1988 PONTIAC FIERO transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 402 of 1825
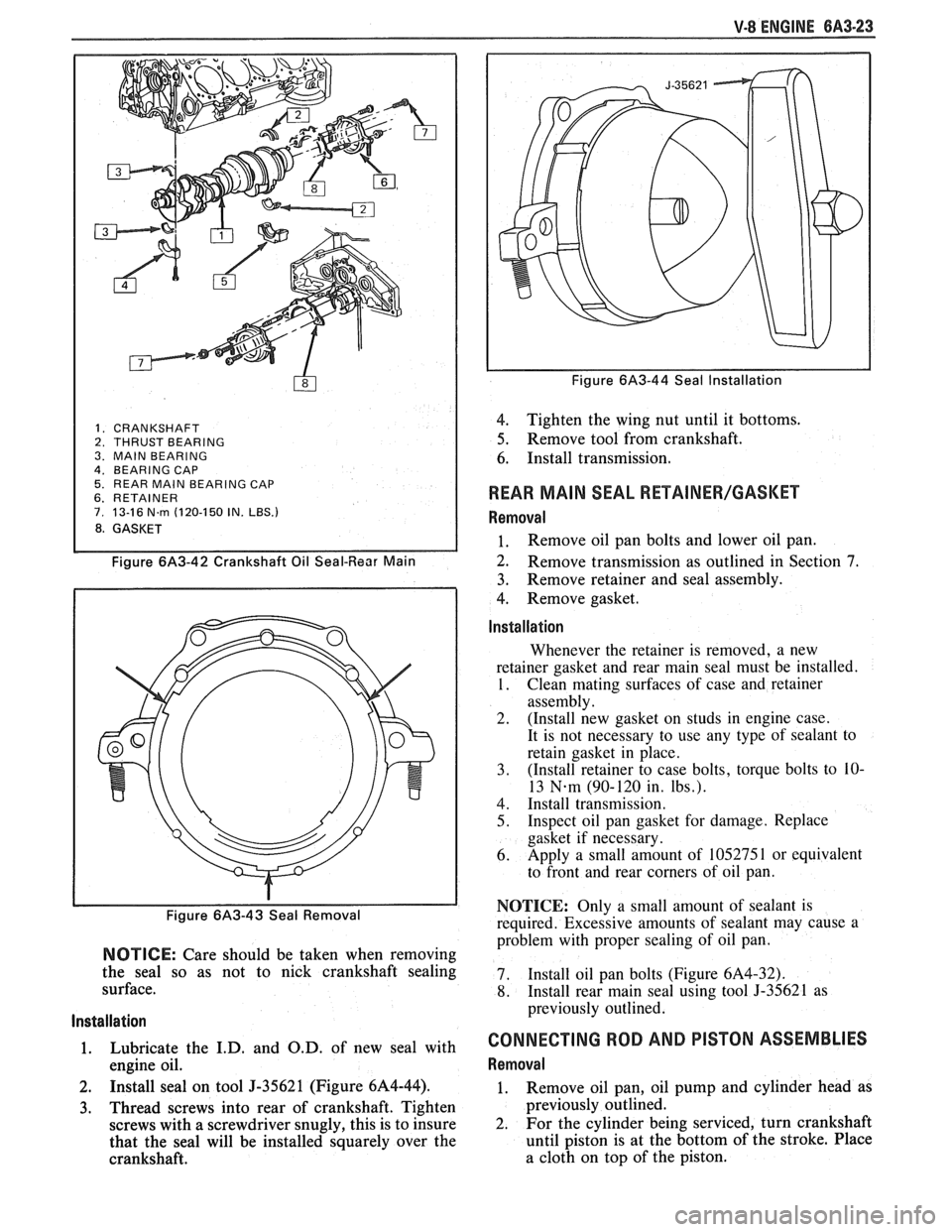
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-23
1. CRANKSHAFT 2. THRUST BEARING
3. MAlN BEARING
4. BEARING CAP 5. REAR MAlN BEARING CAP 6. RETAINER 7. 13-16 N.rn (120-150 IN. LBS.)
8. GASKET
Figure 6A3-42 Crankshaft Oil Seal-Rear Main
Figure 6/43-43 Seal Removal
NOTICE: Care should be taken when removing
the seal so as not to nick crankshaft sealing
surface.
Installation
1. Lubricate the I.D. and O.D. of new seal with
engine oil.
2. Install seal on tool J-35621 (Figure 6A4-44).
3. Thread screws into rear of crankshaft. Tighten
screws with a screwdriver snugly, this is to insure
that the seal will be installed squarely over the
crankshaft.
Figure 6A3-44 Seal Installation
4. Tighten the wing nut until it bottoms.
5. Remove tool from crankshaft.
6. Install transmission.
REAR MAlN SEAL RETAINER/GASKET
Removal
1. Remove oil pan bolts and lower oil pan.
2. Remove transmission as outlined in Section 7.
3. Remove retainer
and seal assembly.
4. Remove gasket.
lnstallation
Whenever the retainer is removed, a new
retainer gasket and rear main seal must be installed.
1. Clean mating surfaces of case and retainer
assembly.
2. (Install new gasket on studs in engine case.
It is not necessary to use any type of sealant to
retain gasket in place.
3. (Install retainer to case bolts, torque bolts
to
10-
13 N-m (90-120 in. Ibs.).
4. Install transmission.
5. Inspect oil pan gasket for damage. Replace
gasket if necessary.
6. Apply
a small amount of 105275
1 or equivalent
to front and rear corners of oil pan.
NOTICE: Only a small amount of sealant is
required. Excessive amounts of sealant may cause a
problem with proper sealing of oil pan.
7. Install oil
pan bolts (Figure
6A4-32).
8. Install rear main seal using tool 5-35621 as
previously outlined.
CONNECTING ROD AND PISTON ASSEMBLIES
Removal
1. Remove oil pan, oil pump and cylinder head as
previously outlined.
2. For
the cylinder being serviced, turn crankshaft
until piston is at the bottom of the stroke. Place
a cloth on top of the piston.
Page 406 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE 6A3-27
3. When finish honing
a cylinder bore to fit a piston,
the hone should be moved up and down at a
sufficient speed to obtain very fine uniform
surface finish marks in a cross-hatch pattern of
approximately
45" to 65" included angle. The
finish marks should be clean but not sharp, free
from imbedded particles and torn or folded
metal.
4. Permanently mark
the piston for the cylinder to
which it has been fitted and proceed to hone
cylinders and fit the remaining pistons.
NOTICE: Handle the pistons with care and do not
attempt to force them through the cylinder until
the cylinder has been honed to correct size as this
type piston can be distorted through careless
handling.
5. Thoroughly
clean the bores with hot water and
detergent. Scrub well with a stiff bristle brush and
rinse thoroughly with hot water. It is extremely
essential that a good cleaning operation be
performed. If any of the abrasive material is
allowed to remain in the cylinder bores, it will
rapidly wear the new rings and cylinder bores in
addition to the bearings lubricated by the
contaminated oil, the bores should be swabbed
and then wiped with a clean dry cloth. Cylinder
should not be cleaned with kerosene or gasoline.
Clean the remainder of the cylinder block to
remove the excess material spread during the
honing operation.
Piston Selection
1. Check USED piston to cylinder bore clearance as
follows:
a. Measure
the "Cylinder Bore Diameter"
with a telescope gage
"2-1/2" (64mm) from
top of cylinder bore").
b. Measure
the
"Piston Diameter" (at skirt
across center line of piston pin).
c. Subtract
piston diameter from cylinder bore
diameter to determine "Piston to Bore
Clearance".
d. Determine if piston to bore clearance is in
the acceptable range.
2. If
used piston is not acceptable, check Piston Size
Chart and determine if a new piston can be
selected to fit cylinder bore within the acceptable
range.
3. If
cylinder bore must be reconditioned, measure
new piston diameter (across center line of piston
pin) then hone cylinder bore to correct clearance
(preferable range).
4. Mark the piston to identify the cylinder for which
it was fitted.
OIL FILTER BYPASS VALVE
Inspection and Replacement
With the oil filter removed, check the spring and
fibre valve for operation. Inspect for a cracked or
broken valve. If replacement is necessary, the oil filter
adapter and bypass valve assembly must be replaced as an
assembly. Clean valve chamber in cylinder block
thoroughly. Torque retaining screws to specifications.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Removal
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Remove air cleaner.
3. Remove hood.
4. Drain radiator.
5. Remove lower radiator hose.
6. Remove upper fan shroud.
7. Remove upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
8. Remove transmission cooler lines.
9. Remove radiator.
10. Remove fan assembly.
1 1. Remove heater hoses.
12. Disconnect
carburetor linkage, includes cruise
control detent cable.
13. Remove vacuum brake booster line.
14. Remove
distributor cap and lay wiring aside.
15. Disconnect necessary wires and hoses.
16. Remove power steering
pump and lay aside.
17. Raise vehicle.
18. Remove exhaust
pipes at exhaust manifold.
19. Remove dust cover.
20. Remove converter bolts.
2 1. Disconnect starter wires.
22. Remove bell housing bolts.
23. Remove
motor mount through bolts.
24. Disconnect fuel lines
at fuel pump.
25. Lower vehicle.
26. Support transmission.
27. Remove
A.I.R./Converter pipe bracket.
28. Remove engine, include removing wire
from
bracket at rear left of engine.
Installation
1. Position engine
assembly in vehicle.
2. Attach
motor mount to engine brackets and
lower engine in place.
3. Remove engine lifting device.
4. Remove transmission floor jack.
5. Raise vehicle on hoist.
6. Install mount "through" bolts. Torque to
specifications.
7. Install bell housing bolts. Torque to
specifications.
8. On vehicles with automatic transmissions, install
I
converter to flywheel attaching bolts. Torque to
specifications.
9. Install flywheel splash shield of converter
housing cover as applicable. Torque attaching
bolts to specifications.
I
10. Install starter wires.
1 1. Connect fuel lines.
12. Connect exhaust pipe at manifold.
13. Lower vehicle on hoist.
14. Reinstall power steering pump, if so equipped.
15. Connect necessary wires and hoses.
Page 407 of 1825

6A3-28 V-8 ENGINE
16. Install
radiator and fan shroud and reconnect
radiator and heater hoses.
17. Fill cooling system.
18. Fill
crankcase with oil. See owner's manual for
specifications.
19. Install air cleaner.
20. Install hood.
21. Connect battery cables.
NOTICE: To avoid possible arcing of battery,
connect positive battery cable first.
22. Start engine, check for leaks and check timing.
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft can be removed while the engine
is disassembled for overhaul, as previously outlined, or
without complete disassembly.
Removal
With the engine removed from the vehicle and the
transmission and/or clutch housing removed
from the engine, mount engine in stand and
clamp securely.
Remove the oil dip stick and oil dip stick tube, (if
applicable).
Remove the starting motor, clutch assembly (if
equipped) and flywheel.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove crankshaft pulley and torsional damper.
Remove oil pan and oil pump.
Remove crankcase front cover, and if so
equipped, remove timing chain and camshaft
sprocket.
Check the connecting rod caps for cylinder
number identification. If necessary, mark them.
Remove the connecting rod caps and push the
pistons to top of bores.
Remove main bearing caps and lift crankshaft out
of cylinder block.
Remove rear main bearing oil seal and main
bearings from cylinder block and main bearing
caps.
Cleaning and Inspection
1. Wash crankshaft in solvent and dry with
compressed air.
2. Measure dimensions of main bearing journals and
crankpins with a micrometer for out-of-round,
taper or undersize. (See Specifications.) 3.
Check crankshaft for run-out by supporting at
the front and rear main bearings journals in
"V"
blocks and check at the front and rear
intermediate journals with a dial indicator. (See
Specifications.)
4. Replace or recondition the crankshaft if out of
specifications.
SPROCKET OR GEAR REPLACEMENT
e Remove crankshaft sprocket using Tool
5-5825, install using Tool J-5590.
Installation
1.
Install rear main bearing oil seal in cylinder block
and rear main bearing cap grooves. Install with
lip of seal toward front of engine. Where seal has
two lips install lip with helix towards front of
engine.
2. Lubricate lips of seal with engine oil. Keep oil off
parting line surface.
3. Install main bearings in cylinder block and main
bearing caps then lubricate bearing surface with
engine oil.
4. Install crankshaft, being careful not to damage
bearing surfaces.
5. Recheck bearing clearances using plastigage.
6. Apply a thin coat of brush-on type oil sealing
compound to block mating surface and
corresponding surface of cap only. Do not allow
sealant on crankshaft or seal.
7. Install main bearing caps with arrows pointing
toward front of engine.
8. Torque all except rear main bearing cap bolts to
specifications. Torque rear main bearing cap bolts
to 10-12 lbs. ft. (14-16
N.m)then tap end of
crankshaft, first rearward then forward with a
lead hammer. This will line up rear main bearing
and crankshaft thrust surfaces.
Retorque all main
bearing cap bolts to specifications.
9. Measure crankshaft end play with a feeler gage.
Force crankshaft forward and measure clearance
between the front of the rear main bearing and the
crankshaft thrust surface.
10. Install flywheel and torque to specifications. A
wood block placed between the crankshaft and
cylinder block will prevent crankshaft from
rotating.
Align dowel hole in flywheel with dowel
hole in crankshaft. On vehicles equipped
with automatic transmissions, install
flywheel with the converter attaching pads
towards transmission.
GENERAL DATA
TYPE .................................................................................................................................. 90" V-8
DISPLACEMENT
............................................................................... 305 Cu. In., 350 Cu. In.
......................................................... LITER (VIN) ................................... ...... 5.0, (E), (F), 5.7 (8)
RPO ......................................................................................................................... L03, LB9, L98
BORE ........................................................................................................................ 3.736, 4.000
STROKE
........................... .. ....................................................................................... 3.480, 3.480
COMPRESSION RATIO
................................................................................... 931, 931, 9.5:1
FIRING ORDER .................................................................................................... 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
Page 412 of 1825

ENGINE COOLING 6B-1
SECTION 6B
NE COOL
General Description ................................ 6B- 1 Off-Vehicle Leak Testing ............................... 6B-9
Radiator
...................................................... 6B- 1 Repairable Leaks ........................ ... .......... 6B- 10
Radiator Cap
......................... .. ............... 6B- 1 Repair Methods ................................................ 6B- 10
Recovery Bottle ......................................... 6B-2 Cooling Fin Removal ................................ 6B- 10 - ............................................. Fans ............................................................... 6B-2 Tube Blocking 6B- 1 1 ............ Header Repair ....................... .... 6B- 1 1 Temperature Switch ..................................... 6B-2 General Core Repair 6B- 1 1 ....................................
........................... Coolant Temperature Fan Switch ................ 6B-2 Tank
Gasket ~eik Repair 6B- 12
................... Thermostat .. 6B-3 Oil
Cooler Gasket Replacement
6B- 13 ............... ................................
...........................................................
Coolant Recovery System 6B-3 Recore 6B- 14 ............................. Special Tools ..................................................... 6B- 14 Diagnosis ..................................................... 6B-3
.............................. ..................................... Service Procedures 6B-3 On-Vehicle Service 6B-14
Cooling System Care
............................... 6B-3 Thermostat ....................................... 6B-14
Draining and Refilling the Cooling Electric Cooling Fan ............................. 6B-15
System
................................................... 6B-7 Water Pump .................... .... ......... 6B-15
Drive Belt
...................... .. .......................... 6B-7 Coolant Recovery Bottle ........................ 6B-16
.......................................... Aluminum Radiator Service .................... 6B-8 Radiator 6B-17
Diagnosis .................................................... 6B-8
Leak Testing
.............................................. 6B-8
On-Vehicle Pressure Testing
...................... .... 6B-9
GENERAL DESCRIPnIBN
The cooling system maintains engine temperature
5" below the filler neck which reads, "Important - for
at an efficient level during all engine operating repair see Harrison Service Manual". Service
conditions. When the engine is cold the system cools procedures for the aluminum plastic radiator are
slowly, or not at all, to allow the engine to warm up described in that manual and in this section.
quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and
Radiator Cap
recovery sub-system, cooling fan, thermostat and
housing, water pump, and drive belts.
Operation of the cooling system requires proper
functioning of all components. Coolant is drawn from
the radiator by the water pump and circulated through
water jackets in the engine block, intake manifold, and
cylinder
head(s), and then directed back to the radiator
where it's cooled.
This system directs some coolant through hoses
to the heater core, to provide for heating and
defrosting. A recovery bottle is connected to the
radiator to recover coolant displaced by expansion
from high temperatures and maintain correct coolant
level. As the coolant cools and contracts it is drawn
back into the radiator by vacuum.
RADIATOR
A cross-flow radiator is used on all models. Tanks
in this type radiator are located to the right and left of
the core, instead of above and below.
Radiators used with automatic transmissions
have oil coolers with inlet and outlet fittings for
transmission fluid circulation. Cars with manual
transmissions use radiators without oil coolers.
Vehicles equipped with air conditioning use a radiator
with extra cooling capability.
An aluminum-plastic radiator, used on some
models, can be identified by a note on the outlet tank A pressure-vent
cap is used on the cross-flow
radiator to allow a buildup of
103 kPa (15 psi) in the
cooling system. This pressure raises the boiling point
of coolant to approximately 125°C (262°F) at sea level.
Do not remove radiator cap to check engine
coolant level; check coolant visually at the
see-through coolant reservoir. Coolant should
be added only
to the reservoir.
CAUTION: As long as there
is
pressure in the cooling system, the
temperature can be considerably
higher than the boiling temperature
of
the solution in the radiator without
causing the solution to boil. Removal
of the radiator cap while engine is hot
and pressure is high will cause
the
solution to boil instantaneously and
possibly with explosive
force, spewing
the solution over engine, fenders and
person removing cap. If the solution
contains flammable antifreeze, such
as alcohol (not recommended for use
at any time), there is also the
possibility
of causing a serious fire.
The pressure-type radiator filler cap contains a
blow off or pressure valve and a vacuum or
atmospheric valve (Figure
1). The pressure valve is
held against its seat by a spring of pre-determined
Page 418 of 1825

ENGINE COOLING BB-7
NOTICE: If recommended quality antifreeze is
used, supplemental inhibitors or additives claiming
to provide increased cooling capability are not
necessary. They may be detrimental to the efficient
operation of the system, and represent an
unnecessary operating expense.
Every 12 months or 15,000 miles, the cooling
system should be serviced as follows;
1. Wash radiator cap and filler neck with clean
water.
2. Check coolant for proper level and freeze
protection.
3. Pressure test system and radiator cap for proper
pressure holding capacity, 103
kPa (15 psi). If
replacement of cap is required, use the proper cap
specified for car model.
4. Tighten hose clamps and inspect all hoses. Replace
hoses whenever cracked, swollen or otherwise
deteriorated.
5. Clean frontal area of radiator core and air
conditioning condenser.
DRAINING AND REFILLING THE COOLING
SYSTEM
Replace hoses every 24 months or 30,000 miles or
earlier if cracked, swollen or otherwise deteriorated.
Every two years or 30,000 miles, whichever first
occurs, the cooling system should be flushed and
refilled using the following recommended procedure:
1. Remove radiator cap, or thermostat housing cap
(VIN
0, J, R and U), when engine is cool by:
a. Slowly
rotating cap counterclockwise to
detent. (Do not press down while rotating.)
b. Wait until any
residual pressure (indicated
by a hissing sound) is relieved.
c. After all hissing ceases, press down on cap
while continuing to rotate
counterclockwise.
CAUTION: To avoid the danger of
being burned, do not remove radiator
cap while engine and radiator are still
hot. Scalding fluid and steam may be
blown out under pressure.
2. Remove the thermostat by using the wire handle
to lift it out of the housing (VIN
0, J, R and U).
3. With the thermostat removed, reinstall the
thermostat housing cap (VIN
0, J, R and U).
4. Open radiator drain valve and block drain plugs
to drain coolant. On VIN R and
9 (P series)
engines, open coolant pipe plugs.
5. Close valve. Reinstall drain plugs, and add
sufficient water to fill system.
6. Run engine, drain and refill the system, as
described in steps
4 and 5 a sufficient number of
times, until the drained liquid is nearly colorless.
Important
BLOCK DRIVE WHEELS, place
transmission in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission) and set the parking brake. 7.
Allow system to drain completely. Then close
radiator drain valve tightly, and reinstall block
drain plugs.
8. Remove recovery cap leaving hoses in place.
Remove coolant recovery tank and empty of
fluid. Flush tank with clean water, drain and
reinstall.
9. Add sufficient ethylene glycol coolant, meeting
GM specification 1825-M, to provide the
required freezing and corrosion protection
- at
least 50 percent solution -37°C (-34°F). Fill
radiator to the base of the radiator fill neck and
add sufficient coolant to the recovery tank to
raise level to the "FULL" mark. Reinstall
recovery tank cap.
10. Run engine, with radiator cap or thermostat
housing cap removed, until normal operating
temperature is reached. (Radiator upper hose
becomes hot.)
11. With engine idling, add coolant until level
reaches bottom of filler neck and reinstall cap,
making certain arrows line up with overflow tube.
CAUTION: Under some conditions, the
ethylene glycol in engine coolant is
flammable. To help avoid being
burned when adding coolant, DO NOT
spill
it on the exhaust system or hat
engine parts.
It is the owner's responsibility to keep the freeze
protection at a level appropriate to the
temperatures which may occur in the area of
vehicle operation.
a. Maintain
cooling system freeze protection
at
-37°C (-34"F), to ensure protection
against corrosion and loss of coolant from
boiling, even though freezing temperatures
are not expected.
b. Add ethylene glycol base coolant that meets
GM Specification 1825-M, when coolant
additions are required because of coolant
loss, or to provide additional protection
against
freezing at temperatures lower than
-37°C (-34°F).
NOTICE: Alcohol or methanol base coolants, or
plain water, are not recommended at any time.
DRlVE BELT
NOTICE: Routine inspection of the belt may
reveal cracks in the belt ribs. These cracks will
not impair belt performance and therefore should
not be considered a problem requiring belt
replacement. However, the belt should be
replaced if belt slip occurs or if sections of the
belt ribs are missing.
A single (serpentine) belt is used to drive all
engine accessories formerly driven by multiple drive
belts. All belt driven accessories are ridgedly mounted
with belt tension maintained by a spring loaded
tensioner.
The drive belt tensioner has the ability to control
belt tension over a fairly broad range of belt lengths.
Page 419 of 1825

68-8 ENGINE COOLING
However, there are limits to the tensioner's ability to
The tensioner has rovisions for a visual check to
compensate for varying lengths of belts. With the
ten- verify that it is in t e "operating range" (see Figures
sioner outside of its operating range, poor tension
608 and 609). R
control andlor damage to the tensioner may result.
ALUMINUM RADIATOR REPAIR
This radiator utilizes an aluminum core with
plastic side tanks. The core and side tanks can be
replaced separately and core repair is easily made with
the hot melt adhesive method. A transaxle oil cooler
is located in one of the side tanks. The oil cooler can
be replaced. The drain cock is located on the lower part
of one of the tanks. The drain cock is also serviceable.
Core
The core is made of aluminum and is of the
crossflow design. It utilizes large tubes that resist
plugging, and repairs to the tubes and core are easily
made using the hot melt adhesive method.
The core is attached to the tanks by clinched tabs
on the core that can be bent back if tank or core
replacement is required.
If the damage to a tube is too severe, a tube can
be blocked or plugged as explained in "Tube Blocking.
" No more than two tubes should ever be blocked on
a core. Also replace the core if more than three tabs are
broken on one side, or if two adjacent tabs are broken.
Tanks
The tanks are attached to the core by the use of
clinched tabs. The clinched tabs can be bent back if the
tanks need to be removed from the core. Bend the tabs
back only enough to remove the tank. Overbending
will weaken the tabs.
A high temperature rubber gasket is used to seal
the mating surface between the core and the tank. (See
Fig. 8). The gasket must be replaced any time a tank
is removed from the core.
Transaxle Oil Cooler
The transaxle oil cooler is located in one of the
radiator side tanks. The oil cooler can be replaced by
removing the tank from the core.
A leaking oil cooler gasket can be replaced
without removing the tank from the core.
Drain Cock
The aluminum/plastic radiator utilizes a two
piece plastic drain cock and a rubber seal. The drain
cock is serviceable (See Fig.
9).
ALUMINUM RADIATOR SERVICE
The aluminum-plastic radiator can be repaired at
the dealership. The following components are easily
replaced:
e Core
e Tanks and gaskets
o Oil coolers and gaskets
e Drain cock and gasket The
tanks cannot be repaired if broken or
cracked. The radiator core can be replaced and the new
core used with the original tanks and oil cooler.
Precautions
As with all cooling system service, take measures
to prevent personal injury and damage to the system.
CAUTION: To help avoid the danger of
being burned, do not remove the
radiator cap while the engine and
radiator are
still hot. Scalding fluid
and steam can be blown out under
pressure if the
cap is taken off too
soon.
NOTICE: DO NOT USE "BOIL OUT" TANKS
OR VATS. Common service methods may
actually destroy an aluminum radiator. Caustic or
lye cleaning solutions must NOT be used for
aluminum radiators.
e Do not open the hood if you can see, or hear,
steam or coolant escaping from the engine
compartment.
e Do not remove radiator cap if radiator feels
warm.
e Do not remove the radiator cap or coolant
recovery tank cap if the coolant in the recovery
tank looks like it is boiling.
Wear eye protection.
e Wear gloves to protect your hands against
excessive heat, or the effects of chemicals on your
skin.
o Prevent dirt and water from entering the
transmission oil cooler.
e Do not use boil-out tanks, or vats, or other tanks
that have been used for copper and brass
radiators. The flux, acid, and caustic cleaners
remaining in these tanks will attack the
aluminum and cause radiator failure.
A separate
test tank containing clean water is strongly
recommended for servicing aluminum-plastic
radiators.
RIOTICE: Never use shop air that is not regulated
at
20 psi (138 kPa) to pressure test radiator.
Pressures over
20 psi (138 kPa) will damage the
radiator.
DIAGNOSIS
Leak Testing
Some core leaks can be detected by merely adding
water to the radiator. It is helpful to clean the core so
that the damaged area can be more easily found.
Page 428 of 1825
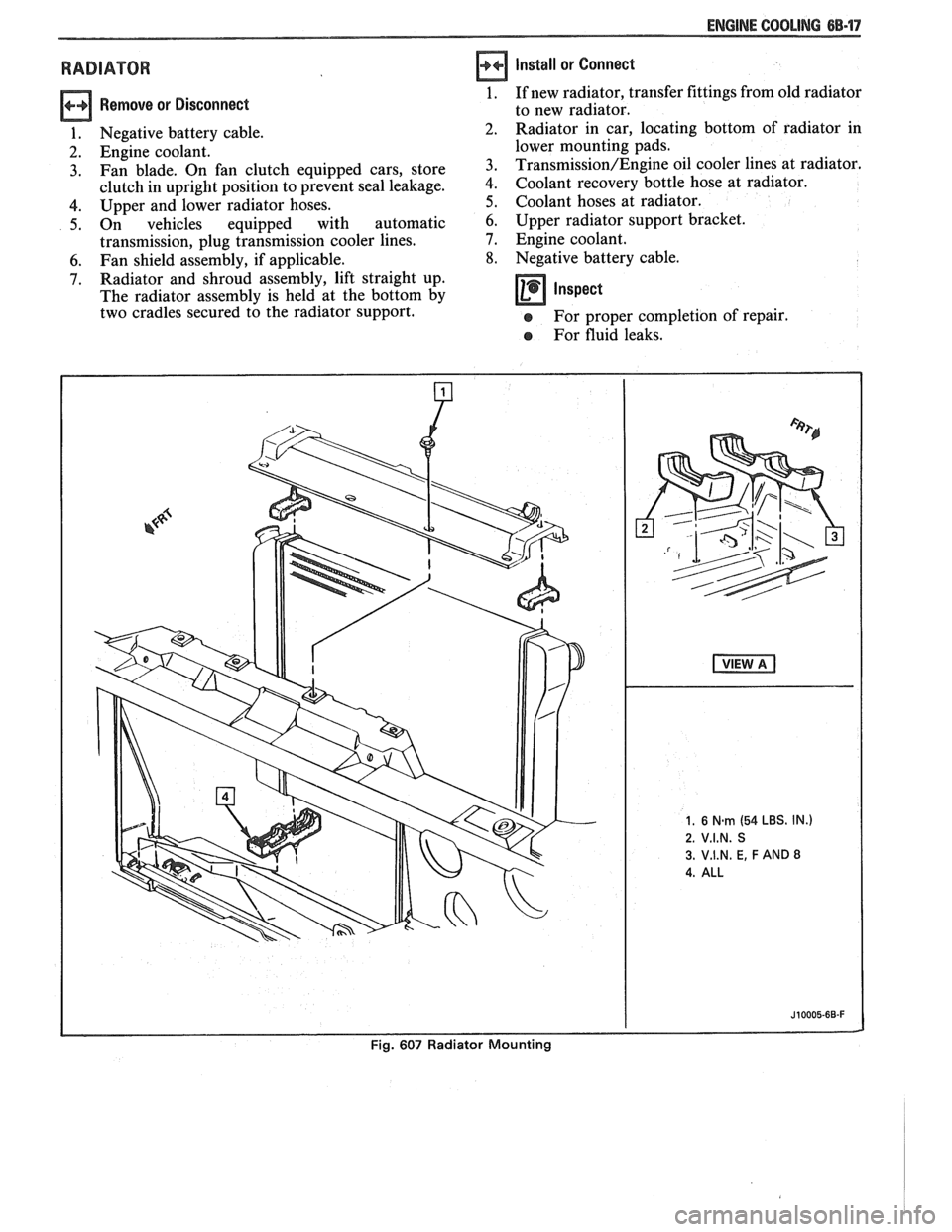
ENGINE COOLING 68.17
RADIATOR
Remove or Disconnect
1. Negative battery cable.
2. Engine coolant.
3. Fan blade. On fan clutch equipped cars, store
clutch in upright position to prevent seal leakage.
4. Upper and lower radiator hoses.
5. On vehicles equipped with automatic
transmission, plug transmission cooler lines.
6. Fan shield assembly, if applicable.
7. Radiator and shroud assembly, lift straight up.
The radiator assembly is held at the bottom by
two cradles secured to the radiator support.
Install or Connect
1. If new radiator, transfer fittings from old radiator
to new radiator.
Radiator in car, locating bottom of radiator in
lower mounting pads.
Transmission/Engine oil cooler lines at radiator.
Coolant recovery bottle hose at radiator.
Coolant hoses at radiator.
6. Upper radiator support bracket.
7. Engine coolant.
8. Negative battery cable.
Inspect -
e For proper completion of repair.
e For fluid leaks.
Page 488 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-3
........ FUEL METER COVER ASSEMBLY C2-7
FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-8
FUEL METER BODY ASSEMBLY ......... C2-9
..... THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) C2-10
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE ........ 62-1 1
THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
.......... C2-11
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED CHECK .......... C2-12
... THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT C2-13
FUEL
HOSEIPIPE ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-13
Materials ...................... C2-13
Fuel Line Repair .................. C2-13
FUEL PUMP RELAY .................. C2-13
............... OILPRESSURESWITCH C2-13
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C2-14
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Check
Chart C-2C
..................... C2-16
SECTION C3
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C3-1
........................ PURPOSE C3-1
VAPOR CANISTER
................... C3-1
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
....... C3-1
IN-TANK PRESSURE CONTROL VALVE
. . C3-2
.... RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION C3-2
........................ DIAGNOSIS C3-2
VISUAL CHECK OF CANISTER
.......... C3-2
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
.......... C3-2
ON-CAR SERVICE ................. C3-2
FUEL VAPOR CANISTER
R/R ............ C3-2
CANISTER HOSES
.................... C3-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C3-2
Canister Purge Valve Check
Chart C-3
...................... C3-4
SECTION
C4
IGNITION SYSTEM I EST
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C4-1
PURPOSE ........................ C4-1
OPERATION ...................... C4-1
.. DIAGNOSIS ................... ... C4-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT EST OPER ...... C4-1
HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED ....... C4-2
CODE12 ........................ C4-2
CHECKING EST PERFORMANCE ........ C4-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C4-2
SETTINGTIMING .................. C4-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C4-2
Ignition System Check
Chart C-4
................... .. . C4-4
SECTION C5
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL (ESC) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
................ C5-1
PURPOSE ..*...................... C5-1
OPERATION
....................... C5-1
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C5-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT ESC OPERATION
. C5-1
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C5-1 ESC
KNOCK SENSOR
................ C5-1
ESCMODULE
...................... C5-1
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C5-2
Electronic Spark Control (ESC) System Check
Chart C-5
...................... C5-4
SECTION C6
AIR INJECTION REACTION (A.I.R.) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C6-1
PURPOSE
.*....................... C6-1
OPERATION
...................... C6-1
AIR CONTROL PEDES VALVE .......... C6-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C6-2
DIAGNOSIS
........................ C6-2
OPERATIONAL CHECKS
.....*........ C6-2
AirPump ...................... C6-2
Hoses and Pipes
................. C6-3
Check Valve
.................... C6-3
ON-CAR SERVICE
.................... C6-3
DRIVEBELT ...................... C6-3
AIR INJECTION PUMP
............... C6-3
AIR INJECTION CONTROL
(PEDES) VALVE
.................. C6-3
AIR INJECTION CHECK VALVE ......... C6-4
PARTS INFORMATION
................ C6-4
AIR Management Check
. Pedes Valve
Chart C-6
..................... C6-6
SECTION C7
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C7-1
PURPOSE
........................ C7-1
OPERATION
...................... C7-1
EGRCONTROL
..................... C7-1
NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE VALVE
...... C7-1
EGR VALVE IDENTIFICATION
.......... C7-2
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C7-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C7-2
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C7-2
EGRVALVE
....................... C7-2
EGR Manifold Passage
............. C7-2
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID
............. C7-3
PARTS INFORMATION
................. C7-3
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Check
Chart C-7
...................... C7-4
SECTION
C8
TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
PURPOSE
........................ C8-1
OPERATION
...................... C8-1
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT TCC
OPERATION
..................... C8-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C8-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C8-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C8-2