1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 10 of 408
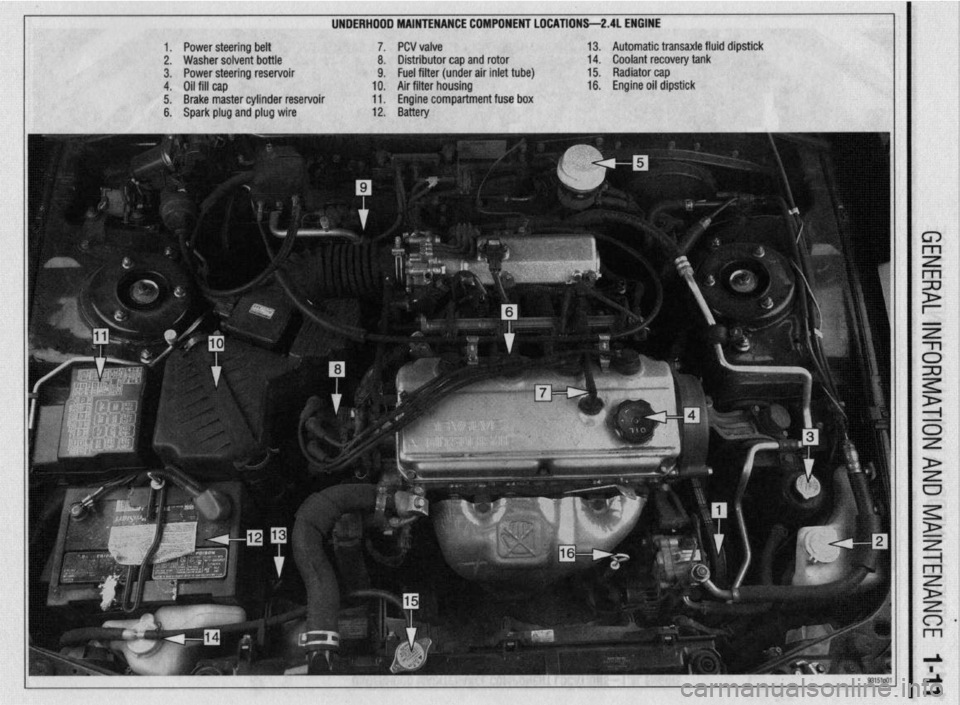
UNDERHDDD MAINTENANCE COMPONENT LOCATIONS-2AL ENGINE
II
1. Power steering belt 7. PCV valve
2. Washer solvent bottle 8. Distributor cap and rotor
3. Power steering reservoir 9. Fuel filter (under air inlet tube)
4. Oil fill cap 10. Air filter housing
5. Brake master cylinder reservoir 11. Engine compartment fuse box
6. Spark plug and plug wire 12. Battery 13. Automatic transaxle fluid dipstick
14. Coolant recovery tank
15. Radiator cap
16. Engine oil dipstick
Page 11 of 408
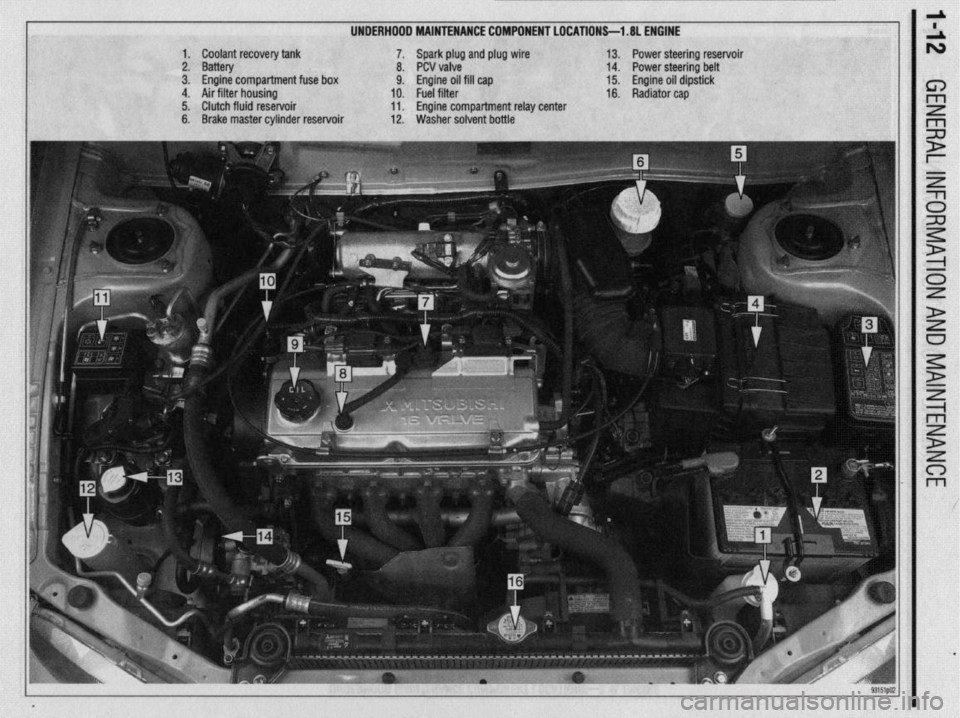
UNDERHOOD MAINTENANCE COMPONENT LOCATIONS-l .8L ENGINE
1. Coolant recovery tank
2. Battery
3. Engine compartment fuse box
4. Air filter housing
5. Clutch fluid reservoir
6. Brake master cylinder reservoir 7. Spark plug and plug wire
8. PCV valve
9. Engine oil fill cap
10. Fuel filter
11. Engine compartment relay center
12. Washer solvent bottle 13. Power steering reservoir
14. Power steering belt
15. Engine oil dipstick
16. Radiator cap
Page 20 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-21
IWSIZXJ FM. 83 A hose clamn that is taa tiaht can
Fig. 82 The cracks developing along this
hose are a result of age-related hardening caise older hoses td separate and ‘iear on
either side of the clamp
lCCS1221 Fig. 84 A soft spongy hose (identifiable by
1 the swollen section) will eventually burst
and should be replaced
IEMOVAL &,INSTALLATION '
1. Remove the radiator pressure cap. her of the sorina tension tvoe (which reouire oliers
3 squeeze the 6bs and loosenj or of the’screw ten-
ion type (which require screw or hex drivers to
oosen). Pull the clamps back on the hose away from
he connection. Never remove the pressure cap while the en-
gine is running, or personal injury from
scalding hot coolant or steam may result. If
possible, wait until the engine has cooled to
remove the pressure cap. If this is not possi-
ble, wrap a thick cloth around the pressure
cap and turn it slowly to the stop. Step back
while the pressure is released from the cool-
ing system. When you are sure all the pres-
sure has been released, use the cloth to turn
and remove the cao.
2. Position a clean container under the radiator
and/or engine draincock or plug, then open the drain
and allow the cooling system to drain to an appropri-
ate level. For some upper hoses, only a little coolant
must be drained. To remove hoses positioned lower
on the engine, such as a lower radiator hose, the en-
tire cooling system must be emptied.
When draining coolant, keep in mind that
cats and dogs are attracted by ethylene gly-
col antifreeze, and are quite likely to drink
any that is left in an uncovered container or
in puddles on the ground. This will prove fa-
tal in sufficient quantity. Always drain
coolant into a sealable container. Coolant
may be reused unless it is contaminated or
several years old. 9. Close the radiator or engine drains and prop-
erly refill the cooling system with the clean drained
engine coolant or a suitable mixture of ethylene gly-
cot coolant and water.
10. If available, install a pressure tester and check
for leaks. If a pressure tester is not available, run the
engine until normal operating temperature is reached
(allowing the system to naturally pressurize), then
check for leaks.
If you are checking for leaks with the system
at normal operating temperature, BE EX-
TREMELY CAREFUL not to touch any moving
or hot engine parts. Once temperature has
been reached. shut the enaine OFF. and
Fig. 85 Hoses are likely to deteriorate from
the inside if the cooling system is not peri-
odically flushed check for leaks around the-hose fittings and
connections which were removed earlier.
INSPECTION
b See Figures 88 and 87
The CV (Constant Velocity) boots should be
checked for damage each time the oil is changed and
any other time the vehicle is raised for service. These
boots keep water, grime, dirt and other damaging
matter from entering the CV-joints. Any of these
could cause early CV-joint failure which can be ex-
pensive to repair. Heavy grease thrown around the in-
side of the front wheel(s) and on the brake
caliper/drum can be an indication of a torn boot.
Thorouahlv check the boots for missina clamos and 3. Loosen the hose clamps at each end of the
rose requiring replacement. Clamps are usually ei-
4. Twist, pull and slide the hose off the fitting,
sking care not to damage the neck of the component
rom which the hose is being removed.
*If the hose is stuck at the connection, do
lot try to insert a screwdriver or other sharp
ool under the hose end in an eff art to free it,
IS the connection and/or hose may become
lamaged. Heater connections especially
nay be easily damaged by such a procedure.
f the hose is to be replaced, use a single-
!dged razor blade to make a slice along the
lortion of the hose which is stuck on the con-
section, perpendicular to the end of the
lose. 00 not cut deep so as to prevent dam-
aging the connection. The hose can then be
keeled from the connection and discarded. Fig. 86 CV-boots must be inspected period-
5.. Clean both hose mounting connections. In-
,pect the condition of the hose clamps and replace
hem, if necessary.
To install:
6. Dip the ends of the new hose into clean en-
fine coolant to ease installation.
7. Slide the clamps over the replacement hose,
hen slide the hose ends over the connections into
rosition.
8. Position and secure the clamps at least l/d in.
6.35mm) from the ends of the hose. Make sure they
Ire located beyond the raised bead of the connector.
Page 27 of 408

l-28 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
may result in skin or eye irritation or frostbite. Al- formed to help maintain the efficiency of the vehicle’s
though low in toxicity (due to chemical stability), in- A/C system. For preventive maintenance, perform the
The idle speed is factory set and usually no ad- halation of concentrated refrigerant fumes is danger- following:
justments are ever necessary. If an adjustment be- ous and can result in death; cases of fatal cardiac
l The easiest and most important preventive
comes necessary, first check that the spark plugs, in- arrhythmia have been reported in people accidentally maintenance for your A/C system is to be sure that it
jectors, idle air control servo and compression subjected to high levels of refrigerant. Some early is used on a regular basis. Running the system for
pressure are all normal. symptoms include loss of concentration and drowsi- five minutes each month (no matter what the season)
Data from various sensors and switches are used ness. + will help ensure that the seals and all internal compo-
by the ECU to determine the proper fuel/air mixture
for optimal engine performance. cGeneraiiy, the limit for exposure is lower nents remain lubricated.
for R-134a than it is for R-12. Exceptional *Some newer vehicles automatically oper-
care must be practiced when handling R- ate the A/C system compressor whenever the
134a. windshield defroster is activated. When run-
Also, refrigerants can decompose at high tempera- ning, the compressor lubricates the A/C sys
tures (near gas heaters or open flame), which may re- tern components; therefore, the A/C system
SYSTEM SERVICE& REPAIR suit in hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid and phos- would not need to be operated each month.
gene (a fatal nerve gas). * In order to prevent heater core freeze-up during
R-12 refrigerant can damage the environment be- A/C operation, it is necessary to maintain proper an-
cause it is a Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), which has tifreeze protection. Use a hand-held coolant tester
been proven to add to ozone layer depletion, leading (hydrometer) to periodically check the condition of
to increasing levels of UV radiation. UV radiation has the antifreeze in your engine’s cooling system.
been linked with an increase in skin cancer, suppres-
sion of the human immune system, an increase in *Antifreeze should not be used longer than
cataracts, damage to crops, damage to aquatic organ- the manufacturer specifies.
isms, an increase in ground-level ozone, and in- . For efficient operation of an air conditioned ve-
creased global warming. hicle’s cooling system, the radiator cap should have a
R-134a refrigerant is a greenhouse gas which, if holding pressure which meets manufacturers specifi-
allowed to vent into the atmosphere, will contribute to cations. A cap which fails to hold these pressures
global warming (the Greenhouse Effect). should be replaced.
It is usually more economically feasible to have a
l Any obstruction of or damage to the condenser
certified MVAC automotive technician perform A/C configuration will restrict air flow which is essential
system service on your vehicle. Some possible rea- to its efficient operation. It is, therefore, a good rule
sons for this are as follows: to keep this unit clean and in proper physical shape.
l While it is illegal to service an A/C system
without the proper equipment, the home mechanic ti See Figure 122
*it is recommended that the A/C svstem be
serviced by an EPA Section 609 cehified au-
tomotivetechnicfan utilizing a refrigerant re-
covery/recycling machfne.
The do-it-yourselfer should not service his/her
own vehicle’s A/C system for many reasons, includ-
ing legal concerns, personal injury, environmental
damage and cost. The following are some of the rea-
sons why you may decide not to service your own ve-
hicle’s A/C system.
According to the U.S. Clean Air Act, it is a federal
crime to service or repair (involving the refrigerant) a
Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) system for
money without being EPA certified. It is also illegal to
vent R-12 and R-134a refrigerants into the atmos-
phere. Selling or distributing A/C system refrigerant
(in a container which contains less than 20 pounds oi
refrigerant) to any person who is not EPA 609 certi-
fied is also not allowed by law.
State and/or local laws may be more strict than the
federal regulations, so be sure to check with your
state and/or local authorities for further information.
For further federal information on the legality of ser-
vicing your AK system, call the EPA Stratospheric
Ozone Hotline.
*Federal law dictates that a fine of up to
$25,000 may be levied on people convicted
of venting refrigerant into the atmosphere.
Additionally, the EPA may pay up to $10,000
for information or services leading to a crimf
nai conviction of the violation of these laws.
When servicing an A/C system you run the risk of
handling or coming in contact with refrigerant, which
Fig. 122 A label with information concern-
ing the A/C system is typically located in the
engine compartment
f would haveto purchase an expensive refrigerant re-
covery/recycling machine to service his/her own ve-
hicle.
l Since only a certified person may purchase re-
frigerant-according to the Clean Air Act, there are
specific restrictions on selling or distributing A/C
system refrigerant-it is legally impossible (unless
certified) for the home mechanic to service his/her
own vehicle. Procuring refrigerant in an illegal fash-
ion exposes one to the risk of paying a $25,000 fine
to the EPA.
R-12 Refrigerant Conversion
If your vehicle still uses R-12 refrigerant, one
way to save A/C system costs down the road is to invesh-
gate the possibility of having your system converted
to R-134a. The older R-12 systems can be easily
converted to R-134a refrigerant by a certified auto-
motive technician by installing a few new compo-
nents and changing the system oil.
The cost of R-12 is steadily rising and will con-
tinue to increase, because it is no longer imported or
manufactured in the United States. Therefore, it is of-
ten possible to have an R-12 system converted to R-
134a and recharged for less than it would cost to just
charge the system with R-12.
If you are interested in having your system con-
verted, contact local automotive service stations for
more details and information.
u See Figures 123 and 124
Although the A/C system should not be serviced
by the do-it-yourselfer, preventive maintenance can
be practiced and A/C system inspections can be per- Fig. 123 A coolant tester can be used to de-
1 termine the freezing and boiling levels of
the coolant in your vehicle
Fig. 124 To ensure efficient cooling system
operation, inspect the radiator cap gasket
and seal
Page 38 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE 1-39
leak. In most cases, you will be able to trace the leak
to a loose fitting or damaged hose.
Evaporating ethylene glycol antifreeze will have a
sweet smell and leave small, white (salt-like) de-
oosits, which can be heloful in tracino a leak. glove box and passenger side floorboard area, and
check the carpet for any signs of moisture. The
smartest way to go about finding a leak visually is to
first inspect any and all joints in the system such as
where the radiator hoses connect to the radiator and
the engine. Another thing to look for is white crusty
stains that are signs of a leak where the coolant has
6. Install the filler plug and tighten to’24 ft. Ibs.
(32 Nm).
7. If raised, carefully lower the vehicle. amount of fluid. The level should ieach thk bottom of me rating on It, lap3 1s a danciara 10 use out some
the oil filler hole. A Qss
tin,t.as ran +tw,, 4liE cars are higher. Overpressurizing the system can
lose, or worse, in the radiator or
your cooling system is con- IIC~KI LUG MU PuaJbly cause an injury or a burn if
s of a leak are probable. There the coolant is hot. Overpressurizing is normally con-
WI” U”.VlUl ,.“,,I I” 9” about finding the source of trolled by the radiator cap which has a vent valve in it
your leak. which is opened when the system reaches it’s maxi-
The first wav should be a visual insnection. Durina mum pressure rating. To pressure test the system: 7 “1sl I ly”lsJa IJ” Wll” IJU
If a the fluid level of
stantly low, the chance cause a rupture in a I:
h.n+n. nrrrn nnA . . . . ..I.
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS the visual inspection, look around the &tire engine -
area including the radiator and the heater hoses. The *The pressure test should be performed with
the enaine OFF.
A good quality ethylene glycol based or other alu-
minum compatible antifreeze is recommended for
use in the vehicles covered by this manual. It is best
to add a 50150 mix of antifreeze and distilled water to
avoid diluting the coolant in the system. interior of the car should be inspected behind the
LEVELCHECK
recovery tank and its marking as a guideline.
*Never overfill the recovery tank.
A coolant level that consistently drops is usually a
sign of a small, hard to detect leak, although in the
worst case it could be a sign of an internal engine “_y “,~--
1 Fia. 190 A visual insaection for leaks will 1
sometimes find a leak. This photo shows Fig. 191 Remove the recovery tank cap to
/ * ,, / evfdence of a leak at the upper radfator
* / /the system allow the pressure tester
to be connected to hose-to-thermostat housing junction
Fig. 189 The coolant level should be be-
1 coo,ant recovery tank tween the FULL and LOW levels on the
“‘~‘_I j Fig. 192 This cooling system requires a Fig. 193 Thread the adapter onto the re-
e’ffi1pg7 / g’051p96 / 1 covety tank threaded adapter for the recovery tank to al-
low the pressure tester to
be connected
Page 39 of 408

l-40 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
aiffiip98 Fig. 194 Pump the cooling system with pres-
sure, making sure not to overpressurize the
1 system or damage can occur
1. Remove the radiator or recovery tank cap.
2. Using the proper adapter, insert it onto the
opening and connect the pressure tester,
3. Begin pressurizing the system by pumping the
pressure tester and watching the gauge, when the
maximum pressure is reached, stop.
4. Watch the gauge carefully and see if the pres-
sure on the gauge drops, if it does, a leak is definitely
present.
5. If the pressure stayed somewhat stable, visu-
ally inspect the system for leaks, If the pressure
dropped, repressurize the system and then visually
inspect the system.
,
/ observe the pressure reading “@‘p~ 1 Fig 195 Watch the gauge on the system and
dropped more than 20%, a leak definitely exists, if
the oressure droo is less than 20%. the svstem is
most likely okay:
, cooling system when hot; serious burns can
Another way coolant is lost is by a internal engine occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
leak, causing the oil to be contaminated or the when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
coolant to be burned in the process of combustion that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
and sent out the exhaust. To check for oil contamina- glyeol antifreeze and could drink any that is
tion, remove the dipstick and check the condition of left in an uncovered container or in puddles
the oil in the oil pan. If the oil is murky and has a on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
white or beige “milkshake” look to it, the coolant is cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
contaminating the oil through an internal leak and the sealable container. Coolant should be reuser
enqine must be torn down to find the leak. If the oil mless it is contaminated or is several years
6. If no signs of a leak are noticed visually, pres-
surize the system to the maximum pressure rating of
the system and leave the uressure tester connected
fl sr about 30 minutes. Return after 30 minutes and
V erify the pressure on the gauge, if the pressure does not verify the situation, removing the spark
plugs one at a time and checking the electrodes for a
green or white tint can verify an internal coolant leak
and identify which cylinder(s) is the culprit and aiding
your search for the cause of the leak. If the spark
plugs appear okay, another method is to use a gas
analyzer or emissions tester, or one of several hand-
held tools that most professional shops possess. This
tools are used to check the cooling system for the
presence of Hydrocarbons (HC’s) in the coolant.
DRAIN & REFILL
p See figures 196 thru 205
Ensure that the engine is completely cool prior to
starting this service.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
Ippears okay, the coolant can be burned and going
jut the tailpipe. A quick test for this is a cloud of
Nhite smoke appearing from the tailpipe, especially
In start-up. On cold days, the white smoke will ap-
Iear, this is due to condensation and the outside
emperature, not a coolant leak. If the “smoke test”
Fig. 196 The draincock is usually located at
Fig. 197 Gently rotate the draincock coun-
the bottom of the radiator
terclockwise to open the draincock . . .
Fig. 199 Allow the fluid to drain until it stops
and tighten the draineock hand tight
93151p27
1. Remove the recovery tank or radiator cap.
2, Raise and support the vehicle.
3. If necessary, remove the splash shield from un
ler the front of the vehicle.
93im76 Fig, 198 . _ . then allow the coolant to drain
out of the radiator and cooling system
Fig. 200 Make sure to heed the caution on
the radiator cap and NEVER open the cap
1 when the engine is hot ,, Fig. 201 Grasp the radiator cap and rotate
it counterclockwise . . .
Page 40 of 408

.
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-41
93151p18 Fig. 202 . , . to remove the cap from the
radiator
93151p17 Fig. 205 Be sure the rubber gasket on the
radiator cap has a tight seal e Fig. 203 Pour the proper *I~ coolant mix- 1 Fig. 204 . . . make sure to fill the coolant
recovery tank to the proper level also ture into the radiator . . .
.I
4. Allow the engine to cool completely and drain fluid. Any brake fluid that is removed from
ie system again.
5. Repeat this processuntil the drained water is
lear
and free of scale.
6. Flush the recovery tank with water and leave ’
mpty. the system should be discarded. Also, do not
allow any brake fluid to come in contact with
a painted surface; it will damage the paint.
When adding fluid to the system, ONLY use fresh
DOT 3 brake fluid from a sealed container. DOT 3
brake fluid will absorb moisture when it is exposed to
.a . . . , .*a. . . * .*. . .
- Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious bums can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep In mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
4. Place a drain pan of suff i ’ 1 . . . ..I .I. 1,~ cient quantities. Always tne atmospnere, wnrcn wnr rower 1r.s oourng pomr. A
container that has been opened once, closed and
placed on a shelf will allow enough moisture to enter
over time to contaminate the fluid within. If your brake
fluid is contaminated with water, you could boil the
brake fluid under hard braking conditions and lose all
or some braking ability. Don’t take the risk, buy fresh
brake fluid whenever you must add to the system.
crenr capacrry unaer me
drain) on the radiator.
rrrasuc perwcss easuy bind; Before open-
ing a plastic radiator petcock, spray it with
some penetrating lubricant. drain coolant into a
earner. sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
The brake master cylinder ~a~~~~r,~~ :A I~nnL.4 n-n 7. Fill and bleed the cooling system as described
Brake fluid contains polyglycol ethers and
polyglycols. Avoid contact with the eyes and ,LEVEL CHECK
wash your hands thoroughly after handling
brake fluid. If vou do oet brake fluid in vour
eyes, flush your eyeswith clean, runniug wa-
a-.. ‘Y-- ar -l-..n-- II -.._ I____ k See Figures 206 thru 211
.a-11-- - __-PA._ radiator and open the petcock (
- w&1--x3_ --mm.._..- . . ..-I...
5. Drain the cooling system completely.
6. Close the petcock.
7. Remove the drain pan.
If necessary, install the splash shield under the 8.
L.-l
venicie.
9. Lower the vehicle.
10. Determine the capacity of the cooling system,
then properly refill the system at the recovery tank
and radiator with a 50/50 mixture of fresh coolant and
fKm”“ll 15 IUMLC” “II- brake booster and fire- der the hood, attached to the
wall on the drivers side of the engine compartment.
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS rer mr 13 mmures. IT eye irriIauon persim, or if you have taken brake fluid internally,
IMMEDIATELY seek medical assistance.
ala in oreerring me sysrem.
12. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the
thermostat opens (the upper radiator hose will be-
come hot). The coolant level should go down, this is
normal as the system bleeds the air pockets out of the
svstem.
IRVf!l ._._. 14. Turn the engine OFF and check for leaks. IMMEDIATELY seek medical assistance.” Brake fluid contains polyglycol ethers and
polyglycols. Avoid contact with the eyes and
wash your hands thoroughly after handling
brakefluid. If you do get brake fluid in your
eyes, flush your eyes with clean, running wa-
or if vou have taken brake fluid internallv.
Before removing the master cylinder reservoir cap,
make sure the vehicle is resting on level ground and Be careful to avoid spilling any brake fluid on
painted surfaces, because the paint coat will
become discolored or damaged.
Observe the fluid level indicators on the master
._ ._ __
‘eve1 should be between the MIN
ano
ivw unes. 13. Refill the system with coolant to the proper ter for 15 minutes; If eye irritation persists, cylinder; the tluld II
..J ..I” I....
FLUSHING & CLEANINGTHE SYSTEM
1. Drain the cooling system completely as de:
scribed earlier.
2. Close the petcock and fill the system with a
cooling system flush (clean water may also be used,
but is not as efficient).
3. Idle the engine until the upper radiator hose
gets hot. Clean, high quality brake fluid is essential to
the safe and proper operation of the brake
system. You should always buy the highest
quality brake fluid that is available. If the
brake fluid becomes contaminated, drain and
flush the system, then refill the master cylin-
der with new fluid. Never reuse any brake clean all dirt away from the top of the master cylinder.
Unscrew the cap and fill the master cylinder until the
level is between the MIN and MAX lines.
If the level of the brake fluid is less than half the
volume of the reservoir, it is advised that you check
the brake system for leaks. Leaks in a hydraulic brake
system most commonly occur at the wheel cylinder
and brake line junction points.
Page 48 of 408

DISTRIBUTOR IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERALINFORMATION 2-2
DIAGNOSISANDTESTING 2-2
SECONDARYSPARKTEST 2-2
CYLINDERDROPTEST 2-2
ADJUSTMENTS 2-3
IGNITION COIL 2-3
TESTING 2-3
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-3
POWERTRANSISTOR
(Ignition Module) 2-4
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-4
DISTRIBUTOR 2-4
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-4 2-2
INSTALLATION 2-4
CRANKSHAFTANDCAMSHAFTPOSITION
SENSORS 2-5
DISTRIBUTORLESS IGNITION
SYSTEM 2-5
GENERALINFORMATION 2-5
DIAGNOSISANDTESTING 2-5
ADJUSTMENTS 2-5
IGNITION COIL(s) 2-5
TESTING 2-5
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-6
POWERTRANSISTOR
(IGNITION MODULE) 2-7
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-7
CRANKSHAFTANDCAMSHAFTPOSITION
SENSORS 2-7
FIRING ORDERS 2-7
CHARGING SYSTEM 2-8
GENERALINFORMATION 2-8
ALTERNATORPRECAUTIONS 2-8
ALTERNATOR 2-8
TESTING 2-8 I
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-9
REGULATOR 2-10
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-10
STARTING SYSTEM 2-10
GENERALINFORMATION 2-10
STARTER 2-10
TESTING 2-10
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-11
SENDING UNITS 2-11
ENGINECOOLANTTEMPERATURE
SENDING UNIT 2-11
TESTING 2-11
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-11
OIL PRESSURESENDING UNIT 2-12
TESTING 2-12
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 2-12