1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE turn signal bulb
[x] Cancel search: turn signal bulbPage 49 of 408

.~ P.X I_ - “, .- I .-., IS ” .~.I .r
2-2 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
nn
ity and trouble: shooting electrical circuits,
please refer to Section 6 of this manual.
I
The ignition system on the 1.5L, 1993-96 1.8L,
2.OL SOHC, 1994-98 2.4L SOHC, 3.OL SOHC, and
3.5L engines uses a pointless type distributor, whose
advance mechanism is controlled by the Engine Con-
trol Unit (ECU). On the 1.5L, 1.8L, 2.4L and 3.5L en-
gines, the distributor houses a built in ignition coil
and ignition power transistor. The 2.8L SOHC and
3.OL SOHC engines utilize a separate coil and tran-
sister assemblv.
When the ignition switch is turned ON, battery
voltage is applied to the ignition coil primary winding.
As the shaft of the distributor rotates, signals are
transmitted from the oowertrain control module to the
9105zp11 Fig. 1 This spark tester looks iust like a
Fiu. 2 This spark tester has an adjustable
spark plug, attach the clip to ground and air-gap for measuring spark strength and
crank the engine to check for spark testing different voltage ignition systems
.
ignition power trar rsistor. These signals activate the
power transistor to cause ignition coil primary wind-
ing current flow from the ignition coil negative termi-
nal through the power transistor to ground repeatedly.
This interruption induces high voltage in the ignition
coil secondarv windinas, which is diverted throuah
the distributor, spark plug cable and spark plug 6
ground, thus causing ignition in each cylinder.
I
SECONDARYSPARKTEST l;h.4-
! ,L ".~
'$ >,%
If See Figures 1 thru 6
91rJszp12 Fig. 4 This spark tester is the easiest to use
iust alace it on a plug wire and the spark
The best way to perform this procedure is to use a Fig. 3 Attach the clip to ground and crank
spark tester (available at most automotive parts stores). the engine to check for spark
I I voltage is detected and the bulb on the tof
-. will flash with each pulse
I nree types ot spark testers are commonly available.
The Neon Bulb type is connected to the spark plug
wire and flashes with each ignition pulse. The Air Gap
type must be adjusted to the individual spark plug gap
specified for the engine. The last type of spark plug
tester looks like a spark plug with a grounding clip on
the side, but there is no side electrode for the spark to
jump to. The last two types of testers allows the user to
not only detect the presence of spark, but also the in-
tensity (orange/yellow is weak, blue is strong).
1. Disconnect a spark plug wire at the spark plug
end.
2. Connect the plug wire to the spark tester and
ground the tester to an appropriate location on the
engine.
3. Crank the engine and check for spark at the
tester.
4. If spark exists at the tester, the ignition system
is functioning properly.
5. If spark does not exist at the spark plug wire,
perform diagnosis of the ignition system using indi-
vidual component diagnosis procedures,
CYLINDER DROPTEST
p See Figures 7, 8, and 9
The cylinder drop test is performed when an en-
gine misfire is evident. This test helps determine
which cylinder is not contributing the proper power.
The easiest way to perform this test is to remove the
plug wires one at a time from the cylinders with the
engine running. 1. Place the transaxle in P, engage the emer-
gency brake, and start the engine and let it idle.
2. Using a spark plug wire removing tool, prefer-
ably the plier type, carefully remove the boot from
one of the cylinders.
i ’
Make sure your body is free from touching
any part of the car which is metal. The sec-
ondary voltage in the ignition system is high and although it cannot kill you, it will shock
you and it does hurt.
3. The engine will sputter, run worse, and possi-
bly nearly stall. If this happens reinstall the plug wire
and move to the next cylinder. If the engine runs no
differently, or the difference is minimal, shut the en-
gine off and inspect the spark plug wire, spark plug,
and if necessary, perform component diagnostics as
covered in this section. Perform the test on all cylin-
ders to verify the which cylinders are suspect.
Page 169 of 408

4-26 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
the signals of input and output sensors, some all the
time and others at certain times and processes each
signal. When the PCM notices that an irregularity has
continued for a specified time or longer from when
the irregular signal was initially monitored, the PCM
judges that a malfunction has occurred and will
memorize the malfunction code. The code is then
stored in the memory of the PCM and is accessible
through the data link (diagnostic connector) with the
use of an electronic scan tool or a voltmeter.
CHECK ENGINE/MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR LIGHT
Among the on-board diagnostic items, a check
engine/malfunction indicator light comes on to notify
the driver of a emission control component irregular-
ity. If the irregularity detected returns to normal or the
PCM judges that the component has returned to nor-
mal, the check engine/malfunction indicator light will
be turned off Moreover, if the ignition is turned OFF
and then the engine is restarted, the check
engine/malfunction indicator light will not be turned
on unttl a malfunction is detected.
The check engine/malfunction indicator light will
come on immediately after the ignition switch is
turned ON. The light should stay lit for 5 seconds
and then will go off. This Indicates that the check en-
gine/malfunction indicator lamp is operating nor-
mally. This does not signify a problem with the sys-
tem.
*The check engine/malfunction indicator
lamp will come on when the terminal for the
ignition timing adjustment is shorted to
ground. Therefore, it is not abnormal that the
light comes on even when the terminal for ig-
nition timing is shorted at time of ignition
timing adjustment.
To test the light, perform the following:
1. Turn the ignition switch ON. Inspect the check
engine/malfunction indicator lamp for Illumination.
2. The light should be lit for 5 seconds and then
should go out.
3. If the lamp does not illuminate, check for open
circuit In the harness, blown fuse or blown bulb.
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
l Before attachrng or detaching the PCM harness
connectors, make sure the ignition switch is OFF and
the negative battery cable is disconnected to avoid
the possibility of damage to the PCM.
l When performing PCM input/output signal di-
agnosis, remove the pin terminal retainer from the
connectors to make it easier to insert tester probes
into the connector.
l When attaching or detaching pin connectors ,
from the PCM, take care not to bend or break any pin
terminals. Check that there are no bends or breaks on
PCM pin terminals before attempting any connec-
tions.
l Before replacing any PCM, perform the PCM
input/output signal diagnosis to make sure the PCM
is functioning properly.
l When measuring supply voltage of PCM-con-
trolled components with a circuit tester, separate 1
tester probe from another. If the 2 tester probes acci-
dentally make contact with each other during mea-
surement, a short circuit WIII result and damage the
PCM.
# See Figures 83
and 84
Remember that the diagnostic trouble code identi-
fication refers only to the circuit, not necessarily to a
specific component. For example, fault code 14 may
indicate an error in the throttle position sensor cir-
cuit; it does not necessarily mean the TPS sensor has
failed Testing of all related wiring, connectors and
the sensor itself may be required to locate the prob-
lem.
The PCM memory is capable of storing multiple
codes. During diagnosis the codes will be transmlt-
ted in numerical order from lowest to highest, regard-
less of the order of occurrence. If multiple codes are
stored, always begin diagnostic work with the lowest
numbered code
Make a note of the following:
1. When battery voltage IS low, no detection of
failure is possible. Be sure to check the battery volt-
age and other conditions before starting the test.
2. Diagnostic items are erased if the battery or the
engine controller connection is detached. Do not dis- connect either of these components until the diag-
nostic material present in the PCM has been read
completely.
3. Be sure to attach and detach the scan tool to
the data link connector with the ignition key OFF. If
the scan tool in connected or disconnected with the
ignition key ON, diagnostic trouble codes may be
falsely stored and the engine warning light may be il-
luminated. WITHASCANTOOL
) See Figures 85 and 86
The procedure listed below is to be used only as a
guide, when using Mitsubishi’s MUT-II, or equivalent
scan tool. For specific operating instructions, follow
the directions supplied with the particular scan tool
bemg used.
1. Remove the underdash cover, if equipped. At-
tach the scan tool to the data link connector, located
on the left underside of the instrument panel.
2. Using the scan tool, read and record the on-
board diagnostic output.
3. Diagnose and repair the faulty components as
required
4. Turn the ignition switch OFF and then turn it
ON.
5. Erase the diagnostic trouble code.
6 Recheck the diaanostic trouble code and make
sure that the normal &de is output.
79232G37 89574g98 Fig. 83 Diagnosis terminal connector loca-
tion-Galant Fig. 85 The data link connector is located
on the left under side of the instrumeni
panel
,--MU DL4GNDSl.S
LGRDIJND
79232638
Fig. 84 Diagnostic connector Iocation-Mi-
‘age
ata link connector
89574994 Fig. 86 Proper connection of the scan tool to read codes on OBD-I vehicles
Page 222 of 408

CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 6-19
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
are all built into 1 multi-function combination
2. Remove the instrument cluster, as outlined 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
earlier in this section. switch that is mounted on the steering col-
2. Using a small screwdriver or other suitable
umn. Refer to Section 8 for procedures re-
3. Remove the retaining screws for the instrument tool, carefully pry the retaining clips from either side
garding the combination switch.
cluster lens and cover assembly. Remove the cover of the switch trim plate.
3.
and lens. Carefully pull the switch and trim plate out of
,
4. Remove the retaining screws for the gauge or the instrument panel.
4. Detach the electrical connectors and remove
warning lamp to be replaced, then remove the gauge
the switch.
or warning lamp.
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION : 5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
To install:
5. Place the gauge or warning lamp into place
and tighten the retaining screws. 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
6. Install the instrument cluster lens and cover 2. Using a suitable prytool, disengage the switch
assembly. retaining tabs.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION 7. Install the instrument cluster. 3. Gently pull the switch from the instrument
8. Connect the negative battery cable. panel.
4. Detach the electrical connector and remove the *On all models the headlights, turn signals,
switch. and on some models, the cruise control func-
5. The installation is the reverse of removal. tion are all built into 1 multi-function combi-
nation switch that is mounted on the steerinq
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION column. Refer to Section 8 for procedures 6
garding the combination switch.
*The headlights, turn signals, dimmer
switch, horn switch, windshield
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
wiper/washer, intermittent wiper switch and *
on some models, the cruise control function # See Figures 71, 72, and 73
the retaining clips from either side of the
switch trim plate . . . Fig. 72 . . . then carefully pull the switch
and trim plate out of the instrument panel Fig. 73 Detach the electrical connectors and
remove the switch
-
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Sealed Beam Headlights
1. Raise the headlights using the pop-up switch.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Unfasten the retaining screws, then remove the
upper and the lower headlight bezels.
4. Remove the headlight retaining ring screws,
and the headlight retaining ring.
5. Pull the headlight partially out, detach the con-
nectar, then remove headlight assembly from the ve-
hicle.
To install:
6. Attach the headlight electrical connector.
7. Properly position the headlight and the retain-
ing ring, then install the retaining screws.
8. Install the headlight bezels and secure with the
retaining screws. 9. Connect the negative battery cable.
Composite Headlights
6 See Figures 74, 75, 76, 77, anU78
Halogen bulbs contain gas under pressure.
Handling the
bulb incorrectly could cause it
to shatter into flying glass fragments. Do
NOT leave the light switch ON. Always allow
the bulb to cool before removal. Handle the
bulb only by the base; avoid touching the
glass itself. Whenever handling a halogen
bulb, ALWAYS follow these precautions:
l Turn the headlight switch OFF and allow the
bulb to cool before changing it. Leave the switch OFF
until the change is complete.
l ALWAYS wear eye protection when changing a
halogen bulb.
l Handle the bulb only by its base. Avoid touch-
ing the glass.
l DO NOT drop or scratch the bulb. l Keep dirt and moisture away from the bulb.
* Place the used bulb in the new bulb’s carton
and dispose of it properly.
1. Open the vehicle’s hood and secure it in an up-
right position.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the socket cover by pulling it straight
off, or turning it clockwise then pulling it off.
4. Carefully twist the bulb and socket counter-
clockwise, then pull the assembly from the headlight
housing.
5. Holding the base of the bulb, detach it from the
connector harness.
To install:
6. Holding the base of the bulb, install it securely
in the connector.
7. Install the connector and bulb assembly in the
housing and twist to lock into position.
8. Install the sealing cover by pushing it on
Page 224 of 408

CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 6-21
Fig. 82 low-beam headlight pattern alignment
93156pE.3 Fig. 85 Remove the washer fluid reservoir
retaining screws . . .
Fig. 83 High-beam headlight pattern alignment
headlight beams on the wall. If done in a garage,
darken the area around the wall as much as possible
by closing shades or hanging cloth over the win-
dows.
3. Turn the headlights ON and markthe wall at
the center of each light’s low br ram, then switch on
the brights and mark the center of each lights high
beam. A short length of maskin g tape which is visible
from the front of the
whir+ ma . ._..._._ . .._ y be used. Although
marking all four po:
sitions is advisable, marking one
position from each
light should be sufficient.
4. If neithar he; ~. __
Irn on one side is working, and if
another like-sized vehicle is available, park the sec-
nnri nm in the wart cnnt whrw the whirlo um md
headli! jhts ON and adjust the beams to marcn me
I. Disconnect the negative battery cable. marks on the wall.
2. Remove any necessary components to access 6.
the bulbs. Have the headlight adjustment checked as
soon as possible by a reputable repair shop.
3. Rotate the bulb sockets and rotate them coun-
terclockwise to remove them.
4. Grasp the bulb and remove it from the socket REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
Parking And Side Marker Lights
p See Figures 84, 85, 88, 87, 88, and 89 !ss the parking and side
1~ nn loo4-98 Galant mod-
I
1 I-
5315@61
lens. 1 Fio. 8
then move the reservoir out of
3. Remove the lens from the front fascia.
4. Grasp the bulb socket and rotate it counter- marker lamp bult, _.. ._“~-
clockwise to remove it from the lamp.
5. Pull the bulb out to remove it from the socket. 5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
6. Installation is the reverse of removal. Front turn Signal
p See Figures 91
1. Disconnect tl
2. Remove the t 0, 91, 92, and 93
I(? n,-.nn+:.m b.Hnn, nnL.L
z Ill7yau”e “allcly ul”IC. 10 retainino screws from the
spot from which the lights were marked. Turn the . ..I_ WIIY I.8 %,I” V”UVL”fdYI T.II”IU Lll” “VlllUlY ,.UU U,,” mark the beams using the same-side light. Then
switch the vehicles so the one to be aimed is back in
the original spot. It must be parked no closer to or
farther away from the wall than the second vehicle.
5. Perform any necessary repairs, but make sure
the vehicle is not moved, or is returned to the exact
by pulling it straight out.
Page 225 of 408
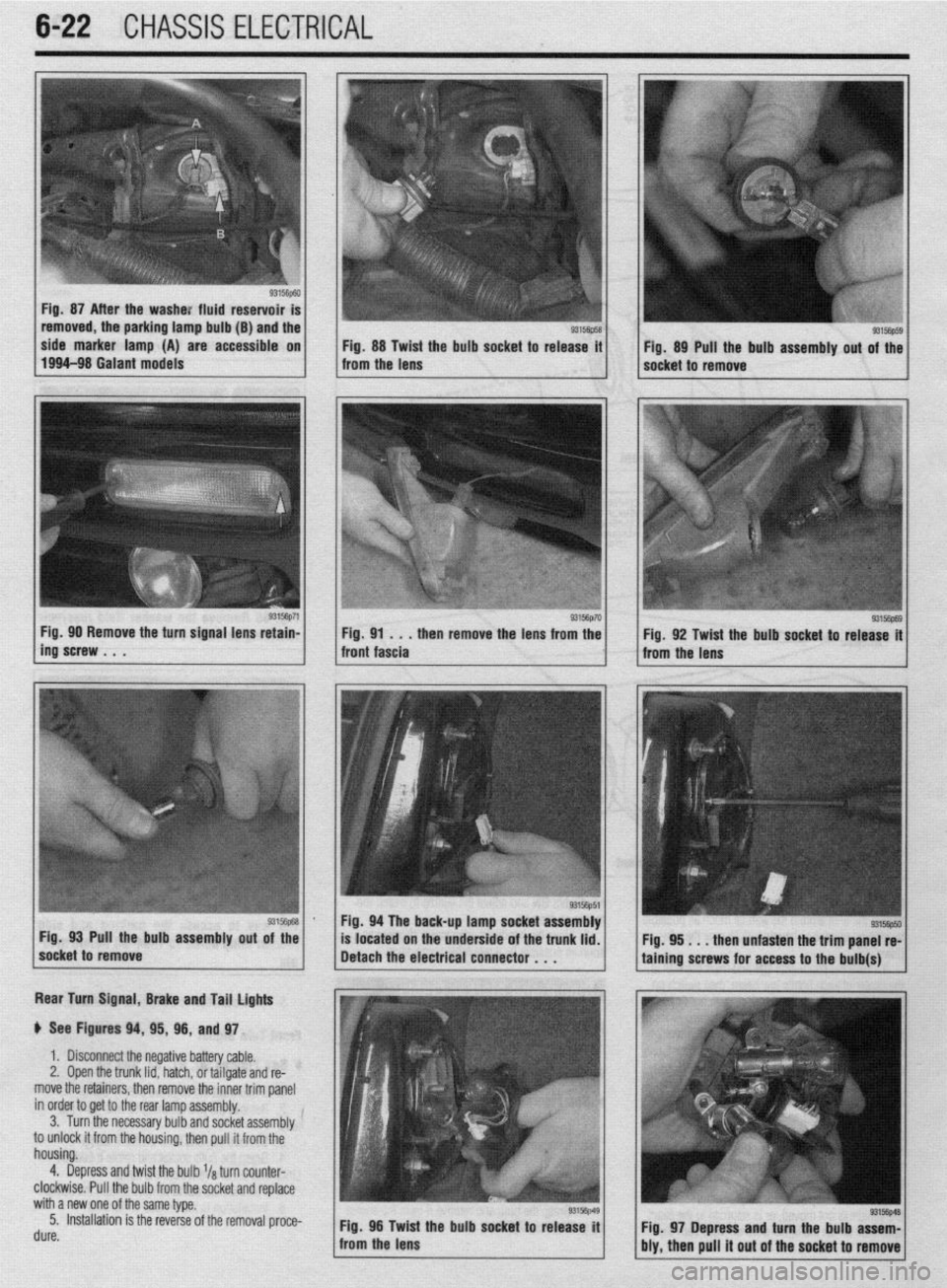
6-22 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
b
Fig. 87 After the washe: fluid reservoir
removed, the parking lamp bulb (B) and the
side marker lamp (A) are accessible on
Fig. 88 Twist the bulb socket to release it
1994-98 Galant models
from the lens Fig. 89 Pull the bulb assembly out of the
socket to remove
g3156p71 / Fig 90 Remove the turn signal lens retain-
ing’screw . . . . then remove the lens from the
Rear Turn Signal, Brake and Tail lights
p See Figures 94, 95, 96, and 97.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2, Open the trunk lid, hatch, or tailgate and re-
move the retainers, then remove the inner trim panel
in order to get to the rear lamp assembly.
3. Turn the necessary bulb and socket assembly
to unlock it from the housing, then pull it from the
housing.
4. Depress and twist the bulb l/a turn counter-
clockwise. Pull the bulb from the socket and replace
with a new one of the same type.
5. Installation is the reverse of the removal proce-
rl. ._^
UUIt?. Fig. 96 Twid
: the bulb socket to release it
from the lens
93156p69 Fig. 92 Twist the bulb socket to release it
from the lens
I
Fig. 94 The back-up lamp socket assembly
Pull the bulb assembly
out of the
located on the underside of the trunk lid.
. . . then unfasten the trim panel re-
Fig. 97 Depress and turn the bulb assem-
bly, then pull it out of the socket to remove
Page 397 of 408

TROUBLESHOOTING 1145
d. Check the sensor wiring at the wheel sensors and the ABS control unit for a loose or
shorted wire and repair as necessary.
Brake Warninu Liaht a. Check the brakefluid~evel and check for possible leakage from the hydraulic lines and
seals. Top off brake fluid and repair leakage as necessary.
b. Check the brake linings for wear and replace as necessary.
c. Check for a loose or shorted brake warning light sensor or wire, and replace or repair
as necessary.
Oil Pressure Warning Light a. Stop the engine immediately. Check the engine oil level and check for a sudden and
rapid oil loss, such as a leaking oil line or oil pressure sensor, and repair or replace as
necessary.
b. Check the oil pressure sensor operation by substituting a known good sensor.
c. Check the oil pressure sensor wire for being shorted to ground. Disconnect the wire
from the oil pressure sensor and with the ignition in the ON position, but not running,
the oil pressure light should not be working. If the light works with the wire discon-
nected, check the sensor wire for being shorted to ground. Check the wire routing to
make sure the wire is not pinched and check for insulation damage. Repair or replace
the wire as necessary and recheck before starting the engine.
d. Remove the oil pan and check for a clogged oil pick-up tube screen.
Parking Brake Warning Light a. Check the brake release mechanism and verify the parking brake has been fully re-
leased.
b. Check the parking brake light switch for looseness or misalignment.
c. Check for a damaged switch or a loose or shorted brake light switch wire, and replace
or repair as necessary.
3. Warning li#ht(s) inoperative with iflnition on,
and engine not started
a. Check for a defective bulb by installing a known good bulb.
b. Check for a defective wire using the appropriate wiring diagram(s).
c. Check for a defective sending unit by removing and then grounding the wire at the
sending unit. If the light comes on with the ignition on when grounding the wire, re-
place the sending unit.
1. Turn siflnais or hazard iiflhts come on, but do not flash
a. Check for a defective flasher unit and replace as necessary.
2. Turn signals or hazard iiflhts do not function on either side
a. Check the fuse and replace, if defective.
b. Check the flasher unit by substituting a known good flasher unit.
c. Check the turn signal electrical system for a defective component, open circuit, short
circuit or poor ground.
3. Turn siflnais or hazard lights only work on one side
a. Check for failed bulbs and replace as necessary.
b. Check for poor grounds in both housings and repair as necessary.
4. One siflnai light does not work
a. Check for a failed bulb and replace as necessary.
b. Check for corrosion in the bulb socket, and clean and repair as necessary.
c. Check for a poor ground at the bulb socket, and clean and repair as necessary.
5. Turn signals flash too slowly
a. Check signal bulb(s) wattage and replace with lower wattage bulb(s). 6. Turn signals flash too fast
a, Check signal bulb(s) wattage and replace with higher wattage bulb(s).
b. Check for installation of the correct flasher unit and replace if incorrect.
7. Four-way hazard flasher indicator iiflhi inoperative
a. Verify that the exterior lights are functioning and, if so, replace indicator bulb.
b. Check the operation of the warning flasher switch and replace if defective.
0. Turn signal indicator ii#ht(s) do not work in either direction
a. Verify that the exterior lights are functioning and, if so, replace indicator bulb(s).
b. Check for a defective flasher unit by substituting a known good unit.
9. One turn signal indicator liflht does not work
a. Check for a defective bulb and replace as necessary.
b. Check for a defective flasher unit by substituting a known good unit.
1. Horn does not operate
a. Check for a defective fuse and replace as necessary.
b. Check for battery voltage and ground at horn electrical connections when pressing the
horn switch. If voltage is present, replace the horn assembly. If voltage or ground is
not present, refer to Chassis Electrical coverage for additional troubleshooting tech-
niques and circuit information.
2. Horn has an unusual tone
a. On single horn systems, replace the horn.
b. On dual horn systems, check the operation of the second horn. Dual horn systems
have a high and low pitched horn. Unplug one horn at a time and recheck operation.
Replace the horn which does not function.
c. Check for debris or condensation build-up in horn and verify the horn positioning. If
the horn has a single opening, adjust the opening downward to allow for adequate
drainage and to prevent debris build-up.
1. Windshield wipers do not operate
a. Check fuse and replace as necessary.
b. Check switch operation and repair or replace as necessary.
c. Check for corroded, loose, disconnected or broken wires and clean or repair as neces-
sary.
d. Check the ground circuit for the wiper switch or motor and repair as necessary.
2. Windshield wiper motor makes a humming noise, gets hot or blows
fuses
a. Wiper motor damaged internally; replace the wiper motor.
b. Wiper linkage bent, damaged or seized. Repair or replace wiper linkage as necessary.
3. Windshield wiper motor operates, but one or both wipers fail to move
a. Windshield wiper motor linkage loose or disconnected. Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
b. Windshield wiper arms loose on wiper pivots. Secure wiper arm to pivot or replace
both the wiper arm and pivot assembly.
4. Windshield wipers will not park
a. Check the wiper switch operation and verify that the switch properly interrupts the
power supplied to the wiper motor.
b. If the wiper switch is functioning properly, the wiper motor parking circuit has failed.
Replace the wiper motor assembly. Operate the wiper motor at least one time before
installing the arms and blades to ensure correct positioning, then recheck using the
highest wiper speed on a wet windshield to make sure the arms and blades do not
contact the windshield trim.
1. Speedometer does not work to minimize sharp bends or kinks.
If the sheathing has been
damaged, replace the ca-
a. Check and verify that the speedometer cable is properly seated into the speedometer ble assembly.
assembly and the speedometer drive gear. b. Check the speedometer cable for adequate lubrication. Remove the cable, inspect for
b. Check the speedometer cable for breakage or rounded-off cable ends where the cable damage, clean, lubricate and reinstall. If the cable has been damaged, replace the ca-
seats into the speedometer drive gear and into the speedometer assembly. If damaged, ble.
broken or the cable ends are rounded off, replace the cable.
c. Check speedometer drive gear condition and replace as necessary. 3. Speedometer works intermittently
d. Install a known good speedometer to test for proper operation. If the substituted a. Check the cable and verify that the cable is fully installed and the fasteners are secure.
speedometer functions properly, replace the speedometer assembly. b. Check the cable ends for wear and rounding, and replace as necessary.