1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 355 of 2438

(5) Install drive belt. See Accessory Drive Belts
this group. (6) Install right front lower fender shield.
(7) Refill Cooling System. See Refilling Cooling
System in this section.
ENGINE THERMOSTATS
The 2.2 and 2.5L engine thermostats are located on
the front of the engine (radiator side) in the water
box which is part of the cylinder head construction
(Fig. 9). Turbo III thermostat is located in the water
box located on the driver side of the cylinder head
(Fig. 10). These thermostats do not have an air bleed notch.
The 3.0L engine thermostat is located in a water
box, formed in the timing belt end of the intake man-
ifold. This thermostat has an air bleed valve, located
in the thermostat flange (Fig. 11). The 3.3/3.8L engine thermostat is located in a wa-
ter box, formed in the drive belt side of the intake
manifold (Fig. 13).
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The engine cooling thermostats are wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. They are designed
to provide the fastest warm up possible by prevent-
ing leakage through them and to guarantee a mini-
mum engine operating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC
(192 to 199ÉF). They also automatically reach wide
open so they do not restrict flow to the radiator as
temperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the radiator,
fan, and ambient temperature, not the thermostat.
OPERATION AND TESTING
The thermostat is operated by a wax filled con-
tainer (pellet) which is sealed so that when heated to
a predetermined temperature. The wax expands
enough to overcome the closing spring and water
pump pressure, which forces the valve to open. Cool-
ant leakage into the pellet will cause a thermostat to
fail open. Do not attempt to free up a thermostat
with a screwdriver. The open too soon type failure mode is included in
the onboard diagnosis. The check engine light will
not be lit by an open too soon condition. If it has
failed open, code 17 will be set. Do not change a ther-
mostat for lack of heat by gauge or heater perfor-
mance, unless code 17 is present, see diagnosis for
other probable causes. Failing shut is the normal
long term mode of failure, and normally, only on
high mileage vehicles. The temperature gauge will
indicate this, Refer to diagnosis in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system down to thermostat level
or below. (2) Remove thermostat housing bolts and housing
(Figs. 9, 10, 11 and 13). (3) Remove thermostat, discard gasket and clean
both gasket sealing surfaces.
INSTALLATIONÐ2.2/2.5L AND TURBO III ENGINES
Place a new gasket (dipped in clean water) on wa-
ter box surface, center thermostat in water box on
gasket. Place housing over gasket and thermostat,
making sure thermostat is in the thermostat hous-
ing. Bolt housing to water box (Figs. 9 and 10).
Tighten bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.). Refill cooling
system (see Refilling System ).
INSTALLATIONÐ3.0L ENGINE
Center thermostat in water box pocket. Check that
the flange is seated correctly in the countersunk por-
tion of the intake manifold water box (Figs. 11 and
12). Install new gasket on water box. Install housing
over gasket and thermostat and tighten bolts to 12
N Im (133 in. lbs. torque).
Fig. 9 Thermostat, Housing, and Water BoxÐ2.2/
2.5L Engine
Fig. 10 Thermostat, Housing, and Water BoxÐTurbo III
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 13
Page 358 of 2438

CLEANING
Drain cooling system (see: Draining Cooling Sys-
tem ) and refill with clean water (see: Refilling
Cooling System ). Run engine with radiator cap in-
stalled until upper radiator hose is hot. Stop engine
and drain water from system. If water is dirty, fill,
run and drain system again until water runs clear.
REVERSE FLUSHING
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system, using air
pressure in a direction opposite to that of the normal
flow of water. This is only necessary with dirty sys-
tems and evidence of partial plugging.
RADIATOR Drain cooling system and remove radiator hoses
from engine. Install suitable flushing gun in radiator
lower hose. Fill radiator with clean water and turn
on air in short blasts. CAUTION: Internal radiator pressure must not ex-
ceed 138 kPa (20 psi) as damage to radiator may re-
sult. Continue this procedure until water runs clear.
ENGINE
Drain radiator (see: Draining Cooling System )
and remove hoses from radiator. Remove engine
thermostat and reinstall thermostat housing. Install
suitable flushing gun to thermostat housing hose.
Turn on water, and when engine is filled, turn on
air, but no higher than 138 kPa (20 psi) in short
blasts. Allow engine to fill between blasts of air.
Continue this procedure until water runs clean. In-
stall thermostat using a new housing gasket. Fill
cooling system (See Refilling Cooling System ).
CHEMICAL CLEANING
One type of corrosion encountered with aluminum
cylinder heads is aluminum hydroxide deposits. Cor-
rosion products are carried to the radiator and depos-
ited when cooled off. They appear as dark grey when
wet and white when dry. This corrosion can be re-
moved with a two part cleaner (oxalic acid and neu-
tralizer) available in auto parts outlets. Follow
manufacturers directions for use.
REFILLING
First clean system to remove old glycol, see Cooling
System Cleaning. Fill system using antifreeze described in Coolant
section. Fill 50 percent of capacity with 100 percent
glycol. Then complete filling system with water. The
2.2/2.5L engines require venting by removal of the
plug on top of the water box (Fig. 1). Turbo III en-
gines require venting by removing the coolant tem-
perature sensor on top of the thermostat housing
(Fig. 2). The 3.3/3.8L Engines require removal of the
Engine Temperature Sending Unit on the front of
the cylinder head (Fig. 3). The thermostat in these
engines do not allow air flow through them. When
coolant reaches the vent holes;
² Install vent plug and tighten to 20 N Im (15 ft. lbs.)
for 2.2/2.5L Engines.
² Install Coolant Temperature Sensor and tighten to
27 N Im (20 ft. lbs.) for Turbo III Engine.
² Install Engine Temperature Sending Unit and
tighten to 7 N Im (60 in. lbs.) for 3.3/3.8L Engines.
Continue filling system until full, this provides bet-
ter heater performance. Be careful not to spill
coolant on drive belts or the generator. Fill coolant reserve system to at least the MAX
mark with 50/50 solution. It may be necessary to add
coolant to the reserve tank to maintain coolant level
between the MAX and MIN mark after three or four
warm-up, cool down cycles and trapped air has been
removed.
Fig. 2 Coolant Temperature SensorÐTurbo III Drain/Fill
Fig. 3 Engine Temperature Sending UnitÐ3.3L and 3.8L Drain/Fill
7 - 16 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 366 of 2438

ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS INDEX
page page
2.2/2.5L Engine Belts Remove/Install-Adjust .... 24
3.0L Engine Belts Remove/Install and Adjust .... 25
3.3/3.8L and Turbo III Engine Accessory Drive Belt Remove and Install
..................... 26
General Information ....................... 24
GENERAL INFORMATION
PROPER BELT TENSION
Satisfactory performance of the belt driven accesso-
ries depends on belt condition (Fig. 1) and proper belt
tension. Two tensioning methods are given in order
of preference:
² Belt tension gauge method.
² Torque equivalent method.
The belt tension gauge method is usually restricted
to use after the vehicle has been raised on a hoist
and the splash shield has been removed.
BELT TENSION GAUGE METHOD Use belt tensioning Special Tool Kit C-4162 for:
² For conventional belts and Poly-V belts.
Adjust the belt tension for a NeworUsed belt as
prescribed in the Belt Tension Chart.
TORQUE EQUIVALENT METHOD Adjustable accessory brackets provided with a
13mm (1/2 in.) square hole for a torque wrench can
use an equivalent torque value for belt adjustment. Equivalent torque values for adjusting these acces-
sory drive belts are specified on the Belt Tension
Charts .
2.2/2.5L ENGINE BELTS REMOVE/INSTALL-
ADJUST
AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR
(1) Loosen the idler bracket pivot screw A and
locking screws B (Fig. 2) to remove and install belt
and/or adjust belt tension.
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS DIAGNOSIS
Fig. 1 Drive Belt Inspection
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 367 of 2438

(2) Adjust belt tension by applying torque to
square hole C on idler bracket. Adjust tension to
specification given in Belt Tension Chart. (3) Tighten in order, first, locking screws B then
pivot screw A to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
POWER STEERING PUMPÐS TYPE
(1) From on top of the vehicle loosen locking screw G.
(2) From under the vehicle loosen the pivot screw
and pivot nut H . (3) After installing a new belt adjust belt tension
with 1/2 in. breaker bar installed in adjusting
bracket. See tension specification in chart. (4) Tighten locking screw G to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(5) Tighten pivot screw H and the pivot nut to 54
N Im (40 ft. lbs.)
GENERATOR BELT
(1) Loosen T-Bolt locking nut E and adjusting
screw F to remove and install Poly V belt and/or ad-
just belt tension. (2) Tighten adjusting screw F to adjust belt tension
to specification shown in Belt Tension Chart. (3) Tighten T-Bolt locking nut E to 54 N Im (40 ft.
lbs.).
3.0L ENGINE BELTS REMOVE/INSTALL AND
ADJUST
AIR CONDITIONING BELT
To remove and install the air conditioning com-
pressor drive belt, first loosen the idler pulley lock
nut, then turn the adjusting screw to raise or lower
the idler pulley (Figs. 3 and 4).
To adjust the air conditioning drive belt, loosen
the idler pulley nut (Fig. 3) and adjust belt tension
Fig. 2 Accessory Drive BeltsÐ2.2 and 2.5L Engines
Fig. 3 Accessory Drive BeltsÐ3.0L Engine
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 25
Page 368 of 2438
by tightening adjusting screw (Figs. 3 and 4 ).
Tighten pulley nut to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) after ad-
justment.
GENERATOR/POWER STEERING PUMP BELT
The Poly-V generator/power steering pump belt is
provided with a dynamic tensioner (Fig. 5) to main-
tain proper belt tension. To remove or install this
belt, Release tension by rotating the tensioner clock-
wise
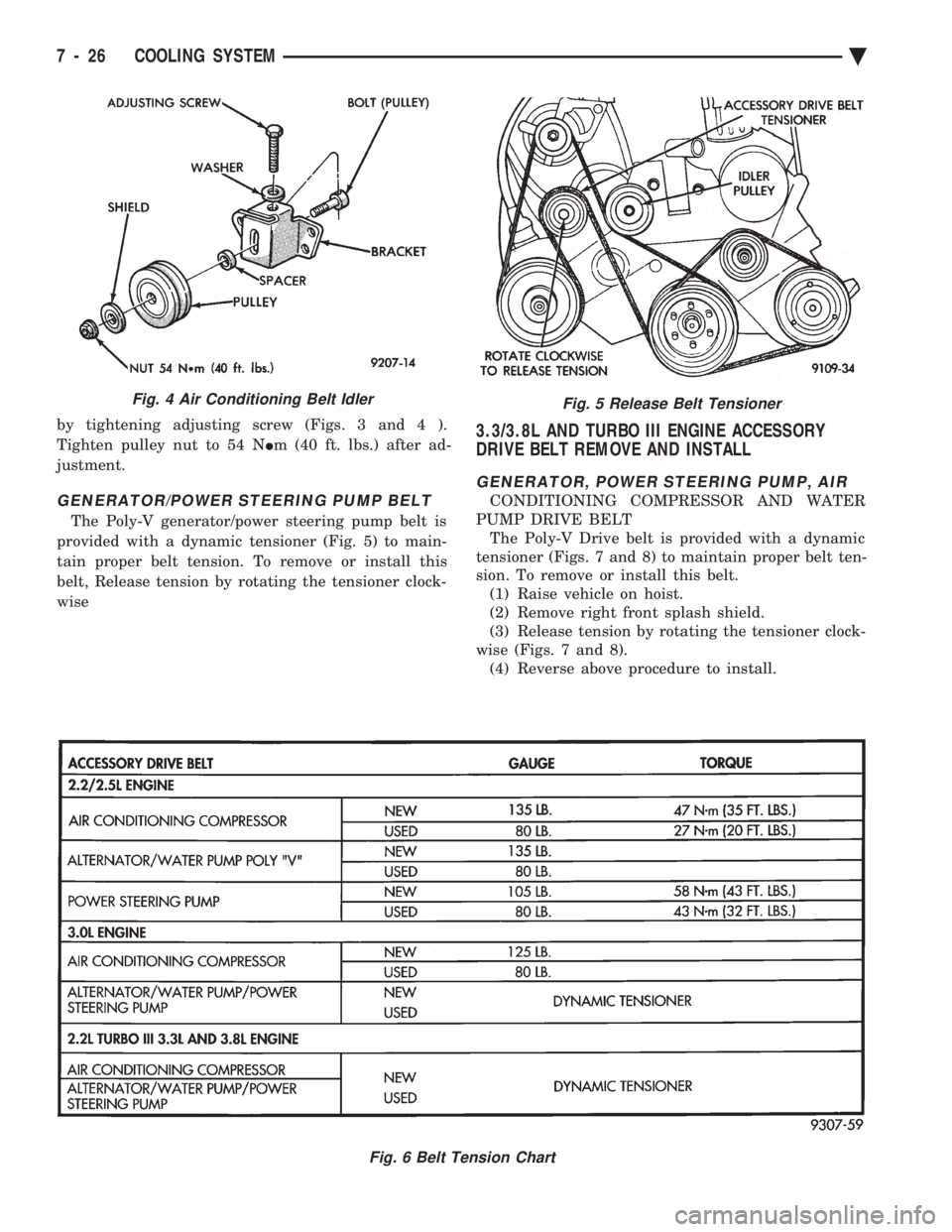
3.3/3.8L AND TURBO III ENGINE ACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT REMOVE AND INSTALL
GENERATOR, POWER STEERING PUMP, AIR
CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR AND WATER
PUMP DRIVE BELT The Poly-V Drive belt is provided with a dynamic
tensioner (Figs. 7 and 8) to maintain proper belt ten-
sion. To remove or install this belt. (1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove right front splash shield.
(3) Release tension by rotating the tensioner clock-
wise (Figs. 7 and 8). (4) Reverse above procedure to install.
Fig. 5 Release Belt Tensioner
Fig. 6 Belt Tension Chart
Fig. 4 Air Conditioning Belt Idler
7 - 26 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 369 of 2438

Fig. 7 Accessory Drive BeltÐ2.2L Turbo III Engine
Fig. 8 Accessory Drive BeltÐ3.3/3.8L Engines
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 27
Page 376 of 2438

It is important when using the Test Indicator that
the battery be level and have a clean top to see the
correct indications. A light may be required to view
the Indicator.
WARNING: DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY BECAUSE OF EXPLOSIVE GASES AT FORM
ABOVE BATTERY.
STATE OF CHARGE TESTS
USING TEST INDICATOR
The built in test hydrometer (Figs. 3, 4 and 5) mea-
sures the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Specific
Gravity (SG) of the electrolyte will show state of
charge voltage. The test indicator WILL NOT show
cranking capacity of the battery. Refer to Battery
Load. Look into the sight glass (Figs. 4 and 5) and
note the color of the indicator (Fig. 5). Refer to the
following description of colors:
² GREEN = 75 to 100 degree state of charge
The battery is adequately charged for further test-
ing and may be returned to use. If the vehicle will
not crank for a maximum 15 seconds, refer to Bat-
tery Load Test in this Group for more information.
² BLACK OR DAR K=0to75degree state of
charge The battery is INADEQUATELY charged and
must be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 volts
or greater) before the battery is tested or returned to
use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharging.
² YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR = Battery must
be replace
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR DOT IS VISI-
BLE. PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A yellow or bright color dot shows electrolyte level
in battery is below the test indicator (Fig. 5). Water
cannot be added to a maintenance free battery. The
battery must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may
be caused by an over charging condition. Refer to
Generator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 30 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF po-
sition, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The
continuous draw is due to various electronic features
or accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period approximately 20
days the Main Fusible Link Connector (Fig. 6)
should be disconnected. This is located near the bat- tery on the engine wiring harness. Disconnection of
this connector will help prevent battery discharging.
Refer to Fig. 7 for Battery Diagnostics.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
(1) Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
(2) Loose or worn generator drive belt.
(3) Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories in-
stalled after delivery. (4) Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use. (5) Defective electrical circuit or component caus-
ing excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Ignition
OFF Draw (IOD). (6) Defective charging system.
(7) Defective battery.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
An open circuit voltage, no load test will show the
state of charge in a battery. Also, if it will pass a
load test of 50 percent of the battery cold crank rat-
ing. Refer to Battery Load Test. If a battery has an
open circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or greater,
and will not pass a load test, it is defective and re-
placement would be required. To test open circuit
voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Remove both battery cables, negative first. If
the battery has been boosted, charged, or loaded just
prior to this operation, allow the battery a few min-
utes to stabilize. (2) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts and measure the open circuit voltage (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Main Fusible Link Connector
8A - 4 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä
Page 383 of 2438

STARTER TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE INDEX
page page
Diagnostic Preparation ..................... 11
General Information ....................... 11 Starter Control Circuit Tests
................ 15
Starter Feed Circuit Tests .................. 11
GENERAL INFORMATION
The starting system (Fig. 1) has:
² Ignition switch
² Starter relay (Fig. 2)
² Neutral starting and back-up switch with auto-
matic transmissions
² Clutch pedal mounted starter interlock switch
with manual transmissions
² Wiring harness
² Battery
² Starter motor with an integral solenoid
These components form two separate circuits. A
high amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up
to 300+ amps, and a control circuit that operates on
less than 20 amps.
DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATION
Before going on with starting system diagnostics,
verify: (1) The battery top, posts, and terminals are clean.
(2) The generator drive belt tension and condition
is correct. (3) The battery state-of-charge is correct.
(4) The battery will pass load test.
(5) The battery cable connections at the starter
and engine block are clean and free from corrosion. (6) The wiring harness connectors and terminals
are clean and free from corrosion. (7) Proper circuit grounding.
(8) Refer to Starter System Diagnostics (Fig. 3).
STARTER FEED CIRCUIT TESTS
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt/ampere tester (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled to
prevent engine start while performing the following
tests.
(1) Connect a volt-ampere tester (Fig. 4) to the bat-
tery terminals (Fig. 5). Refer to the operating in-
structions provided with the tester being used. (2) Disable ignition system as follows:
² VEHICLES WITH CONVENTIONAL DISTRIBU-
TORS: Disconnect the ignition coil cable from the
distributor cap. Connect a suitable jumper wire be-
tween the coil cable end-terminal and a good body
ground (Fig. 6).
Fig. 1 Starting Components/Wiring
Fig. 2 Starter Relay
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 11