1988 FIAT TEMPRA water pump
[x] Cancel search: water pumpPage 2 of 171

Running The Vehicle
NEVER start the engine unless the gearbox is in neutral (or
'Park' in the case of automatic transmission) and the hand
brake is fully applied.
NEVER run catalytic converter equipped vehicles without the
exhaust system heat shields in place.
TAKE CARE when parking vehicles fitted with catalytic
converters. The 'cat' reaches extremely high temperatures and
any combustible materials under the car, such as long dry
grass, could be ignited.
Personal Safety
NEVER siphon fuel, antifreeze, brake fluid or other such toxic
liquids by mouth, or allow contact with your skin. Use a
suitable hand pump and wear gloves.
BEFORE undertaking dirty jobs, use a barrier cream on your
hands as a protection against infection. Preferably, wear
suitable gloves, available from DIY outlets.
WEAR IMPERVIOUS GLOVES for sure when there is a risk of
used engine oil coming into contact with your skin. It can
cause cancer.
WIPE UP any spilt oil, grease or water off the floor
immediately.
MAKE SURE that spanners and all other tools are the right size
for the job and are not likely to slip. Never try to 'double-up'
spanners to gain more leverage.
SEEK HELP if you need to lift something heavy which may be
beyond your capability. Don't forget that when lifting a heavy
weight, you should keep your back straight and bend your
knees to avoid injuring your back.
NEVER take risky short-cuts or rush to finish a job. Plan ahead
and allow plenty of time.
BE METICULOUS and keep the work area tidy
-
you'll avoid
frustration, work better and lose less.
KEEP children and animals right-away from the work area and
from unattended vehicles.
ALWAYS tell someone what you're doing and have them
regularly check that all is well, especially when working alone
on, or under, the vehicle.
Fire!
Petrol (gasoline) is a dangerous and highly flammable liquid
requiring special precautions. When working on the fuel
system, disconnect the vehicle battery earth (ground) terminal
whenever possible and always work outside, or in a very well
ventilated area. Any form of spark, such as that caused by an
electrical fault, by two metal surfaces striking against each
other, by a central heating boiler in the garage 'firing up', or
even by static electricity built up in your clothing can, in a
confined space, ignite petrol vapour causing an explosion.
Take great care not to spill petrol on to the engine or exhaust
system, never allow any naked flame anywhere near the work
area and, above all, don't smoke.
Invest in a workshop-sized fire extinguisher. Choose the
carbon dioxide type or preferably, dry powder but NEVER a
water type extinguisher for workshop use.
DON'T disconnect any fuel pipes on a fuel injected engine
without following the advice in this manual. The fuel in the
line is under very high pressure
-
sufficient to cause serious
injury. Remember that many injection systems have residual
pressure in the pipes for days after switching off. If necessary
seek specialist advice.
Fumes
Petrol (gasoline) vapour and that given off by many solvents,
thinners, and adhesives are highly toxic and under certain
conditions can lead to unconsciousness or even death, if
inhaled. The risks are increased if such fluids are used in a
confined space so always ensure adequate ventilation. Always
read the maker's instructions and follow them with care.
Never drain petrol (gasoline) or use solvents, thinners
adhesives or other toxic substances in an inspection pit. It is
also dangerous to park a vehicle for any length of time over
an inspection pit. The fumes from even a slight fuel leak can
cause an explosion when the engine is started.
v ,,, Oil;::;s
Page 23 of 171

Screw with broad flange retaining rear flexible block to body (M12 x 1.25)..
Nut for stud retaining rear swinging arm to subframe (M16 x 1.5)
Nut for screw retaining lower damper to suspension (M12 x 1.25)
Screw retaining top of damper to mount (M10 x 1.25)
Nut for pivot pin retaining rear hub (M22 x 1.5)
Bolt retaining stabilizer bar to rear suspension arm (M10 x 1.25)
Bolt retaining stabilizer bar support plate to rear suspension arm (M8)
Wheel stud (M12 x 1.25)
Nut with self-locking flange retaining headlight alignment corrector
receiver to rear suspension (M8)
Nut with self-locking flange retaining lower receiver rod pin (M6)
Bolt with normal notched flange retaining automatic headlight
alignment device mount (M8)
Bolt with normal notched flange retaining receiver connection bracket with
rear suspension wishbone (M6)
Nut for bolt retaining square lever to wishbone (M8)
A B c D E Torque (Nm)
• • • • • 108
• • • • • 150
• • • • • 88
• • • • • 60
• • • • • 280
• • • • • 56
• • • • • 28
• • • • • 86
• • • • • 6.4
• • • • • 3.9
• • • • • 12
• • • • • 3.9
• • • • • 15
PART G: IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS
Finding the Numbers
G1: There are four sets of identification numbers in all. First,
there is the Vehicle Identification (V.I.N.) Number, or chassis
number (a). Second, is the engine number. Position (b) is the
engine number position on all engines; the engine illustrated
is
the 1.4 and 1.6 petrol engine. Also, see G4 and G5.
Third, there is the Model and Data Plate (c). See G3.
G2: Fourth, you will
need the Paint
Identification Plate
if you need to buy
paint. You'll find it
on the inside of the
hatchback door.
The numbers
shown on the plate
give the following
information: 1 -
Paint manufacturer; 2
-
Colour name; 3
-
Colour code;
4
-
Respray and touch-up code.
Vehicle Identification Numbers
See illustration G1, part a. There are two groups of codes
which are unique to your car. You should never buy a car
without checking first that the V.I.N, shown on the car matches
that on the vehicle registration document. The vehicle code is
also shown at position c on the Model and Data Plate and the
chassis serial number is also shown at position a.
Model and Data Plate
G3: The numbers
stamped on the
plate stand for the
following:
A
-
Manufacturer;
B
-
Homologation
number; C
-
Vehicle
identity code;
D
-
Chassis serial
number;
E
-
Maximum
authorised weight of vehicle, fully laden; F
-
Maximum autho-
rised weight of vehicle, fully laden plus trailer; G
-
Maximum
authorised weight on front axle; H
-
Maximum authorised
weight on rear axle; I
-
Engine type; L
-
Body code (see below);
M - Number for buying spares; N
-
Smoke opacity index
(diesel engines only).
Engine
Numbers
G4: On all petrol engines,
the number is on the top
of the crankcase at the
gearbox end.
G5: On diesel engines, look
on the crankcase, above the
water pump housing.
1
2
3
4
G2
r
B
r
B I B I
r
B
C I D I
r
B
I E I Kn
o o I F I Kq o o 1- I <3 I Kq o o
2- | H I Kq
o
MOTORE ENGINE
I I
N VERSIONE-VERSION •f
PER RICAM8:
N*
FOR SPARED
L I
1 G3
Page 64 of 171

SAFETY FIRST! • Step 7:
Disconnect the
electrical leads from
the following: the
inlet manifold
• Step 2: Disconnect both battery leads, negative
terminal first.
Q Step 3: Drain the cooling system and depressurise the
fuel system, if yours is a fuel injection engine
-
see PART
F:
FUEL AND EXHAUST
• Step 6B:
INJECTION
ENGINES.
Disconnect the
engine end of the
accelerator cable (a),
the idle speed check
actuator (b) and the
injector supply (c).
• Step 8: Detach
the exhaust
downpipe from the
manifold.
• Step 9: Remove
the dipstick
(arrowed) and the
cylinder head
coolant temperature
sensor (arrowed).
• Step 10: Also remove all the HT leads (along with the
distributor cap). Place them to one side.
• Step 11: Undo the brake servo hose from the manifold.
Q Step 4: Remove the air cleaner by releasing the spring
clips (a) at the front of the unit and the screw on the top face
(b) and disconnect the hoses
recovery pipe clips from beneath the rear of the housing, once
it is free to lift up.
Q Step 5: Disconnect the crankcase vent hose from the
cylinder head and the inlet tract or the SPI injector unit, as
appropriate and blank off with a bolt of suitable size.
• Step 6A:
CARBURETTOR
ENGINES.
Disconnect the
engine end of the
accelerator cable
from its idler and
the choke cable
from its mounting.
Q Step 12: Remove the
water hoses connected to
the inlet manifold and
thermostat.
• Step 13 A:
CARBURETTOR
ENGINES. Disconnect the
fuel pipe from the carbu-
rettor and both pipes
from the fuel pump.
(Label both the pipes and
stubs so that they will be
reconnected the
right way round.)
• Step 13B:
INJECTION
ENGINES.
Disconnect the fuel
supply and return
hoses from the
injector unit housing
(a). Plug the ends.
• Step 14A: CARBURETTOR ENGINES. Disconnect the
distributor vacuum pipe and oil vapour pipes from the carbu-
rettor.
vacuum sensor
(arrowed), the
manifold coolant
temperature sensors
(arrowed) and the
throttle position
switch and any
other leads which your engine may have.
Page 69 of 171

G Step 17: Now repeat this operation on the remaining
valves.
G Step 18: Wash the whole cylinder head again using
paraffin and an old brush, making sure that all traces of
grinding paste are removed, then dry off. Use compressed air
if
available.
SAFETY FIRST!
•
Treat
compressed air with respect. Always wear
goggles
to protect your eyes.
•
Never
allow the airline nozzle near any of the body Sep apertures.
H INSIDE INFORMATION! Check the height of the valve
springs against new ones if possible, but if not, compare
them with each other. If any are shorter than the others,
play safe and replace the complete set. They are bound
to have suffered fatigue which could cause premature
valve failure. H
G Step 19: To install the valves, start from one end.
Lubricate a valve stem with fresh engine oil and slide it in to its
guide.
G Step 20: Locate a new valve stem seal over the stem of
the valve
(if applicable) and push down into contact with the
guide. Position the seal on its seat using a suitable metal tube.
G Step 21: Refit the flat washer and spring seat.
G Step 22: Position the inner and outer springs and the
spring
cap.
G Step 23: Re-apply the valve spring compressor and
compress
the springs enough to allow you to engage the split
collets
in
the stem grooves.
D INSIDE INFORMATION! Grease the grooves so that the
collets will 'stick' in place. The collets are easily fitted by
'sticking' the backs of them onto the end of a screw-
driver with some grease and feeding them into
position. B
G Step 24: Carefully release the spring compressor and
check
that the collets are correctly located. Tap the end of the
stem with
a hammer, to bed them in.
G Step 25: Fit the remaining valves.
Job 5. Petrol engine -
dismantling.
G Step 1: Familiarise yourself with the layout of the engine.
Refer to
illustration Job
2-1
for an exploded view of the
engine
components.
G Step 2: Drain the engine oil. Remove the cylinder head.
See
Job 2.
G Step 3: Remove the distributor. See PART D: IGNITION
• Step 4:
Remove the petrol
pump and spacer
block, if the
mechanical type
(a). (Electric fuel
pumps are in the
fuel tank.)
• Step 5:
Remove and
discard the oil filter
illustration Job
5-4,
• Step 6: Remove the water pump complete with its distri-
bution pipe, and the power steering pump (if fitted).
Q Step 7: Remove the alternator, the crankshaft pulley, the
crankshaft and camshaft sprockets, the cam belt tensioner
and the cam belt cover backplate.
• Step 8:
Remove the
auxiliary shaft
sprocket...
• Step 9: ...the
end plate and
seal, and remove
the auxiliary shaft.
• Step 10:
Undo and remove
the clutch, and
then the flywheel.
• Step 11: Turr
engine assembly c
remove the sump
and remove the crankcase breather (see
part b) with its pipe.
Page 74 of 171

• Step 30: Fit
the crankshaft
pulley and
tighten. See
Chapter 3,
Facts and
Figures.
• Step 31: Fit the
water pump and
distribution pipe.
• Step 32A: Refit the
flywheel. Do not unbolt the
TDC sensor (1) from the oil seal
housing at its mounting plate
bolts
(2)
unless it is essential to
do so.
• Step 32B: If
the sensor
mounting plate has
to be disturbed, you
will need the FIAT
special tool illus-
trated here (inset) in
order to reposition it
correctly. Position
the timing mark on
the crankshaft
pulley with the zero
degrees mark on the outer timing belt cover (and double
check that the timing mark on the flywheel
-
rubber bung
removed
-
is aligned at zero degrees).
With the bracket fitted to the oil seal housing, fit the FIAT
special tool onto the bracket in place of the sensor with a slot
in the tool fitting exactly over the TDC pin on the flywheel.
When everything is lined up, position the bracket accurately
and tighten the bolts. Remove the tool and refit the sensor.
IMPORTANT NOTE: During assembly, a shear-bolt will
have been fitted to prevent accidental movement of the
bracket. If you need to undo it, you will need to drill it
out and you should replace it with a new one obtained
from your FIAT dealership.
• Step 33: Refit the clutch. See PARTB: TRANSMISSION,
Job 4.
Q Step 34: Refit the fuel pump and pushrod using new
gaskets on both sides of the spacer block, 0.3 mm thick
between the spacer and the engine and 0.7 mm between the
spacer and the pump. See PART F: FUEL AND EXHAUST for
information on setting the pump position.
• Step 35:
Lubricate the sealing
ring and screw on a
new oil filter.
• Step 36:
Before refitting the
distributor, (see
PART D: IGNITION)
refit, if necessary,
the oil pump drive
gear.
• Step 37: Refit
all remaining
auxiliary compo-
nents (including the
oil vapour recovery
device, shown here),
using new gaskets
as necessary and
referring to
Chapter
3,
Facts
and Figures for the
torque settings.
Q Step 38: Reconnect the engine to the transmission. See
Job 11.
Q Step 39: Refit the complete unit to the car. See Job
9.
• Step 40: fl INSIDE INFORMATION! Before fitting the
spark plugs and with a fully charged battery, turn the
engine on the starter until the oil warning light goes
out. This primes the lubrication system and gives more
immediate oil pressure on initial start up after overhaul-
a critical time in the life of an engine. B
• Step 41: Fit the spark plugs and start the engine
-
this
might take a few seconds more than normal on the initial start
up.
• Step 42: Allow the engine to warm up on fast idle
until
it
reaches working temperature and then slow it down to its
normal speed (if adjustable
-
see PART F: FUEL AND
EXHAUST)
Page 80 of 171

FACT FILE: DIESEL ENGINES AND SPECIAL TOOLS
• As the
construction and
assembly of the
diesel engine is,
for the best part,
the same as the
petrol engines,
this section details
only those proce-
dures which are
specific to the
diesel.
• Major differ-
ences lie in the
areas of the
cylinder head and
camshaft drive
belt.
• Where
inspection of
components such
as crankshaft,
camshaft, pistons,
conrods, cylinder
head face, flywheel
etc. is not detailed
within this
section, refer to
the relevant infor-
mation in the
Petrol Engine
section, Job 6,
under Checking
for wear -
information which is common to all engine types.
• In view of the complexity of the diesel engine's camshaft drive arrangement, the need for special tooling and the
accuracy required in adjusting camshaft
timing and injection pump timing, we
strongly recommend that any work involving
disturbance of the timing belt or injection
pump is entrusted to a FIAT dealer.
• The following information is provided only
for those who have technical experience of
diesel engines, along with access to the
required tooling.
• Familiarise yourself with this drawing,
showing the cylinder head, block and other
major components referred to in the
following text.
1
-
cylinder block 2
-
sump 3
-
cylinder head 4
-
injection pump mounting 5
-
oil pick-up and pump 6
-
threaded bush 7
-
rear crank seal carrier 8
-
front cover/oil seal 9
-
plate
10
-
head gasket 11
-
camshaft rear bearing 12
-
camshaft front bearing 13
-
exhaust manifold 14
-
intake manifold 15
-
coolant pipe 16
-
water pump 17
-
cam cover 18
-
gasket
19-seal 20
-
valve 21
-
valve guide 22
-
spring seat 23
-
thermostat housing 24
-
oil filler cap 25
-
compression washer
1
-
strainer with gauze filter 2
-
geared oil pump 3
-
oil pressure relief valve 4
-
total capacity cartridge oil filter with safety valve to cut out filter element becomes blocked 5
-
main oil delivery pipe supplying various / components 6
-
oil delivery pipe to camshaft
IHSupply circuit I
I Return
circuit
a
-
camshaft b
-
vacuum pump c
-
bucket tappets d
-
valve guides e
-
valves f
-
piston g
-
gudgeon pin assemblie; h
-
conrod i
-
crankshaft j
-
crank journal k
-
flywheel
Page 84 of 171
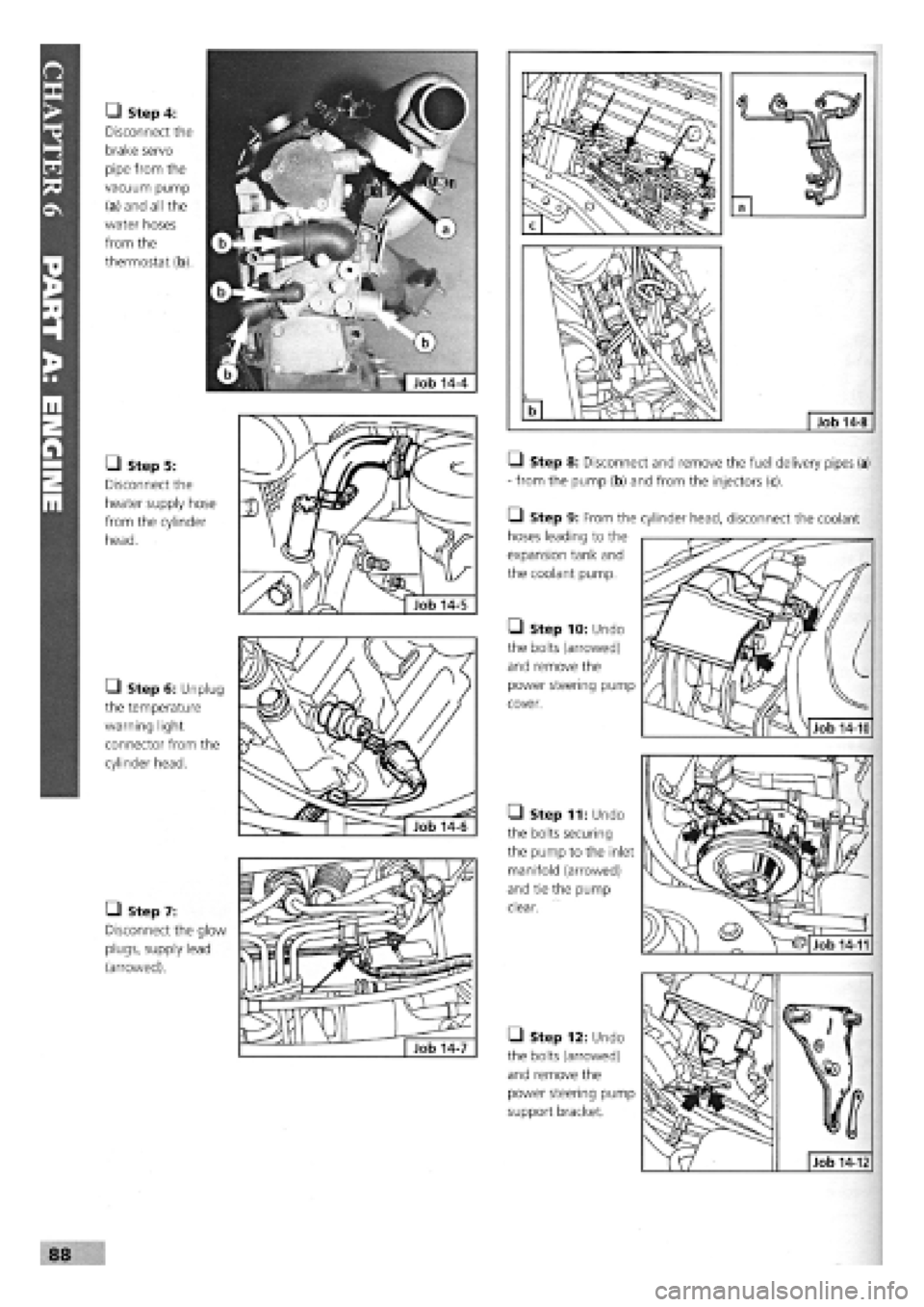
• Step 4:
Disconnect the
brake servo
pipe from the
vacuum pump
(a) and all the
water hoses
from the
thermostat (b).
• Step 5:
Disconnect the
heater supply hose
from the cylinder
head.
• Step 6: Unplug
the temperature
warning light
connector from the
cylinder head.
• Step 7:
Disconnect the glow
plugs, supply lead
(arrowed).
Q Step 8: Disconnect and remove the fuel delivery pipes (a)
- from the pump (b) and from the injectors (c).
• Step 9: From the
hoses leading to the
expansion tank and
the coolant pump.
• Step 10: Undo
the bolts (arrowed)
and remove the
power steering pump
cover.
• Step 11: Undo
the bolts securing
the pump to the inlet
manifold (arrowed)
and tie the pump
clear.
• Step 12: Undo
the bolts (arrowed)
and remove the
power steering pump
support bracket.
88
cylinder head, disconnect the coolant
Job 14-10
Job 14-12
Job 14-11
Page 91 of 171

Q Step 2: Before starting the engine, make sure all your
electrical connections are sound and your fuel, oil and coolant
connections are correct and secure.
Q Step 3: Run the engine to working temperature and then
allow to cool. Re-check all fluid levels.
Job 20. Diesel engine.
Mountings - replacement.
See
Job
12
and Job
18,
Step 20
Job 21. Diesel engine/
transmission (removed from car)
- separation.
Q Step 1: Remove the starter motor.
• Step 2: On the turbo version, undo the flange bolts see
Job
18,
Step 16A and withdraw the drive-shaft extension, if
still
fitted.
Q Step 3: Unbolt and remove the rear engine plate and the
gearbox, being careful to support the gearbox weight as it is
withdrawn.
Job 22. Diesel engine/
transmission (removed from car)
- reconnection.
Q Step 1: Before proceeding, check the condition of the
clutch and
its release mechanism. Make sure the driven plate
is
properly centred on the flywheel
-
see PART B: TRANS-
MISSION.
Q Step 2: Now reverse the order of separation, but be
careful when
engaging the gearbox input shaft with the
clutch
driven plate that you don't 'hang' its weight on the
splines.
Also,
see
Job 11.
Job 23. Diesel engine -
dismantling.
This Job should
be read in conjunction with Job 5 The
engines are
broadly similar although the information given in
this Job takes
priority for diesel engines. It is MOST
IMPORTANT that you read the FACT FILE on page 84.
SAFETY FIRST!
•
The inside
of diesel engines are particularly filthy
places!
•
Old diesel
oil
is
carcinogenic!
•
Wear suitable
impervious gloves!
I
• Step 1: Remove the timing belt and cylinder head. See
Jobs
13
and 14.
Q Step 2: Remove the alternator, water pump and
thermostat housing distribution pipe.
• Step 3: Remove the crankshaft timing belt sprocket.
Q INSIDE INFORMATION! Note that the bolt securing
the crankshaft sprocket has a left-hand thread and must
be undone clockwise. D
• Step 4: Unbolt the timing belt tensioner and idler pulleys.
• Step 5: Remove the injection pump sprocket.
Q INSIDE INFORMATION! You will need two FIAT tools
for this operation. One (No. 1860473000) is to prevent
the sprocket from turning when undoing the nut, and
the other (extractor No. 1842128000) to pull the sprocket
from the injection pump shaft. Alternatively it may be
possible to improvise a means of preventing sprocket
rotation, and a suitable three-leg puller may be carefully
used to withdraw the sprocket. Take care not to lose the
pump shaft Woodruff key. B
• Step 6:
Unbolt and
detach the
support bracket
(a) from the rear
of the injection
pump (b). Unbolt
the pump flange
and bracket
nuts, and
remove the
pump and its
front bracket (c).
• Step 7: Remove and discard the old oil filter.
Step 8: Remove the crankcase breather, the low-oil-
pressure switch and the oil pressure gauge sensor from the
front face of the engine.
• Step 9: Turn the engine upside down and remove the
flywheel and the sump.