1988 PONTIAC FIERO maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 152 of 1825

STEERING WHEELS AND COLUMNS 385.1
SECTION 3B5
STEER NG WHEELS AND COLUMNS
NOTICE: All steering wheel and column fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect
the performance of vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They
must be replaced
with one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. 'Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly
to assure proper retention of all parts. There is to be no welding as
it may result in extensive damage and weakening
of the metal.
For prevailing torque
nut(s) and bolts(s), refer to the "Reuse of Prevailing Torque Nut(<) and Bolt(s) " chart
in Section OA.
CONTENTS
..................... ................................................................... GENERAL DESCRIPTION .. 3B5-1 ............................................. ........................ MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS .. 3B5-1 ON-CAR SERVICE ........................................................................................................ 3B5-2
Steering Column ............................................................................................................ 3B5-2 ......................................................................................................... Intermediateshaft 3B5-3
Park Lock Cable .................................................................... 3B54 ......................................................................................... Checking For Accident Damage 3B5-5 ............................................................................ Unit Repair Intermediate Shaft Assembly 3B5-6
..................................................................................... Standard Column @lanual Trans) 3B5-7 ......................................................... ....................... Standard Column (Auto Trans) .. 3B5-13 Tilt Column (Manual Trans) ............................................................................................. 3B5-19
Tilt Column (Auto Trans). ................................................................................................ 3B5-27
................ .................... TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS .. .. 3B5-35
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................................................................................................... 3B5-35
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
STEERING COLUMN
The function locking energy absorbing steering
column includes three important features in addition
to the steering function:
1. 'The column is energy absorbing, designed to
compress in a front-end collision to minimize the
possibility of an injury to the driver of the car.
2. The ignition switch and lock are mounted
conveniently on this column.
3. With the column mounted lock, the ignition and
steering operations can be locked to inhibit theft
of the car.
The turn signal lever provides for control of
headlight beams, windshield washer and wipers.
The column may be easily
disassembled and Fig. 385-1 Steering Wheel Alignment ~ypical
reassembled. To insure the energy absorbing action, it
on a flat surface to determine steering wheel
is important that only the specified screws, bolts, and
position at which vehicle follows a straight path.
nuts be used as designated and that they are tightened
2. With front wheels set straight ahead, check to the specified torque.
position of flat on wormshaft designating steering
When the column assembly is removed from the
gear high point. This flat should be at the top side
car, special care must be taken in handling it. Use of
of the shaft at 12 o'clock position.
a steering puller other than the One 3, if gear has been moved off high when recommended in this manual, a sharp blow on the
setting wheels in straight ahead position, loosen
end of the steering shaft or shift lever, leaning on the
assembly, or dropping the assembly could shear or adjusting
sleeve clamps on both left and right
hand tie rods, then turn both sleeves an equal
loosen the plastic fasteners which maintain column
rigidity. number
of turns in the same direction
to bring
gear back
on high point.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS NOTICE: Turning the sleeves an unequal number
Steering Wheel Alignment and High Point of turns or in different directions will disturb the
Centering toe-in setting of the wheels.
1. Set front wheel in straight ahead position, This 3. Readjust toe-in as outlined in Section 3A (if
can be checked by driving vehicle
a short distance necessary).
Page 188 of 1825

STEERING LINKAGE 3B6-1
SECTION 3B6
STEERING LINKAGE
The following notice applies to one or more steps in the assembly
procedure of components in this portion of the manual as Notice indicated at
appropriate locations by the terminology "See Caution on Page
1 of this
Section
" .
NOTICE: These fasteners are important attaching parts in that they
could affect the performance of vital components and systems,
andlor could
result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one of the same
part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do
not use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque
values must be used as specified during reassembly to assure proper retention
of these parts. For prevailing torque
nut(s) and bolt(s), refer to the "Reuse of
Prevailing Torque
Nut(s) and Bolt(s)" chart in Section 10.
CONTENTS
General Description ........................................... 3B6- 1 Relay Rod ............................................................ 3B6-3
Maintenance and Adjustments ............................... 3B6- I Idler Arm ............................................................. 3B6-4
On-Car Service ........................................................ 3B6-2 Pitman Arm ......................................................... 3B6-5
Tie Rods .............................................................. 3B6-2 Specifications ........................................................... 3B6-6
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
A parallelogram type steering linkage connects both
steering gear. The right end of the relay rod is supported by
front wheels to the steering gear through the
pitman arm,
the idler arm which pivots on a support attached to the
The right and left tie rods are attached to the steering arms
frame rail. The
pitman arm and idler arm remain parallel to
and to the relay rod by ball studs. The left end of the relay
each other while they move through symmetrical arcs. See
rod is supported by the
pitman arm, which is driven by the Fig. 3B6-2.
MAONTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
CHELKlNC STtLRING LINKAGE WEIR A? VltlItD FROhl ABOVL
POSITION DIAL INDICATOR
-TO CHECK MOVEMENT
AT THIS POINT
FRONT
OF
MOVE WHEEL IN AND OUT AT FRONT AND BACK
Fig. 3B6-1--Checking Linkage Wear
SUSPENSION AND STEERING LINKAGE CHECK
1. Raise car on one side at frame torque box located
directly behind the front wheel so that tire is
approximately one inch off the floor.
2. Position dial indicator as shown in Fig.
3B6- I .,
3. Position steering wheel so that it is in the locked
position.
4. Grasp front wheel as shown in Fig.
3B6- I. With wheels
in straight ahead position, move wheel back and forth
without moving steering wheel. Gage reading should
not exceed 2.74 mm
(. 108 ").
5. If gage reading is not within specifications, a check
should be made of all suspension and linkage gears.
RELAY ROD HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
The relay rod position can be adjusted at the idler arm
attach men^. It is important for the height adjustment to be
equal from side-to-side. If not adjusted properly, right-hand
turns and left-hand turns could exhibit differell1
characteristics in handling. This is sometimes called
"orbital steer." Refer to Fig.3B6-5 for setting relay rod
height.
Page 194 of 1825

POWER Sf EERING 387-1
SECTION 3B7
POWER STEER NG GEAR AND PUMP
The following notice applies to one or more steps in the assembly procedure of components in this portion
of the manual as indicated at appropriate locations. "See Notice on Page
1 of this Section".
NOTICE: Steering column fasteners are important attaching parts in that they may affect the performance
of vital components and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a replacement
part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly to assure
proper retention of these parts. For prevailing torque
nut(s) and bolt(s), refer to the "Reuse of Prevailing Torque
Nut(s) and Bolt(s)" chart in Section 10.
CONTENTS
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
Bleeding Hydraulic System
................................................................................................. 3B7- 1
Fluid Level ......................................................................................................................... 3B7- 1
Power Steering Gear Adj. ..................................................................................................... 3B7- 1
Drive Belt Tension .............................................................................................................. 3B7-2
Hydraulic System Checks .................................................................................................. 3B7-2
Hydraulic System Test ......................................................................................................... 3B7-2
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Steering Gear Removal
...................................................................................................... 3B7-3
Pitman Shaft Seal .................................................................................................................. 3B7-3
Pump Removal ..... , ................................................................................................................ 3B7-4
................................................................................................................... Hoses and Pipes 3B7-4
Pump Pulley ....................................................................................................................... 3B7-4
.................................................................................. Pump Brackets/Hoses/Cooling Pipes 3B7-5
........................................................................................ Pump Overhaul .................... ..... 3B7- 12
Gear Overhaul .................................................................................................................... 3B7- 13
SPECIAL TOOLS ............................................................................................................ 3B7-17 ......................... .......................................................... GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS .. 3B7- 18
MAlNKNANGE AND ADJUSTMENTS
BLEEDING HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Fill fluid reservoir to proper level and let remain
undisturbed for at least two minutes.
Start engine and run momentarily.
Shut engine off to add fluid.
Repeat above procedure until fluid level remains
constant after running engine.
Raise front end of vehicle so that wheels are off
the ground.
Start engine and increase engine speed to
approximately
1500 rpm.
Turn the wheels (off ground) right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
Lower the car and turn wheels right and left on
the ground.
Shut engine off, check fluid level and refill as
required.
If fluid is extremely foamy, allow vehicle to stand
a few minutes with engine off while you run
through the following:
a. Check belt
tightness and check for a bent or
loose pulley. (Pulley should not wobble with
engine running.) b.
Check
to make sure hoses are not touching
any other parts of the car, particularly sheet
metal and exhaust manifold.
c. Check fluid
level, filling to proper level if
necessary. Air in the fluid is the most
frequent cause of objectionable pump noise.
d. When air is present, bleed system as
described in operations 1 through 10. If the
pump will not bleed after a few trials,
proceed as outlined under Hydraulic
System Checks. FLUID LEVEL
1. Check fluid level in the reservoir by checking the
dip stick when fluid is at operating temperature.
2. Fill, if necessary, to proper level with GM Power
Steering Fluid, or equivalent.
POWER STEERING GEAR ADJUSTMENTS
Adjustment of the power steering gear in the
vehicle is discouraged because of the difficulty involved
in adjusting the worm thrust bearing preload and the
confusing effects of the hydraulic fluid in the gear. The
steering gear adjustment is made only as a correction
and not as a required periodic adjustment.
Page 195 of 1825

387-2 POWER STEERING
The effect of improperly adjusted worm thrust
bearings or an improperly adjusted over-center preload
could cause a handling stability complaint.
To properly adjust the power steering gear, the
assembly MUST be removed from the vehicle and
adjustments performed as outlined.
For removal of the power steering gear assembly
see "Power Steering Gear".
DRIVE BELT TENSION
All drive belt tension specifications can be found
in the Engine Cooling Section 6B.
When adjusting a power steering pump belt,
never pry against the pump reservoir or pull against the
filler neck. Two systems are used for belt adjustment.
On some
models, the pump is loosened from the
bracket and moved outward to increase the tension. On
other models, a half-inch square drive hole is located
in the bracket, and this hole is used to rotate the
pump-and-bracket assembly outward to increase belt
tension.
Place belt tension gage, J-23600 or equivalent
midway between the pulleys on drive belt being
checked.
POWER SKERING ADAPER GAGE J-5176-01 J-22326
PRESSURE HOSE TO
P/S GEAR PRESSURE HOSE
Figure 387-1 Test Gage Installation
To adjust pump:
1.
Loosen the pump attaching bolts and adjust the
belt to correct tension by moving the pump
outward, away from the engine.
2. Snug all pump mounting bolts and remove pry
bar.
3. Tighten all pump mounting bolts to specified
torque.
4. Check belt tension using the tension gage.
NOTICE: Do not move pump by prying against
reservoir or by pulling on filler neck, or damage
may occur.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CHECKS
The following procedure outlines methods to
identify and isolate power steering hydraulic circuit difficulties.
The test provides means of determining
whether power steering system hydraulic parts are
actually
defective.
Before performing hydraulic circuit test,
carefully check belt tension, fluid level and condition
of driving pulley.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM TEST
(Figure 387- lj
Fluid must be at normal operating temperature.
Check front tires for correct pressure. All tests are
made with engine idling. If necessary, adjust engine
idle speed to correct specifications listed in Section 6C
and proceed as follows:
1. Stop engine, disconnect pressure hose from pump
and install Tool
5-5176 using a spare pressure
hose between gage and pump. Gage must be
between shut-off valve and pump. Open shut-off
valve.
2. Remove filler cap from pump reservoir and check
fluid level. Fill pump reservoir to full mark on dip
stick. Start engine and, momentarily holding
steering wheel against stop, check connections at
Tool J-5 176 for leakage.
3. Bleed system as outlined under Maintenance and
Adjustments.
4. Insert thermometer (Tool J-5421) in reservoir
filler opening. Move
/steering (wheel/ from stop to
stop several times until thermometer indicates
that hydraulic fluid in reservoir has reached
temperature of
150" to 170°F (65" to 77°C).
N OTI G E: To prevent scrubbing flat spots on tires,
do not turn steering wheel more than five times
without rolling vehicle to change tire-to-floor
contact area. Front end of vehicle can be lifted for
this test.
5. Start engine and check fluid level, adding fluid if
required. When engine is at normal operating
temperature, the initial pressure read on the gage
(valve open) should be in the 80-125 psi (550-860
kPa) range. Should this pressure be in excess of
200 psi (1380
kPa) - check the hoses for
restrictions and the poppet valve for proper
assembly.
6. Close gate valve fully
3 times. Record the highest
pressures attained each time.
N OTI C E: Do not leave valve fully closed for more
than
5 seconds as the pump could be damaged
internally.
a. If
the pressures recorded are within the
listed specs and the range of readings are
within 50 psi (345
kPa), the pump is
functioning within specs.
b. If the pressures recorded are high, but do
not repeat within 50 PSI (345
kPa), the flow
controlling valve is sticking. Remove the
valve, clean it and remove any burrs using
Page 196 of 1825
POWER STEERING 387-3
crocus cloth or fine hone. If the system 4. If the pump checks within specifications, leave
contains some dirt, flush it. If it is the valve open and turn (or have turned) the
exceptionally dirty, both the pump and the steering wheel into both corners. Record the
gear must be completely disassembled, highest pressures and compare with the
cleaned, flushed and reassembled before maximum pump pressure recorded. If this
further usage. pressure cannot be built in either (or one) side of
- the gear, the gear is leaking internally and must
c. If
the pressures recorded are constant, but
be disassembled and repaired. See "Unit Repair"
more than
100 PSI (690 kPa), below the
at the end of this section.
spec.9 rep1ace the flow 8. Shut off engine, remove testing gage, spare hose,
valve and recheck. If the pressures are still
low, replace the rotating group in the pump. reconnect pressure hose, check fluid
level and/or
make needed repairs.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
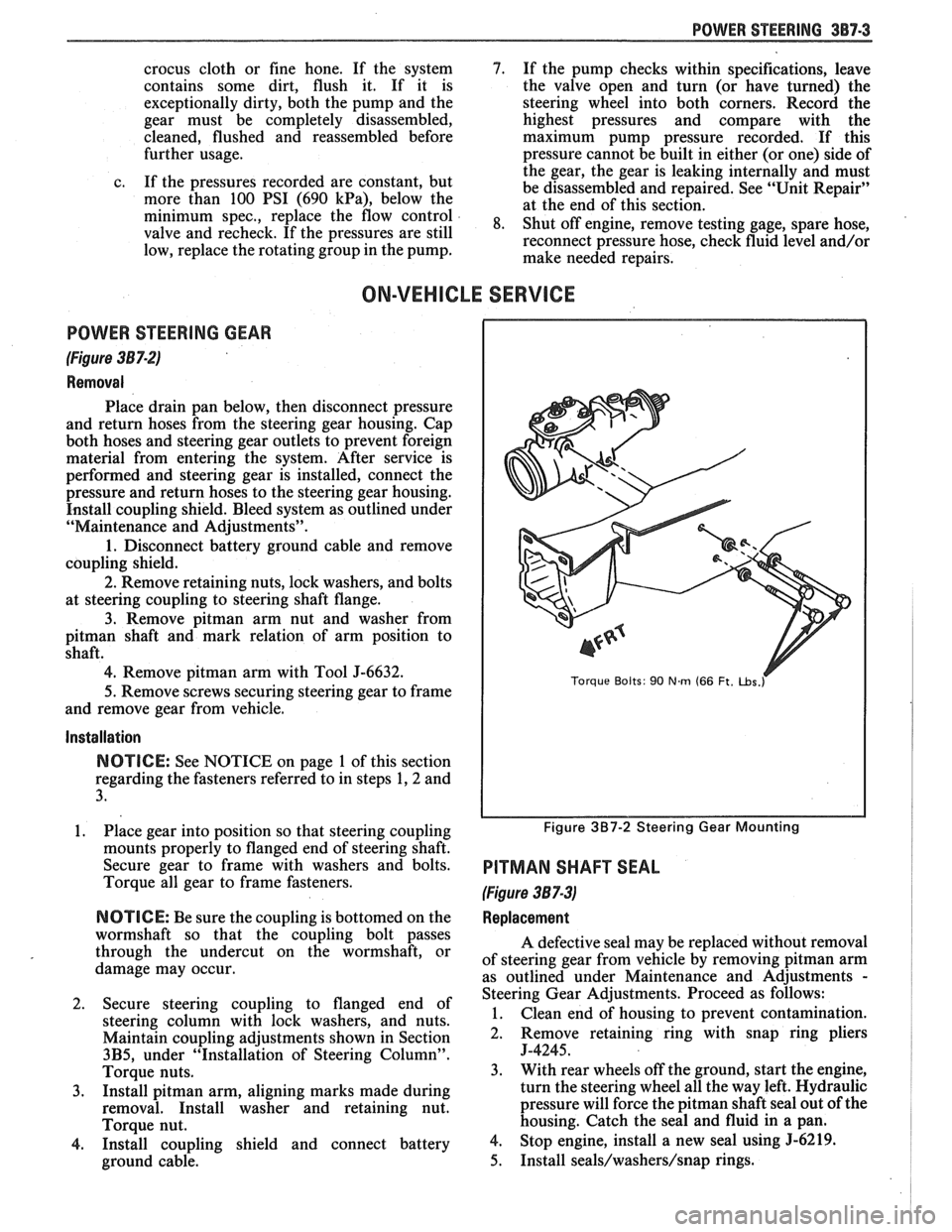
POWER STEERING GEAR
(Figure 387-2)
Removal
Place drain pan below, then disconnect pressure
and return hoses from the steering gear housing. Cap
both hoses and steering gear outlets to prevent foreign
material from entering the system. After service is
performed and steering gear is installed, connect the
pressure and return hoses to the steering gear housing.
Install coupling shield. Bleed system as outlined under
"Maintenance and Adjustments".
1. Disconnect battery ground cable and remove
coupling shield.
2. Remove retaining nuts, lock washers, and bolts
at steering coupling to steering shaft flange.
3. Remove pitman arm nut and washer from
pitman shaft and mark relation of arm position to
shaft.
4. Remove pitman arm with Tool J-6632.
5.
Remove screws securing steering gear to frame
and remove gear from vehicle.
Installation
NOTICE: See NOTICE on page 1 of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in steps 1,2 and
3.
1. Place gear into position so that steering coupling
mounts properly to flanged end of steering shaft.
Secure gear to frame with washers and bolts.
Torque all gear to frame fasteners.
NOTICE: Be sure the coupling is bottomed on the
wormshaft so that the coupling bolt passes
through the undercut on the wormshaft, or
damage may occur.
2. Secure steering coupling to flanged end of
steering column with lock washers, and nuts.
Maintain coupling adjustments shown in Section
3B5, under "Installation of Steering Column".
Torque nuts.
3. Install pitman arm, aligning marks made during
removal. Install washer and retaining nut.
Torque nut.
4. Install coupling shield and connect battery
ground cable.
Torque Bolts: 90 Nm (66 Ft. ~bs.r
Figure 3B7-2 Steering Gear Mounting
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
(Figure 387-3)
Replacement
A defective seal may be replaced without removal
of steering gear from vehicle by removing
pitman arm
as outlined under Maintenance and Adjustments
-
Steering Gear Adjustments. Proceed as follows:
1. Clean end of housing to prevent contamination.
2. Remove retaining
ring with snap ring pliers
J-4245.
3. With rear wheels off the ground, start the engine,
turn the steering wheel all the way left. Hydraulic
pressure will force the
pitman shaft seal out of the
housing. Catch the seal and fluid in a pan.
4. Stop engine, install a new seal using 5-6219.
5. Install seals/washers/snap rings.
Page 197 of 1825

3B7-4 POWER STEERING
6. Reinstall pitman arm as described earlier, Add
fluid as required, check and bleed system until
correct fluid level is obtained.
POWER STEERING PUMP
Removal
1. Place drain pan below, then disconnect hoses at
pump or steering gear. When hoses are
disconnected, secure ends in raised position to
prevent drainage of fluid.
2. Install caps at hose fittings to prevent loss of fluid
from pump.
3. Remove drive belt.
Figure 3B7-3 Pitman Shaft Seal Replacement
4. Remove pump from vehicle.
Installation
1. Position pump assembly on vehicle and install
attaching parts loosely.
2. Gonl7.zct and tighten hose fittings.
3. Fill reservoir. Bleed pump by turning pulley
backward (counter-clockwise as viewed from
front) until air bubbles cease to appear.
4. Install drive belt over pulley.
5. Tension belt as outlined under "Maintenance and
Adjustments". Do not pry on pump reservoir.
6. Bleed as outlined under "Bleeding Power
Steering Systems".
POWER STEERING HOSES AND PIPES
It is important that the power steering hoses and
pipes be installed correctly. Hoses and pipes installed
out of position may be subjected to chafing or other
abuses during high pump pressure. Always make
installations with the front wheels in straight ahead
position. Do not twist hoses unncessarily during
installation.
NOTICE: Do not start engine with any power
steering hose or pipe disconnected. After
connecting the power steering hoses, make sure
that ample clearance has been provided between
the hoses and the drive belt, sheet metal or any
other components where hose rub or interference
could result. If the return hose or pipe connections
are removed for any reason at either connection,
replace the existing "crimped" clamp with a
"worm drive" clamp for proper sealing.
PUMP PULLEY
(Figure 38 7-41
Removal
1. Install tool as shown in Figure 3B7-4. Be sure
pilot bolt bottoms in the pump shaft by turning
nut to the top of the pilot bolt.
2. Install puller jaws and retainer sleeve.
3. Remove pulley by holding pilot bolt and turning
nut counterclockwise.
Installation
1. Place
pulley on end of pump shaft and install tool
as shown in Figure 3B7-4. Be sure pilot bolt
bottoms in shaft by turning nut to the top of the
pilot bolt.
2. Install pulley by holding pilot bolt and turning
nut clockwise.
Page 232 of 1825

TIRES AND WHEELS 3E-1
RES AND WHEELS
NOTICE: All wheel bolt and nut fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect the
performance of vital components and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced
with one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly
to assure proper retention of parts.
CONTENTS
Diagnosis ............................................... Section 3 Tire Repair ................................................... 3E-5
General Information .......................... ..... 3E-1 Waddle ........................................................ 3E-5
........ Replacement Tires ....................... ... 3E- 1 Measuring Wheel Runout ............................ 3E-6
P-Metric Tires ...................... .. ................... 3E-2 Spare Tire ...................................................... 3E-6 ................................................ Tire Placard 3E-2 Match Mounting ......................................... 3E-7
.......................................................... Wheels 3E-2 Balancing Tire and Wheel ............................ 3E-7
....................... Maintenance and Adjustments .............. 3E-2 General Balance Precautions 3E-7 ...................................... Wheel Repair .............................................. 3E-2 Off-Car Balancing 3E-8 .............................. Metric Wheel Nuts and Studs .................... .. 3E-3 On-Car Balancing .. ...... 3E-8
......................................... Inflation of Tires ........................................ 3E-3 Wheel Weights 3E-8 .................... Tire Rotation ........................... ...... . 3E-3 Correcting Non-Uniform Tires 3E-8 .......................... Tire Chain Usage ........................................ 3E-4 Aluminum Wheel Cleaning 3E-9 Aluminum Wheel Hub Cap ......................... 3E-9 Service Operations ..................................... 3E-4 Aluminum Wheel Porosity Repair .............. 3E-9 ......................... Wheel Removal .... .......... 3E-4 Aluminum Wheel Refinishing ...................... 3E-9 Tire Mounting and Dismounting ................. 3E-5 Wheel Nut Torque 3E-10 ......................................
GENERAL INFORMATION ~t is recommended that new tires be installed in
pairs on the same axle. If it is necessary to replace only
The tires and are one tire, it should be paired with the tire having the
designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to and
most tread, to equalize braking traction. including the full rated load capacity when inflated to
Although they may appear different in tread
the recommended inflation pressures.
design, tires built by different manufacturers with
Correct tire pressures, wheel alignment and identical TPC specification numbers, can be
driving techniques have an important influence on tire
intermixed on the same car. life. Heavy cornering, excessive rapid acceleration, and
heavy braking will increase tire wear.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
Fig. 1
A Tire Performance Criteria (TPC) specification
number is molded in the sidewall near the tire size of
all original equipment tires. This specification number
assures that the tire meets
GM's performance
standards for traction, endurance, dimensions, noise,
handling, rolling resistance, and others. Usually, a
specific TPC number is assigned to each tire size.
When replacing tires, only the size, load range,
and construction as originally on the car are
recommended. This can best be accomplished by
replacing with tires of the same TPC specification
number. Use of any other tire size or construction type
may seriously affect ride, handling,
speedometer/odometer calibration, car ground
clearance and tire clearance to the body and chassis.
This does not apply to the spare furnished with the car.
v// TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Fig. 1 Tire Identification
Page 233 of 1825
3E.2 TIRES AND WHEELS
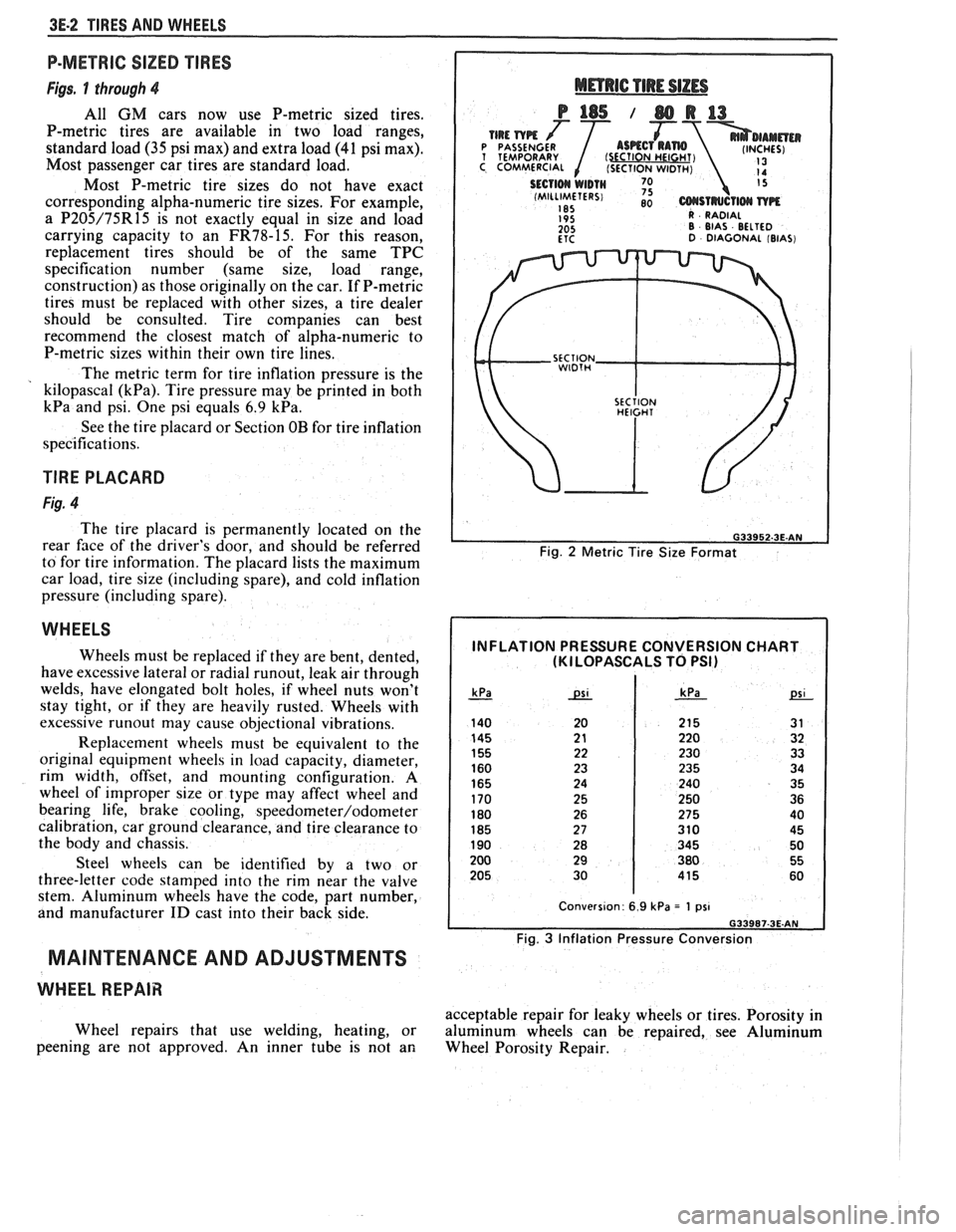
P-METRIC SIZED TIRES
Figs. 1 through 4
All GM cars now use P-metric sized tires.
P-metric tires are available in two load ranges,
standard load
(35 psi max) and extra load (41 psi max).
Most passenger car tires are standard load.
Most P-metric tire sizes do not have exact
corresponding alpha-numeric tire sizes. For example,
a
P205/75R15 is not exactly equal in size and load
carrying capacity to an
FR78-15. For this reason,
replacement tires should be of the same TPC
specification number (same size, load range,
construction) as those originally on the car. If P-metric
tires must be replaced with other sizes, a tire dealer
should be consulted. Tire companies can best
recommend the closest match of alpha-numeric to
P-metric sizes within their own tire lines.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the
kilopascal
(kPa). Tire pressure may be printed in both
kPa and psi. One psi equals 6.9 kPa.
See the tire placard or Section OB for tire inflation
specifications.
TlRE PLACARD
Fig. 4
The tire placard is permanently located on the
rear
face of the driver's door, and should be referred
to for tire information. The placard lists the maximum
car load, tire size (including spare), and cold inflation
pressure (including spare).
WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented,
have excessive lateral or radial
runout, leak air through
welds, have elongated bolt holes, if wheel nuts won't
stay tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with
excessive
runout may cause objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the
original equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter,
rim width, offset, and mounting configuration.
A
wheel of improper size or type may affect wheel and
bearing life, brake cooling,
speedometer/odometer
calibration, car ground clearance, and tire clearance to
the body and chassis.
Steel wheels can be identified by a two or
three-letter code stamped into the rim near the valve
stem. Aluminum wheels have the code, part number,
and manufacturer
ID cast into their back side.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
WHEEL REPAIR
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or
peening are not approved. An inner tube is not an
Fig. 2 Metric Tire Size Format
INFLATION PRESSURE CONVERSION CHART (KI LOPASCALS TO PSI)
Fig. 3 Inflation Pressure Conversion
acceptable repair for leaky wheels or tires. Porosity in
aluminum wheels can be repaired, see Aluminum
Wheel Porosity Repair.