17.10). Compare it
to the Specifications, to make sure the
clearance is correct.
14If the clearance is not as specified, seek
the advice of a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist - if the crankshaft
journals are in good condition (see Sec-
tion 13), it may be possible simply to renew
the shells to achieve the correct clearance. If
this is not possible, the crankshaft must bereground by a specialist, who can also supply
the necessary undersized shells. First though,
make sure that no dirt or oil was trapped
between the bearing shells and the
connecting rod or cap when the clearance
was measured. Also, recheck the crankpin
diameter. If the Plastigage was wider at one
end than the other, the crankpin journal may
be tapered (see Section 13).
15Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the journal and the
bearing surface. Be very careful not to scratch
the bearing - use your fingernail or the edge of
a credit card.
Final piston/connecting rod
refitting
16Make sure the bearing surfaces are
perfectly clean, then apply a uniform layer of
clean molybdenum disulphide-based grease,
engine assembly lubricant, or clean engine oil,
to both of them. You’ll have to push the piston
into the cylinder to expose the bearing surface
of the shell in the connecting rod.
17Slide the connecting rod back into place
on the crankpin (big-end) journal, refit the big-
end bearing cap, and then tighten the bolts in
two stages, as described above.
18Repeat the entire procedure for the
remaining piston/connecting rod assemblies.
19The important points to remember are:
(a) Keep the backs of the bearing shells and
the recesses of the connecting rods and
caps perfectly clean when assembling
them.
(b) Make sure you have the correct
piston/rod assembly for each cylinder -
use the etched cylinder numbers to
identify the front-facing side of both the
rod and its cap.
(c) The arrow on the piston crown must face
the timing belt end of the engine.
(d) Lubricate the cylinder bores with clean
engine oil.
(e) Lubricate the bearing surfaces when
refitting the big-end bearing caps after the
running clearance has been checked.
20After all the piston/connecting rod
assemblies have been properly installed,
rotate the crankshaft a number of times by
hand, to check for any obvious binding.1With the engine refitted in the vehicle,
double-check the engine oil and coolant
levels. Make a final check that everything has
been reconnected, and that there are no tools
or rags left in the engine compartment.
2With the spark plugs removed and the
ignition system disabled by unplugging the
ignition coil’s electrical connector, remove
fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump. Turn the
engine on the starter until the oil pressure
warning light goes out.
3Refit the spark plugs, and connect all the
spark plug (HT) leads (Chapter 1). Reconnect
the ignition coil wiring, refit the fuel pump fuse,
then switch on the ignition and listen for the fuel
pump; it will run for a little longer than usual,
due to the lack of pressure in the system.
4Start the engine, noting that this also may
take a little longer than usual, due to the fuel
system components being empty.
5While the engine is idling, check for fuel,
coolant and oil leaks. Don’t be alarmed if
there are some odd smells and smoke from
parts getting hot and burning off oil deposits.
If the hydraulic tappets have been disturbed,
some valve gear noise may be heard at first;
this should disappear as the oil circulates fully
around the engine, and normal pressure is
restored in the tappets.
6Keep the engine idling until hot water is felt
circulating through the top hose, check that it
idles reasonably smoothly and at the usual
speed, then switch it off.
7After a few minutes, recheck the oil and
coolant levels, and top-up as necessary
(Chapter 1).
8If they were tightened as described, there is
no need to re-tighten the cylinder head bolts
once the engine has first run after reassembly
- in fact, Ford state that the bolts must notbe
re-tightened.
9If new components such as pistons, rings
or crankshaft bearings have been fitted, the
engine must be run-in for the first 500 miles
(800 km). Do not operate the engine at full-
throttle, or allow it to labour in any gear during
this period. It is recommended that the oil and
filter be changed at the end of this period.
19 Engine -
initial start-up after overhaul
2B•22 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
procarmanuals.com
Page 100 of 279

This Chapter is concerned with those
features of the engine management system
that supply clean fuel and air to the engine,
meter it in the required proportions, and
dispose of the results. Since the emission
control sub-systems modify the functions of
both the fuel and exhaust sub-systems, all of
which are integral parts of the whole engine
management system, there are many cross-
references to Chapters 5 and 6. Information
on the electronic control system, its fault
diagnosis, sensors and actuators, is given in
Chapter 6.
The air intake system consists of several
plastics components designed to eliminate
induction roar as much as possible. The air
intake tube (opening behind the direction
indicator/headlight assembly) is connected,
via small and large resonators located under
the front left-hand wing, to the air cleaner
assembly in the engine compartment. Once it
has passed through the filter element and the
air mass meter, the air enters the plenum
chamber mounted above the throttle housing
and inlet manifold; the resonator mounted in
the engine compartment further reduces noise
levels.
The fuel system consists of a plastic tank
(mounted under the body, beneath the rear
seats), combined metal and plastic fuel hoses,
an electric fuel pump mounted in the fuel tank,
and an electronic fuel injection system.
The exhaust system consists of an exhaust
manifold, the front downpipe and catalytic
converter and, on production-fit systems, a
rear section incorporating two or three
silencers and the tailpipe assembly. The
service replacement exhaust system consists
of three or four sections: the front
downpipe/catalytic converter, the
intermediate pipe and front silencer, and the
tailpipe and rear silencer. On some versions,
the tailpipe is in two pieces, with two rear
silencers. The system is suspended
throughout its entire length by rubber
mountings.
Extreme caution should be exercised when
dealing with either the fuel or exhaust
systems. Fuel is a primary element for
combustion. Be very careful! The exhaust
system is an area for exercising caution, as it
operates at very high temperatures. Serious
burns can result from even momentary
contact with any part of the exhaust system,
and the fire risk is ever-present. The catalytic
converter in particular runs at very high
temperatures - refer to the information in
Chapter 6.
Warning: Many of the procedures
in this Chapter require the
removal of fuel lines and
connections, which may result in
some fuel spillage. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautionswhen you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand. Before carrying out any operation
on the fuel system, refer also to the
precautions given in “Safety first!” at the
beginning of this manual, and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly-dangerous and
volatile liquid, and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed.
Warning: The fuel system will
remain pressurised for long
periods of time after the engine is
switched off - this pressure must
be released before any part of the system
is disturbed. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautions
when you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
1The fuel system referred to in this Chapter
is defined as the fuel tank and tank-mounted
fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit, the fuel
filter, the fuel injectors and the pressure
regulator in the injector rail, and the metal
pipes and flexible hoses of the fuel lines
between these components. All these contain
fuel, which will be under pressure while the
engine is running and/or while the ignition is
switched on.
2The pressure will remain for some time after
the ignition has been switched off, and must
be relieved before any of these components is
disturbed for servicing work.
3The simplest method is simply to
disconnect the fuel pump’s electrical supply
while the engine is running - either by
removing the fuel pump fuse (number 14), or
by lifting the red button on the fuel cut-off
switch (see Section 13) - and to allow the
engine to idle until it dies through lack of fuel
pressure. Turn the engine over once or twice
on the starter to ensure that all pressure is
released, then switch off the ignition; do not
forget to refit the fuse (or depress the redbutton, as appropriate) when work is
complete.
4The Ford method of depressurisation is to
use service tool 29-033 fitted to the fuel rail
pressure test/release fitting - a Schrader-type
valve with a blue plastic cap, located on the
union of the fuel feed line and the fuel rail - to
release the pressure, using a suitable
container and wads of rag to catch the spilt
fuel. Do notsimply depress the valve core to
release fuel pressure - droplets of fuel will
spray out, with a consequent risk of fire, and
of personal injury through fuel getting into
your eyes.
Warning: Either procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run. Remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
5Note that, once the fuel system has been
depressurised and drained (even partially), it
will take significantly longer to restart the
engine - perhaps several seconds of cranking
- before the system is refilled and pressure
restored.
Warning: The fuel system
pressure must be released before
any part of the system is
disturbed - see Section 2. Petrol
is extremely flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on any part of
the fuel system. Don’t smoke, or allow
open flames or bare light bulbs, near the
work area. Don’t work in a garage where a
natural gas-type appliance (such as a
water heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot
light is present. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
Disconnecting and connecting
quick-release couplings
1Quick-release couplings are employed at all
unions in the fuel feed and return lines.
2Before disconnecting any fuel system
component, relieve the residual pressure in
the system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
3 Fuel lines and fittings-
general information
2 Fuel system - depressurisation
1 General information and
precautions
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 101 of 279

3Release the protruding locking lugs on each
union, by squeezing them together and
carefully pulling the coupling apart. Use rag to
soak up any spilt fuel. Where the unions are
colour-coded, the pipes cannot be confused.
Where both unions are the same colour, note
carefully which pipe is connected to which,
and ensure that they are correctly
reconnected on refitting (see illustration).
4To reconnect one of these couplings, press
them together until the locking lugs snap into
their groove. Switch the ignition on and off
five times to pressurise the system, and check
for any sign of fuel leakage around the
disturbed coupling before attempting to start
the engine.
Checking
5Checking procedures for the fuel lines are
included in Chapter 1.
Component renewal
6If you must renew any damaged sections,
use original-equipment replacement hoses or
pipes, constructed from exactly the same
material as the section you are replacing. Do
not install substitutes constructed from
inferior or inappropriate material, or you could
cause a fuel leak or a fire.
7Before detaching or disconnecting any part
of the fuel system, note the routing of all
hoses and pipes, and the orientation of all
clamps and clips. Replacement sections must
be installed in exactly the same manner.8Before disconnecting any part of the fuel
system, be sure to relieve the fuel system
pressure (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap. Also
disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead -
see Chapter 5, Section 1. Cover the fitting
being disconnected with a rag, to absorb any
fuel that may spray out.
Air cleaner assembly
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
2Unclip the air mass meter from the air
cleaner cover (see Chapter 6).
3Disconnect the crankcase breather hose,
either from the air cleaner housing or from the
cylinder head cover union (see illustration).
4Remove the rubber retaining band (see
illustration). Withdraw the air cleaner
assembly, lifting it upwards out of its
grommets, and releasing it from the rubber
connector sleeve in the inner wing panel.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Ensure that the housing pegs seat
correctly in their grommets, and that the
intake mouth is fully engaged inside the
connector sleeve (see illustration).
Air intake components
Note:Depending on the reason for removal,
these components can be removed either
individually, or as one assembly. For example,
unplugging the two electrical connectors and
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted),
will allow the air cleaner assembly cover to be
removed with the air mass meter, the
resonator and the plenum chamber.
Air mass meter
6Refer to Section 4 of Chapter 6.
Resonator (engine compartment)
7Unbolt the resonator support bracket from
the engine compartment front crossmember.
Slacken the two clamp screws securing the
resonator to the air mass meter and plenum
chamber hoses. Swing the resonator clear of
the thermostat housing, and unplug the intake
air temperature sensor’s electrical connector
(see illustration). Withdraw the resonator.
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Plenum chamber
9Prising out the rubber plugs covering them,
undo the chamber’s fasteners (see
illustration). Slacken the clamp screw
securing the chamber to the resonator hose.
10Lift the chamber and (where fitted)
disconnect the vacuum hose from its
underside. Withdraw the chamber - note the
two rubber spacers (one on each throttle
4 Air cleaner assembly and air
intake components -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•3
4
4.5 Ensure air filter housing intake mouth
is fully engaged inside connector sleeve4.7 Unplugging intake air temperature
sensor’s electrical connector4.9 Plenum chamber fasteners (arrowed) -
four shown here, some vehicles may only
have three
3.3 Disconnect fuel line quick-release
couplings by squeezing together protruding
locking lugs and pulling coupling apart4.3 Disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head union4.4 Remove rubber retaining band to
withdraw air cleaner assembly
procarmanuals.com
Page 103 of 279

which pulley, disconnect the first cable end
nipple from the throttle actuator’s upper
pulley, then slide the cable outer upwards out
of the actuator housing. Disconnect the
second cable in the same way from the
actuator’s lower pulley.
6Working in the passenger compartment,
reach up to the top of the accelerator pedal.
Pull the end fitting and collar out of the pedal,
then release the cable inner wire through the
slot in the pedal. Tie a length of string to the
end of the cable.
7Returning to the engine compartment, pull
the cable through the bulkhead until the string
can be untied and the pedal-to-actuator cable
removed.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Use the string to draw the pedal-
to-actuator cable through the bulkhead.
Ensure that each cable end is connected to
the correct actuator pulley.
9Adjust both cables as described below.
Adjustment
Note:Both sections of the cable must be
adjusted together, even if only one has been
disturbed.
10Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
11Remove the metal clip from the adjuster
of each cable section (see illustration), and
lubricate the adjusters’ grommets with soapy
water.
12Remove any slack by pulling both cable
outers as far as possible out of their
respective adjusters.
13Unplug the TCS throttle actuator’s
electrical connector, and prise off its cover.
Lock both pulleys together by pushing a
locking pin (a pin punch or a similar tool of
suitable size) into their alignment holes.
Disconnect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable’s end nipple from the throttle linkage.
14Have an assistant depress the accelerator
pedal fully. The pedal-to-actuator cable outer
will move back into the adjuster; hold it there,
and refit the clip.
15Connect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable end nipple to the throttle linkage, andcheck that the cable outer’s grommet is
correctly secured in the housing bracket.
16Again have the assistant depress the
accelerator pedal fully. The actuator-to-
throttle housing cable outer will move back
into the adjuster; hold it there, and refit the
clip.
17Remove the locking pin from the pulleys.
Check that the throttle valve moves smoothly
and easily from the fully-closed to the fully-
open position and back again, as the
assistant depresses and releases the
accelerator pedal. Re-adjust the cable(s) if
required.
18When the setting is correct, refit the TCS
throttle actuator’s cover and electrical
connector, then refit the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
1Disconnect the cable inner wire from the
pedal - see Section 5 or 6, as appropriate.
2Undo the retaining nuts and bolt, then
withdraw the pedal assembly (see
illustration).
3Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Adjust the cable(s) as described in
the relevant Section of this Chapter.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
Fuel pump operation check
1Switch on the ignition and listen for the fuel
pump (the sound of an electric motor running,
audible from beneath the rear seats). Assuming
there is sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump
should start and run for approximately one or
two seconds, then stop, each time the ignition
is switched on. Note:If the pump runs
continuously all the time the ignition is switched
on, the electronic control system is running in
the backup (or “limp-home”) mode referred to
by Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
ECU itself, and the vehicle should therefore be
taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the
complete system, using the correct diagnostic
equipment; do not waste time trying to test the
system without such facilities.
2Listen for fuel return noises from the fuel
pressure regulator. It should be possible to
feel the fuel pulsing in the regulator and in the
feed hose from the fuel filter.
3If the pump does not run at all, check the
fuse, relay and wiring (see Chapter 6).
Fuel pressure check
3A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with an
adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve on the
fuel rail pressure test/release fitting
(identifiable by its blue plastic cap, and
located on the union of the fuel feed line and
the fuel rail) is required for the following
procedure. If the Ford special tool 29-033 is
available (see Section 2), the tool can be
attached to the valve, and a conventional-type
pressure gauge attached to the tool.
4If using the service tool, ensure that its tap
is turned fully anti-clockwise, then attach it to
the valve. Connect the pressure gauge to the
service tool. If using a fuel pressure gauge
with its own adaptor, connect it in accordance
with its maker’s instructions (see illustration).
5Start the engine and allow it to idle. Note
the gauge reading as soon as the pressure
stabilises, and compare it with the pressure
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
(a) If the pressure is high, check for a
restricted fuel return line. If the line is
clear, renew the pressure regulator.
8 Fuel pump/fuel pressure -
check
7 Accelerator pedal -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4
6.11 Location of TCS throttle actuator-to-
throttle housing cable adjuster (arrowed)7.2 Removing the accelerator pedal
assembly8.4 A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with
an adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve
on the fuel rail pressure test/release fitting,
is needed to check fuel pressure
procarmanuals.com
Page 104 of 279
(b) If the pressure is low, pinch the fuel return
line. If the pressure now goes up, renew
the fuel pressure regulator. If the pressure
does not increase, check the fuel feed
line, the fuel pump and the fuel filter.
6Detach the vacuum hose from the fuel
pressure regulator; the pressure shown on the
gauge should increase. Note the increase in
pressure, and compare it with that listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications. If the pressure
increase is not as specified, check the
vacuum hose and pressure regulator.
7Reconnect the regulator vacuum hose, and
switch off the engine. Verify that the fuel
pressure stays at the specified level for five
minutes after the engine is turned off.
8Carefully disconnect the fuel pressure
gauge. Be sure to cover the fitting with a rag
before slackening it. Mop up any spilt petrol.
9Run the engine, and check that there are no
fuel leaks.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t smoke,
or allow open flames or bare light bulbs,
near the work area. Don’t work in a garage
where a natural gas-type appliance (such
as a water heater or clothes dryer) with a
pilot light is present. If you spill any fuel on
your skin, rinse it off immediately with
soap and water. When you perform any
kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
Note: Ford specify the use of their service tool
23-038 (a large box spanner with projecting teeth
to engage the fuel pump/sender unit retaining
ring’s slots) for this task. While alternatives are
possible, as shown below, in view of the difficulty
experienced in removing and refitting the
pump/sender unit, owners are strongly advised
to obtain this tool before starting work. The help
of an assistant will be required.
1Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap. Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
2Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
3Unbolt or fold forwards (as appropriate) the
rear seat base cushion (see Chapter 11).
Withdraw from the vehicle’s floor the grommet
covering the fuel pump/sender unit. Wash off
any dirt from the tank’s top surface, and dry it;
use a vacuum cleaner to clean the immediate
surroundings of the vehicle’s interior, to
reduce the risk of introducing water, dirt and
dust into the tank while it is open.
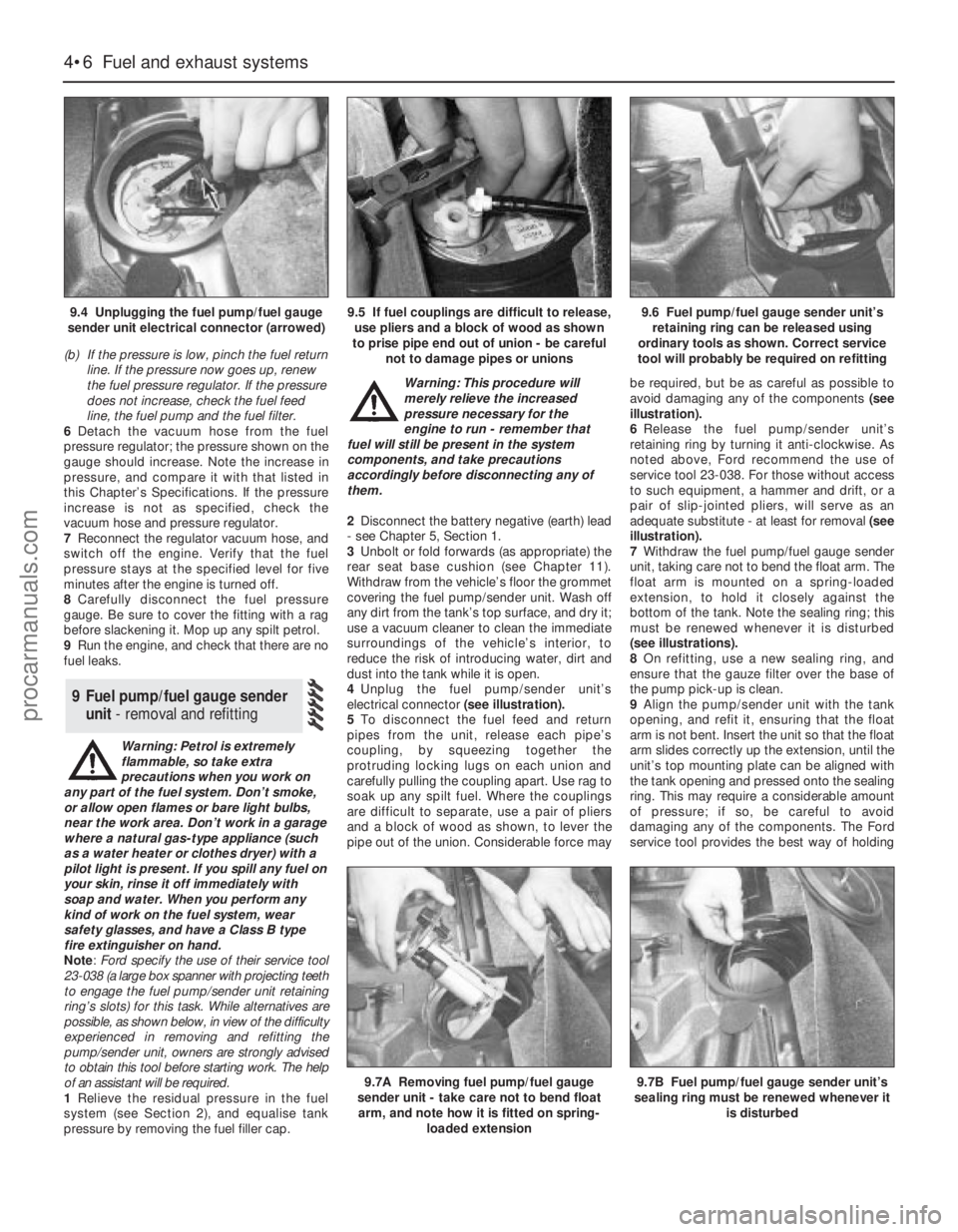
4Unplug the fuel pump/sender unit’s
electrical connector (see illustration).
5To disconnect the fuel feed and return
pipes from the unit, release each pipe’s
coupling, by squeezing together the
protruding locking lugs on each union and
carefully pulling the coupling apart. Use rag to
soak up any spilt fuel. Where the couplings
are difficult to separate, use a pair of pliers
and a block of wood as shown, to lever the
pipe out of the union. Considerable force maybe required, but be as careful as possible to
avoid damaging any of the components (see
illustration).
6Release the fuel pump/sender unit’s
retaining ring by turning it anti-clockwise. As
noted above, Ford recommend the use of
service tool 23-038. For those without access
to such equipment, a hammer and drift, or a
pair of slip-jointed pliers, will serve as an
adequate substitute - at least for removal (see
illustration).
7Withdraw the fuel pump/fuel gauge sender
unit, taking care not to bend the float arm. The
float arm is mounted on a spring-loaded
extension, to hold it closely against the
bottom of the tank. Note the sealing ring; this
must be renewed whenever it is disturbed
(see illustrations).
8On refitting, use a new sealing ring, and
ensure that the gauze filter over the base of
the pump pick-up is clean.
9Align the pump/sender unit with the tank
opening, and refit it, ensuring that the float
arm is not bent. Insert the unit so that the float
arm slides correctly up the extension, until the
unit’s top mounting plate can be aligned with
the tank opening and pressed onto the sealing
ring. This may require a considerable amount
of pressure; if so, be careful to avoid
damaging any of the components. The Ford
service tool provides the best way of holding
9 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender
unit- removal and refitting
4•6 Fuel and exhaust systems
9.4 Unplugging the fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit electrical connector (arrowed)9.5 If fuel couplings are difficult to release,
use pliers and a block of wood as shown
to prise pipe end out of union - be careful
not to damage pipes or unions9.6 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit’s
retaining ring can be released using
ordinary tools as shown. Correct service
tool will probably be required on refitting
9.7A Removing fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit - take care not to bend float
arm, and note how it is fitted on spring-
loaded extension9.7B Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit’s
sealing ring must be renewed whenever it
is disturbed
procarmanuals.com
Page 105 of 279
the ring square to the tank and turning it at the
same time.
10Maintain the pressure while an assistant
refits and engages the retaining ring. When
the ring is engaged in the tank lugs, turn it
clockwise to tighten it until it is secured.
11The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal. Observe the colour-
coding to ensure that the fuel pipes are
reconnected to the correct unions.
Warning: The fuel system pressure
must be released before any part
of the system is disturbed - see
Section 2. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautions when
you work on any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or clothes
dryer) with a pilot light is present. If you spill
any fuel on your skin, rinse it off
immediately with soap and water. When you
perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses, and have a
Class B type fire extinguisher on hand.
1A fuel tank drain plug is not provided; it is
therefore preferable to carry out the removal
operation when the tank is nearly empty.
Before proceeding, disconnect the battery
negative (earth) lead, and syphon or hand-
pump the remaining fuel from the tank.
Alternatively, disconnect the feed pipe from
the fuel filter (see Chapter 1), and connect a
spare length of hose to this so that when the
ignition is switched on, the fuel pump will
empty the tank into a clean container. If this
approach is adopted, ensure that the
container is large enough to take all the fuel in
the tank, and be careful to take all suitable
precautions to prevent the risk of fire. Note:
Before disconnecting or opening any part of
the fuel system, relieve the residual pressure
(see Section 2), and equalise tank pressure by
removing the fuel filler cap. Also disconnect
the battery negative (earth) lead - see Chap-
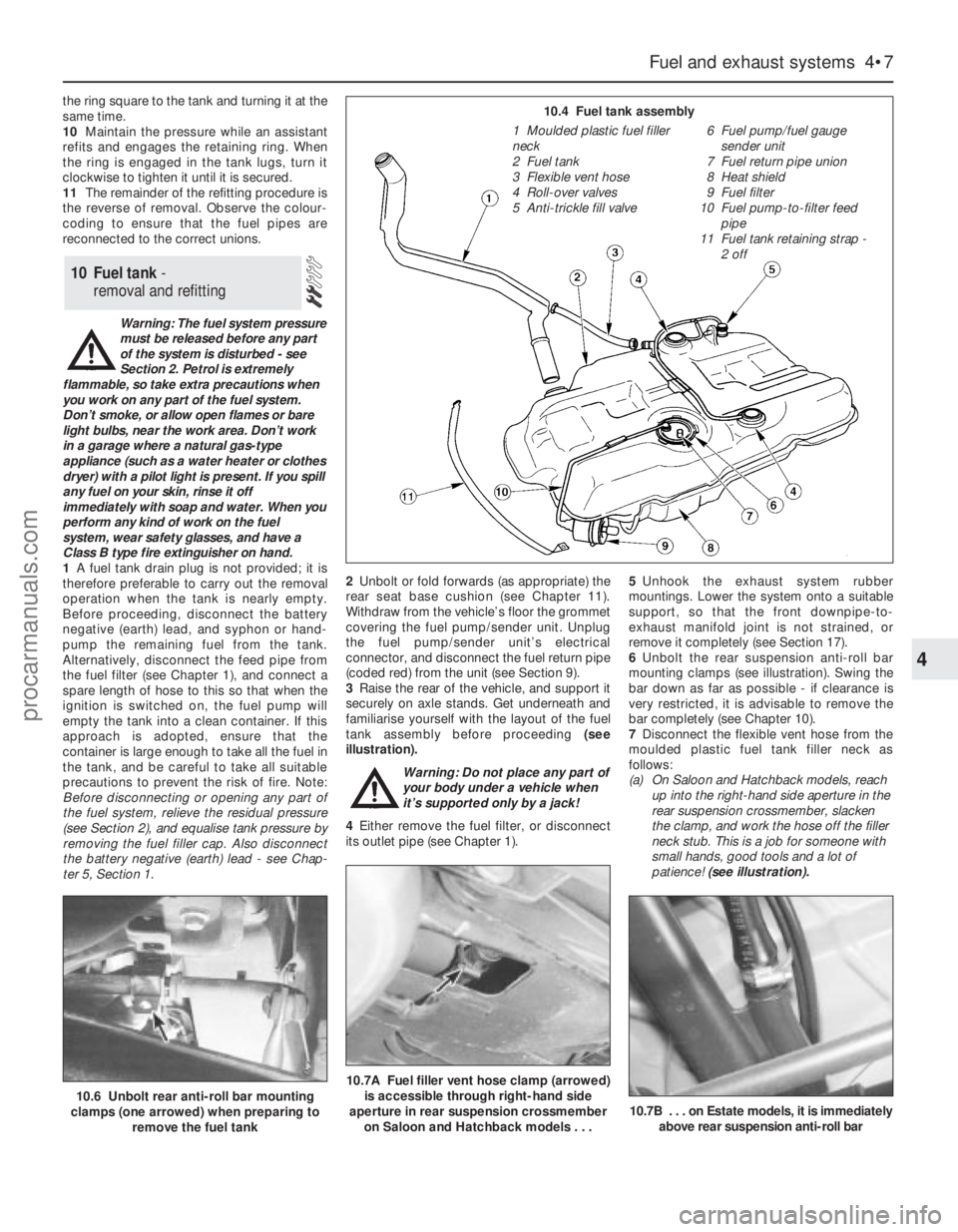
ter 5, Section 1.2Unbolt or fold forwards (as appropriate) the
rear seat base cushion (see Chapter 11).
Withdraw from the vehicle’s floor the grommet
covering the fuel pump/sender unit. Unplug
the fuel pump/sender unit’s electrical
connector, and disconnect the fuel return pipe
(coded red) from the unit (see Section 9).
3Raise the rear of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands. Get underneath and
familiarise yourself with the layout of the fuel
tank assembly before proceeding (see
illustration).
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
4Either remove the fuel filter, or disconnect
its outlet pipe (see Chapter 1).5Unhook the exhaust system rubber
mountings. Lower the system onto a suitable
support, so that the front downpipe-to-
exhaust manifold joint is not strained, or
remove it completely (see Section 17).
6Unbolt the rear suspension anti-roll bar
mounting clamps (see illustration). Swing the
bar down as far as possible - if clearance is
very restricted, it is advisable to remove the
bar completely (see Chapter 10).
7Disconnect the flexible vent hose from the
moulded plastic fuel tank filler neck as
follows:
(a) On Saloon and Hatchback models, reach
up into the right-hand side aperture in the
rear suspension crossmember, slacken
the clamp, and work the hose off the filler
neck stub. This is a job for someone with
small hands, good tools and a lot of
patience! (see illustration).
10 Fuel tank -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•7
4
10.6 Unbolt rear anti-roll bar mounting
clamps (one arrowed) when preparing to
remove the fuel tank10.7A Fuel filler vent hose clamp (arrowed)
is accessible through right-hand side
aperture in rear suspension crossmember
on Saloon and Hatchback models . . .
10.7B . . . on Estate models, it is immediately
above rear suspension anti-roll bar
10.4 Fuel tank assembly
1 Moulded plastic fuel filler
neck
2 Fuel tank
3 Flexible vent hose
4 Roll-over valves
5 Anti-trickle fill valve6 Fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit
7 Fuel return pipe union
8 Heat shield
9 Fuel filter
10 Fuel pump-to-filter feed
pipe
11 Fuel tank retaining strap -
2 off
procarmanuals.com
Page 108 of 279

Renewal
3Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
4Remove the plenum chamber (see Sec-
tion 4).
5Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage (see Section 5 or 6, as
appropriate). Where fitted, also disconnect
the cruise control actuator cable (see Chap-
ter 12).
6Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator). Similarly release and unplug the
throttle potentiometer’s electrical connector.
7Clearly label, then detach, all vacuum hoses
from the throttle housing.
8Remove the throttle housing mounting
screws (see illustration), then detach the
throttle housing and gasket from the inlet
manifold. Discard the gasket - this must be
renewed whenever it is disturbed.
9Using a soft brush and carburettor cleaner,
thoroughly clean the exterior of the throttle
housing, then blow out all passages with
compressed air.
Caution: Do not clean the throttle
housing’s bore, the throttle valve,
or the potentiometer, either by
scraping or with a solvent. Just
wipe them over carefully with a clean soft
cloth.
10Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Fit a new gasket, and tighten the
housing screws to the specified torque.
Fuel rail and injectors
Check
11Refer to the procedure in the fuel system
check (see Section 15).
Renewal
Note:For simplicity, and to ensure the
necessary absolute cleanliness on
reassembly, the following procedure
describes the removal of the fuel rail
assembly, complete with the injectors and
pressure regulator, so that the injectors can be
serviced individually on a clean work surface.
It is also possible to remove and refit an
individual injector once the fuel system has
been depressurised and the battery has been
disconnected. If this approach is followed,
read through the complete procedure, and
work as described in the relevant paragraphs,
depending on the amount of preliminary
dismantling required. Be careful not to allow
any dirt to enter the system (see
illustrations).
12Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
13Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
14Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
15If the additional clearance is required,
disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage (see Section 5 or 6, as
appropriate). Where fitted, also disconnect
the cruise control actuator cable (see Chap-
ter 12).
16Releasing the wire clips, unplug the four
fuel injector electrical connectors.
17Disconnect the fuel feed and return lines
at the quick-release couplings next to the
braking system vacuum servo unit, then
unclip the fuel hoses from the inlet manifold;
use rag to soak up any spilt fuel. Note:Do not
disturb the threaded couplings at the fuel rail
unions unless absolutely necessary; these aresealed at the factory. The quick-release
couplings will suffice for all normal service
operations.
18Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union, and the
vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator
(see illustration).
19Unscrew the three bolts securing the fuel
rail, and withdraw the rail, carefully prising it
out of the inlet manifold, and draining any
remaining fuel into a suitable clean container
(see illustrations). Note the seals between
the rail noses and the manifold; these must be
renewed whenever the rail is removed.
20Clamping the rail carefully in a vice fitted
with soft jaws, unscrew the two bolts securing
each injector, and withdraw the injectors.
Place each in a clean, clearly-labelled storage
container.
21If you are renewing the injector(s), discard
the old injector, the nose seal and the O-rings.
If you are simply renewing leaking injector O-
4•10 Fuel and exhaust systems
16.8 Undo screws (arrowed) to remove
throttle housing16.12A Fuel injectors can be unbolted
(arrowed) . . .16.12B . . . and removed individually if
required, but it is better to remove them
with the fuel rail, if servicing is necessary.
O-ring seals (arrowed) must be renewed
whenever injector is removed
16.18 Injector removal - disconnect fuel
lines at quick-release couplings (A), unclip
hoses (B), disconnect vacuum hose from
regulator (C), unplug electrical
connectors (D) - three of four shown - and
disconnect breather hose from union (E)
16.19A Unscrew bolts (arrowed) . . .
16.19B . . . and withdraw fuel rail with
injectors and pressure regulator - renew
nose seals (arrowed) whenever rail is
disturbed
procarmanuals.com
Page 109 of 279

rings, and intend to re-use the same injectors,
remove the old nose seal and O-rings, and
discard them.
22Further testing of the injector(s) is beyond
the scope of the home mechanic. If you are in
doubt as to the status of any injector(s), it can
be tested at a dealer service department.
23Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Lubricate each nose seal and O-ring with
clean engine oil on installation.
(b) Locate each injector carefully in the fuel
rail recess, ensuring that the locating tab
on the injector head fits into the slot
provided in the rail. Tighten the bolts to
the specified torque.
(c) Fit a new seal to each fuel rail nose, and
ensure the seals are not displaced as the
rail is refitted. Ensure that the fuel rail is
settled fully in the manifold before
tightening the three bolts evenly and to
the torque wrench setting specified.
(d) Fasten the fuel feed and return quick-
release couplings as described in Sec-
tion 3.
(e) Ensure that the breather hose, vacuum
hose and wiring are routed correctly, and
secured on reconnection by any clips or
ties provided.
(f) On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times, to activate the fuel pump and
pressurise the system, without cranking
the engine. Check for signs of fuel leaks
around all disturbed unions and joints
before attempting to start the engine.
Fuel pressure regulator
Check
24Refer to the fuel pump/fuel pressure
check procedure (see Section 8).
Renewal
25Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the engine
to run - remember that fuel will
still be present in the system components,
and take precautions accordingly before
disconnecting any of them.26Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
27Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
28Disconnect the vacuum hose from the
regulator.
29Unscrew the two regulator retaining bolts,
place a wad of clean rag to soak up any spilt
fuel, and withdraw the regulator (see
illustration).
30Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Renew the regulator sealing O-ring
whenever the regulator is disturbed.
Lubricate the new O-ring with clean
engine oil on installation.
(b) Locate the regulator carefully in the fuel
rail recess, and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times, to activate the fuel pump and
pressurise the system, without cranking
the engine. Check for signs of fuel leaks
around all disturbed unions and joints
before attempting to start the engine.
Idle speed control valve
Check
31Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
32Raise the front of the vehicle, and support
it securely on axle stands.
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
33Unplug the valve’s electrical connector
(see illustration).
34Connect a 12-volt battery across the
valve’s terminals - positive (+) to terminal 37
(the green/yellow wire) and negative (-) to
terminal 21 (the black/yellow).
Caution: It is essential that the
correct polarity is observed, or
the diode incorporated in the
valve may be damaged.
35A distinct click should be heard each time
contact is made and broken. If not, measure
the resistance between the terminals. If the
resistance is as specified, the valve is okay
(but there may be a problem with the wiring or
the ECU). If the resistance is not as specified,
renew the valve (see below).36Plug in the valve’s electrical connector.
Renewal
37Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
38Raise the front of the vehicle, and support
it securely on axle stands.
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
39Unplug the valve’s electrical connector.
40Unscrew the two retaining bolts, and
withdraw the valve from the inlet manifold
(see illustration).
41Since the valve’s individual components
are not available separately, and the complete
assembly must be renewed if it is thought to
be faulty, there is nothing to be lost by
attempting to flush out the passages, using
carburettor cleaner or similar solvent. This
won’t take much time or effort, and may well
cure the fault.
42Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Clean the mating surfaces carefully, and
always fit a new gasket whenever the
valve is disturbed.
(b) Tighten the bolts evenly and to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Once the wiring and battery are
reconnected, start the engine and allow it
to idle. When it has reached normal
operating temperature, check that the idle
speed is stable, and that no induction (air)
leaks are evident. Switch on all electrical
loads (headlights, heated rear window,
etc), and check that the idle speed is still
correct.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•11
4
16.43 Location of idle-increase solenoid
valve (A) and diode (B)
16.29 Disconnect vacuum hose, and
unscrew bolts (arrowed) to withdraw fuel
pressure regulator16.33 Access to idle speed control valve is
from underneath vehicle - unplug electrical
connector (arrowed) to check valve16.40 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
idle speed control valve
procarmanuals.com