1988 PONTIAC FIERO transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 1115 of 1825
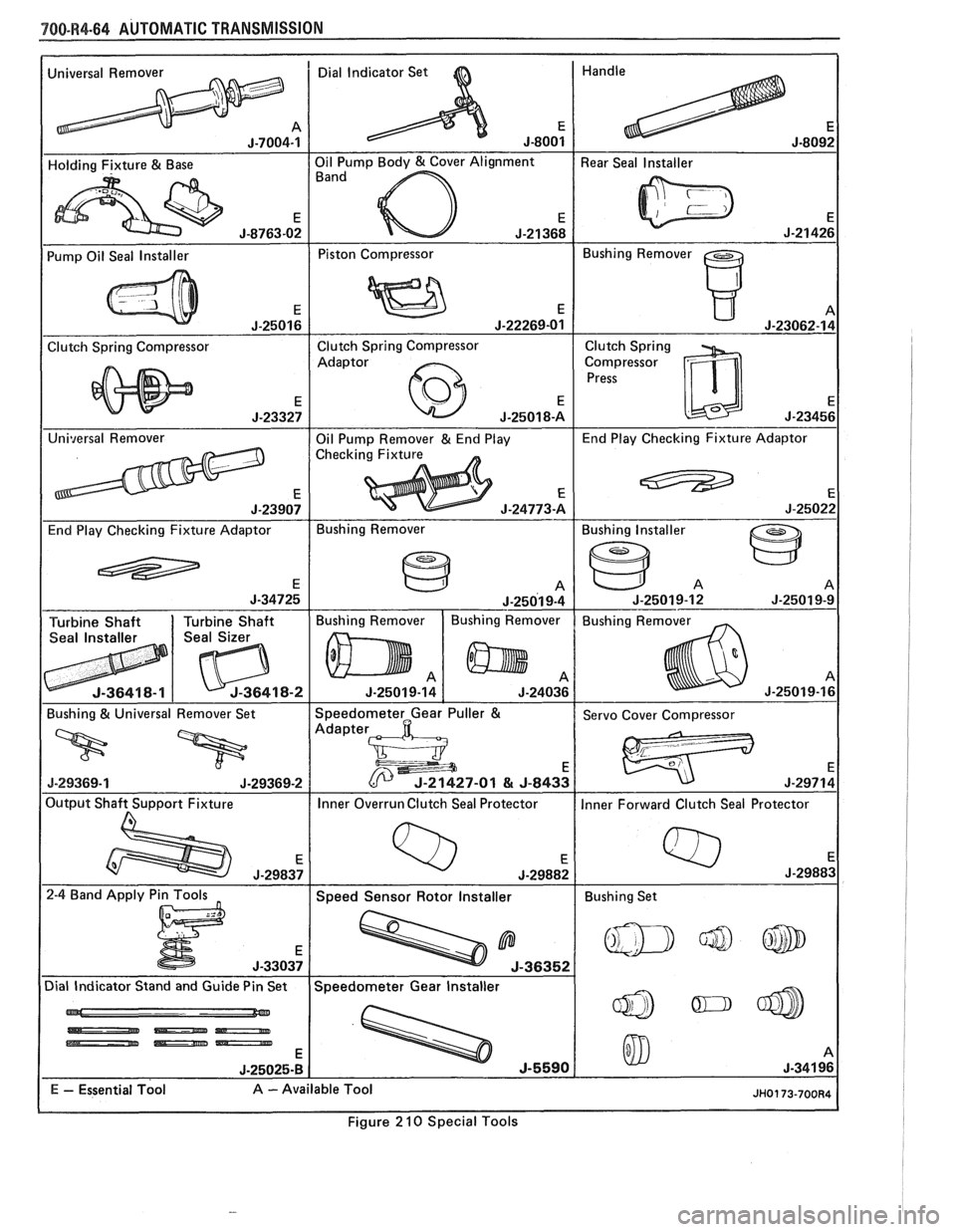
780-R4-64 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
-
Universal Remover Dial Indicator Set
I - -
1 Pump Oil Seal Installer I Piston Compressor 1 Bushing Remover I
Clutch Spring Compressor Clutch Spring
Compressor
J-25022
End Play Checking Fixture Adaptor Bushing
Remover
Figure
2 10 Special Tools
Page 1116 of 1825
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 7A-1
SECTION 7
AUTOMAT C TRANSM
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION .................................... 7A
ON VEHICLE SERVICE .................................................................................................. 7A 1
700-R4 UNIT REPAIR .................................................................................................. 700-R4
SECTION 7A
TRANSM ON GENERAL NFORMAT
CONTENTS
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION NOISE AND VIBRATION
INFORMATION
..................... .. .............. 7A- I ANALYSIS .................... .... .............. 7A-3
TRANSMISSION DEFINITIONS TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL
Throttle Positions
.......................... .. ..... 7A-2 INFORMATION ....................................... 7A-3
Shift Conditions .................................... .... . 7A-2 TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL
Noise Conditions
....................................... 7A-2 CHECKING
PRELIMINARY CHECKING PROCEDURE
............................................ 7A-3
PROCEDURE
......................................... 7A-3
The information contained in this section is common to all automatic transn~issions. For on-vehicle service
procedures refer to Section
7A1. For complete Diagnosis and Unit Repair refer to the specific transrllission sections.
For vehicles sold in Canada also refer to the appropriate Canadian Service Manual Supplement for-
driveuhility
diagnosis.
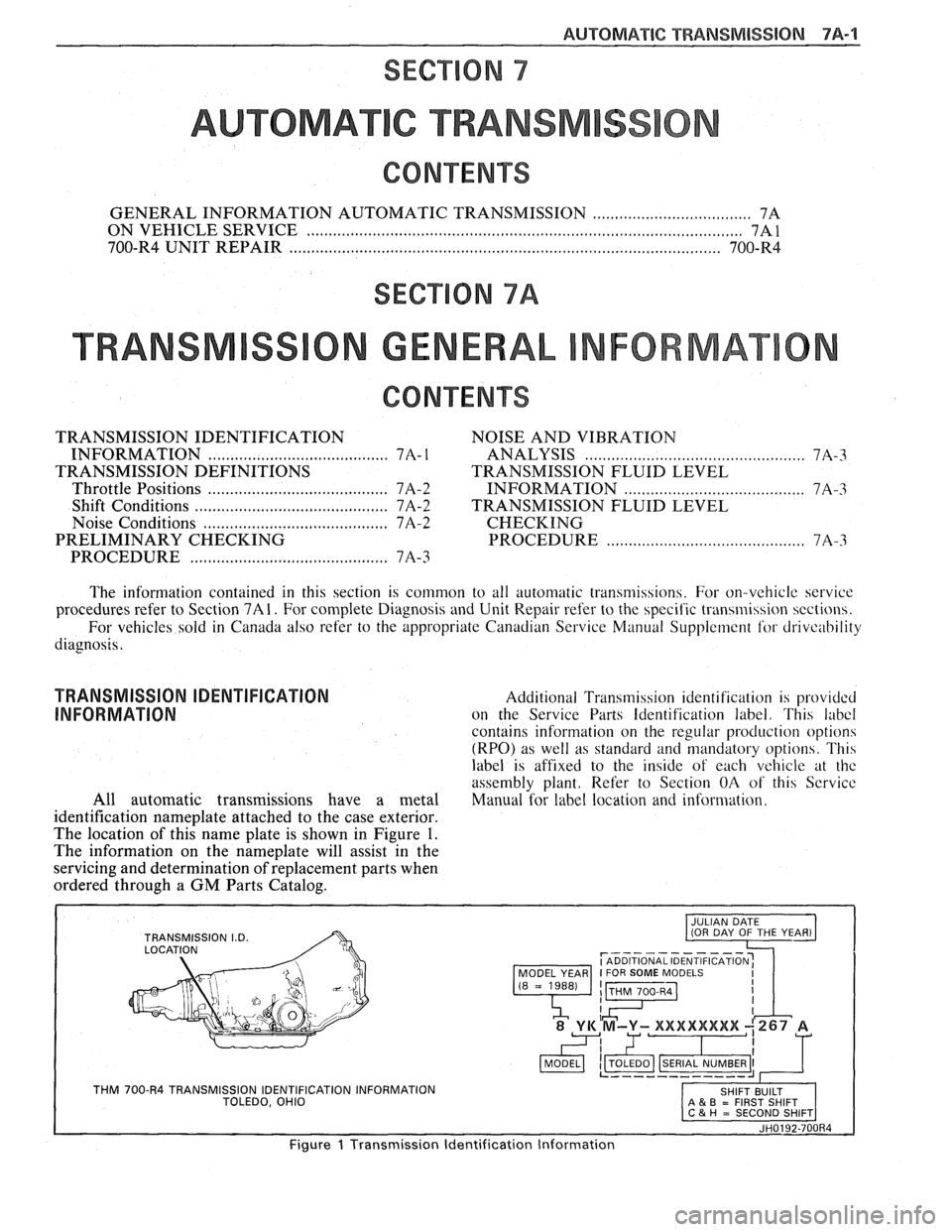
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION Additional Transmibsion identification is pr-ov~dcd
INFORMATION on the Service Parts Identification label. This labcl
contains information on the regular production option
(RPO) as well as standard and mandatory options. Th14
label is affixed to the inde of each vehrcle at thc
assembly plant. Refer to Section OA of this Scrvice
All automatic transmissions have a metal Manual for label location and information.
identification nameplate attached to the case exterior.
The location of this name plate is shown in Figure
1.
The information on the nameplate will assist in the
servicing and determination of replacement parts when
ordered through a GM Parts Catalog.
r----------- I ADDITIONAL IDENTIFICATION: MODEL YEAR I FOR SOME MODELS
THM 700-R4 TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION TOLEDO, OHIO A & B = FIRST SHIFT
JH0192-700R4
Figure 1 Transmission Identification Information
Page 1117 of 1825

7A-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
I I
M - INDICATES TRANSMISSION
TYPE IN OPTION LIST. (SPECIFIC MODEL CODE IS FOUND ON THE I MX - DESIGNATES
11 SERVICE PARTS IDEMTIFICATIOM I 1 00 MOT REMOVE I
1G3AR47YXE5
C90 C95 DF3 D3C 033 0 GI GW9 G60 GU2 G89
JAl JA4 KO5 K22 Kg9 LV2 NA5 NB1 NKl NK3 N33 N67 GJW
T87 UJ3 U23 U35
VO8 V10 WC3 WG2 YT9 Y56 OIL 6SC 428 421 420
Figure 2 Service Parts ldentificaiton Label
TRANSMISSION DEFINITIONS
The following definitions are being provided to
establish a common language and assist the user in
describing transmission related conditions. Some of
these terms or conditions are used in the transmission
sections of this Service Manual.
Throttle Positions
Minimum Throttle - the least amount of
throttle opening required for an upshift.
Light Throttle - approximately 1/4 of
accelerator pedal travel.
Medium Throttle - approximately 1/2 of
accelerator pedal travel.
Heavy Throttle - approximately 3/4 of the
accelerator pedal travel.
Wide Open Throttle (WOT) - full travel of
the accelerator pedal.
Full Throttle Detent Downshift - a quick
apply of the accelerator pedal to its full travel,
forcing a downshift.
Zero Throttle Coastdown - a full release of
the accelerator pedal while the vehicle is in
motion and in drive range.
Engine Braking - a condition where the engine
is used to slow the vehicle by manually
downshifting during a zero throttle coastdown.
Shift Conditions
'a Bump - a sudden and forceful apply of a clutch
or band.
Q Chuggle - a bucking or jerking condition that
may be engine related. May be most noticeable
when the converter clutch is engaged. Similar to
the feel of towing a trailer.
e Delayed - a condition where a shift is expected
but does not occur for a period of time. Samples
of this condition could be described as clutch or
band engagement does not occur as quickly as
expected during a part throttle or wide open
throttle apply of the accelerator or, when
manually downshifting to a lower range. Also
defined as "LATE" or, "EXTENDED."
Double Bump ("Double Feel") - two sudden
and forceful applies of a clutch or band.
Early - a condition where the shift occurs before
the vehicle has reached a proper speed and tends
to labor the engine after the upshift.
End Bump - a firmer feel at the end of a shift as
compared to the feel at the start of the shift. Also
defined as "END FEEL" or, "SLIP BUMP."
Firm - a noticeable quick apply of a clutch or
band that is considered
normal with a medium
to heavy throttle shift. Should not be confused
with "HARSH" or "ROUGH."
Flare - a quick increase in engine rpm
accompanied with a momentary loss of torque.
This most generally occurs during a shift. Also
defined as "SLIPPING.
"
Harsh ("Rough") - a more noticeable apply of
a clutch or band as compared to "FIRM." This
condition is considered undesireable at any
throttle position.
Hunting - a repeating quick series of upshifts
and downshifts that causes a noticeable change in
engine rpm. An example could be described as a
4-3-4 shift pattern. Also defined as
"BUSYNESS.
"
Initial Feel - a distinct firmer feel at that start
of a shift as compared to the finish of the shift.
Late - a shift that occurs when the engine is at
a higher than normal rpm for a given amount of
throttle.
Shudder - a repeating jerking sensation similar
to "CHUGGLE" but more severe and rapid in
nature. This condition may be most noticeable
during certain ranges of vehicle speed. May also
be used to define the condition after converter
clutch engagement.
Slipping - a noticeable increase in engine rpm
without a vehicle speed increase.
A slip usually
occurs during or after initial clutch or band
engagement.
Soft - a slow, almost unnoticeable clutch apply
with very little shift feel.
Surge - a repeating engine related feeling of
acceleration and deceleration that is less intense
than "CHUGGLE.
"
Tie-Up - a condition where two opposing
clutches are attempting to apply at the same time
causing the engine to labor with a noticeable loss
of engine rpm.
,e Conditions
Gear Noise - a whine, most noticeable in first
gear and reverse that is related to vehicle speed.
A gear noise condition may become less
noticeable or go away after an upshift.
Pump Noise - a high pitch whine that increases
in intensity with engine
rpm. This condition may
also be noticeable in
"PARK" and "NEUTRAL"
operating ranges with the vehicle stationary.
Page 1118 of 1825

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 7A-3
PRELIMARY CHECKING PROCEDURE
The condition of an automatic transmission not
operating properly may be influenced by one, or a
combination of the following items:
e Fluid level high/low
(Refer to Section 7A1)
e Engine performance
(Refer to Sections 6 and 6E)
T.V. cable adjustment
(Refer to Section
7A1)
e Manual linkage adjustment
(Refer to Section
7A1)
e Internal fluid leaks
(Refer to Transmission Unit Repair section)
e Electrical system
(Refer to Section 6E and 8A)
e Transmission or other mechanical component
(Refer to Transmission Unit Repair section)
e Vacuum modulator
(Refer to appropriate Hydraulic Diagnosis
Section)
NOISE AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS
A noise or vibration that is noticeable when the
vehicle is in motion, MAY NOT be the result of the
transmission.
If noise or vibration is noticeable in "Park"
(P)
and "Neutral" (N) with engine at idle, but is less
noticeable as
RPM's increase, the cause may be from
poor engine performance.
e Tires for
- Uneven wear
- Imbalance
- Mixed sizes
- Mixed radial and bias ply
(Refer to Section 3E)
e Suspension components for
- Alignment and wear
- Loose fasteners
(Refer to Section 3C)
e Engine/Transmission mounts for
- Damage
- Loose bolts
(Refer
to Sections 6A and 7A2)
e Transmission case mounting holes for:
- Missing bolts, nuts, studs
- Stripped threads
- Cracks
e Flywheel for:
- Missing or loose bolts
- Cracks
- Imbalance
(Refer to Section 6A)
e Torque converter for: - Missing or loose bolts or lugs - Missing or loose balance weights
- Imbalance
TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL INFORMATION
Checking fluid level, color and condition at
regular intervals will provide early diagnosis
information about the transmission. This information
may then be used to correct a condition that, if not
detected early, could result in major transmission
repairs.
When adding or changing fluid, use only
DEXRONO 11, or equivalent. Refer to Section OB of
this Service Manual for maintenance information and
servicing intervals.
Fluid level should be checked when it reaches
normal operating temperatures of
190-200°F.
(88-93°C). This temperature is reached after
approximately 15 miles (24 km) of highway
driving.
e Fluid color - Should be dark red (may be dark green)
NOTICE: Do not overfill. Overfilling will cause
foaming, loss of fluid and possible damage to the
transmission.
Inaccurate fluid level readings will result if
checked immediately after the vehicle has been
operated:
- In high abmient temperatures above 90°F
(32°C)
- At sustained high speeds
- In heavy city traffic during hot weather
- As a towing vehicle - In commercial service (taxi or police use)
TRANSMISSION FLUID CHECKING
PROCEDURE
(Refer to Figure 3)
1. Park vehicle on level ground.
2. Apply parking
brake and block wheels.
3. Start
engine and operate vehicle for 15 minutes or
until a normal operating temperature is reached.
4. Move gear
selector through all gear positions.
5. Move
gear selector to "Park" (P).
6. Check fluid level, color and condition.
Page 1119 of 1825
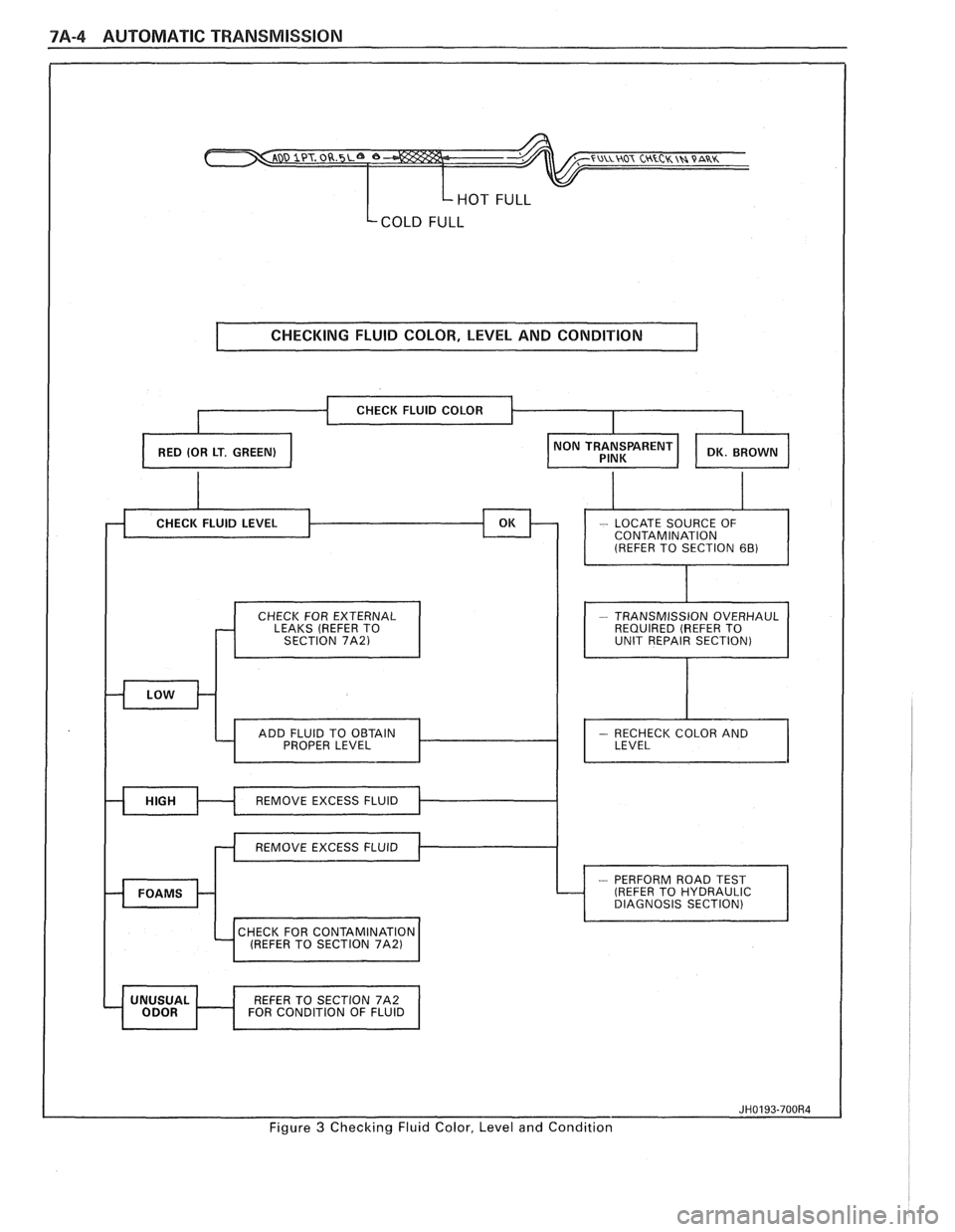
7A-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
HOT FULL
Lcom FULL
I CHECKING FLUID COLOR, LEVEL AND CONDITION 1
CHECK FOR EXTERNAL
LEAKS (REFER TO
SECTION
7A21 I I
- TRANSMISSION OVERHAUL
REQUIRED (REFER TO
UNIT REPAIR SECTION)
I
CHECK FOR CONTAMINATION 4 (REFER TO SECTION 71\21 1
REFER TO SECTION 7A2
FOR CONDITION OF FLUID I
Figure 3 Checking Fluid Color, Level and Condition
Page 1120 of 1825

AUTOMATIC TMNSMISSION ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 7A1-1
SECTION 7Al
AUTOMAT C TRANSM
ON VEH CLE SERV
CONTENTS
GENERAL SERVICE T.V. Cable
PROCEDURES Diagnosis ........................ .. ....................... 7A 1-6
Parts Cleaning, Inspection and
Replacement
....................................... 7A1-7
Replacement
............................ ... .... 7A1- 1 Adjustment ............................................. 7A1-7
Flexplate/Torque Converter Changing Fluid and Filter ............................. 7A1-7
........................... Vibration Test Procedure 7A1-2 700-R4 Serviceable Components
Fluid Leak Diagnosis
..................................... 7A 1-2
Servo Assembly .......................................... 7A 1-7
Methods For Locating Leaks
.................... 7Al-2 Speedometer Drive Gear .............................. 7A 1-1 1
Repairing the Leak .................................. 7A 1-2 Spccdomctcr Driven Gciu .......................... 7A1-1 1 Possible Points of Fluid Leaks .................. 7A1-2 Governor ............................................. 7A 1- 1 1
Case Porosity Repair .................................. 7A 1-3 Filler Tube .............................................. 7A1-12
Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Regulator Valve
........................... 7A 1- 12
Electrical Controls
.................................. 7Al-3
Auxiliary Valve Body ................................. 7A1-13
Diagnosis
................................... .... ........ 7A 1-3 Valve Body ............................................. 7A 1- 13
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE Rear Oil Seal ............................................ 7A 1- 14
Shift Control Cable
Oil Cooler Lines And Fittings
................... 7A1-14
Replacement
............................................ 7A 1-3 Oil Cooler Flushing .............................. 7A 1 - 14 ................................................ Adjustment 7A1-3 Transmission Assenlbly Removal and
Floor Shift Control
................... .. ................ 7A1-3
Installation ........................... .. ............ 7A1- 14
Park/Lock Control Cable .............................. 7A 1-4
Park/Neutral and Back Up Lamp
Switch
................................................. 7A1-5
GENERAL SERVICE PROCEDURES
PARTS CLEANING, INSPECTION AND
REPLACEMENT
Use appropriate safety equipment such as:
- Safety glasses
- Safety shoes
- Gloves
Keep work area and tools clean
Clean transmission exterior before removing
parts
Do not use wipe cloths or rags
Do not use solvents on:
- Rubber seals
- Plastic/Teflon@ thrust washers
Blow out all passages with compressed air
Clean out small passages with fine wire
Handle parts carefully to prevent damage
Lubricate all internal parts with transmission
fluid during assembly
When installing screws, bolts or studs into
aluminum always dip the threads in transmission
fluid
Always use a torque wrench for proper torque
€3 Recondition damaged or stripped aluminum
threads with thread inserts
@ Replace all gaskets and o-ring seals
- Do not use gasket cement or sealers
@ Replace Teflon@ and rubber lip seals only when
necessary and install using the appropriate seal
protector
s Manual linkage for:
- Wear at pivoting points - Bent or broken links and rods
s All seals, gaskets, o-rings and mating surfaces for:
- Nicks
- Cuts
- Damage
€3 Snap rings for:
- Expansion or compression
- Distortion
- Nicks
- Proper ring to groove fit
s Bearings and thrust surfaces for:
- Wear
- Scoring
Page 1121 of 1825

7A1-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Pitting
FLEXPLATE/TORQUE CONVERTER VIBRATION
TEST PROCEDURE
1. Start engine
2. With engine at idle speed and the transmission in
"Park"
(P) or "Neutral" (N), observe vibration.
3. Shut off engine.
Remove or Disconnect
e Flexplate cover attaching bolts
s Flexplate to torque converter attaching
bolts
e Rotate torque converter 120 (1/3 turn)
Install
or Connect
e Flexplate to torque converter attaching
bolts
- Torque bolts to 47 N.m (35 Ibs. ft.)
s Flexplate cover bolts
- Torque bolts to 6 N-m (53 lbs. in.)
4. Start engine and check for vibration. Repeat this
procedure un
ti1 the best possible balance is
obtained.
NOTICE: Some engine/transmission
combinations cannot be balanced in this manner
due to limited clearances between the torque
converter bolts and engine. Be sure bolts do not
bottom out in lug nuts or the torque converter
cover could be dented and cause internal damage.
FLUID LEAK DIAGNOSIS
The cause of most external leaks can generally be
located and repaired with the transmission in the car.
METHODS FOR LOCATING LEAKS
General Method
s Verify that the leak is transmission fluid.
a Thoroughly clean the suspected leak area.
s Operate the car for about 15 miles or until normal
operating temperatures are reached.
e Park the car over clean paper or cardboard.
s Shut off engine and look for fluid spots on paper.
a Make necessary repairs.
Powder Method
e Thoroughly clean the suspected leak area with
solvent.
a Apply an aerosol type powder (foot powder) to
the suspected leak area.
s Operate the car for about 15 miles or until normal
operating temperatues are reached.
s Shut off engine.
e Inspect suspected leak area and trace the leak
path through the powder to find the source.
a Make necessary repairs.
Dye And Black Light Method
A fluid dye and black light kit is available from
various tool manufacturers.
s Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for
the amount of dye to be used.
a Detect the leak with the black light.
e Correct cause of leak.
REPAIRING THE LEAK
Once the leak has been pinpointed and traced
back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined in order for it to be repaired properly. If a
gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the
new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange
must be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a
leak, check to be sure that the following conditions are
correct as they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
s Fluid level/pressure is too high.
e Plugged vent or drain-back holes.
s Improperly torqued fasteners or dirty/damaged
threads.
a Warped flanges or sealing surface.
e Scratches, burrs or other damage to the sealing
surface.
e Damaged or worn gasket.
e Cracking or porosity of the component.
s Improper sealant used (where applicable).
Seals
e Fluid level/pressure is too high.
a Plugged vent or drain-back holes.
s Damaged seal bore (scratched, burred or nicked).
e Damaged or worn seal.
e Improper installation.
a Cracks in component.
e Manual or output shaft surface scratched, nicked
or damaged.
a Loose or worn bearing causing excess seal wear.
Possible Points of Oil Leak
I. Transmission/Transmission oil pan :
Attaching bolts not correctly torqued
s Improperly installed or damaged gasket
s Oil pan or mounting face not flat
2, Case Leak :
@ Filler pipe "multi-lip seal" damaged or
missing
a Filler pipe bracket mislocated
s T.V. cable "multi-lip" seal missing,
damaged or improperly installed
a Governor cover or "0" ring damaged or
missing
@ Speedometer driven gear/speed sensor seal
damaged
e Manual shaft seal damaged
s Oil cooler connector fittings loose or
damaged
Page 1122 of 1825

AUTOMATIC TMNSMISSION ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 7A1-3
e Propeller shaft oil seal worn or damaged
o Governor cover
e Line pressure pipe plug loose
@ Porous casting
3. Leak at converter end:
Converter seal damaged
- Seal lip cut. (Check converter hub for
damage.)
- Bushing moved forward and damaged
- Garter spring missing from seal
o Converter leak in weld area. (Refer to
Torque Converter.)
Porous casting (Case or pump)
4. Fluid comes out vent pipe or fill tube:
Over-filled
Water or coolant in fluid. Fluid will appear
milky.
e Case porous
e Incorrect fluid level indicator
e Plugged vent
e Drain back holes plugged
Mispositioned oil pump to case gasket (if
equipped)
Case Porosity Repair
1. Clean the leak area with solvent and air dry.
CAUTION: Epoxy adhesive may cause
skin irritations and eye damage. Read
and follow all information on the
container label as provided by the
manufacturer.
2. Mix a sufficient amount of epoxy adhesive,
# 1052533, or equivalent, following the
manufacturer's recommendations.
3. While the transmission case is hot, apply epoxy
adhesive with a clean, dry soldering acid brush.
4. Allow the epoxy adhesive to cure for three hours
before starting the engine.
5. Repeat fluid leak diagnosis procedures.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ELECTRICAL
CONTROLS
The Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) system uses
controls that are internal as well as external to the
transmission. For internal control components of the
TCC system, refer to the I-Iydraulic Diagnosis Section
for for wiring diagrams and switch locations.
The external control components of the TCC
system include:
1. Brake Release Switch - To avoid stalling the
engine when braking, the converter clutch is
released any time the brakes are applied.
2. Electronic Control ModuOe - Receives input
signals and grounds TCC solenoid to apply clutch
when proper operating conditions are met.
3. Throttle Position Sensor - Sends throttle
position information to Electronic Control
Module.
4. Vacuum Sensor - Sends engine vacuum (load)
information to Electronic Control Module.
5. Vehicie Speed Sensor - Sends vehicle speed
information to Electronic Control Module.
6. Coolant Temperature Sensor - Sends engine
coolant temperature information to Electronic
Control Module.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
To properly diagnose the Torque Converter
Clutch (TCC) system perform all electrical testing first
and then the hydraulic testing. Refer to the appropriate
Driveability and Emissions Section (6E) for additional
Torque Converter Clutch Information
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
SI-IIFT CONTROL CABLE
Remove or Disconnect (Fig. 1)
1. Negative battery cable.
2. Raise car, see Section OA.
3. Cable attachments at transmission.
4. Lower car.
5. Console, see Section
8C.
6. Cable at control lever and base.
7. Cable from floor.
install or Connect
1. Cable to floor.
2. Cable at base and control lever.
3. Console, see Section 8C.
4. Place control lever in "NEUTRAL"
5. Raise car.
6. Cable attachments at transmission.
7. Adjust cable.
8. Lower car.
9. Negative battery cable.
Adjust (Fig. 1)
1. Place control lever in "N" (Neutral).
2. Raise car, see Section 0.4.
3. Loosen cable
attachment at shift lever.
4. Rotate shift lever "clockwise" to park detent and
then back to neutral.
5. Tighten cable attachment.
15
N-m (11 lbs. ft.)
Important
Levg must be held out of "PARK" when
torquing nut.
6. Lower car.
7. Check cable adjustment by rotating control lever
thru the detents.
Remove or Disconnect (Fig. 2)
1. Negative battery cable.
2. Console, see Section 8C.
3. Cable at control lever and base.