1986 TOYOTA CAMRY V20 radiator cap
[x] Cancel search: radiator capPage 228 of 2389

1. RUN± ENGINE AT IDLE SPEED WITH AIR
CONDITIONING ON FOR 10 MINUTES
2. STOP ENGINE
3. DISCONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE FROM BATTERY
4. REMOVE BATTERY
5. (2VZ±FE ENGINE)
REMOVE IGNITOR BRACKET, RADIATOR FAN AND
CONDENSER FAN
6. DISCONNECT CONNECTOR FOR MAGNETIC
CLUTCH, TEMPERATURE SWITCH AND REVOLU-
TION DETECTING SENSOR
7. DISCHARGE REFRIGERANT FROM REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM
8. DISCONNECT TWO HOSES FROM COMPRESSOR
SERVICE VALVES
Cap the open fitting immediately to keep moisture out of
the system.
9. REMOVE COMPRESSOR
(a) Loosen the drive belt.
(b) Remove the compressor mounting bolts and the
compressor.
± AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMCompressorAC±26
Page 235 of 2389

CONDENSER
(See page AC±12)
ON±VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. CHECK CONDENSER FINES FOR BLOCKAGE OR
DAMAGE
If the fins are clogged, wash them with water and dry with
compressed air.
NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the fins.
If the fins are bent, straighten them with a screwdriver or pliers.
2. CHECK CONDENSER FITTINGS FOR LEAKAGE
Repair as necessary.
REMOVAL OF CONDENSER
1. DISCHARGE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
2. REMOVE BATTERY, IGNITOR BRACKET RADIATOR
FAN, CONDENSER FAN
3. DISCONNECT LIQUID TUBE AND DISCHARGE HOSE
FROM CONDENSER FITTINGS
HINT: Cap the open fittings immediately to keep moisture
out of the system.
4. REMOVE CONDENSER
Remove four brackets and four bolts.
INSTALLATION OF CONDENSER
(See page AC±12)
1. INSTALL CONDENSER
Install the brackets and bolts, making sure the rubber cush-
ions fit on the mounting flanges correctly.
2. CONNECT LIQUID TUBE, DISCHARGE HOSE TO
CONDENSER
Torque:
Liquid tube 130 kg±cm (9 ft±Ib, 13 N±m)
Discharge hose 130 kg±cm (9 ft±Ib, 13 N±m)
3. REINSTALL CONDENSER FAN, RADIATOR FAN
IGNITOR BRACKET AND BA¿¿ERY
4. IF CONDENSER WAS REPLACED, ADD
COMPRESSOR OIL TO COMPRESSOR
Add 40 ± 50 cc (1.4 ± 1.7 fl.oz.)
Compressor oil: DENSOOIL 6,
SUNISO NO. 5GS or equivalent
5. EVACUATE AIR FROM AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
6. CHARGE AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM WITH
REFRIGERANT AND CHECK FOR GAS LEAKAGE
Specified amount: 600 ± 750 g (1.3 ± 1.7 Ib)
± AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMCondenserAC±33
Page 989 of 2389

The cooling system is composed of the water jacket (inside the cylinder block and cylinder head), radiator,
water pump, thermostat, electric fan, hoses and other components.
Coolant which is heated in the water jacket is pumped to the radiator, through which an electric fan blows air
to cool the coolant as it passes through. Coolant which has been cooled is then sent back to the engine by
the water pump, where it cools the engine.
The water jacket is a network of channels in the shell of the cylinder block and cylinder head through which
coolant passes. It is designed to provide adequate cooling of the cylinders and combustion chambers which
become heated during engine operation.
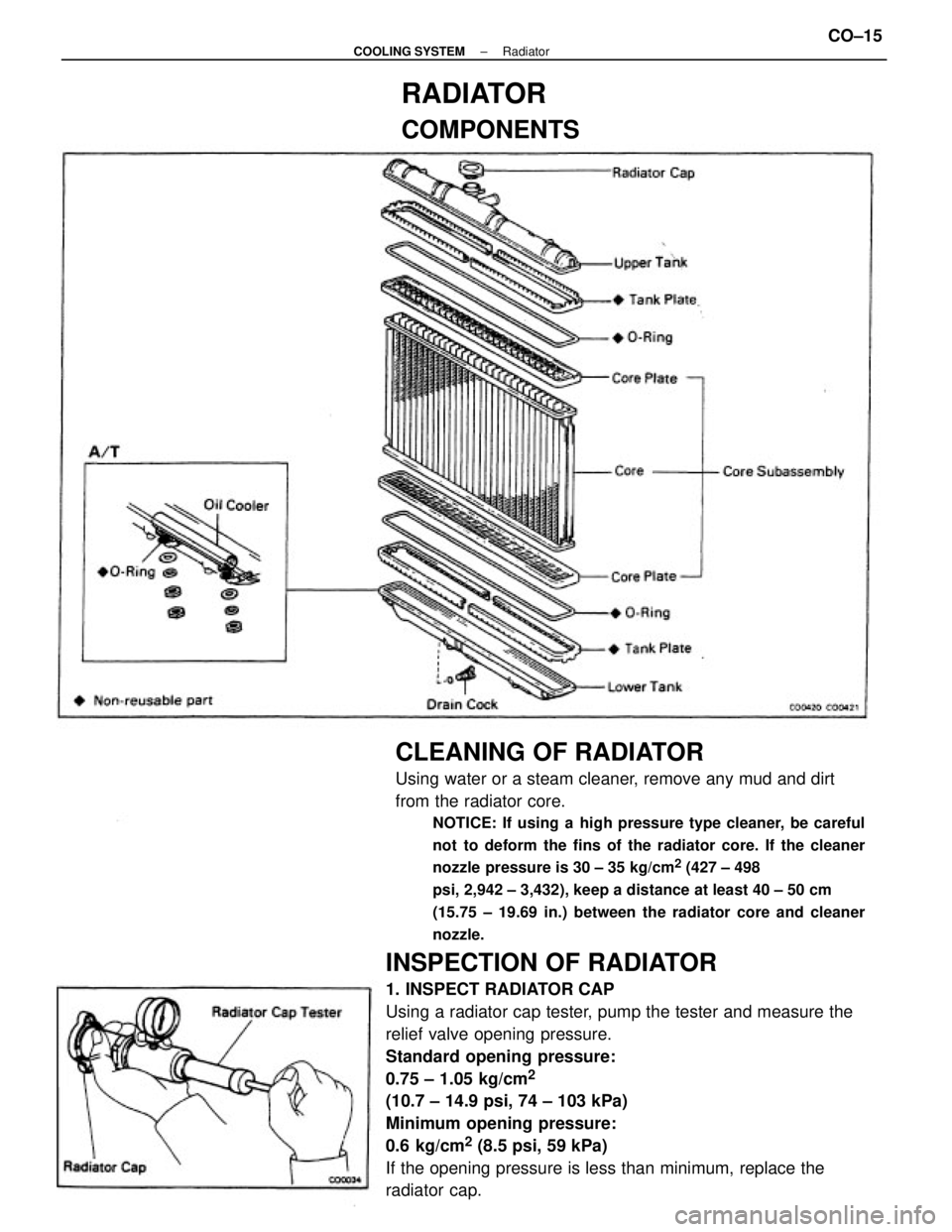
RADIATOR
The radiator performs the function of cooling the coolant which has passed through the water jacket and be-
come hot, and it is mounted in the front of the vehicle. The radiator consists of an upper tank and lower tank,
and a core which connects the two tanks. The upper tank contains the inlet for coolant from the water jacket
and the filler inlet. It also has a hose attached through which excess coolant or steam can flow. The lower
tank has an outlet and drain cock for the coolant. The core contains many tubes through which coolant flows
from the upper tank to the lower tank as well as cooling fins which radiate heat away from the coolant in the
tubes.
The air sucked through the radiator by the electric fan, as well as the wind generated by the vehicle's travel,
passes through the radiator, cooling the coolant. Models with automatic transmission include an automatic
transmission fluid cooler built into the lower tank of the radiator. A fan with an electric motor is mounted be-
hind the radiator to assist the flow of air through the radiator. The fan operates when the coolant tempera-
ture becomes high in order to prevent it from becoming too high.
RADIATOR CAP
The radiator cap is a pressure type cap which seals the radiator, resulting in pressurization of the radiator as
the coolant expands. The pressurization prevents the coolant from boiling even when the coolant tempera-
ture exceeds 100°C (212°F). A relief valve (pressurization valve) and a vacuum valve (negative pressure
valve) are built into the radiator cap. The relief valve opens and lets steam escape through the overflow pipe
when the pressure generated inside the cooling system exceeds the limit (coolant temperature: 110 ±
120°C, 230 ± 248°F, pressure; 0.3 ±1.0 kg/cm
2, 4.3 ±14.2 psi, 29.4 ± 98.1 kPa). The vacuum valve opens to
alleviate the vacuum which develops in the coolant system after the engine is stopped and the coolant tem-
perature drops.
The valves's opening allows the coolant in the reservoir tank to return to the cooling system.
RESERVOIR TANK
The reservoir tank is used to catch coolant which overflows the cooling system as a result of volumetric ex-
pansion when the coolant is heated. The coolant in the reservoir rank returns to the radiator when the cool-
ant temperature drops, thus keeping the radiator full at all times and avoiding needless coolant loss. Check
the reservoir tank level to find out if the coolant needs to be replenished.
WATER PUMP
The water pump is used for forced circulation of coolant through the cooling system. It is mounted on the
front of the cylinder block and driven by a timing belt.
THERMOSTAT
The thermostat has a wax type by±pass valve and is mounted in the water inlet housing. The thermostat in-
cludes a type of automatic valve operated by fluctuations in the coolant temperature. This valve closes when
the coolant temperature drops, preventing the circulation of coolant through the engine and thus permitting
the engine to warm up rapidly. The valve opens when the coolant temperature has risen, allowing the cir-
culation of coolant. Wax inside the thermostat expands when heated and contracts when cooled. Heating
the wax thus generates pressure which overpowers the force of the spring which keeps±the valve closed,
thus opening the valve. When the wax cools, its contraction causes the force of the spring to take effect
once more, closing the valve. The thermostat in this engine operates at a temperature of 82°C (180°F).
± COOLING SYSTEMDescriptionCO±3
Page 990 of 2389

3. (3S±FE)
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
CAUTION: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not re-
move it while the engine and radiator are still hot
as fluid and steam can be blown out under pressure.
(b) Drain the coolant from the .radiator and engine drain cocks.
(Engine drain cock at the right rear of engine block.)
(c) Close the drain cocks.
Torque (Engine drain cock):
130 kg±cm (9 ft±Ib, 13 N±m) HINT: If the engine tends to overheat, removal of the
thermostat will adversely effect cooling efficiency.
CHECK AND REPLACEMENT OF
ENGINE COOLANT
1. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL AT RESERVE TANK
The coolant level should be between the ºLOWº and
ºFULLº lines.
If low, check for leaks and add coolant up to the ºFULLº
line.
Dirt, leaves or insects on radiator or condenser
Hoses, Water pump, thermostat housing, radiator,
heater, core, plugs or head gasket leakage
Thermostat faulty
Incorrect ignition timing
Electric cooling system faulty
Radiator hose plugged or rotted
Water pump faulty
Radiator plugged or cap faulty
Cylinder head or block cracked or water passage
clogged
2. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT QUALITY
There should not be any excessive deposits of rust or scales
around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and the cool-
ant should be free from oil.
If excessively dirty, replace the coolant.
Check thermostat
Reset tinning
Inspect electric cooling system
Replace hose
Replace water pump
Check radiator and cap
Repair as necessary
TROUBLESHOOTING
CO±12, 13
IG±17, 20
CO±20, 22 Clean radiator or condenser
Repair as necessary Engine overheats
Possible causeRemedy Problem
CO±6, 9 Page
± COOLING SYSTEM
TroubleshootingCO±4
Page 991 of 2389

3. (3S±FE)
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
CAUTION: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not re-
move it while the engine and radiator are still hot
as fluid and steam can be blown out under pressure.
(b) Drain the coolant from the .radiator and engine drain cocks.
(Engine drain cock at the right rear of engine block.)
(c) Close the drain cocks.
Torque (Engine drain cock):
130 kg±cm (9 ft±Ib, 13 N±m) HINT: If the engine tends to overheat, removal of the
thermostat will adversely effect cooling efficiency.
CHECK AND REPLACEMENT OF
ENGINE COOLANT
1. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL AT RESERVE TANK
The coolant level should be between the ºLOWº and
ºFULLº lines.
If low, check for leaks and add coolant up to the ºFULLº
line.
Dirt, leaves or insects on radiator or condenser
Hoses, Water pump, thermostat housing, radiator,
heater, core, plugs or head gasket leakage
Thermostat faulty
Incorrect ignition timing
Electric cooling system faulty
Radiator hose plugged or rotted
Water pump faulty
Radiator plugged or cap faulty
Cylinder head or block cracked or water passage
clogged
2. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT QUALITY
There should not be any excessive deposits of rust or scales
around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and the cool-
ant should be free from oil.
If excessively dirty, replace the coolant.
Check thermostat
Reset tinning
Inspect electric cooling system
Replace hose
Replace water pump
Check radiator and cap
Repair as necessary
TROUBLESHOOTING
CO±12, 13
IG±17, 20
CO±20, 22 Clean radiator or condenser
Repair as necessary Engine overheats
Possible causeRemedy Problem
CO±6, 9 Page
± COOLING SYSTEMCheck and Replacement of Engine CoolantCO±4
Page 992 of 2389

(d) To release the air, loosen the union bolt of the water out-
let five revolutions.
(e) Slowly fill the system with coolant.
Use a good brand of ethylene±glycol base coolant,
mixed according to the manufacturer's directions.
Capacity (w/ Heater):
M/T 9.5 liters (10.0 US qts, 8.4 Imp. qts)
A/T 9.4 liters (9.9 US qts, 8.3 Imp. qts)
(f) Tighten the union bolt of the water outlet.
Torque: 180 kg±cm (13 ft±Ib, 18 N±m)
(g) Install the radiator cap.
(h) Start the engine and check for leaks.
(i) Recheck the coolant level and refill as necessary.
HINT: When the coolant has been depleted, refill with
coolant and repeat steps (d) to (i). 4. (2VZ±FE)
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
CAUTION: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not re-
move it while the engine and radiator are still hot as fluid
and steam can be blown out under pressure.
(b) Drain the coolant from the radiator and engine drain cocks.
(Engine drain cocks are at the front center and rear right
of the cylinder block.)
(c) Close the drain cocks.
Torque (Engine drain cock):
300 kg±cm (22 ft±Ib, 29 N±m)
NOTICE:
wDo not use alcohol type coolant.
wThe coolant should be mixed with demineralized
water or distilled water.
Capacity (w/ Heater).
M/T 6.4 liters (6.8 US qts, 5.6 Imp. qts)
A/T (2WD) 6.3 liters (6.7 US qts, 5.5 Imp. qts)
A/T (4WD) 6.8 liters (7.2 US qts, 6.0 Imp. qts)
(e) Install the radiator cap.
(f) Start the engine and check for leaks.
(g) Recheck the coolant level and refill as necessary. (d) Fill the system with coolant.
Use a good brand of ethylene±glycol base coolant, mixed
according to the manufacturer's directions.
Using coolant which includes more than 5O%
ethylene±glycol (but less than 70%) is recommended.
± COOLING SYSTEMCheck and Replacement of Engine CoolantCO±5
Page 1002 of 2389
INSPECTION OF RADIATOR
1. INSPECT RADIATOR CAP
Using a radiator cap tester, pump the tester and measure the
relief valve opening pressure.
Standard opening pressure:
0.75 ± 1.05 kg/cm
2
(10.7 ± 14.9 psi, 74 ± 103 kPa)
Minimum opening pressure:
0.6 kg/cm
2 (8.5 psi, 59 kPa)
If the opening pressure is less than minimum, replace the
radiator cap.
CLEANING OF RADIATOR
Using water or a steam cleaner, remove any mud and dirt
from the radiator core.
NOTICE: If using a high pressure type cleaner, be careful
not to deform the fins of the radiator core. If the cleaner
nozzle pressure is 30 ± 35 kg/cm
2 (427 ± 498
psi, 2,942 ± 3,432), keep a distance at least 40 ± 50 cm
(15.75 ± 19.69 in.) between the radiator core and cleaner
nozzle.
RADIATOR
COMPONENTS
± COOLING SYSTEMRadiatorCO±15
Page 1003 of 2389
REMOVAL OF RADIATO
1. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO±4 or 5)
2. REMOVE BATTERY
3. REMOVE IGNITION COIL (2VZ±FE), IGNITER AND
BRACKET ASSEMBLY
4. DISCONNECT COOLANT RESERVOIR HOSE
5. DISCONNECT RADIATOR NOSE
6. DISCONNECT COOLING FAN MOTOR
CONNECTOR(S)
7. (A/T)
DISCONNECT OIL COOLER HOSES
8. REMOVE RADIATOR AND ELECTRIC COOLING
FAN(S)
Remove the two bolts, supports and radiator.
9. REMOVE ELECTRIC COOLING FANS FROM RADIATOR
DISASSEMBLY OF RADIATOR
(See page CO±15)
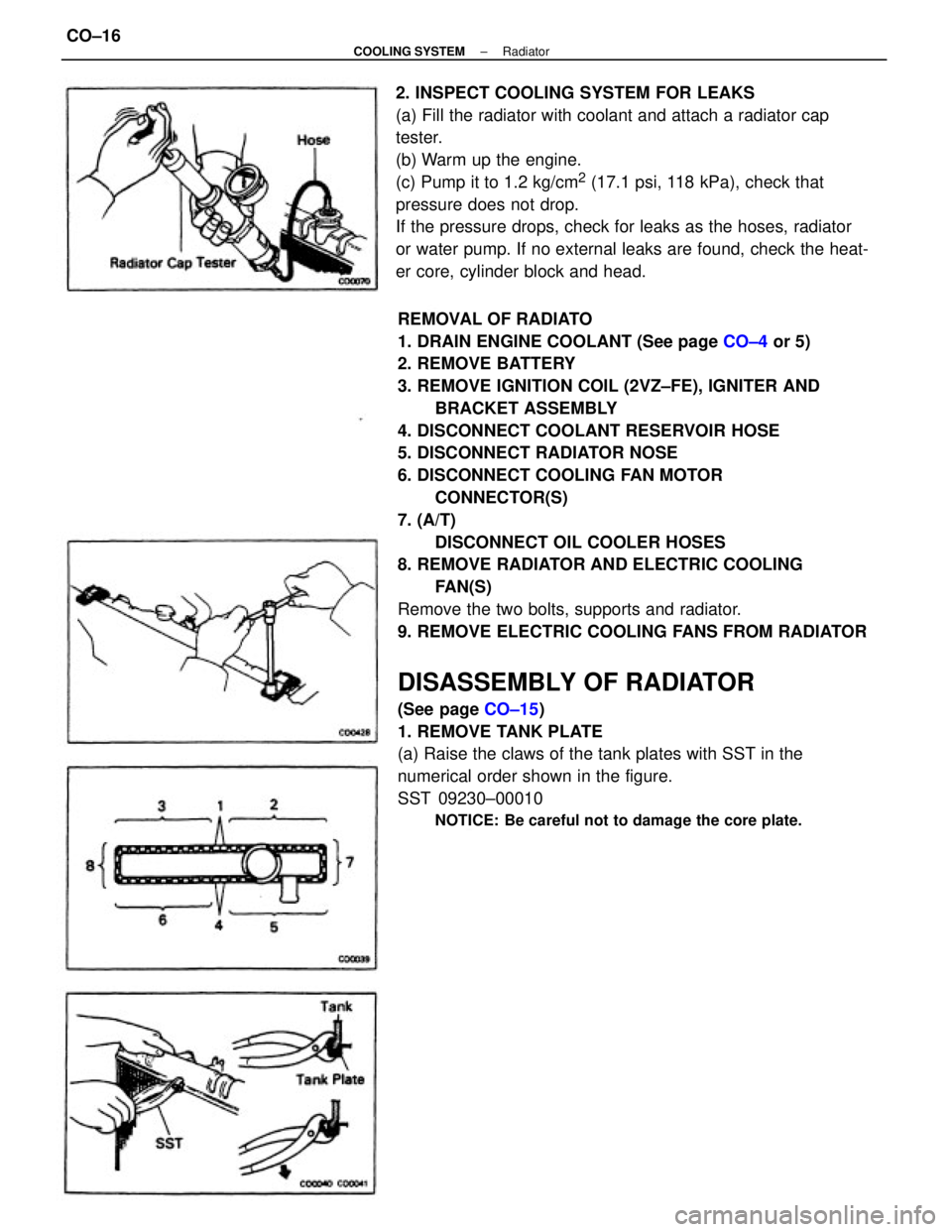
1. REMOVE TANK PLATE
(a) Raise the claws of the tank plates with SST in the
numerical order shown in the figure.
SST 09230±00010
NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the core plate.
2. INSPECT COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
(a) Fill the radiator with coolant and attach a radiator cap
tester.
(b) Warm up the engine.
(c) Pump it to 1.2 kg/cm
2 (17.1 psi, 118 kPa), check that
pressure does not drop.
If the pressure drops, check for leaks as the hoses, radiator
or water pump. If no external leaks are found, check the heat-
er core, cylinder block and head.
± COOLING SYSTEMRadiatorCO±16