1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 275 of 2438

MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB II diagnostics tester. The proper
application and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB II DIAGNOSTIC TESTER Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB II
Diagnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics
are performed. Refer to those sections for proper test-
ing procedures and the DRB II operators manual for
its proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of connector halves or terminals
not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
carefully reformed to increase contact tension. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable Anti-
Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even if the
fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which a fail-
ure occurred. If the failure conditions are no longer
present. The following conditions may result in inter-
mittent illumination of the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp. All other failures will cause the lamp to
remain on until the ignition switch is turned off. Cir-
cuits involving these inputs to the (CAB) should be
investigated if a complaint of intermittent warning
system operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal sys-
tem voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen
at the (CAB), normal operation resumes. (2) Anti-Lock relay. If the relay fails to make the
ground circuit connection or is an intermittent
ground. The (CAB) will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Light until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the (CAB) or modula-
tor assembly. May cause the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Anti-Lock Light is turned on for approxi-
mately 1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault. A
(CAB) fault can only be erased by the technician us-
ing the DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault
can be stored at a time. The number of key cycles
since the most recent fault was stored is also dis-
played. Most functions of the (CAB) and ABS system
can be accessed by the technician for testing and di-
agnostic purposes by using the DRB II.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching; the
fault is latched and (ABS) is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 125
Page 301 of 2438

ANTILOCK BRAKES OPERATION AND
PERFORMANCE
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System represents
the current state-of-the-art in vehicle brake systems
and offers the driver increased safety and control
during braking. This is accomplished by a sophisti-
cated system of electrical and hydraulic components.
As a result, there are a few performance characteris-
tics that may at first seem different but should be
considered normal. These characteristics are dis-
cussed below. More technical details are discussed
further in this section.
PEDAL FEEL
Since the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System uses the
vehicle's conventional brake system power booster
and master cylinder. The brake pedal feel during
normal braking is the same as on a conventional
Non ABS equipped vehicle. When the Antilock system becomes activated dur-
ing hard braking due to a wheel lockup tendency.
The brake pedal effort will increase do to the master
cylinder pressure being isolated from the brake sys-
tem. Some brake pedal movement and associated
noises may be felt and heard by the driver. This is
normal operation of the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System due to pressurized brake fluid being trans-
ferred to and from the wheel brakes.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
During Antilock Brake system operation, brake
pressures are modulated by cycling electric solenoid
valves. The cycling of these valves can be heard as a
series of popping or ticking noises. In addition, the
cycling may be felt as a pulsation in the brake pedal.
If Antilock operation occurs during a hard applica-
tion of the brakes, some pulsation may be felt in the
vehicle body due to fore and aft movement of vehicle
suspension components. Although ABS operation is available at virtually
all vehicle speeds, it will automatically turn off at
speeds below 3 to 5 mph. Wheel lockup may be per-
ceived at the very end of an anti lock stop and is con-
sidered normal.
TIRE NOISE & MARKS
Although the ABS system prevents complete wheel
lock-up, some wheel slip is desired in order to
achieve optimum vehicle braking performance. During brake fluid pressure modulation, as the
brake fluid pressure is increased, wheel slip is al-
lowed to reach up to 30%. This means that wheel
rolling speed is 30% less than that of a free rolling
wheel at a given vehicle speed. This slip may result
in some tire chirping, depending on the road surface.
This sound should not be interpreted as total wheel
lock-up. Complete wheel lock up normally leaves black tire
marks on dry pavement. The Antilock Brake System
will not leave dark black tire marks since the wheel
never reaches a locked condition. Tire marks may
however be noticeable as light patched marks.
VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
Antilock Brakes provide the driver with some
steering control during hard braking, however there
are conditions where the system does not provide any
benefit. In particular, hydroplaning is still possible
when the tires ride on a film of water. This results in
the vehicles tires leaving the road surface rendering
the vehicle virtually uncontrollable. In addition, ex-
treme steering maneuvers at high speed or high
speed cornering beyond the limits of tire adhesion to
the road surface may cause vehicle skidding, inde-
pendent of vehicle braking. For this reason, the ABS
system is termed Antilock instead of Anti-Skid.
SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System has been de-
signed with the following self diagnostic capabilities. The self diagnostic ABS startup cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. At
this time an electrical check is completed on the ABS
components such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity
and System and other Relay continuity. During this
check the Amber Antilock Light is on for approxi-
mately 1-2 seconds. Further Antilock Brake System functional testing
is accomplished once the vehicle is set in motion,
known as drive-off. (1) The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are ac-
tivated briefly to verify function.
Fig. 5 Controller Antilock Brake CAB
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 15
Page 304 of 2438

WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
One Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS), is located at each
wheel (Fig. 5 and 6), and sends a small AC signal to the
control module CAB. This signal is generated by mag-
netic induction. The magnetic induction is created,
when a toothed sensor ring (Tone Wheel) (Fig. 7) passes
a stationary magnetic Wheel Speed Sensor. The CAB
converts the AC signal generated at each wheel into a
digital signal. If a wheel locking tendency is detected,
the CAB will then modulate hydraulic pressure to pre-
vent the wheel or wheels from locking.
The front Wheel Speed Sensor is attached to a boss
in the steering knuckle (Fig. 5). The tone wheel is
part of the outboard constant velocity joint (Fig. 5). The rear Wheel Speed Sensor is mounted to the cal-
iper adapter (Fig. 6) and the rear tone wheel is an
integral part of the rear wheel hub (Fig. 7). The
speed sensor air gap is NOT adjustable.
The four Wheel Speed Sensors are serviced individ-
ually. The front Tone Wheels are serviced as an as-
sembly with the outboard constant velocity joint. The
rear Tone Wheels are serviced as an assembly with
the rear brake hub. Correct Antilock system operation is dependent on
the vehicle's wheel speed signals, that are generated
by the Wheel Speed Sensors. The vehicle's wheels
and tires must all be the same size and type to gen-
erate accurate signals. In addition, the tires must be
inflated to the recommended pressures for optimum
system operation. Variations in wheel and tire size
or significant variations in inflation pressure can
produce inaccurate wheel speed signals.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB
The Antilock Brake Controller is a small micropro-
cessor based device which monitors the brake system
and controls the system while it functions in the An-
tilock mode. The CAB is mounted on the top of the
right front frame rail and uses a 60-way system con-
nector (Fig. 8). The power source for the CAB is
through the ignition switch in the Run or On posi-
tion. THE CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE
CAB IS NOT ON THE CCD BUS The primary functions of the CAB are:
(1) Detect wheel locking tendencies.
(2) Control fluid modulation to the brakes while in
Antilock mode. (3) Monitor the system for proper operation.
Fig. 5 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 6 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 7 Rear Tone Wheel (Typical)
5 - 18 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 306 of 2438

ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP DIODE
The Warning Lamp Relay on the Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System has been replaced with a diode. The
diode is used to control the function of the warning
lamp and is located inside the CAB module wiring
harness. The diode is a replaceable component of the
wiring harness, and will not require replacement of
the entire wiring harness if only the diode is diag-
nosed to have failed. When the system relay is de-energized, the Anti-
lock warning lamp will be lit. This will occur because
a ground path exists for the Antilock warning lamp
through the Antilock warning lamp diode and the
system relay armature. When the system relay is en-
ergized by the CAB, the system relay armature will
no longer provide a ground and the lamp will turn
off. Thus, the lamp will be lit if either the CAB is
disconnected or a system fault causes the Antilock to
be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 11 and 12) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay Energized
From pin 57, the CAB energizes the Antilock sys-
tem relay coil, thus the electrical current flow in the
coil closes the system relay. Then electrical current
is provided to pins 47 and 41 of the CAB to provide
power to the modulator valves. The CAB turns off the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp by breaking the ground path through pin 15 of
the CAB.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP ON
System Relay De-Energized.
When the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is on,
there is no electrical current flow from the CAB at
pin 57 and the System Relay coil is NOT energized.
No electrical current flows to pin 47 and 41 (modula-
tor valve power), or to the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode. Thus, the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
not energized. The Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
now grounded through the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode and pin 15 of the CAB turning on the Amber
Antilock Warning Lamp.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions and
diagrams. The function of the various hydraulic con-
trol valves in the ABS system will be described. The
fluid control valves mentioned below, control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of Antilock braking. For explanation purposes we will assume all speed
sensors are sending the same wheel speed informa-
tion, requiring the same hydraulic fluid modulation
at the same rate.
NORMAL BRAKING
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Closed (Fig. 1)
The brake pedal is applied. The travel of the brake
pedal closes primary and secondary circuits from the
master cylinder fluid supply. Brake fluid from the
master cylinder primary and secondary circuits flows
through the build/decay valves to the wheel brakes.
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Open (Fig. 2)
Fig. 11 Pump Motor Relay Location On AA Body W/O Power Distribution Center
Fig. 12 Pump Motor Relay Location On AJ BodyWith Power Distribution Center
5 - 20 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 308 of 2438
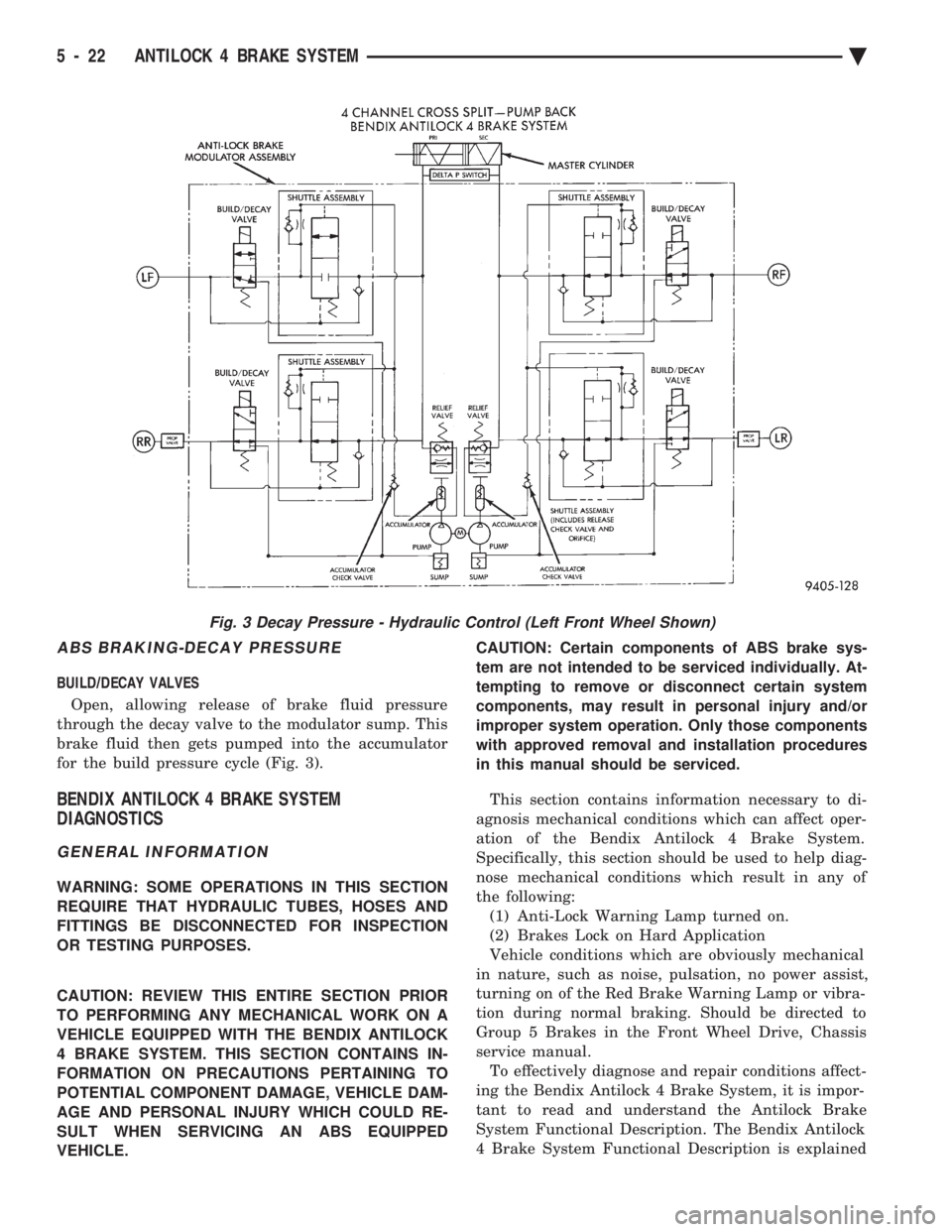
ABS BRAKING-DECAY PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES Open, allowing release of brake fluid pressure
through the decay valve to the modulator sump. This
brake fluid then gets pumped into the accumulator
for the build pressure cycle (Fig. 3).
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
DIAGNOSTICS
GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNING: SOME OPERATIONS IN THIS SECTION
REQUIRE THAT HYDRAULIC TUBES, HOSES AND
FITTINGS BE DISCONNECTED FOR INSPECTION
OR TESTING PURPOSES.
CAUTION: REVIEW THIS ENTIRE SECTION PRIOR
TO PERFORMING ANY MECHANICAL WORK ON A
VEHICLE EQUIPPED WITH THE BENDIX ANTILOCK
4 BRAKE SYSTEM. THIS SECTION CONTAINS IN-
FORMATION ON PRECAUTIONS PERTAINING TO
POTENTIAL COMPONENT DAMAGE, VEHICLE DAM-
AGE AND PERSONAL INJURY WHICH COULD RE-
SULT WHEN SERVICING AN ABS EQUIPPED
VEHICLE. CAUTION: Certain components of ABS brake sys-
tem are not intended to be serviced individually. At-
tempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components, may result in personal injury and/or
improper system operation. Only those components
with approved removal and installation procedures
in this manual should be serviced.
This section contains information necessary to di-
agnosis mechanical conditions which can affect oper-
ation of the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System.
Specifically, this section should be used to help diag-
nose mechanical conditions which result in any of
the following: (1) Anti-Lock Warning Lamp turned on.
(2) Brakes Lock on Hard Application
Vehicle conditions which are obviously mechanical
in nature, such as noise, pulsation, no power assist,
turning on of the Red Brake Warning Lamp or vibra-
tion during normal braking. Should be directed to
Group 5 Brakes in the Front Wheel Drive, Chassis
service manual. To effectively diagnose and repair conditions affect-
ing the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System, it is impor-
tant to read and understand the Antilock Brake
System Functional Description. The Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System Functional Description is explained
Fig. 3 Decay Pressure - Hydraulic Control (Left Front Wheel Shown)
5 - 22 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 310 of 2438

manual. May result in contact with moving parts or
over extension of cables, resulting in component fail-
ure and an open circuit.
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB diagnostics tester. The proper ap-
plication and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB DIAGNOSTIC TESTER
Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB Di-
agnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics are
performed. Refer to those sections for proper testing
procedures and the DRB operators manual for its
proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of wiring harness connector halves
or terminals not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
checked and carefully reformed to increase contact
tension with its mating terminal. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
(5) Connector push-in, spread, and corrosion.
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the set Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable the
Antilock function for the entire ignition cycle even if
the fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which it oc-
curred, if the failure condition is no longer present.
The following conditions may result in intermittent
illumination of the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp.
All other failures will cause the lamp to remain on
until the ignition switch is turned off. Circuits in-
volving these inputs to the CAB should be investi-
gated if a complaint of intermittent warning system
operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage: If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the Am-
ber Antilock Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at
the CAB, normal operation resumes.
(2) Antilock system and pump/motor relay. If the
relays fail to make the ground circuit connection or
has an intermittent ground. The CAB will turn on
the Amber Antilock Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Antilock Warning Light
until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the CAB or modulator
assembly, may cause the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Antilock Light is turned on for approximately
1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion, known as drive-off.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB or
erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the CAB fault. A
CAB fault can only be erased by the technician using
the DRB diagnostic tester. More than one fault can
be stored at a time. The number of key cycles since
the most recent fault was stored is also displayed.
Most functions of the CAB and ABS system can be
accessed by the technician for testing and diagnostic
purposes by using the DRB.
5 - 24 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 1570 of 2438

REMOVE ALL SHIMS BEFORE REASSEM-
BLING ENGINE ALTERNATIVE METHOD Ð With the weight of
the crankshaft being supported by a jack under the
counterweight adjacent to the bearing being checked. (3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 2). (In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspect area).
Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing being
checked to the proper specifications. (4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 3) with the metric scale
provided on the package. Locate the band closest to the
same width. This band shows the amount of clearance
in thousandths of a millimeter. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper present.
Record all readings taken. Refer to Engine Specifica-
tions. Plastic-Gage generally is accompanied by
two scales. One scale is in inches, the other is a
metric scale. (5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076mm (.001-.003 inch) is usually
the most appropriate for checking engine bearing
proper specifications.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The following
is the recommended procedure for the use of Plasti-
gage: (1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod to
be checked is at the bottom of its stroke. (2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil. (3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approxi-
mately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch.) off center and away from
the oil hole (Fig. 2). In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing plastigage in the suspect area. (4) Before assembling the rod cap with Plastigage in
place, the crankshaft must be rotated until the con-
necting being checked starts moving toward the top of
the engine. Only then should the cap be assembled and
torqued to specifications. Do not rotate the crank-
shaft while assembling the cap or the Plastigage
may be smeared, giving inaccurate results. (5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 3) with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band closest
to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differences
in readings between the ends indicate the amount
of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Refer to Engine Specifications. Plastigage generally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is in
inches, the other is a metric scale. (6) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076mm (.001-.003 inch) is usually
the most appropriate for checking engine bearing
proper specifications.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items. (1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause them
to be spongy. (2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required. During this time, turn engine off and let set for a few
minutes before restarting. Repeat this several times
after engine has reached normal operating tempera-
ture. (3) Low oil pressure.
(4) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head of Balance Shaft Engines
Only is plugged with debris. (5) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked oil
pump pick up. (6) Worn valve guides.
(7) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring retainer
(2.2/2.5L engines). (8) Rocker arm loose, adjuster or tappet stuck or at
maximum extension and still leaves lash in the system. (9) Faulty lash adjuster or tappet.(a) Check for sponginess while still installed in
engine. Depress part of rocker arm just over adjuster
or pushrod . Normal adjusters should feel very firm.
Spongy adjusters can be depressed to the bottomed
position easily. (b) Remove suspected lash adjuster or tappet, pry
off retainer cap or snap ring and disassemble. Do
not reuse retainer caps . Do not interchange parts
and make sure that care and cleanliness is exercised
in the handling of parts. (c) Clean out dirt and varnish with solvent.
(d) Reassemble with engine oil.
(e) Check for sponginess.
(f) If still spongy, replace with new adjuster.
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (including aluminum head
spark plug threads) can be repaired. Essentially, this
repair consists of drilling out worn or damaged
threads, tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil (or
equivalent) Tap, and installing an insert into the
tapped hole. This brings the hole back to its original
thread size.
9 - 4 ENGINE Ä
Page 1785 of 2438

SYSTEMS TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING A TEST
WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link con-
nector located in the engine compartment near the
powertrain control module (PCM). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off
the engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel).
The lamp should light for 3 seconds then go out (bulb
check).
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states,
HIGH and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot
recognize the difference between a selected switch po-
sition versus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a de-
fective switch. If the change is displayed, it can be
assumed that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is
functional. From the state display screen access ei-
ther State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Dis-
play Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle only)
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C (Speed Control) Vent Solenoid
S/C (Speed Control) Vacuum Solenoid
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid (3 speed auto-
matic transaxle)
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Added Adaptive Fuel
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idl Spd
Engine Speed
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-On Info
Fault #3 Key-On Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). With the exception of an intermit-
tent condition, if a device functions properly during
its test, it can be assumed that the device, its associ-
ated wiring, and its driver circuit are in working or-
der.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Fuel Injector #1
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 45