1991 ACURA NSX air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 1015 of 1640

14. Relieve fuel pressure (see section 11).
Do not smoke while working on fuel
system; keep open flame or spark away from work
area. Drain fuel only into an approved container.
1 5. Disconnect the fuel feed pipe and the return hose
(page 5-21).
16. Remove the ignition coil covers, the wire harness covers, the ignition coils and the connectors (page
6-23).
17. Remove the water hoses, then remove the expan- sion tank (page 5-21).
18. Remove the breather hose, and the air cleaner housing (page 5-22).
19. Remove the brake booster hose, the evaporative emission (EVAP) control canister hose and other
hoses from the intake manifold and throttle body
(page 5-22).
20. Remove the emission control box (page 5-23). Do not disconnect emission hose.Disconnect the three connectors before
removing.
21. Remove the connector, the terminal and the alternator.
22. Disconnect the following engine wire harness con- nectors, then remove the harness clamps from thecylinder head and the intake manifold.
Front cylinder head:
Crankshaft position (CKP)/cylinder position
(CYP) sensor connector
Air conditioning (A/C) compressor magnetic clutch connector
Heated oxygen sensor (H02S) connector
Ground cable terminals Three injector connectors (cylinders No. 4, 5
and 6)
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor connector
Ignition control module (ICM) connector
Condenser connector
Engine oil pressure gauge sending unit
connector
VTEC solenoid valve connector
VTEC pressure switch connector
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
connector
ECT sending unit connector
Accelerator pedal opening sensor connector
(throttle body)
Radiator fan control sensor connector
Rear cylinder head: Engine oil pressure switch connector (oil cooler
base)
Heated oxygen sensor connector
Three injector connectors (cylinders No. 1, 2
and 3)
Idle air control (IAC) valve connector
Knock sensor connector
Throttle actuator motor connector
Throttle position sensor connector
VTEC solenoid valve connectorVTEC pressure switch connector
ICM connector
Ground terminal
ICM CONNECTORS THROTTLE ACTUATOR
MOTOR CONNECTOR
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR CONNECTOR
ACCELERATOR PEDAL OPENING
SENSOR CONNECTORProCarManuals.com
Page 1083 of 1640
How to Read Flowcharts
A flowchart is designed to be used from start to final repair. It's like a map showing you the shortest distance. But
beware: if you go off the "map" anywhere but a "stop" symbol, you can easily get lost.
(bold type)
(bold type)
Describes the conditions or situation to start a troubleshooting flowchart.
Asks you to do something; perform a test, set up a condition etc.
Asks you about the result of an action, then sends you in the appropriate troubleshooting direction.
The end of a series of actions and decisions, describes a final repair action and sometimes directs you
to an earlier part of the flowchart to confirm your repair.
NOTE:
The term "Intermittent Failure" is used in these charts. It simply means a system may have had a failure, but it checks
out OK at this time. If the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the dash does not come on, check for poor connections
or loose wires at all connections related to the circuit that you are troubleshooting (see illustration below).
Most of the troubleshooting flowcharts have you reset the Engine Control Module (ECM) and try to duplicate the Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC). If the problem is intermittent and you can't duplicate the code, do not continue through
the flowchart. To do so will only result in confusion and, possibly, a needlessly replaced ECM.
"Open"
and
"Short"
are
common electrical terms.
An
open
is a
break
in a
wire
or at a
connection.
A
short
is an
accidental connection of a wire to ground or to another wire. In simple electronics, this usually means something won't
work at all. In complex electronics (like ECM's), this can sometimes mean something works, but not the way it's sup-
posed to.
If the electrical readings are not as specified when using the test harness, check the test harness connections before
proceeding.
TIGHT
LOOSEProCarManuals.com
Page 1084 of 1640

PGM-FI System
System Description
INPUTS
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
OUTPUTS
FRONT HO2S
REAR HO2S
MAP Sensor
CKP/CYP Sensor
ECT Sensor
TP Sensor
IAT Sensor
VSS
FRONT KS
REAR KS
Ignition Timing Adjuster
EGR Valve Lift Sensor
A/T Fl Signals
TCS Signals
Starter Signal
ALT FR Signal
Air Conditioning Signal
A/T Gear Position Switch Signal
Neutral Switch Signal (M/T)
Clutch Switch Signal (M/T)
VTEC Pressure Switch
Battery Voltage (IGN.1)
Fuel Pump Terminal Voltage
Fuel Injectors
PGM-FI Main Relay (Fuel Pump)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
IAC Valve
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
ICM
EVAP Purge Control Solenoid Valve
Fuel Pump Relay
EGR Control Solenoid Valve
IAB Control Solenoid Valve
Engine Compartment Fan Relay
VTEC Solenoid Valve
TCS Control Signals
FRONT HO2S HEATER
REAR HO2S HEATER
PGM-FI System
The PGM-FI system on this model is a sequential multiport fuel injection system.
Fuel Injector Timing and Duration
The ECM contains memories for the basic discharge durations at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. The
basic discharge duration, after being read out from the memory, is further modified by signals sent from various sensors
to obtain the final discharge duration.
Idle Air Control
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
When the engine is cold, the A/C compressor is on, the transmission is in gear (A/T only) or the alternator (ALT) is charg-
ing, the ECM controls current to the IAC valve to maintain correct idle speed.
Ignition Timing Control
The ECM contains memories for basic ignition timing at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. Ignition timing
is also adjusted for engine coolant temperature.
A knock control system is also used. When detonation is detected by the knock sensor (KS), the ignition timing is
retarded.
Other Control Functions
1. Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECM provides a rich mixture by increasing fuel injector duration.
2. Fuel Pump Control
When the ignition switch is initially turned on, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies
current to the fuel pump for two seconds to pressurize the fuel system.
When the engine is running, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies current to the fuel pump.
When the engine is not running and the ignition is on, the ECM cuts ground to the PGM-FI main relay which cuts
current to the fuel pump.
Excellent engine performance is achieved through the use of VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Valve Lift Electron-
ic Control System), intake air bypass control and discharge volume control of the fuel pump.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1085 of 1640

3. Fuel Cut-off Control
During deceleration with the throttle valve closed, current to the fuel injectors is cut off to improve fuel economy
at speeds over 1,500 rpm.
Fuel cut-off action also takes place when engine speed exceeds, 8,300 rpm, regardless of the position of the
throttle valve, to protect the engine from over-revving.
4. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
When the ECM receives a demand for cooling from the air conditioning system, it delays the compressor from being
energized, and enriches the mixture to assure smooth translation to the A/C mode.
5. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge Control Solenoid Valve
When the engine coolant temperature is below 1 58 °F (70°C) the ECM supplies a ground to the EVAP purge control
solenoid valve which cuts vacuum to the EVAP purge control diaphragm valve.
6. Intake Air Bypass (IAB) Control Solenoid Valve
When the engine speed is below 4,800 rpm, the IAB control solenoid valve is activated by a signal from the ECM.
Intake air then flows through the smaller chamber, and hight torque is delivered. To increase air flow at engine speeds
higher than 4,800 rpm, the solenoid valve is deactivated by the ECM, and the intake air flows through the larger
chamber.
7. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control Solenoid Valve
When the EGR is required for control of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions, the ECM supplies ground to the EGR
control solenoid valve which supplies regulated vacuum to the EGR valve.
ECM fail-safe/back-up Functions
1. Fail-Safe Function
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM ignores that signal and assumes a pre-programmed
valve for that sensor that allows the engine to continue to run.
2. Back-up Function
When an abnormality occurs in the ECM itself, the fuel injectors are controlled by a back-up circuit independent of
the system in order to permit minimal driving.
3. Self-diagnosis Function [Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)]
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM lights the MIL and stores the diagnostic trouble code
in erasable memory. When the ignition is initially turned in, the ECM supplies ground for the MIL for two seconds
to check the MIL bulb condition.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1091 of 1640
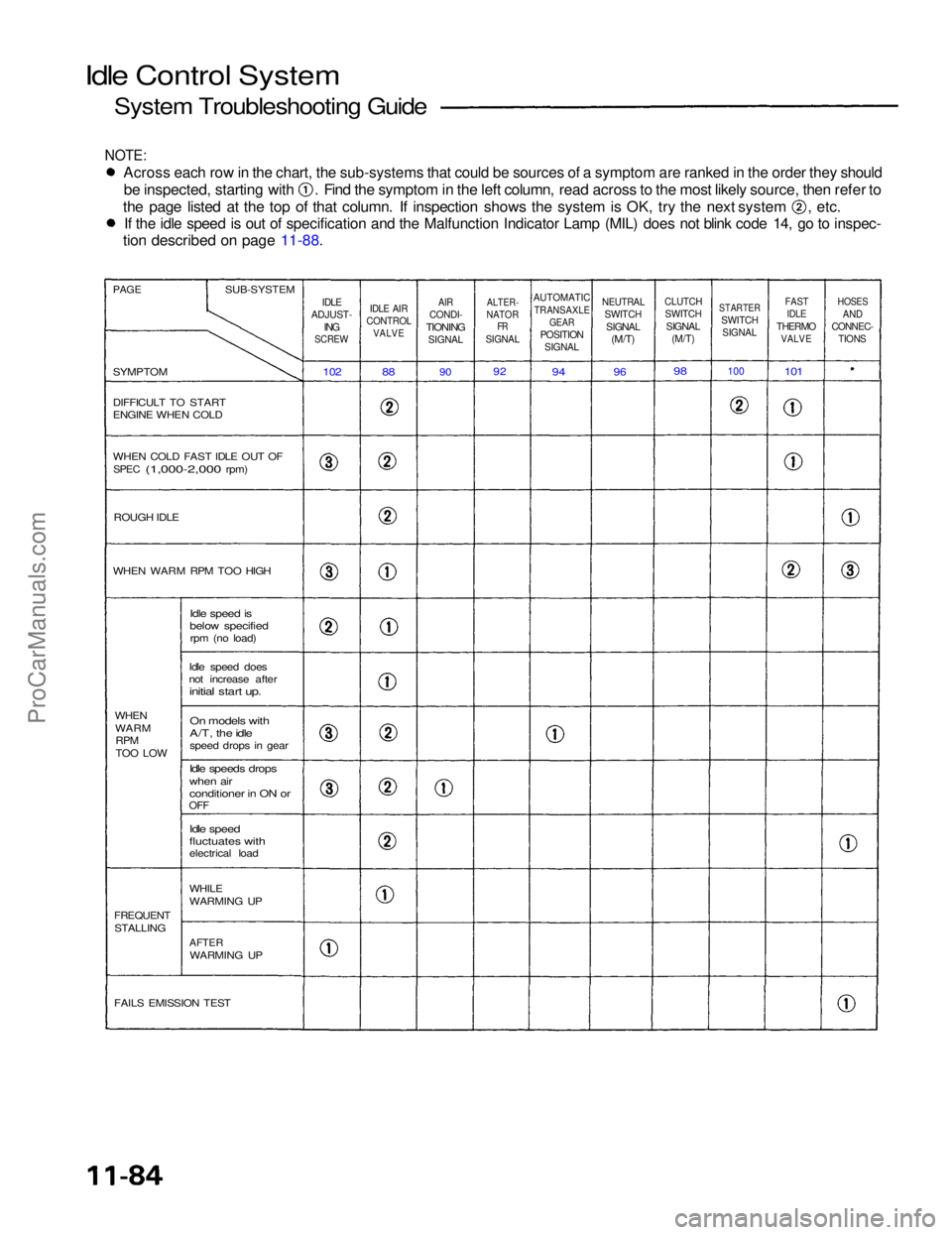
Idle Control System
System Troubleshooting Guide
NOTE:
Across each row in the chart, the sub-systems that could be sources of a symptom are ranked in the order they should
be inspected, starting with . Find the symptom in the left column, read across to the most likely source, then refer to
the page listed at the top of that column. If inspection shows the system is OK, try the next system , etc.
If the idle speed is out of specification and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) does not blink code 14, go to inspec-
tion described on page 11-88.
PAGE
SUB-SYSTEM
SYMPTOM
DIFFICULT TO START
ENGINE WHEN COLD
WHEN COLD FAST IDLE OUT OF
SPEC
(1,000-2,000
rpm)
ROUGH IDLE
WHEN WARM RPM TOO HIGH
Idle speed is
below specified
rpm (no load)
Idle speed does
not increase after
initial start up.
WHEN WARM
RPM
TOO LOW
On models with
A/T, the idle
speed drops in gear
Idle speeds drops
when air
conditioner in ON or
OFF
Idle speed
fluctuates with
electrical load
WHILE
WARMING UP
FREQUENT
STALLING
AFTER
WARMING UP
FAILS EMISSION TEST
IDLE
ADJUST-
ING
SCREW
IDLE AIR
CONTROL
VALVE
AIR
CONDI-
TIONING
SIGNAL
ALTER-
NATOR
FR
SIGNAL
NEUTRAL
SWITCH
SIGNAL
(M/T)
STARTER
SWITCH
SIGNAL
FAST
IDLE
THERMO
VALVE
HOSES
AND
CONNEC-
TIONS
CLUTCH
SWITCH
SIGNAL
(M/T)
AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
GEAR
POSITION
SIGNAL
102
88
90
92
94
96
98
100
101ProCarManuals.com
Page 1094 of 1640

1. When the idle speed is out of specification and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) does not blink code 14, check
the following items:
Adjust the idle speed (see page 11-102)
Air conditioning signal (see page 11 -90)
ALT FR signal (see page 11-92)
A/T gear position switch signal (see page 11-94)Neutral switch signal (M/T) (see page 11-96)
Clutch switch signal (M/T) (see page 11-98)
Starter switch signal (see page 11-100)Fast idle thermo valve (see page 11-101)
Hoses and connections
IAC valve and its mounting O-rings
2. If the above items are normal, substitute a known-good IAC valve and readjust the idle speed (see page 11-102). If the idle speed still cannot be adjusted to specification (and the MIL does not blink code 14) after IAC valve
replacement, substitute a known-good ECM and recheck. If symptom goes away, replace the original ECM.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1095 of 1640
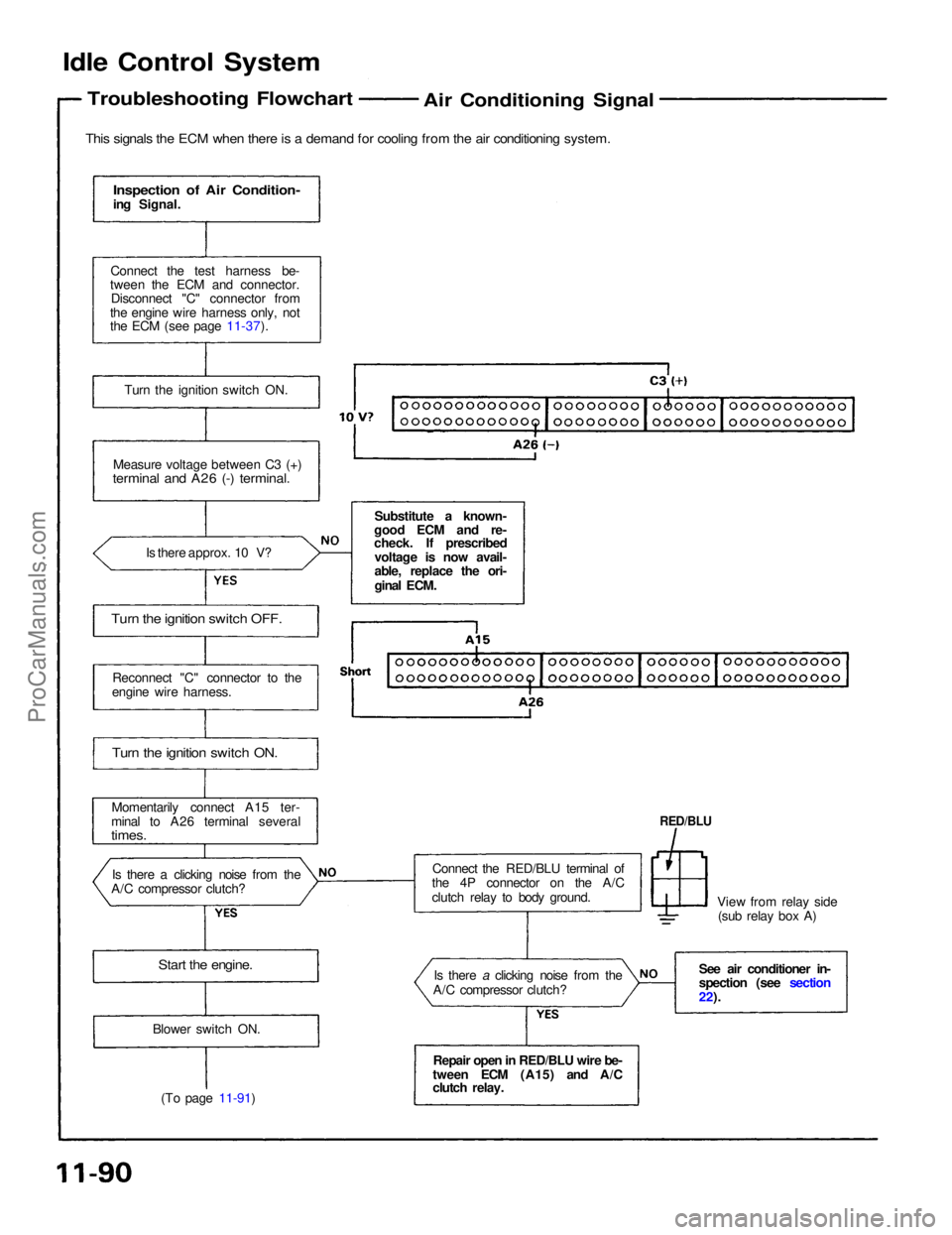
Idle Control System
Troubleshooting Flowchart
Air Conditioning Signal
This signals the ECM when there is a demand for cooling from the air conditioning system.
Inspection of Air Condition-
ing Signal.
Connect the test harness be-
tween the ECM and connector. Disconnect "C" connector from
the engine wire harness only, not
the ECM (see page 11-37).
Turn the ignition switch ON.
Measure voltage between C3 (+)
terminal and A26 (-) terminal.
Is there approx. 10 V?
Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Reconnect "C" connector to the
engine wire harness.
Turn the ignition switch ON.
Momentarily connect A15 ter-
minal to A26 terminal several
times.
Is there a clicking noise from the
A/C compressor clutch?
Start the engine.
Blower switch ON.
(To page 11-91) Repair open in RED/BLU wire be-
tween ECM (A15) and A/C
clutch relay. Is there a clicking noise from the
A/C compressor clutch?
Connect the RED/BLU terminal of
the 4P connector on the A/C
clutch relay to body ground. View from relay side
(sub relay box A)
RED/BLU
See air conditioner in-
spection (see section
22).
Substitute a known-
good ECM and re-
check. If prescribed
voltage is now avail-
able, replace the ori-
ginal ECM.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1096 of 1640
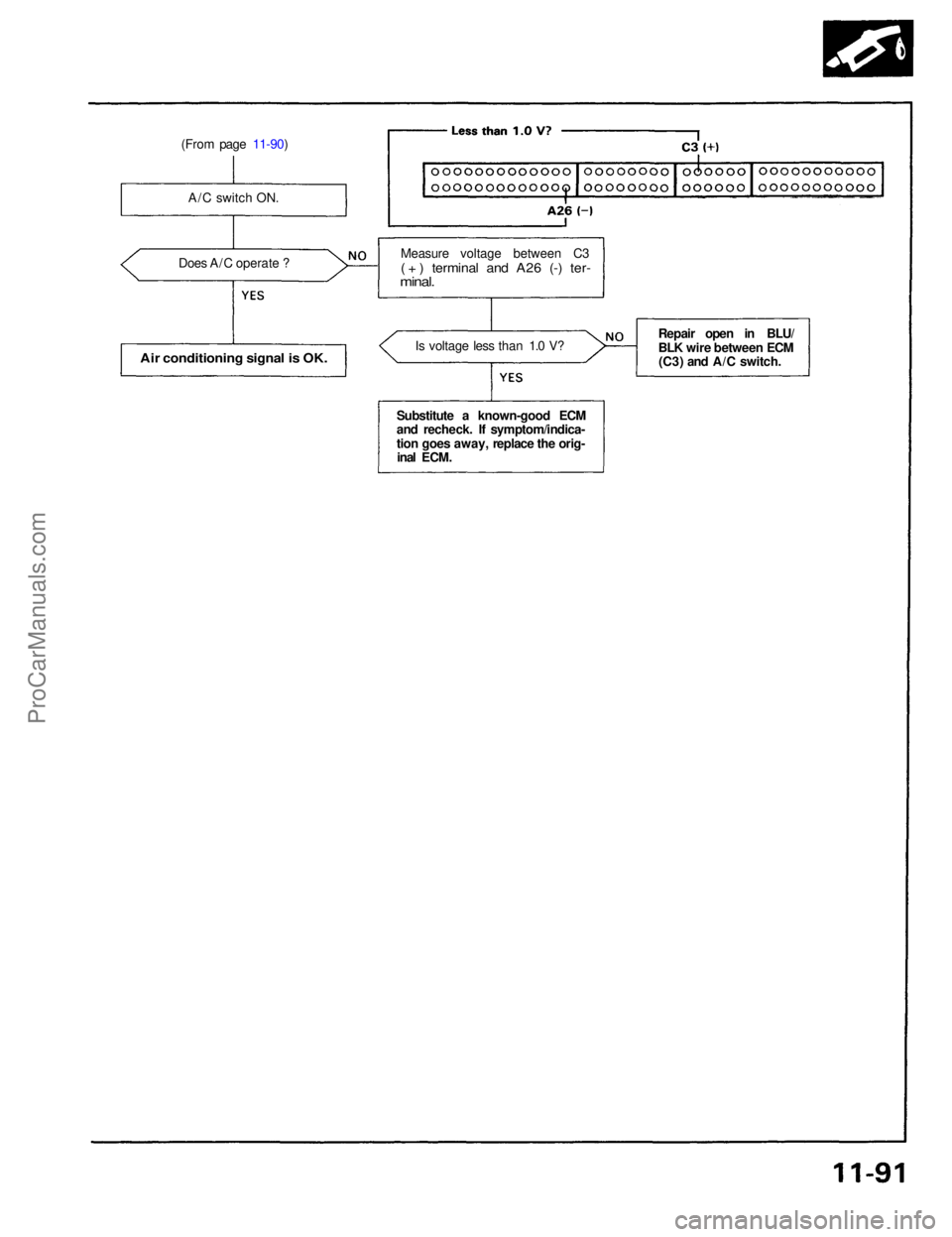
(From page 11-90)
A/C switch ON.
Does A/C operate ?
Air conditioning signal is OK.
Is voltage less than 1.0 V?
Measure voltage between C3
( + ) terminal and A26 (-) ter-
minal.
Substitute a known-good ECM
and recheck. If symptom/indica-
tion goes away, replace the orig- inal ECM. Repair open in BLU/
BLK wire between ECM
(C3) and A/C switch.ProCarManuals.com