1968 DATSUN 510 fuel type
[x] Cancel search: fuel typePage 9 of 252

4
CHAPTER
ONE
chassIs
number
Write
the
numbers
down
and
carry
them
ill
your
wallet
Service
Hints
Throughout
thIs
manual
keep
two
conven
bons
ill
mmd
Front
refers
to
the
front
of
the
vehicle
The
left
and
nght
sides
of
the
ve
hicle
refer
to
a
person
sittIng
ill
the
car
facing
forward
For
example
the
steenng
wheelIS
on
the
left
hand
Side
All
dimensIOns
and
capacities
are
expressed
ill
units
fanuhar
to
a
Umted
States
mechaniC
such
as
illches
and
pounds
Metric
measurements
are
also
given
Metnc
tools
are
reqUITed
to
work
on
the
Datsun
CD
DATSUN
IENGINE
CAPACITY
IMAX
HP
RPM
IWHEELBASE
IENGINE
NUMBER
FAR
NO
NlSSAN
MOTOR
co
LTD
YOKOHAMA
JAPAN
TYPEI
510
1595
cc
961P
6600
rpm
mm
L
1
00988
P61
l
O
1
l
M
Table
1
MAIN
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
DIMENSIONS
r
ITEM
Sedan
Wagon
Plm
up
EnglDe
Type
L16
L16
L16
Valve
Arrangement
Overhead
Cam
Overhead
Cam
Overhead
Cam
Bore
3
26n
ID
83mm
3
2677
ID
83mm
3
2677
ID
83mm
Stroke
2902
ID
73
7mm
2
902
ID
73
7mm
2
902
In
73
7mm
Displacement
97
3
cu
ID
l595cc
97
3
cu
In
l595cc
97
3
cu
ID
1595cc
CompressIOn
Ratio
851
851
851
MaXimum
SAE
Hompower
96
@
5
600
rpm
96
@
5
600
rpm
96
@
5
600
rpm
MaXimum
SAE
Torque
998ft
Ib
138
kg
m
998ft
Ib
138
kg
m
9911
ft
Ib
138
kg
m
Fuel
Octane
85
85
85
Lengtb
1622
ID
4
12Omm
163
2
ID
4
I45mm
168
9
ID
4
290mm
Width
61
4
ID
l
560mm
61
4
ID
1
560mm
62
8
In
Cl
595mm
Height
55
lID
1
400mm
565
ID
Cl
435mm
60
8
ID
Cl
545mm
Wheelbase
95
3
ID
2
42Omm
95
3
ID
2
420mm
99
6
In
2
530mm
Room
Space
Inner
Length
63
3
In
1
61Omm
673
ID
1
710mm
72
8
ID
1
850mm
Inner
Width
499
ID
1
27Omm
507
ID
1
29Omm
563
In
1
430mm
Inner
Height
44
4
In
1
130mm
44
61D
1
135mm
15
7
ID
399mm
Tread
Front
50
4
ID
28Omm
502
In
1
275mm
492
In
1
250mm
Rear
504
In
1
280mm
496
In
Cl
260mm
499
ID
1
267mm
Road
Clearance
741n
l88mm
64
ID
l63mm
787
ID
200mm
Weight
4
Speed
2
0611b
935
kg
2
138
Ib
970
kg
2
127
Ib
965
kg
Automatic
2
114Ib
959
kg
2
182
Ib
990
kg
Minimum
Turning
RadiUS
157ft
48m
157ft
48m
171
ft
52m
Seating
Capaaty
5
5
2
Battery
Volt
12
12
12
Capacity
400rSOAH
400r50AH
40
or
60
AH
Connection
Negative
ground
Negative
ground
Negative
ground
Fuel
Tank
Capaaty
11
9
gal
45
liter
11
9
gal
45
liter
108
gal
41J
r
011
Pan
Capacity
42
qts
40
liter
4
2
qb
40
liter
1
06
gal
40
Iller
011
Filter
Capaaty
74
ql
07
liter
74
ql
0
7
liter
1
48
Pint
0
7
liter
Transmission
Capaaty
1
8
ql
1
7
liter
18
ql
1
7
Iller
2
11
qt
20
Iller
Dlflerenbal
Capaaty
85
ql
80
liter
11
ql
1
0
liter
87
ql
0
83
lIter
Coolant
Capaaty
7
2
ql
6
8
liter
7
2
ql
6
8
lIter
7
2
qt
6
8
Iller
Clutch
Type
Dry
Single
diSC
Dry
slDgle
diSC
Dry
slDgle
diSC
Draphragm
spnng
Diaphragm
spnng
Diaphragm
spnng
l
Page 14 of 252

CHAPTER
THREE
TROUBLESHOOTING
TroubleshootIng
the
Datsun
can
be
relatlvely
simple
1f
done
lOgically
The
first
step
must
always
be
to
define
symptoms
as
closely
as
pos
Sible
Subsequent
steps
mvolve
testIng
and
an
alyzmg
areas
which
could
cause
the
symptoms
Procedures
m
thiS
chapter
analyze
typical
symp
toms
and
give
lOgical
methods
of
isolation
These
are
not
the
only
methods
There
may
be
several
approaches
to
solvmg
a
problem
but
all
must
have
one
thmg
m
common
a
lOgical
systematic
approach
TROUBLESHOOTING
EQUIPMENT
The
followmg
eqUipment
is
necessary
to
prop
erly
troubleshoot
an
engme
1
Voltmeter
Ammeter
and
Ohmmeter
2
Hydrometer
3
Compression
Tester
4
Vacuum
Gauge
5
Fuel
Pressure
Gauge
6
Dwell
Meter
7
Tachometer
8
StroboscopiC
Trming
Light
9
Exhaust
Gas
Analyzer
Items
1
through
8
are
essentlal
Item
9
is
necessary
for
exhaust
elDlSSion
control
comph
ance
The
followmg
is
a
bnef
description
of
the
functlon
of
each
mstrument
Voltmeter
Ammeter
and
Ohmmeter
For
testIng
the
ignitlon
and
electncal
systems
a
good
voltmeter
is
reqUIred
For
automotIve
use
an
mstrument
covenng
0
20
volts
is
salls
factory
It
should
have
an
accuracy
of
about
Ih
volt
which
excludes
the
common
auto
moUve
type
found
in
instrument
panels
An
ohmmeter
measures
electncal
reSiStance
and
is
reqUired
to
check
electncal
contInUity
open
and
short
circwts
and
for
testing
fuses
and
hghts
The
ammeter
measures
electncal
current
One
for
automotIve
use
should
cover
0
10
and
0
100
amperes
An
ammeter
is
useful
for
checkmg
bat
tery
chargmg
and
startIng
current
The
starter
and
generator
procedures
m
tlus
manual
use
an
ammeter
to
check
for
shorted
wmdmgs
Several
inexpensive
VOM
s
volt
ohmmeters
combme
all
mstruments
and
fit
easily
mto
any
tool
box
The
ammeter
ranges
are
often
too
small
for
auto
motIve
work
thougll
Hydrometer
A
hydrometer
is
necessary
to
check
battery
condition
and
charge
It
measures
specific
grav
ity
of
the
electrolyte
in
each
cell
Compression
Tester
The
compressiOn
tester
measures
compression
Page 15 of 252

10
CHAPTER
THREE
pressure
bUllt
up
In
each
cylInder
The
readIngs
when
properly
Interpreted
IndIcate
general
cyl
Inder
and
valve
condltlOn
Vacuum
Gauge
The
vacuum
gauge
IS
easy
to
use
but
dIfficult
for
an
Inexpenenced
mechanIC
to
Interpret
The
results
when
conSIdered
WIth
other
findIngs
can
prOVIde
valuable
clues
to
pOSSIble
trouble
Connect
the
vacuum
gauge
WIth
a
T
connec
tIon
In
the
hose
from
the
carburetor
to
the
vacuum
advance
on
the
dIstnbutor
Start
the
engme
and
let
It
warm
up
thoroughly
Vacuum
readIng
should
be
steady
at
18
22
Inches
NOTE
Subtract
1
Inch
from
reading
for
every
1000
feet
of
altitude
Figure
1
shows
numerous
tYPical
readIngs
WIth
InterpretatIons
Results
are
not
conclusive
WIthout
companng
to
other
tests
such
as
com
preSSIOn
readIngs
Fuel
Pressure
Gauge
ThIS
Instrument
IS
VItal
for
evaluatIng
fuel
pump
performance
Often
a
vacuum
gauge
and
fuel
pressure
gauge
are
combIned
Dwell
Meter
A
dwell
meter
measures
the
dIstance
In
de
grees
of
cam
rotatIon
that
the
breaker
pOInts
remaIn
closed
while
the
engme
IS
runnIng
SInce
thIS
angle
IS
determmed
by
breaker
pOInt
gap
the
dwell
angle
IS
an
accurate
IndIcatIon
of
pOInt
gap
Many
tachometers
Intended
for
tunIng
and
testIng
Incorporate
a
dwell
meter
as
well
Follow
the
manufacturer
s
InstructIon
to
measure
dwell
on
the
Datsun
Tachometer
A
tachometer
IS
essential
for
tunIng
Datsuns
WIth
exhaust
emission
control
deVices
IgmtIOn
turung
and
carburetor
adjustments
must
be
per
formed
at
the
specified
Idle
speed
The
best
In
strument
for
thIS
purpose
IS
one
WIth
a
range
of
0
1
000
or
0
2
000
rpm
Extended
range
0
6
000
or
8
000
Instruments
lack
accuracy
at
lower
speeds
The
InStrument
should
be
capable
of
detecting
changes
of
25
rpm
Stroboscopic
Timing
Light
ThIS
Instrument
pernuts
accurate
IgnitIon
tImIng
By
f1ashmg
a
bght
at
the
preCISe
Instant
cylInder
No
1
fires
the
posItIon
of
the
crank
shaft
pulley
at
that
Instant
can
be
seen
Marks
on
the
pulley
bne
up
With
a
reference
pOInter
on
the
block
dunng
the
tIming
procedure
SUltable
bghts
are
neon
bulb
types
and
xenon
strobe
hghts
Neon
tunmg
bghts
are
ddticult
to
see
and
must
be
used
in
dImly
bt
areas
Xenon
strobe
bghts
can
be
used
In
bnght
sunbght
Use
the
bght
accordIng
to
the
manufacturer
s
InStruC
tIons
Exhaust
Analyzer
Of
all
Instruments
descnbed
here
this
IS
the
least
bkely
to
be
owned
by
a
home
mechanic
One
Instrument
samples
the
exhaust
gases
from
the
taIlpIpe
and
measures
the
thermal
conduc
tIVIty
of
the
exhaust
gas
SInce
different
gases
conduct
heat
at
varYIng
rates
thermal
conduc
tIVIty
of
the
exhaust
IS
a
good
IndIcatIon
of
gases
present
This
Instrument
IS
VItal
for
accurately
checkIng
the
effectIveness
of
exhaust
emIssion
control
adjustments
but
IS
too
expenSIve
for
an
amateur
mechanIC
to
conSIder
buying
STARTER
Starter
system
troubles
are
relatIvely
easy
to
ISolate
The
followmg
are
common
symptoms
and
cures
1
Engme
cranks
very
slowly
or
not
at
all
Turn
on
the
headhghts
If
the
bghts
are
very
dun
most
likely
the
battery
or
the
connecting
WireS
are
at
fault
Check
the
battery
using
the
pro
cedures
descnbed
in
the
Tune
up
chapter
Check
wmmgfur
e
s
wom
andd
connectIom
H
the
battery
and
connectIng
WIres
check
good
turn
the
headlIghts
on
and
try
to
crank
the
engIne
H
the
lIghts
dIDl
drastIcally
the
starter
is
probably
shorted
to
ground
Remove
the
starter
and
test
it
usmg
the
procedures
gIven
in
Chapter
NIne
If
the
lights
remain
bnght
or
dun
slIghtly
when
crankIng
the
engme
the
trouble
may
be
in
the
starter
solenOId
or
wmng
To
ISolate
the
trouble
short
the
two
large
solenoid
ternunals
together
not
to
ground
if
the
starter
cranks
normally
check
the
solenoid
and
wmng
up
to
the
Page 27 of 252

22
CHAPTER
FOUR
CD
Normal
plug
appearance
noted
by
the
brown
to
graYish
tan
deposits
and
slight
electrode
wear
This
plug
rndlcates
the
correct
plug
heat
range
and
proper
air
fuel
ratio
f
j
l
Carbon
fouling
dlstrngUlshed
by
dry
fluffy
black
carbon
deposits
which
may
be
caused
by
an
over
nch
alr
fuel
mixture
excessIVe
hand
chokrng
clogged
air
filter
or
excessive
Idling
lJ
6
1
4i
Z
011
fouling
rndlcated
by
wet
OIly
depOSits
caused
by
011
pumprng
past
worn
rrngs
or
down
the
rntake
valve
gUides
A
hotter
plug
temporanly
reduces
011
depOSits
but
a
plug
that
IS
too
hot
leads
to
pre
IgmtlOn
and
possible
engrne
damage
Red
brown
yellow
and
white
coatrngs
caused
by
fuel
and
011
additives
These
depOSits
are
not
harm
ful
If
they
remarn
rn
a
powdery
form
C
I
Shrny
yellow
glaze
on
rnsulator
cone
IS
caused
when
the
powdery
depOSits
from
fuel
and
011
additives
melt
Meltrng
occurs
dunng
hard
acceleration
after
prolonged
Idling
This
glaze
conducts
electnclty
and
shorts
out
the
plug
Overheated
plug
rndlcated
by
burned
or
blistered
rnsulator
tip
and
badly
worn
electrodes
This
condl
bon
may
be
caused
by
pre
Igmtlon
cooling
system
defects
lean
air
fuel
ratiOS
low
octane
fuel
or
over
advanced
Igmbon
bmrng
Spark
plug
condition
photos
courtesy
of
At
Spark
Plug
DIvision
General
Motors
Corporation
The
procedures
given
below
would
generally
apply
to
eIther
type
In
the
dual
pomt
system
one
set
of
pomts
IS
known
as
the
advance
set
and
the
other
the
retard
set
Complete
details
are
given
m
Chapter
Nme
Figure
4
IS
a
detaIl
of
the
dual
pomt
system
1
Remove
dIStnutor
cap
Clean
It
carefully
to
remove
grease
or
dIrt
2
Examme
the
mSIde
of
the
cap
for
d1rt
or
ex
ceSSIve
wear
Look
for
SIgns
of
carbon
tracks
arcmg
from
contact
to
contact
mSIde
the
dIS
trIbutor
cap
Carbon
tracks
mdlcate
defects
or
cracks
and
If
found
the
cap
should
be
replaced
3
Remove
the
rotor
and
mspect
for
exceSSIve
wear
around
the
top
metal
contact
wiper
surface
If
defectlve
replace
As
a
matter
of
good
prac
nce
the
rotor
should
be
replaced
whenever
the
contact
pomts
are
replaced
4
Use
a
screwdriver
to
gently
open
the
contact
pomts
If
they
show
wear
or
plttmg
remove
the
I
7
r
Page 42 of 252
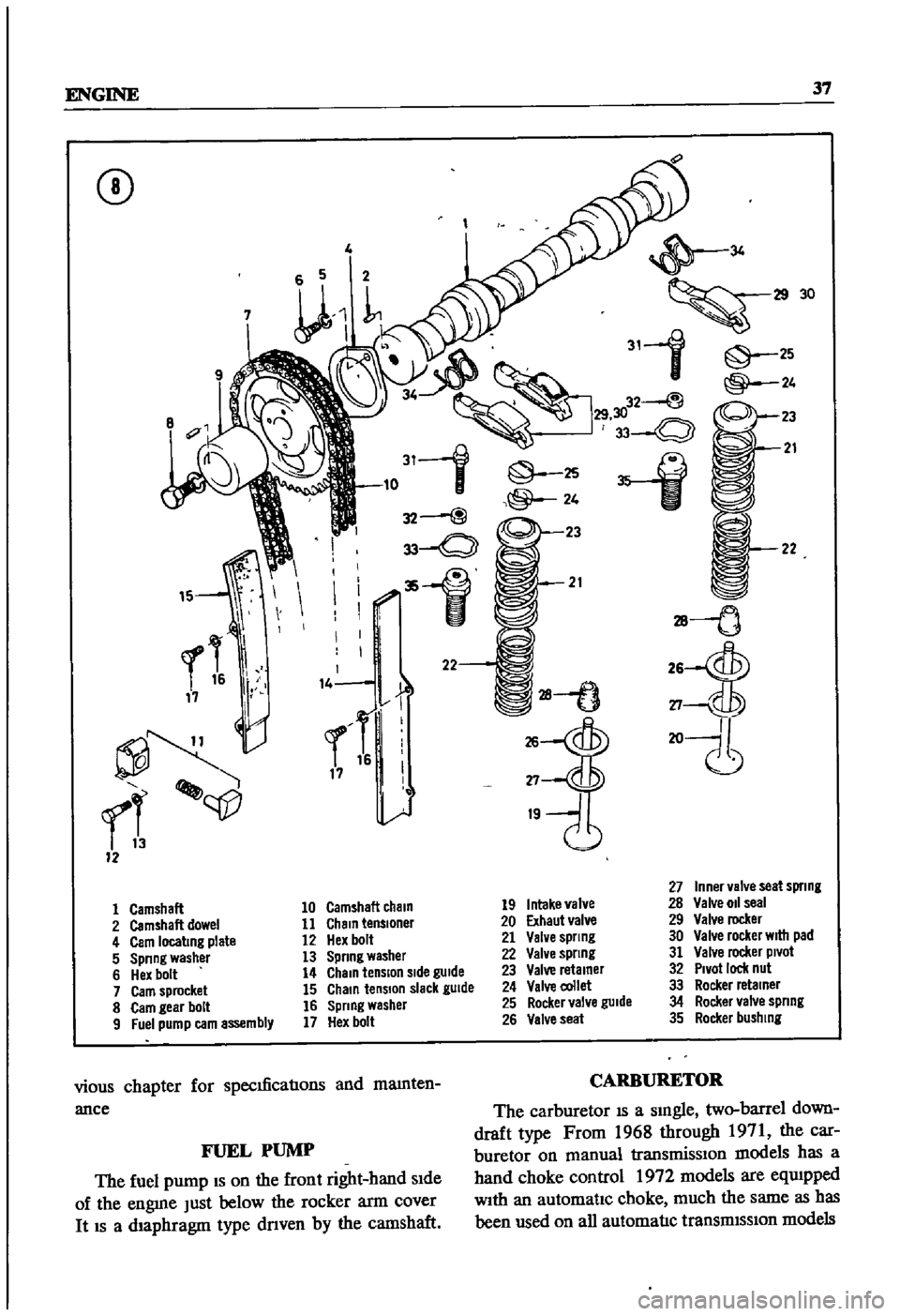
ENGINE
37
CD
4
11lL
8
311
@
2S
10
32
@
@
24
33
Q
23
1
21
rl
qp
12
26
27
19
34
30
31
1
25
@
24
W
32
@
30
33
0
21
28
tJ
2S
ctJ5J
27
20
II
27
Inner
valve
seat
spnng
1
Camshaft
10
Camshaft
cham
19
Intake
valve
28
Valve
011
seal
2
Camshaft
dowel
11
Chain
tensloner
20
Exhaut
valve
29
Valve
rocker
4
Cam
locating
plate
12
Hex
bolt
21
Valve
spnng
30
Valve
rocker
WIth
pad
5
Spnng
washer
13
Spnng
washer
22
Valve
spnng
31
Valve
rocker
Pivot
6
Hex
bolt
14
Chain
tension
Side
gUide
23
Valve
retamer
32
Pivot
ICICk
nul
7
Cam
sprocket
15
Chain
tension
slack
gUide
24
Valve
collet
33
Rocker
retainer
8
Cam
gear
bolt
16
Spnng
washer
25
Rocker
valve
guide
34
Rocker
valve
spnng
9
Fuel
pump
earn
assembly
17
Hex
bolt
26
Valve
seat
35
Rocker
bushing
vious
chapter
for
specmcaoons
and
mamten
ance
CARBURETOR
The
carburetor
IS
a
smgle
two
barrel
down
draft
type
From
1968
through
1971
the
car
buretor
on
manual
transmissIOn
models
has
a
hand
choke
control
1972
models
are
eqUIpped
With
an
automatic
choke
much
the
same
as
has
been
used
on
all
automaoc
transmISSion
models
FUEL
PUMP
The
fuel
pump
IS
on
the
front
right
hand
Side
of
the
engme
Just
below
the
rocker
arm
cover
It
IS
a
diaphragm
type
dnven
by
the
camshaft
Page 43 of 252

38
CHAPTER
SIX
EMISSION
CONTROL
DEVICES
All
Datsuns
have
a
sealed
type
of
crankcase
emISSion
control
device
and
an
exhaust
emISsion
control
deVice
Models
sold
m
Cahfornla
smce
1970
also
have
an
evaporative
emisSion
control
deVice
An
rmportant
part
of
the
exhaust
control
device
is
the
air
pump
located
at
the
bottom
left
hand
side
of
the
engme
It
IS
dnven
by
a
belt
off
of
the
crankshaft
pulley
and
supphes
air
to
the
exhaust
system
In
1972
an
electric
blower
in
corporated
m
the
air
cleaner
replaced
the
mechanical
pumI
ENGINE
REMOVAL
Expenence
has
shown
It
IS
easier
to
remove
the
engine
and
the
transmission
as
a
smgle
UnIt
than
to
remove
the
engme
alone
Once
the
en
gine
and
transmiSSIon
are
out
of
the
vehIcle
the
tranSmIssion
can
be
detached
from
the
engme
To
remove
the
engme
transmISsion
proceed
as
follows
1
Scribe
ahgnment
marks
on
the
hood
around
the
hmges
ThIS
will
make
remstallatlon
eaSIer
2
Remove
the
two
bolts
that
secure
each
hInge
and
remove
the
hood
It
is
not
necessary
to
re
move
the
hood
support
from
the
engme
firewall
3
DISconnect
the
lower
radIator
hose
from
the
right
hand
SIde
of
the
engine
and
at
the
bottom
of
the
radIator
ThIS
will
pernnt
coolant
to
dram
from
the
engme
and
the
radIator
4
Remove
the
draIn
plugs
from
the
engine
pan
and
translIDSsIon
and
completely
dram
lubn
cants
Into
suitable
contamers
5
DISconnect
the
battery
cables
from
the
bat
tery
loosen
the
two
hold
down
clamps
and
re
move
the
battery
NOTE
The
location
and
number
of
hoses
to
be
removed
from
the
air
cleaner
varies
from
model
to
model
It
IS
normally
easier
to
remove
the
hoses
from
the
sources
rather
than
try
to
dISconnect
them
from
yndemeath
the
air
cleaner
The
1972
model
Will
requlre
dlsconnectlOn
of
the
electrica1
cirCUit
In
the
air
cleaner
system
wing
nut
from
the
top
of
the
air
cleaner
and
remove
the
aIr
cleaner
7
DIsconnect
the
upper
radiator
hose
from
the
radiator
and
the
thermostat
housmg
Remove
the
hose
8
Disconnect
the
two
heater
hoses
from
the
nght
hand
side
of
the
engme
TIe
these
bac
so
they
won
t
interfere
with
removal
of
the
engme
9
Remove
the
radIator
grille
by
unscrewing
all
mountmg
screws
10
Remove
the
four
mounting
screws
holding
the
fan
shield
to
the
backside
of
the
radiator
11
Remove
the
four
mountmg
bolts
holdIng
the
radiator
In
place
In
automatic
tranSmISsion
models
dISconnect
the
two
transnnsslOn
oIl
cooler
lInes
from
the
bottom
of
the
radiator
Pull
the
radiator
straight
up
to
remove
Remove
the
fan
shield
12
Loosen
the
adjustment
and
mounting
bolts
from
the
retamIng
brackets
on
the
alternator
and
air
pump
If
so
eqwpped
The
alternator
is
lo
cated
at
the
bottom
nght
hand
Side
of
the
engme
and
the
air
pump
on
the
lower
left
hand
Side
13
Loosen
tenSIon
on
the
two
dnve
belts
re
move
the
belts
from
the
alternator
and
air
pump
and
then
from
the
fan
pulleys
14
Remove
the
bolts
holdIng
the
fan
and
pulley
to
the
water
pump
assembly
and
remove
the
fan
and
pulley
15
DISconnect
the
fuel
hne
from
the
fuel
pump
16
DIsco
ect
accelerator
control
linkage
and
choke
WIre
at
the
carburetor
17
Disconnect
the
wiring
from
the
starter
motor
alternator
Ignition
coIl
oIl
pressure
switch
and
temperature
transmItting
unit
NOTE
The
following
steps
are
per
formed
from
under
the
car
lack
up
the
front
of
the
car
and
position
stands
under
the
front
support
points
to
proVide
working
room
under
the
vehicle
WARNING
Never
climb
under
a
vehicle
that
is
supported
by
the
lack
only
If
stands
are
not
avflllable
sturdy
wooden
blocks
can
be
U3ed
6
Disconnect
all
hoses
that
lead
to
the
air
cleaner
remove
two
bolts
that
hold
the
air
cleaner
to
its
mountmg
bracket
unscrew
the
18
Remove
two
bolts
holdIng
the
clutch
operat
Ing
cylInder
to
the
flywheel
hOUSIng
shown
m
Page 67 of 252

CHAPTER
SEVEN
FUEL
SYSTEM
The
fuel
system
mcludes
the
fuel
tank
straIner
pump
carburetor
arr
cleaner
and
necessary
lines
Inspect
components
for
leaks
and
deterioratIOn
whenever
mamtenance
is
done
The
fuel
stramer
should
be
mspected
peri
odIcally
and
cleaned
AIR
CLEANER
The
au
filter
element
is
viscous
paper
and
does
not
require
cleanmg
Replace
It
every
24
000
mlles
or
more
frequently
under
harsh
condItIons
Several
mInor
differences
exist
between
vehicles
dependmg
on
the
type
of
emisSIOn
con
trol
device
used
Figure
1
shows
location
of
the
air
cleaner
on
the
engme
and
parts
compnsing
the
cleaner
system
on
model
years
through
1969
Figure
2
shows
the
changes
for
1970
and
later
Warm
air
is
supplIed
to
the
air
cleaner
from
the
exhaust
mamfold
to
prevent
carburetor
Icmg
AIR
CLEANER
REMOVAL
AND
REPLACEMENT
1
Unthread
the
WIng
nut
atop
the
cleaner
assembly
2
Remove
the
two
bolts
holdIng
the
air
cleaner
to
the
support
3
Disconnect
the
aIr
cleaner
duct
from
the
base
of
the
cleaner
intake
throat
4
LIft
off
the
aIr
cleaner
body
and
remove
the
aIr
filter
as
shown
m
Figure
3
To
remove
the
arr
cleaner
proceed
as
follows
1
Perform
steps
1
through
4
above
2
Unscrew
the
band
bolt
at
the
base
of
the
air
cleaner
3
DIsconnect
all
hoses
leadmg
to
the
air
cleaner
4
Pull
up
on
the
body
of
the
air
cleaner
and
remove
from
carburetor
5
Except
for
the
au
filter
element
thoroughly
clean
all
parts
6
Reverse
the
steps
above
for
reassembly
FUEL
STRAINER
The
fuel
stramer
IS
located
on
the
nght
hand
side
of
the
engme
compartment
Figure
4
shows
the
fuel
stratner
hoses
clamps
and
the
mount
Ing
clIp
that
holds
the
fuel
stramer
In
place
The
fuel
stramer
IS
of
the
cartrIdge
type
and
uses
a
fiber
mat
and
nylon
as
strainer
elements
The
fuel
stramer
should
be
mspected
frequently
for
foreIgn
material
and
replaced
at
least
every
24
000
rmles
1
DIsconnect
the
inlet
and
outlet
hoses
from
the
fuel
stratner
Make
certatn
that
the
mlet
hose
bottom
IS
not
permItted
to
fall
below
the
level
of
the
fuel
tank
or
leakage
wIll
occur
Page 74 of 252
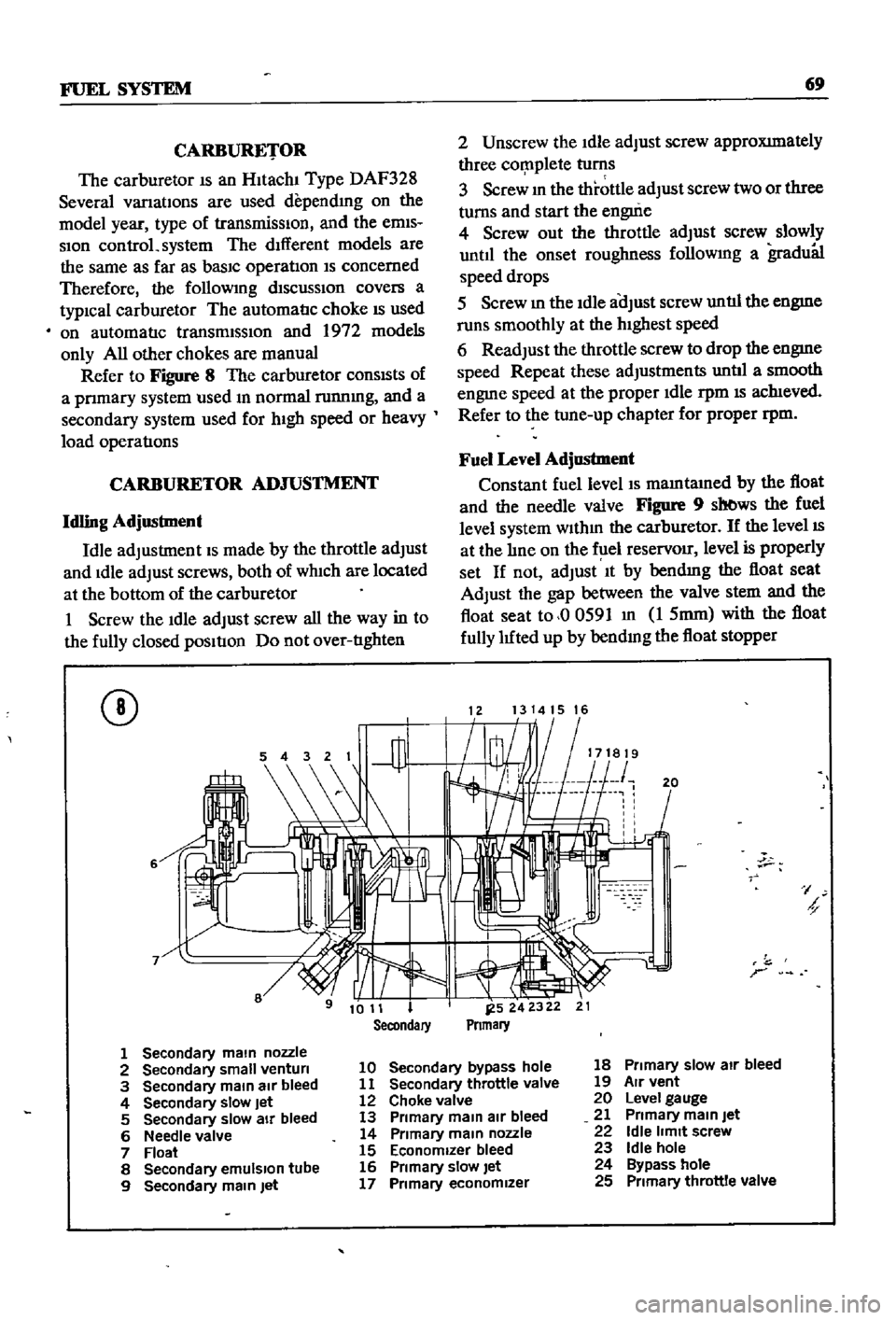
FUEL
SYSTEM
69
CARBURETOR
The
carburetor
IS
an
Hltach1
Type
DAF328
Several
varIations
are
used
dependmg
on
the
model
year
type
of
transmissIOn
and
the
emIS
SIon
control
system
The
dIfferent
models
are
the
same
as
far
as
basiC
operation
IS
concerned
Therefore
the
followmg
dISCUSSIon
covers
a
typIcal
carburetor
The
automatIc
choke
IS
used
on
automatIc
transmISSIon
and
1972
models
only
All
other
chokes
are
manual
Refer
to
Figure
8
The
carburetor
conSIsts
of
a
pnmary
system
used
m
normal
runnmg
and
a
secondary
system
used
for
hIgh
speed
or
heavy
load
operatIons
CARBURETOR
ADJUSTMENT
Idling
Adjustment
Idle
adjustment
IS
made
by
the
throttle
adjust
and
Idle
adjust
screws
both
of
wh1ch
are
located
at
the
bottom
of
the
carburetor
1
Screw
the
Idle
adjust
screw
all
the
way
in
to
the
fully
closed
pOSItIon
Do
not
over
tIghten
CD
6
2
Unscrew
the
Idle
adjust
screw
approXImately
three
cor
nplete
turns
3
Screw
m
the
throttle
adjust
screw
two
or
three
turns
and
start
the
engui
e
4
Screw
out
the
throttle
adjust
screw
slowly
until
the
onset
roughness
followmg
a
gradu81
speed
drops
5
Screw
m
the
Idle
aOJust
screw
untIl
the
engme
runs
smoothly
at
the
hIghest
speed
6
Readjust
the
throttle
screw
to
drop
the
engme
speed
Repeat
these
adjustments
untIl
a
smooth
engme
speed
at
the
proper
Idle
rpm
IS
ach1eved
Refer
to
the
tune
up
chapter
for
proper
rpm
Fuel
Level
Adjustment
Constant
fuel
level
IS
mamtamed
by
the
float
and
the
needle
valve
Figure
9
sb
ws
the
fuel
level
system
wlthm
the
carburetor
If
the
level
IS
at
the
lIne
on
the
f
lel
reservOir
level
is
properly
set
If
not
adjust
It
by
bendmg
the
float
seat
Adjust
the
gap
between
the
valve
stem
and
the
float
seat
to
00591
m
1
5mm
with
the
float
fully
luted
up
by
bendmg
the
float
stopper
1213141516
20
I
h
r
1
Secondary
main
nozzle
2
Secondary
small
venturi
10
Secondary
bypass
hole
18
Primary
slow
air
bleed
3
Secondary
main
air
bleed
11
Secondary
throttle
valve
19
Air
vent
4
Secondary
slow
Jet
12
Choke
valve
20
Level
gauge
5
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
13
Primary
main
air
bleed
21
Primary
main
Jet
6
Needle
valve
14
Primary
main
nozzle
22
Idle
limit
screw
7
Float
15
Economizer
bleed
23
Idle
hole
8
Secondary
emulSion
tube
16
Primary
slow
let
24
Bypass
hole
9
Secondary
main
Jet
17
Primary
economizer
25
Primary
throttle
valve