1988 PONTIAC FIERO spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 714 of 1825

DWI\/EABILITV AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN 5) 6E3-B-5
CU"T SUP, MISSES
Definition: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine
speed, usually more pronounced as engine load increases. The
exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
@ Perform careful visual check as described at
start of Section
"B".
@ Check for missing cylinder by:
1. Disconnect IAC valve. Start engine.
Remove one spark plug wire at a time
using insulated pliers.
2. If there is an rpm drop on all cylinders
(equal to within
50 rpm), go to "ROUGH,
UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE,
STALLING" symptom. Reconnect IAC
valve.
3. If
there is no rprn drop on one or more
cylinders, or excessive variation in drop,
check for spark on the suspected
cylinder(s) with J 26792 (ST-125) Spark
Gap Tool or equivalent.
If no spark, see
Section
"6D" for intermittent operation or
miss. If there is spark, remove spark
plug(s) in these cylinders and check for:
- Cracks
- Wear
- Improper gap
- Burned electrodes
- Iieavy deposits
@ Perform compression check on questionable
cylinder(s) found above. If compression is low,
repair as necessary. See Section
"6".
@ Disconnect all injector harness connectors.
Connect
5-34730-2 injector test light or
equivalent 6 volt test light between the
harness terms, of each injector connector and
note light while cranking. If test light fails to blink
at any connector, it is a faulty injector drive
circuit harness, connector, or terminal.
@ Perform the injector balance test. See CHART C-
2A.
s CHECK:
- Spark plug wires by connecting ohmmeter to
ends of each wire in question. If meter reads over
30,000 ohms, replace wire(s1.
- Fuel System - Plugged fuel filter, water, low
pressure. See
CHART A-7.
- Valve timing.
- Secondary voltage using a shop ocilliscope or a
spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125) or equivalent.
@ Visually inspect distributor cap and rotor for
moisture, dust, cracks, burns, etc. Spray cap and
plug wires with, fine water mist to check for
shorts.
@ A miss condition can be caused by EM1
(Electromagnetic Interference) on the reference
circuit.
EM1 can usually be detected by
monitoring engine rpm with a "Scan" tool. A
sudden increase in rpm with little change in
actual engine rpm change, indicates
EM1 is
present. If the problem exists, check routing of secondary
wires, check all distributor ground circuits.
@ Remove rocker covers. Check for bent pushrods,
worn rocker arms, broken valve springs, worn
camshaft lobes. Repair as necessary. See Section
"6A".
BACKFIRE
Definition: Fuel ignites in intake manifold, or
in exhaust system, making a loud popping noise.
CHECK:
- Loose wiring connector or air duct at MAF
sensor.
- Compression - Look for sticking or leaking
valves.
- EGR operation for being open all the time. See
CHART C-7.
- EGR gasket for faulty or loose fit .
- Valve timing.
- Output voltage of ignition coil using a shop
ocilliscope or spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125) or
equivalent.
- Spark plugs for crossfire also inspect (distributor
cap, spark plug wires, and proper routing of plug
wires).
- Ignition system for intermittent condition. (See
Section
"6D").
- Engine timing - see Emission Control
Information label.
- Perform fuel system diagnosis check, CIIART A-
7A.
- Perform injector balance test, CHART C-2A.
- Deceleration valve (2.8L ~nanualltrans) - See
Section
"C6".
- A.I.R. system check valves - See Section "C-6".
Page 716 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN S) 6E3-B-7
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS 08 ODORS
Definition: Vehicle fails an emission test. Vehicle has excessive "rotten egg" smell.
Excessive odors do not necessarily indicate excessive emissions.
r Perform "Diagnostic Circuit Check."
e IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE CO AND HC,
(or also has excessive odors):
@ Check items which cause car to run RICH.
@ Make sure engine is at normal
operating temperature.
@ CHECK:
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
- Incorrect timing. See vehicle emission
control information label.
- Canister for fuel loading. See CHART C-3.
- Injector balance. See CHART C-2A.
- PCV valve for being plugged, stuck, or
blocked PCV hose, or fuel in the crankcase.
- Spark plugs, plug wires, and ignition
components. See Section
"6D".
- Check for lead contamination of catalytic
converter (look for removal of fuel filler
neck restrictor).
- Check for properly installed fuel cap.
@ If the system is running rich, (block learn
less than
118), refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on
facing page of Code
45.
e IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE NOx:
e Check items which cause car to run LEAN,
or to run too hot.
- EGR valve for not opening. See CHART
C-7.
- Vacuum leaks. - Coolant system and coolant fan for
proper operation. See CHART C-12.
- Remove carbon with top engine cleaner.
Follow instructions on can.
- Check ignition timing for excessive base
advance. See emission control
information label.
@ If the system is running lean, (block learn
greater than
138), refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on
facing page of Code
44.
Page 817 of 1825
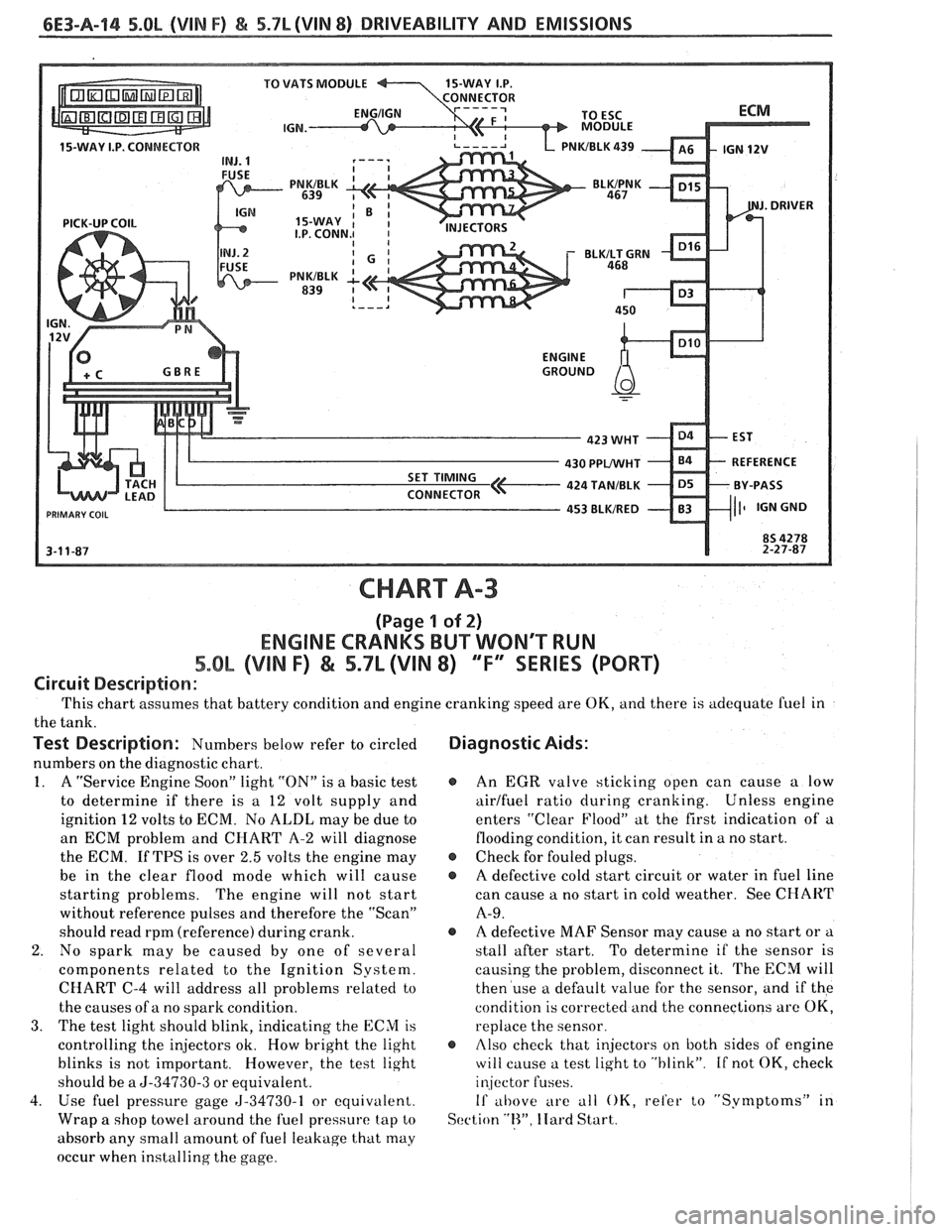
6E3-A-14 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHART A-3
(Page 1 of 2)
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WON'T RUN
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SRIES (PORT)
Circuit Description :
This chart assumes that battery condition and engine cranking speed are OK, and there is adequate fuel in
the tank.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Diagnostic Aids:
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. A "Service Engine Soon" light "ON" is a basic test @ An EGR valve sticking open can cause a low
to determine if there is a
12 volt supply and airlfuel ratio during cranking. Unless
engine
ignition
12 volts to ECM. No ALDL may be due to enters
"Clear Flood" at the first indication of a
an ECM problem and CHART
A-2 will diagnose flooding
condition, it can result in a no start.
the ECM. If TPS is over
2.5 volts the engine may @ Check for fouled plugs.
be in the clear flood mode which will cause
@ A defective cold start circuit or water in fuel line
starting problems. The engine
will not start can
cause a no start in cold weather. See
CHART
without reference pulses and therefore the "Scan" A-9.
should read rpm (reference) during crank. @ A defective MAF Sensor may cause a no start or a
2. No spark may be caused by one of several stall
after start. To determine if the sensor is
components related to the Ignition System. causing
the problem, disconnect it. The
ECM will
CHART C-4 will address all problems related to then
use a default value for the sensor, and if the
the causes of a no spark condition. condition
is corrected and the connections are
OK,
3. The test light should blink, indicating the ECM is replace the sensor.
controlling the injectors ok. How bright the light
@ rllso check that injectors on both sides of engine
blinks is not important. However, the test light
will cause a test light to "blink". If not OK, check
should be a
5-34730-3 or equivalent. injector fuses.
4. Use fuel
pressure gage 5-34730-1 or equivalent. If al~ove are all OK, refer to "Symptoms" it1
Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure tap to Scction "R". Ilard Start.
absorb any small amount of fuel leakage that may
occur when installing the gage.
Page 867 of 1825

6E3-B-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Problem may or may not turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light, or store a code.
DO NOT use the Trouble Code Charts in
An intermittent "Service Engine Soon" light
Section A for intermittent problems. The fault must
with no stored code may be caused by:
be present to locate the problem. If a fault is
@ Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at
intermittent, use of Trouble Code Charts
may result
spark plug wires or plugs.
in replacement of good parts.
"Service Engine Soon" light wire to
ECM
@ Most intermittent problems are caused by
shorted to ground. (CKT 419).
faulty electrical connections or wiring. Perform
Diagnostic "Test" Terminal wire to ECM,
careful check as described at start of Section
shorted to
ground.(CKT 451)
"B". Check for:
@ ECM power grounds. See ECSI wiring
@ Poor mating of the connector halves, or diagrams.
terminals not fully seated in the connector
@ Loss of trouble code memory. To check,
body (backed out). disconnect TPS and idle engine until "Service
@ Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Engine Soon" light comes on. Code 22 should be
All connector terminals in problem circuit
stored, and kept in memory when ignition is
should be carefully reformed or replaced to turned "OFF". If not, the ECM is faulty.
insure proper contact tension.
@ Check for an electrical system interference
@ Poor terminal to wire connection. This caused by a defective relay, ECM driven
requires removing the terminal from the
solenoid, or switch. They can cause a sharp
connector body to check. See "Introduction"
electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
to Section
"6E". occur when the faulty component is operated.
@ If a visual check does not find the cause of the @ Check for improper installation of electrical
problem, the car can be driven with a voltmeter
options, such as lights,
%way radios, etc.
connected to
a suspected circuit. A "Scan" tool
EST wires should be kept away from spark plug
can also be used for monitoring input signals to wires, distributor wires, distributor housing,
the ECM to help detect intermittent conditions. coil, and generator. Wire from
ECM to
An abnormal voltage, or "Scan" reading, when distributor
(CKT 453) should be a good
the problem occurs, indicates the problem
may connection.
be in that circuit. If the wiring and connectors
@ Check for open diode across AIC compressor
check OK and a Trouble Code was stored for a
clutch, and for other open diodes (see wiring
circuit having a sensor, except for Codes
43, 44, diagrams).
and 45, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
HARD START
Definition: Engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long
time. Does eventually run, or may start but immediately dies.
Perform careful check as described at start of
Section
"B".
@ Make sure driver is using correct starting
procedure.
@ CHECK:
- TPS for sticking or binding or a high TPS
voltage with the throttle closed (should read
less than
.700 volts).
- High resistance in coolant sensor circuit or
sensor itself. See Code 15 chart or with
a
"Scan" tool compare coolant temperature with
ambient temperature on a cold engine.
- Fuel pressure CHART A-7.
- Water contaminated fuel.
- EGR operation. Be sure valve seats properly and
is not staying open. See CHART C-7.
- Both injector fuses (visually inspect).
- Ignition system - Check distributor for:
Proper Output with ST-125.
Worn shaft.
Bare and shorted wires.
Pickup coil resistance and connections.
Loose ignition coil ground.
Moisture in distributor cap.
@ If problem exists in cold weather, check cold start
valve. See CHART A-9.
Page 868 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-8-3
@ A faulty in-tank fuel pump check valve will @
allow the fuel in the lines to drain back to the
tank after the engine is stopped. To check for
this condition:
e
Perform Fuel System Diagnosis, CHART A-7.
@ Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes,
@
or heavy deposits. Repair or replace as
necessary. If
engine starts but then immediately stalls
open distributor by-pass line. If engine then
starts and runs OK, replace pickup coil.
If engine starts and stalls disconnect MAF
sensor. If engine then
r~lns and sensor
connections are OK, replace
thr. )t.ft+rl'.
Basic engine problem.
HESITATION, SAG, STUMBLE
Definition: Momentary lack of response as the accelerator i., pl,ihcc! dowt-
Can occur at all car speeds. Usually most severe when first tryine, lo m,tlir. LII~.
car move, as from a stop sign. May cause the engine to sta!! 1, e er., riu~~~!~
s Perform careful visual check as described at
start of Section
"B".
@ CHECK:
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7. Also, check
for water contaminated fuel.
- Air leaks at air duct between MAF sensor and
throttle body.
- Spark plugs for being fouled or faulty wiring.
- Mem-Cal number. Also check service bulletins
for latest Mem-Cal.
- TPS for binding or sticking. Voltage should
increase at
a steady rate as throttle is moved
toward WOT.
- Ignition timing. See emission control
information label.
- Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9
or more than 16 volts.
- HE1 ground, CKT 453.
- Canister purge system for proper operation.
See CHART C-3.
- EGR - See CHART C-7.
e Perform injector balance test CHART C-2A.
SURGES AND/OR CHUGGLE
Definition: Engine power variation under steady
throttle or cruise. Feels like the car speeds up and
slows down with no change in the accelerator pedal.
@ Be sure driver understands transmission
converter clutch and
AJC compressor operation
in owner's manual.
Perform careful visual inspection as described
at start of Section
"B".
e CHECK:
- Loose or leaking air duct between MAF sensor
and throttle body.
- Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9
or more than 16 volts.
- EGR - There should be no EGR at idle. See
CHART C-7.
- Vacuum lines for kinks or leaks.
- Ignition timing. See emission control
information label.
- In-line fuel filter. Replace if dirty or plugged.
- Fuel pressure while condition exists. See
CHART A-7.
@ Inspect oxygen sensor for silicon contamination
from fuel, or use of improper RTV sealant. The
sensor may have a white, powdery coating and
result in a high but false signal voltage (rich
exhaust indication). The ECM will then reduce
the amount of fuel delivered to the engine,
causing a severe driveability problem.
@ Remove spark plugs. Check for cracks, wear,
improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Also check condition of distributor
cap, rotor, and spark plug wires.
@ To help determine if the condition is caused by a
rich or lean system, the car should be driven at
the speed of the complaint. Monitoring block
learn at the complaint speed will help identify
the cause of the problem.
If the system is lean
(block learn greater than
1381, refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
on facing page of Code 44. If
the system is running rich (block learn less than
1181, refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing page
of Code
45.
Page 870 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS S.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-B-5
Definition: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine
speed, usually more pronounced as engine load increases. The
exhaust has
a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
@ Perform careful visual check as described at blink
at any connector, it is a faulty injector drive
start of Section
"B". circuit harness, connector, or terminal.
@ Check for missing cylinder by: @ Perform the Injector Balance Test. See CHART
1. Disconnect IAC valve. Start engine. C-2A.
Remove one spark plug wire at a time
@ CHECK:
using insulated pliers. - Spark plug wires by connecting ohmmeter to
2. If there is an rpm drop on all cylinders ends
of each wire in question. If meter reads over
(equal to within
50 rpm), go to "ROUGH, 30,000
ohms, replace wire(s).
UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE, - Fuel System - Plugged fuel filter, water, low
STALLING" symptom. Reconnect IAC pressure. See CHART A-7.
valve.
- Valve timing.
3. If there is no rpm drop on one or more - Secondary voltage using a shop ocilliscope or a
cylinders, or excessive variation in drop, spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125)
or equivalent.
check for spark on the suspected
@ Visually inspect distributor cap and rotor for
cylinder(s) with J 26792 (ST-125) Spark moisture, dust, cracks, burns, etc. Spray cap and
Gap Tool or equivalent. If no spark, see plug wires with fine water mist to check for
Section 6D for Intermittent Operation or shorts.
Miss. If there is spark, remove spark
@ A miss condition can be caused by EM1
plug(s) in these cylinders and check for: (Electromagnetic Interference) on the reference
- Cracks circuit. EM1 can usually be detected by
- Wear monitoring engine rpm with a "Scan" tool. A
- Improper Gap sudden
increase in rpm with little change in
- Burned Electrodes actual engine rpm change, indicates EM1 is
- Heavy Deposits present.
@ Perform compression check on questionable If
the problem exists, check routing of secondary
cylinder(s) found above. If compression is low, wires, check
all distributor ground circuits.
repair as necessary. See Section
"6". @ Remove rocker covers. Check for bent pushrods,
@ Disconnect all injector harness connectors. worn
rocker arms, broken valve springs, worn
Connect
5-34730-2 Injector Test Light or camshaft
lobes. Repair as necessary. See Section
equivalent 6 volt test light between the
"6A".
harness terms, of each injector connector and
note light while cranking. If test light fails to
BACKFIRE
Definition: Fuel ignites in intake manifold, or
in exhaust system, making a loud popping noise.
@ CHECK: - Spark plugs for crossfire also inspect (distributor
- Loose wiring connector or air duct at MAF
cap, spark plug wires, and proper routing of plug
sensor. wires).
- Compression - Look for sticking or leaking - Ignition system for intermittent condition. (See
valves. Section
"6D").
- EGR operation for being open all the time. See - Engine timing - see emission control information
CHART C-7. label.
- EGR gasket for faulty or loose fit. - Perform fuel system diagnosis check, CHART A-
- Valve timing. 7A.
- Output voltage of ignition coil using a shop - Perform injector balance test CI-IART C-2A.
ocilliscope or spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125) or
- A.I.R. system check valves - See Section "C-6".
equivalent.
Page 872 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) 6E3-B-7
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS
Definition: Vehicle fails an emission test. Vehicle has excessive "rotten egg" smell.
Excessive odors do not necessarily indicate excessive emissions.
@ Perform "Diagnostic Circuit Check."
@ IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE CO AND HC,
(or also has excessive odors):
@ Check items which cause car to run RICH.
@ Make sure engine is at normal
operating temperature.
@ CHECK:
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
- Incorrect timing. See vehicle emission
control information label.
- Canister for fuel loading. See CHART C-3.
- Injector balance. See CHAR'I' C-2A.
- PCV valve for being plugged, stuck, or
blocked PCV hose, or fuel in the crankcase.
- Spark plugs, plug wires, and ignition
components. See Section
"6D".
- Check for lead contamination of catalytic
converter (look for removal of fuel filler
neck restrictor).
- Check for properly installed fuel cap.
@ If the system is running rich, (block learn
less than
118), refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on
facing page of Code
45.
@ IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE NOx:
@ Check items which cause car to run LEAN,
or to run too hot.
- EGR valve for not opening. See CHART
C-7.
- Vacuum leaks.
- Coolant system and coolant fan for
proper operation. See CHART C-12.
- Remove carbon with top engine cleaner.
Follow instructions on can.
- Check ignition timing for excessive base
advance. See emission control
information label.
@ If the system is running lean, (block learn
greater than
138), refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on
facing page of Code 44.
Page 973 of 1825

6E-12 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - FUEL INJECUION
and MPH) for abbreviations used in this Section, but
all types are acceptable.
NA/F - AI WFUEL (NF RATIO)
A.I.R.
- AIR INJECTOR REACTION SYSTEM - Air
flow from pump is directed into engine exhaust
manifold
and/or converter to reduce exhaust
emissions.
ALDL - ASSEMBLY LINE DIAGNOSTIC LINK - Used
at assembly to evaluate Computer Command Control,
and for service to flash the "Service Engine Soon"
light
if there are trouble codes. It also is used by
"Scan" tools to obtain ECM serial data.
BARO - BAROMETRIC ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
SENSOR
- Reads atmospheric pressure.
B + - Battery Positive Terminal (12 Volts) or
system voltage with the engine running
(approximately 13.8
v.)
CALPAK - A device used with fuel injection to
allow fuel delivery in the event of a PROM or ECM
malfunction.
CALIBRATOR - (PROM) - An electronic component
that can be
specifically programmed to meet engine
operating requirements for a
specific vehicle model.
It plugs into the Engine Control Module
(ECM).
CCC - COMPUTER COMMAND CONTROL - has an
electronic control module to control airlfuel and
emission systems.
CLCC - CLOSED LOOP CARBURETOR CONTROL -
Used to describe oxygen sensor to ECM to MIC
solenoid circuit operation.
C3I - Computer Controlled Coil Ignition. Produces
the ignition spark without the aid of an ignition
distributor.
CCP - CONTROLLED CANISTER PURGE - ECM
controlled solenoid valve that permits manifold
vacuum to purge the evaporative emissions from the
charcoal canister.
CID - CUBIC INCH DISPLACEMENT - Used to
describe engine size.
UL OR ULOOP - "CLOSED LOOP" - Describes ECM
fuel control when using oxygen sensor information.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR - Device that
senses the engine coolant temperature, and passes
that information to the engine control module.
CONV. - CATALYTIC CONVERTER, THREE-WAY -
EXHAUST CONVERTER. Containing platinum and
palladium to speed up conversion of
HC and CO, and
rhodium to accelerate conversion of NO,.
CO - CARBON MONOXIDE - One of the pollutants
found in engine exhaust.
6V - CRANKCASE VENTlhaflON - Prevents fumes
in crankcase from passing into the atmosphere, by
drawing them into the intake manifold and burning
them in the the combustion process.
DIAGNOSTIC CODE - Pair of numbers obtained
from flashing "Service Engine Soon" light or
displaying on a "Scan" tool. This code can be used to
determine the system malfunction.
DIAGNOSTIC TERM. - Lead of ALDL Connector
which is grounded to get a Trouble Code.
It is
grounded with the engine running to enter the "Field
Service Mode".
DIS - Direct Ignition System. Produces the
ignition spark without the aid of an ignition
distributor.
DVM (10 Meg.) - Digital Voltmeter with 10 Million
ohms resistance
- used for measurement in electronic
systems.
DWELL - The amount of time (recorded on a dwell
meter in degrees of crankshaft rotation) that current
passes through a closed switch; for example, ignition
contact points or internal switch in an electronic
control module.
EAC - ELECTRIC AIR CONTROL - Used on A.I.R.
system to direct air flow to air switching valve or to
atmosphere.
EAS - ELECTRIC AIR SWITCHING - used to direct air
flow to catalytic converter or exhaust ports of the
engine.
ECM - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ELECTRONIC) -
A metal case (located in passenger compartment)
containing electronic circuitry which electrically
controls and monitors airlfuel and emission systems
on computer command control, and turns
"ON" the
"Service Engine Soon" light when a malfunction
occurs in the system.
EFI - ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION - Computer
Command Control using throttle body fuel injection.
EGR - EXHAUST GAP REClRCUbATlON - Method of
reducing NO, emission levels by causing exhaust gas
to be added to airlfuel mixture in combustion
chamber, thus cooling combustion.
EECS - EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS CONTROL
SYSTEM
- Used to prevent gasoline vapors in the fuel
tank from entering the atmosphere.
EFE - EARLY FUEL EVAPORATION - Method of
warming the intake manifold during cold engine
operation. Provides efficient airlfuel mixing.
ENERGIZEIDE-ENERGIZE - When current is passed
through a coil (energized) such as the canister purge
solenoid, the plunger is pulled into the solenoid.