1988 FIAT TEMPRA air bleeding
[x] Cancel search: air bleedingPage 42 of 171

• Job 20. Check/adjust clutch. CABLE OPERATED CLUTCH
The clutch mechanism is self-adjusting, although the cable
linkage can stretch over a period of time and may need
adjustment. The adjuster is on top of the gearbox, reached
from inside the engine bay.
20C. 'Work' the clutch pedal
(X) a few times, pull back the
carpet from under the pedal,
then measure the full travel of
the pedal, which should be
between 140 and 150 mm.
/
\
/ \
/ u / Xl
1 ' ' / . V y 2
Jdi V 1 \
X. 1 —
20C
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH
20B. Check the
pipework and slave
cylinder, on the
gearbox casing,
from beneath the
20D. If not, note that after
slackening the locknut, turning
the adjusting nut inwards
along the threaded rod
(arrowed) will increase pedal
travel. Tighten the lock-nut
against the inner nut after
adjustment.
• Job 21. Check auto, transmission selector cable.
It should only be possible to start the engine when the gear
selector is in the 'P' or 'N' position. Place it in each of the
other positions and try to start the car. If it starts, the fault
must be put right! Also check that, with the ignition off and
the selector lever in 'D' (Drive), 'L' (Low), 'R' (Reverse) or 'N'
(Neutral), the timed warning buzzer should sound. If it
doesn't, the selector cable adjustment may be faulty.
See Chapter
6,
Repairs and Replacements, PART B:
TRANSMISSION AND CLUTCH, Job 8 for adjustment details.
PART D: IGNITION AND ELECTRICS
See FACT FILE: DISCONNECTING THE BATTERY on page 36
SAFETY FIRST!
• You may minimise the risk of shock when the engine is running by wearing thick rubber gloves and by NEVER
working on the system in damp weather or when standing on damp ground. Read Chapter 1, Safety First! before
carrying out any work on the ignition system.
• ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEMS INVOLVE VERY HIGH VOLTAGES! All manufacturers recommend that only trained
personnel should go near the high-tension circuit (coil, distributor and HT wiring) and it is ESSENTIAL that anyone
wearing a medical pacemaker device does not go near the ignition system.
• Stroboscopic timing requires the engine to be running
-
take great care that parts of the timing light or parts of
you don't get caught up in moving components!
• Don't have loose clothing or hair.
46
FACT FILE: CABLE OR HYDRAULIC
CLUTCH?
• Most earlier Tipos and Tempras had a
cable-operated clutch, while later ones
are hydraulic.
• 2 OA. You
can easily tell
which system
your car is
fitted with.
The hydraulic
pipe (if fitted)
runs almost
horizontally,
across the
back of the engine bay.
• There is no separate clutch fluid reservoir
-
it shares
the brake fluid reservoir.
• Clutch cables (when fitted) are inclined to break
without warning.
• It pays to keep the operating mechanism well lubri-
cated and renew the cable every few years.
car. If the pipe
appears cracked,
replace it. If the
slave cylinder
oozes fluid, replace
it, in both cases bleeding the system. See Chapter
6,
Repairs
and Replacements.
Page 48 of 171

• Job 32. Change petrol fuel filter. IMPORTANT NOTES:
• Wear plastic gloves and goggles and have a large rag
and a suitable fire extinguisher ready.
• Place a container beneath the filter to catch fuel
spillage.
• After fitting the new filter in place, refit the casing,
ensure no traces of fuel are left, reconnect the battery and
restart the engine.
• Check carefully to ensure there are no leaks before
refitting the cover.
• Job 33. Drain diesel fuel filter.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Some models are fitted with a water-
in-fuel sensor. Drain the filter when the warning light
comes on. Unplug the sensor from the base of the filter,
first.
FUEL INJECTION
MODELS
32A. The filter is under the
car, ahead of the fuel tank.
E3 INSIDE INFORMATION:
Remove the visible screws
holding the flexible
plastic cover in place.
You can now pull the
front down and out of
the way. E3
32B. Undo the clamp,
remove the outer
casing and renew the
special paper filter,
from your FIAT
dealership. There is
an arrow on the
casing to remind you
which way round it
must be fitted.
33. The fuel filter is
located in the rear of
the engine
compartment. Water
carried in the fuel
accumulates in the
bottom of the filter,
and should not be
allowed to build up.
To drain it position a receptacle under the filter, then unscrew
the knurled tap at the bottom of the filter by a couple of turns.
Do so at the recommended interval, or if the panel indicator
comes on. (See Chapter
2,
Getting to Know Your
Car.)
H INSIDE INFORMATION: Plastic fuel pipes become
brittle and snap. Extra care needed! E3
SAFETY FIRST!
• The high pressure pipework on a fuel injection
system can retain its pressure for days even after the
engine has been switched off.
• When you disconnect the pipework, a jet of fuel can
be emitted under very high pressure
-
strong enough
to penetrate the skin or damage the eyes.
• NEVER work on the fuel pipework when the engine
is running (except when bleeding Diesel injectors).
• ALWAYS place a rag over a union while it is being
undone until all the pressure has been let out of the
system.
• You are recommended to wear strong rubber gloves
and goggles when disconnecting the fuel injection
system's high pressure pipework. Always disconnect
VERY slowly, letting pressure out progressively.
• See Chapter 6, PART F: Job 8 for details of how to
depressurise the system.
• Disconnect the battery negative earth before
working on the fuel system.
• Work outdoors and away from sources of flame or
ignition.
• ALWAYS wear rubber gloves
-
don't let your
skin
come into contact with fuel.
IMPORTANT NOTE: All Tipo/Tempra diesel engines are
self-bleeding and there should be no need to bleed air
out of the system manually.
• Job 34. Change diesel fuel filter.
Drain the fuel filter. Unscrew the complete filter canister from
its head, in the same way that you would an engine oil filter.
First undip the sensor plug (if fitted) from the base of the unit.
^ 34A. If it is too tight to
^^ - unscrew by hand, use an oil
filter wrench on the lower,
flatted zone (C). Wipe the underside of the filter head,
fill the new filter
with fuel...
34B. ...lightly
lubricate its seal
with fuel, then
screw it onto the
filter head. Once it
is 'nipped up',
tighten it as far as
possible by hand,
without
'murdering' it
-
so
that you CAN
remove it next
time!
Page 49 of 171

IMPORTANT NOTE: • All Tipo/Tempra diesel engines are
self-bleeding and there should be no need to bleed air
out of the system manually.
• If the engine does not eventually re-start, check all the
unions for the fuel inlet pipe and the other unions,
replacing the sealing washers if necessary, to eliminate
any air leaks.
Q Job 35. Check/adjust petrol engine idle and
emissions.
Setting the idle speed and mixture is not just a matter of
making
the car run smoothly and economically; it's also a
question of allowing it to run within the legal hydrocarbon
(HC), Nitrous Oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO) emission
limits. If it
is
outside limits, the car will fail the annual test.
(However, a worn engine will fail even if the carburettor or
injection system is correctly set up.)
FACT FILE: ESSENTIAL
PREPARATIONS
• When tuning the engine you should
adjust the carburettor (when fitted) last
of all, as its settings will be affected by
the state of tune of the rest of the engine.
• Ignition dwell angle and timing must be correct, the
air
filter
should be clean, there should be no air leaks
on
the induction system, and all electrical components
and
the air conditioning (if fitted) should be switched
off.
• Get the engine to full operating temperature before
checking and adjusting.
• If
you
warm the engine on tick-over (instead of on a
journey), it won't be hot enough until you have heard
the electric cooling fan cut in twice.
Q INSIDE INFORMATION: These jobs require the use of a
tachometer (rev-counter) and an exhaust gas analyser to
achieve any degree of accuracy. If you don't own them -
and relatively inexpensive tools are now available
-
you
may
wish
to have the work carried out by your local FIAT
dealer. D
ROUGH
GUIDE: Within each section is a description of how
you
can
get the car running tolerably well without any
specialist
equipment, so that you can take it to your FIAT
dealership
for accurate (and MoT-able!) tuning.
35A. Check the float
level with the carburettor
in the position shown.
Distance (c) should be
30mm with gasket fitted.
Bend tab (2) to adjust
-
but the tab should
remain virtually perpen-
dicular. Do NOT adjust
items (1)or (3)1
35B. IDLE SPEED
ADJUSTMENT: Connect a
rev-counter according to
the maker's instructions,
and check the idle speed.
clockwise increases the
idle speed, anti-clockwise
reduces it. Set the idle
speed in accordance with
Chapter
3,
Facts and
Figures.
ROUGH GUIDE: Turn the screw until the engine is running at
the slowest speed at which it runs smoothly and evenly.
MIXTURE ADJUSTMENT: Check that the idle speed is correct
and make sure that the engine is at full operating temper-
ature. Connect an exhaust gas analyser as instructed by the
maker. If the CO reading is outside the range shown in
Chapter
3,
Facts and Figures, adjustment as follows:
Use a narrow-blade screwdriver and turn the screw (2)
clockwise to weaken (reduce) or anti-clockwise to richen
(increase) the reading.
ROUGH GUIDE: Turn the mixture screw inwards (clockwise).
As you do so, the tick-over speed will increase, until the point
comes where the engine starts to run 'lumpily'. Back off the
screw until the engine runs smoothly again, and then some
more until the speed just starts to drop. At this point, screw
the adjuster back in by a quarter-turn and you'll be
somewhere near the optimum setting for smooth running.
IMPORTANT NOTE: After setting the mixture adjustment,
re-check and, if necessary, re-adjust the idle speed.
CARBURETTOR MODELS ONLY
TAMPER PROOFING: All Tipo carburettors originally had a
tamper-proof seal placed over the mixture adjustment screw.
These
seals are to prevent anyone unauthorised from altering
the
mixture and exhaust emissions. In certain countries these
seals
must be retained by law.
If the
seal
is
a plastic cap placed over the adjuster screw, it can
be
broken
off with pliers. If it is a plug within the screw recess,
force
it out with a sharp object.
35C. This illustration
shows the correct
settings for the
choke fast idle
adjustment (manual
choke only) and the
automatic anti-
flooding device
adjustment. See
following page.
Page 112 of 171

PART F: FUEL AMD EXHAUST SYSTEMS
PART F: Contents
Job 1. Fuel system types. Job 9. Electric fuel pump, petrol engine (S.P.I.)
-
Job 2. Carburettor
-
removal and refitting. replacement.
Job 3. Petrol injection unit
-
removal and refitting. Job 10. Fuel tank
-
removal and refitting.
Job 4. Accelerator cable, carburettor engines
-
replacement Job 11. Hot air hoses/thermo-valves
-
general.
and adjustment. Job 12. Lambda sensor (S.P.I, engines)
-
replacement.
Job 5. Carburettor choke cable
-
replacement and Job 13. Fuel evaporation system.
adjustment. Job 14. Exhaust system
-
replacement.
Job 6. Accelerator cable, petrol injection engines -Job 15. Turbocharger, diesel engine
-
replacement.
replacement and adjustment. Job 16. Diesel injection pump
-
removal and refitting.
Job 7. Diesel engines. Accelerator cable
-
replacement and Job 17. Diesel injectors
-
remove and refit.
adjustment. Job 18. Bleeding Diesel fuel system.
Job 8. Mechanical fuel pump, petrol engine (carburettored) -
replacement.
Job 1. Fuel system types.
FACT FILE: FUEL INJECTION/ELECTRONIC
IGNITION PRECAUTIONS
OBSERVE THE FOLLOWING PRECAUTIONS
WHEN WORKING ON PETROL-ENGINED
VEHICLES WITH FUEL INJECTION - ELECTRONIC
IGNITION SYSTEMS:
• never start the engine when the electrical terminals are
poorly connected or loose on the battery poles;
• never use a quick battery charger to start the engine;
• never disconnect the battery from the car circuit with the
engine running;
• when charging the battery quickly, first disconnect the
battery from the vehicle circuit;
• if the vehicle is placed in a bodyshop drying oven after
painting at a temperature of more than 80 degrees Celsius,
first remove the injection/ignition ECU;
• never connect or disconnect the ECU multiple connector
with the ignition key in MARCIA position;
• always disconnect battery negative lead before carrying out
electrical welding on vehicle.
Note that some systems contain one memory that is always
active (stand-by memory) and that stores learnt self-adaptive
values. Because this data is lost when the battery is discon-
nected, this operation should be carried out as infrequently as
possible.
Refer to illustrations in Job 1 for typical layouts.
It's a good idea to familiarise yourself with the type of fuel
system fitted to your car. These are the main types.
• Type 1: This is the 1400/1600cc carburettored engines
fuel system.
SAFETY FIRST!
• The high pressure pipework on a petrol or diesel fuel
injection system can retain its pressure for days even
after the engine has been switched off.
• When you disconnect the pipework, a jet of fuel can
be emitted under very high pressure
-
strong enough to
penetrate the skin or damage the eyes.
• NEVER work on the fuel pipework when the engine is
running (except when bleeding Diesel injectors
-
see Job
18.
• ALWAYS place a rag over a union while it is being
undone until all the pressure has been let out of the
system.
• You must wear strong rubber gloves and goggles
when disconnecting the fuel injection system's high
pressure pipework. Always disconnect VERY slowly,
letting pressure out progressively.
• See Job 8 for details of how to depressurise the
system.
• Disconnect the battery negative earth before working
on the fuel system.
• Work outdoors and away from sources of flame or
ignition.
• ALWAYS wear rubber gloves
-
don't let your skin come
into contact with fuel.
1 - overflow pipe 2 - safety valve/roll over cut-off device 3 - fuel tank 4 - carburettor 5 - fuel supply, pump to carburettor 6 - mechanical fuel pump
7 - fuel filter 8 - fuel supply, tank to pump 9 - excess fuel return, carburettor to tank 10 - breather pipe, between highest and lowest Job
1-1
Page 122 of 171
• Step 22: Inspect the timing belt and if
-
• it is contaminated with any liquid,
• has damaged teeth,
• or frayed edges,
• or it has covered more than 30000 km,
-
fit a new one.
D INSIDE INFORMATION: Some FIAT mechanics
recommend that the belt is replaced as a matter of
course. The cost of a new belt compared to the cost
of a damaged engine, makes it a false economy not to
do so.
E9
Q Step 23: Place the timing belt over the sprockets,
keeping it tight on the run between the pump and camshaft.
Q Step 24: Push the adjusting pulley into the belt and nip
up the lock nut. Without the aid of the special tool, the
adjustment is roughly correct when you can twist the belt at
its longest point between thumb and finger through a quarter
turn (90 degrees).
• Step 25: Turn the engine two full revolutions, re-check
the timing and belt tension. Adjust if necessary and tighten
the adjusting pulley lock nut.
B INSIDE INFORMATION! CHECKING INJECTION
ADVANCE. This cannot be done without the use of a dial
gauge and special adapter to fit on the rear of the
pump. We strongly recommend that although your
engine may seem to be running well, you get it checked
by your FIAT dealer. B
Job 17. Diesel injectors -
remove and refit.
Q Step 1: Clean thoroughly around each injector to prevent
dirt from entering the cylinders when removing the injectors.
Q Step 2: Unscrew the fuel pipe union at the injector, using
a flare nut wrench (split ring spanner).
• Step 3: Loosen the union at the injection-pump-end of
each injector pipe. Disconnect the fuel-return unions at the
injector and move the return pipes away.
• Step 4:
Unscrew the
injector using a
deep 27 mm A/F
socket, or,
preferably, a
proper injector
socket
(arrowed).
Collect the
injector and its
base washer. All seals should be renewed every time the
injector is removed.
• Step 5:
Thoroughly clean
the injector
before refitting,
as dirt here can
cause cylinder
leakage, as can
the re-use of a
sealing washer,
so always renew
them.
• Step 6:
Injector efficiency
and spray pattern
can only be
checked by your
FIAT dealer, or a
Diesel or injection
specialist with test
equipment. This is
an inexpensive
check to have
carried out, while
the injectors are out.
• Step 7: Refit the injector, tightening it to the specified
tightening torque. See Chapter 3, Facts and Figures.
• Step 8: Reconnect all parts in the reverse order. Run the
engine at a fast idle initially to clear air from the high pressure
side of the fuel system.
Job 18. Bleeding Diesel fuel
system.
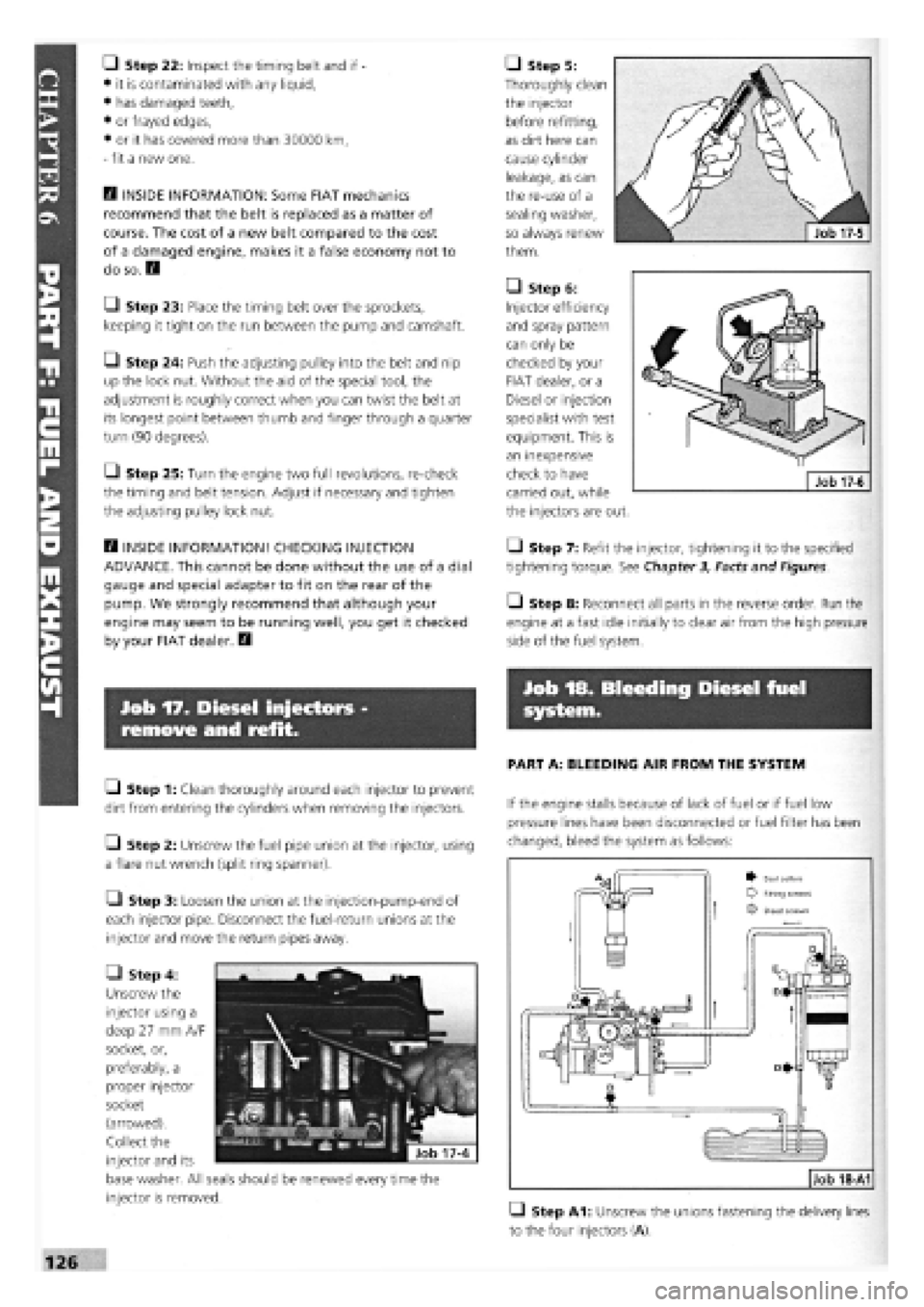
PART A: BLEEDING AIR FROM THE SYSTEM
If the engine stalls because of lack of fuel or if fuel low
pressure lines have been disconnected or fuel filter has been
changed, bleed the system as follows:
• Step A1: Unscrew the unions fastening the delivery lines
to the four injectors (A).
Job 18-A1
^ Seal collars Fifing screws
O Bleed screws
Page 123 of 171
• Step A2: Start the engine and run until fluid emerges
from the loose injector fitting.
G Step A3: Keep the engine running and tighten the four
injector fittings.
B INSIDE INFORMATION: If the engine will not start,
check all fuel inlet pipe union points (see illustration Job
18-A1,
part D) and also the pipe fittings (Job 18-A1,
part E). Replace seal washers to eliminate the possibility
of air leaks. H
PART B: BLEEDING WATER FROM DIESEL
Bleed off water from the fuel filter as follows:
• Step B1: Unscrew the water bleed screw (Job 18-A1,
part B) under the filter.
• Step B2: Unscrew air bleed screw (Job 18-A1, part Q
above the filter.
• Step B3: Let water and fuel emerge until no more water
is present, then tighten, firstly the water bleed screw (B) under
filter, and then the air bleed screw (C) above the filter.
PART G: STEERING AND SUSPENSION
PART G: Contents
Job
1.
The systems explained.
Job
2.
Steering wheel
-
removal and refitting
Job 3. Track rod end balijoint
-
replacement.
Job
4.
Steering rack gaiter
-
replacement.
Job 5. Steering rack
-
replacement.
Job
6.
Power steering pump
-
removal and refitting
Job
7.
Lower wishbone
-
replacement.
Job 8. Bleeding the power steering.
Job 9. Front anti-roll bar
-
removal and refitting.
Job 10. Rear anti-roll bar (when fitted).
Job 11. Front shock absorber
-
replacement.
Job 12. Front wheel bearing
-
replacement.
Job 13. Rear shock absorbers and coil springs
-
replacement.
Job 14. Rear suspension and wheel bearings
-
replacement.
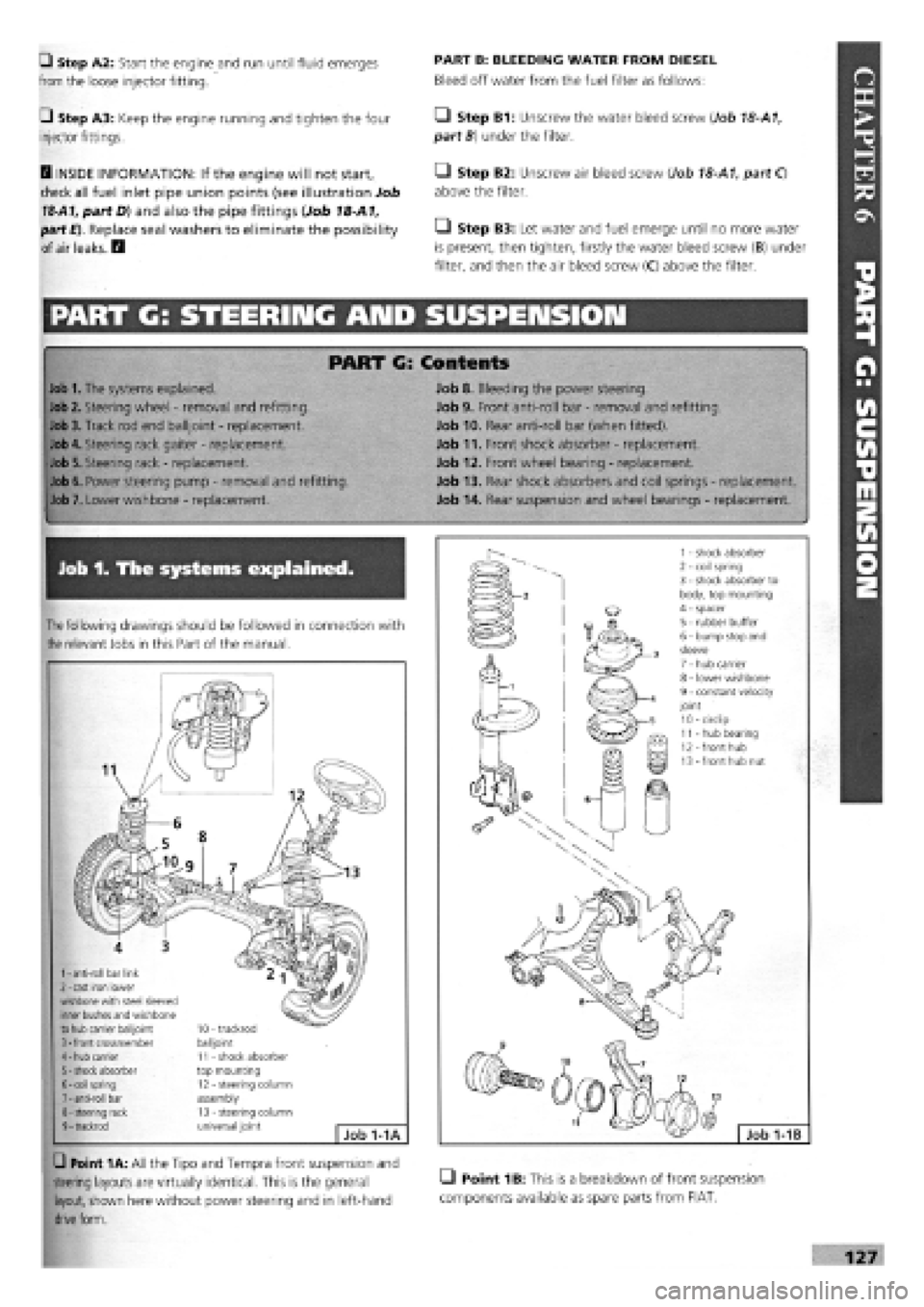
Job 1. The systems explained.
The
following drawings should be followed in connection with
the
relevant Jobs in this Part of the manual.
1
-
anti-roll bar link 2
-
cast iron lower wishbone with steel sleeved inner bushes and wishbone to hub carrier balijoint 3
-
front crossmember 4
-
hub carrier 5
-
shock absorber 6
-
coil spring 7
-
anti-roll bar 8
-
steering rack 9
-
trackrod
10 - trackrod balijoint 11 - shock absorber top mounting 12 - steering column assembly 13 - steering column universal joint Job 1-1A
G Point 1A: All the Tipo and Tempra front suspension and
steering layouts are virtually identical. This is the general LI Point 1B: This is a breakdown of front suspension
layout, shown here without power steering and in left-hand components available as spare parts from FIAT,
drive
form.
Page 134 of 171

• Step 3: ...and
remove the caliper
support bracket.
Ll Step 4: Unscrew
the disc fixing bolts and
withdraw the disc.
clean and undamaged.
• Before refitting the disc,
ensure that the mating
surfaces
-
hub to disc, are
Job 10. Master cylinder
replacement.
H INSIDE INFORMATION: • On right-hand drive cars, the
master cylinder is on the driver's side and is VERY
different to get at, behind the engine.
• To remove the master cylinder on these cars you may
need to remove the complete assembly
-
master cylinder,
servo and pedal assembly
-
from inside the car. Q
• Step 1: IMPORTANT NOTE: Protect all paint surfaces
from possible brake fluid spillage before starting work.
You know what a good paint stripper it is!
• Step 2: Syphon off as much brake fluid as possible or
bleed it out
through one of the
front brakes until
the master cylinder
makes 'sucking'
noises.
• Step 3:
Remove the
reservoir from the
master cylinder.
138
• Step 4: Use a spanner
-
preferably a purpose-made split
ring spanner
-
to undo all the pipe unions from the master
cylinder.
• Step 5:
Undo the nuts
securing the
master cylinder
to the servo and
remove it.
• Step 6: Refit
in the reverse
order and refer
to Job
77
for
bleeding the
brakes.
Job 11. Servo check
and refit.
remove
Q INSIDE INFORMATION: • Before condemning the
servo for lack of efficiency, check the condition of the
one-way valve and vacuum pipe connecting it to the
inlet manifold.
• Ease the valve out of the front of the servo and
disconnect the pipe from the inlet manifold.
• Check that you can only blow one way through the
valve
-
from the servo end towards the inlet manifold (or
the brake vacuum pump
-
Diesel models).
• The vacuum pipe can suffer failure in many ways. Age
can harden it until it cracks, causing an air leak which
sometimes results in a whistling noise and rough slow-
running.
• Loose connections could also produce the same result.
• The other type of vacuum hose failure is an implosion
(where the hose is sucked flat by the vacuum) often
because oil has softened the hose.
• This is not so easily detected, as it rarely upsets the
engine performance and resumes its normal shape
shortly after the engine is stopped.
• The inner lining can also deteriorate, causing a
blockage. Q
• Step 1: Follow Job
10
to remove the master cylinder.
• Step 2: From inside the car, unhook the accelerator cable
from the pedal fork.
• Step 3:
Undo the
fixing nuts,
remove the
retaining
plate and
pedal
assembly.
•
eP^BH
1
| Mitx
IfP^K p{B||n (Or Hot
I
a^®. i kS^^^Ap
i
/is ^8*5211^3
in A
Mil
11 SaBPffe
l|i§
# J
Job 11-3
Page 138 of 171

• Step 1:
Push a tight
fitting length
of plastic or
rubber tubing
(a) onto the
first bleed
screw (b) and
immerse the
other end in a
small quantity
of brake fluid
(c) contained in a glass jar in such a way that no air can
accidentally be pulled up the tube.
• Step 2: With a ring spanner (illustrations Job 17-1, part,
d), undo the brake bleed screw (at the drum brake backplate
or on the disc caliper body) by half a turn. Have your helper
push the brake pedal to the floor and hold it there while you
lock up the bleed valve. Then release the pedal slowly. Repeat
several times, with the following suggested dialogue:
YOU. (Open bleed screw) "Open!"
(called
out
loud)
HELPER.
(Pushes
pedal down) "Down!"
YOU.
(Close
bleed screw) "Closed!"
HELPER. (Letspedal up) "Up!"
-
repeated, as necessary.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Take great care not to let the master
cylinder run out of brake fluid. Otherwise you will
introduce fresh air into the system and have to start
again. Use ONLY fresh brake fluid from a previously
unopened container.
• Step 3: Top up the fluid reservoir frequently while
repeating the bleeding operation until all air is expelled from
the brake line (no bubbles appear in the tube or jar).
LI Step 4: Bleed each remaining brake in the same way,
going to the right-hand front next, followed by the right-hand
rear, and finishing with the left-hand front brake. Top up fluid
and check all connections for leaks.
Job 18. Handbrake cables -
replacement.
• Step 1: Familiarise yourself with the handbrake cable
layout. The following instructions refer to this drawing.
FRONT CABLE
Q Step 2: Jack up and support the rear of the car on axle
stands.
LI Step 3: From inside the car, remove the handbrake lever
cover by undoing the single fixing screw and fully release the
handbrake.
D Step 4: Unscrew the adjusting nut from the end of the
cable. You will find it underneath the base of the handbrake
lever.
• Step 5: From under the car, release the front ends of the
rear cables from the equaliser, then pull the front cable
through the floor aperture.
LI Step 6: Refit in the reverse order and adjust the cable nut
until the lever travels no more than three notches on the
ratchet when you pull the brake on, and when released, the
wheels still revolve freely.
REAR CABLES
• Step 7: Carry out Steps 1 to 3.
• Step 8: Unscrew the adjusting nut to the end of its
thread.
• Step 9: Unhook the front of the rear cables from the
equaliser. See Step 5
• Step 10: In the case of rear drum brakes, detach the
cables from the brakes as described in Job 5, Steps 3 and
4.
LI Step 11: In the case of disc rear brakes, see Job 8, Step
1.
• Step 12: Re-assemble in reverse order.
1 - handbrake lever and toothed sector 2 - front cable and anchorage 3 - rear cables 4 - support plate
5 - equaliser 6 - adjusting nut 7 - cable mounting bracket 8 - handbrake lever cover
Job 18-1
• Step 13: Adjust the handbrake
cable until the lever comes up no more
than three notches and when released,
allows both of the rear wheels to revolve
freely. Try spinning them by hand with
rear of the car raised off the ground.