1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE suspension
[x] Cancel search: suspensionPage 29 of 408

.
l-30 GENERAL'INFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
n Pylon@ inserts, the clip
be removed prior to siidi then the insert can be re
After installing the replacement
strip and pull up while twisting counterclockwise.
The backing strip will snap out of the retaining tab.
Do this for the remaining tabs until the refill is free of
the blade. The length of these refills is molded into
the end and they should be replaced with identical
types. cate the front end is out of alignment or that the tires
are out of balance.
TIRE ROTATION
# See Figures 137 and 138
Tires must be rotated periodically to equalize wear
patterns that vary with a tire’s position on the vehicle.
Tires will also wear in an uneven way as the front
1 Fin 1% Tha Trinlarlna@
cle might have any kind. Aftermarket blades and arms
rarely use the exact same type blade or refill as the
original equipment. Here are some typiel aftermarket
blades; not all may be available for your vehicle:
The Anco@ type uses a release button that is
pushed down to allow the refill to slide out of the
yoke jaws. The new refill slides back into the frame
,
and locks in place.
Some Trico@ refills are removed by locating where
the metal backing strip or the refill is wider. Insert a
small screwdriver blade between the frame and metal
backing strip. Press down to release the refill from
the retaining tab.
Other types of Trico@’ refills have two metal tabs
which are unlocked by squeezing them together. The
rubber filler can then be withdrawn from the frame
iaws. A new refill is installed bv insertina the refill lowed to touch the olass steering/suspension system wears to the point where
the alianment should be reset.
# See Figure 138
Common sense and good driving habits will af-
ford maximum tire life. Fast starts, sudden stops
and hard cornering are hard on tires and will
shorten their useful life span. Make sure that you
don’t overload the vehicle or run with incorrect
pressure in the tires. Both of these practices will in-
crease tread wear.
*For optimum tire life, keep the fires prop
eriy inflated, rotate them often and have the
wheel alignment checked periodically.
Inspect your tires frequently. Be especially care-
ful to watch for bubbles in the tread or sidewall,
deep cuts or underinflation. Replace any tires with
bubbles in the sidewall. If cuts are so deep that they
penetrate to the cords, discard the tire. Any cut in
the sidewall of a radial tire renders it unsafe. Also
look for uneven tread wear patterns that may indi- Rotating the tires will ensure maximum life for the
tires as a set, so you will not have to discard a tire
early due to wear on only part of the tread. Regular
DIRECTIONAL TIRES DIRECTIONAL TIRES
jnto the front frame jaws and &ding it rearward to
engage the remaining frame jaws. There are usually
four jaws; be certain when installing that the refill is
engaged in all of them. At the end of its travel, the
tabs will lock into place on the front jaws of the wiper
blade frame.
Another type of refill is made from polycarbonate.
The refill has a simple locking device at one end
which flexes downward out of the groove into which
the jaws of the holder fit, allowing easy release. By
sliding the new refill through all the jaws and push-
ing through the slight resistance when it reaches the
end of its travel, the refill will lock into position.
To replace the Tridon@ refill, it is necessary to re-
move the wiper blade. This refill has a plastic backing
strip with a notch about 1 in. (25mm) from the end.
Hold the blade (frame) on a hard surface so that the
frame is tightly bowed. Grip the tip of the backing Fig. 138 A label with information concern-
ing the tires is typically located on one of
the door pillars
tion”
Page 30 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENANdE 1-31
When rotating “unidirectional tires,” make sure
that they always roll in the same direction. This
means that a tire used on the left side of the vehicle
must not be switched to the right side and vice-versa.
Such tires should only be rotated front-to-rear or
rear-to-front, while always remaining on the same
side of the vehicle. These tires are marked on the
sidewall as to the direction of rotation; observe the
marks when reinstalling the tire(s).
Some styled or “mag” wheels may have different
offsets front to rear. In these cases, the rear wheels
must not be used up front and vice-versa. Further-
more, if these wheels are equipped with unidirectional
tires, they cannot be rotated unless the tire is re-
mounted for the proper direction of rotation.
*The compact or space-saver spare is
strictly for emergency use. it must never be
included in the tire rotation or placed on the
vehicle for everyday use. check the installed tire for any sign of interference
with the body or suspension while the vehicle is stop-
ping, turning sharply or heavily loaded.
Snow Tires
Good radial tires can produce a big advantage in
slippery weather, but in snow, a street radial tire does
not have sufficient tread to provide traction and con-
trol. The small grooves of a street tire quickly pack
with snow and the tire behaves like a billiard ball on a
marble floor, The more open, chunky tread of a snow
tire will self-clean as the tire turns, providing much
better grip on snowy surfaces.
To satisfy municipalities requiring snow tires dur-
ing weather emergencies, most snow tires carry either
an M + S designation after the tire size stamped on
the sidewall, or the designation “all-season.” In gen-
eral, no change in tire size is necessary when buying
snow tires.
Most manufacturers stronqlv recommend the use styled wheels, see if inexpensive steel
wheels are available, Although the look of
the vehicle will change, the expensive
wheels will be protected from salt, curb hits
and pothole damage.
TIRESTORAGE
If they are mounted on wheels, store the tires at
proper inflation pressure. All tires should be kept in a
cool, dry place. If they are stored in the garage or
basement, do not let them stand on a concrete floor;
set them on strips of wood, a mat or a large stack of
newspaper. Keeping them away from direct moisture
is of paramount importance. Tires should not be
stored upright, but in a flat position.
INFLATION & INSPECTION
b See Figures 140 thru 147
TIRE DESIGN
p See Figure 139
for maximum satisfaction, tires should be used in
sets of four. Mixing of different types (radial, bias-
belted, fiberglass belted) must be avoided. In most
cases, the vehicle manufacturer has designated a
type of tire on which the vehicle will perform best.
Your first choice when replacing tires should be to
use the same type of tire that the manufacturer rec-
ommends.
When radial tires are used, tire sizes and wheel di-
ameters should be selected to maintain ground clear-
ante and tire load caoacitv eauivalent to the oriainal
specified tire. Radial tiresshould always be used in
sets of four. of 4 snow tires on their
lehicies for reasons of stabil-
ity. If snow tires are fitter
1 only to the drive wheels, the
opposite end of the vehil cle may become very unsta-
ble when braking or turn
ring on slippery surfaces.
This instability can lead to unpleasant endings if the
A*:,,“- r-..l, ^_.. ..& ^_^^, &I.
UIIVU MII I LUUII~~MLL iue slide in time.
Note that snow tires, whether 2 or 4, will affect ve-
hicle handling in all non-snow situations. The stiffer,
heavier snow tires will noticeably change the turning
and braking characteristics of the vehicle. Once the
snow tires are installed, you must re-learn the behav-
ior of the vehicle and drive accordingly.
*Consider buying extra wheels on which to
mount the snow tires. Once done, the “snow
iheeis” can be installed and removed as
needed. This eliminates the potential
dam- age to tires or wheels from seasonal removal
and installation. Even if your vehicle has
lb The importance of proper tire inflation cannot be
overemphasized. A tire employs air as part of its
structure. It is designed around the supporting
strength of the air at a specified pressure. For this
reason, improper inflation drastically reduces the
tire’s ability to perform as intended. A tire will lose
some air in day-to-day use; having to add a few
pounds of air periodically is not necessarily a sign of
a leaking tire.
Two items should be a permanent fixture in every
glove compartment: an accurate tire pressure gauge
and a tread depth gauge. Check the tire pressure (in-
eluding the spare) regularly with a pocket type gauge.
Too often, the gauge on the end of the air hose at
vnr rr corner narane is not accurate because it suffers
~rs check tire oressure when the
Radial tires should never be used on only the
XI I._.
‘-’ --“‘“’ J s too much abuse. Alwa!
tires are cold, as pressure increases with tempera-
ture. If you must move the vehicle to check the tire
front axle.
When selecting tires, pay attention to the original
size as marked on the tire. Most tires are described
using an industry size code sometimes referred to as
P-Metric. This allows the exact identification of the
tire specifications, regardless of the manufacturer. If
selecting a different tire size or brand, remember to
METRIC TIRE SIZES
(MILLIMETERS)
145 CDNStRUCtlDN l-6-E
R - RADIAL
D
WA9
Fig. 139 P-Metric tire coding Fig. 140 Tires should be checked frequently
I I Fig. 141 Tires with deep cuts, or cuts which
for any sion of auncture or damaoe
buioe, should be replaced immediately
l DRIVE WHEEL HEAW
ACCELERATION
l OVERINFLATION
*LACK OF ROTATION
Fig. 142 Examples of inflation-related tire
RADIAL TIRE
fig. 143 Radial tires have a characteristic
sidewall bulge; don’t try to measure pres-
sure by looking at the tire. Use a quality air
pressure gauge
Page 31 of 408
.
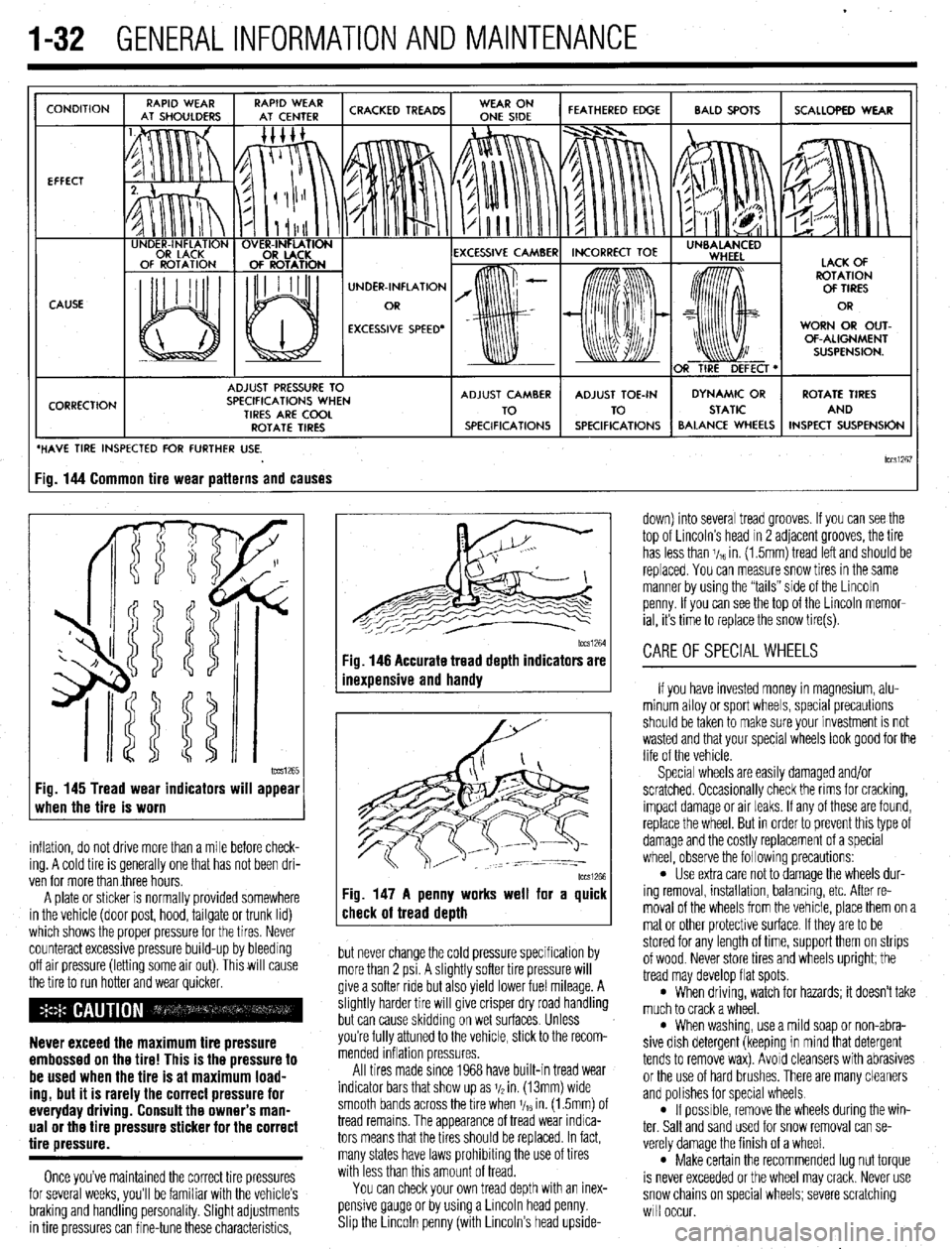
1-32 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
CONDITION
EFFECT
CAUSE
CORRECTION UNDER-INFLATION
EXCESSIVE SPEED’ WORN OR OUT-
OF-ALIGNMENT
ADJUST PRESSURE TO
SPECIFICATIONS WHEN
TIRES ARE COOL
ROTATE TIRES
/ BALANCE WHEELS INSPECT SUSPENSION
HAVE TIRE INSPECTED FOR FURTHER USE.
lCCSi267 ig. 144 Common tire wear patterns and causes
1~~~1265 Fig. 145 Tread wear indicators will appear
when the tire is worn
inflation, do not drive more than a mile before check-
ing. A cold tire is generally one that has not been dri-
ven for more than three hours.
A plate or sticker is normally provided somewhere
in the vehicle (door post, hood, tailgate or trunk lid)
which shows the proper pressure for the tires. Never
counteract excessive pressure build-up by bleeding
off air pressure (letting some air out). This will cause
the tire to run hotter and wear quicker.
Never exceed the maximum tire pressure
embossed on the tire! This is the pressure to
be used when the tire is at maximum load-
ing, but it is rarely the correct pressure for
everyday driving. Consult the owner’s man-
ual or the tire pressure sticker for the correct
tire pressure.
Once you’ve maintained the correct tire pressures
for several weeks, you’ll be familiar with the vehicle’s
braking and handling personality. Slight adjustments
in tire pressures can fine-tune these characteristics,
1~~~1264 Fig. 146 Accurate tread depth indicators are
inexuensive and handv
Fig. 147 A penny works well for a quick
check of tread death
but never change the cold pressure specification by
more than 2 psi. A slightly softer tire pressure will
give a softer ride but also yield lower fuel mileage. A
slightly harder tire will give crisper dry road handling
but can cause skidding on wet surfaces. Unless
you’re fully attuned to the vehicle, stick to the recom-
mended inflation pressures.
All tires made since 1968 have built-in tread wear
indicator bars that show up as j/2 in. (13mm) wide
smooth bands across the bre when V,~ in. (1.5mm) of
tread remains. The appearance of tread wear indica-
tors means that the tires should be replaced. In fact,
many states have laws prohibiting the use of tires
with less than this amount of tread.
You can check your own tread depth with an inex-
pensive gauge or by using a Lincoln head penny.
Shp the Lrncoln penny (with Lincoln’s head upside- down) into several tread grooves. If you can see the
top of Lincoln’s head in 2 adjacent grooves, the tire
has less than V,~ in. (1.5mm) tread left and should be
replaced. You can measure snow tires in the same
manner by using the “tails” side of the Lincoln
penny. If you can see the top of the Lincoln memor-
ial, its time to replace the snow tire(s).
CAREOFSPECIALWHEELS
If you have invested money in magnesium, alu-
minum alloy or sport wheels, special precautions
should be taken to make sure your investment is not
wasted and that your special wheels look good for the
life of the vehicle.
Special wheels are easily damaged and/or
scratched. Occasionally check the rims for cracking,
impact damage or air leaks. If any of these are found,
replace the wheel. But in order to prevent this type of
damage and the costly replacement of a special
wheel, observe the following precautions:
l Use extra care not to damage the wheels dur-
ing removal, installation, balancing, etc. After re-
moval of the wheels from the vehicle, place them on a
mat or other protective surface. If they are to be
stored for any length of time, support them on strips
of wood. Never store tires and wheels upright; the
tread may develop flat spots.
l When driving, watch for hazards; it doesn’t take
much to crack a wheel.
l When washing, use a mild soap or non-abra-
sive dish detergent (keeping in mind that detergent
tends to remove wax). Avoid cleansers with abrasives
or the use of hard brushes. There are many cleaners
and polishes for special wheels.
l If possrble, remove the wheels during the win-
ter. Salt and sand used for snow removal can se-
verely damage the finish of a wheel.
l Make certain the recommended lug nut torque
is never exceeded or the wheel may crack. Never use
snow chains on special wheels; severe scratching
will occur.
Page 32 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANC-E 1133
Used fluids such as engine oil, transaxle fluid, an-
tifreeze and brake fluid are hazardous wastes and
must be disposed of properly. Before draining any
fluids, consult with your local authorities; in many ar-
eas, waste oil, antifreeze, etc. is being accepted as a
part of recycling programs. A number of service sta-
tions and auto parts stores are also accepting waste
fluids for recycling.
Be sure of the recycling center’s policies before
draining any fluids, as many will not accept different
fluids that have been mixed together.
ENGINE OIL
6 See Figure 148
WMitsubishi recommends that SAE 5W-30
viscosity engine oil should be used for all clia
mate conditions, however, SAE low-30 is ac
ceptable for vehicles operated in moderate-
to-hot climates. the SAE number, the lighter the oil; the lower the vis-
cosity, the easier it is to crank the engine in cold
weather but the less the oil will lubricate and protect
the engine in high temperatures. This number is
marked on every oil container.
Oil viscosity’s should be chosen from those oils
recommended for the lowest anticipated temperatures
during the oil change interval. Due to the need for an
oil that embodies both good lubrication at high tem-
peratures and easy cranking in cold weather, multi-
grade oils have been developed. Basically, a multi-
grade oil is thinner at low temperatures and thicker at
high temperatures. For example, a low-40 oil (the W
stands for winter) exhibits the characteristics of a 10
weight (SAE 10) oil when the car is first started and
the oil is cold. Its lighter weight allows it to travel to
the lubricating surfaces quicker and offer less resis-
tance to starter motor cranking than, say, a straight
30 weight (SAE 30) oil. But atier the ensine reaches
operating temperature, the low-40 oil begins acting
like straight 40 weight (SAE 40) oil, its heavier weight
providing greater lubrication with less chance of
foaming than a straight 30 weight oil. Synthetic oil is not for every car and every type of
driving, so you should consider your engine’s condi-
tion and your type of driving. Also, check your car’s
warranty conditions regarding the use of synthetic oils.
FUEL
All models equipped with a SOHC (Single Over-
head Camshaft) engine are designed to operate using
regular unleaded fuel with a minimum of 87 octane.
All models equipped with a DOHC (Dual Overhead
Camshaft) engine are designed to operate using reg-
ular unleaded fuel with a minimum of 91 octane. Mit-
subishi warns that using gasoline with a lower octane
rating can cause persistent and heavy knocking, and
may cause internal engine damage.
If your vehicle is having problems with rough idle
or hesitation when the enoine is cold, it mav be
caused by low volatility fuel. If this occurs, iry a dif-
ferent grade or brand of fuel.
'OPERATION 1~ FOREIGN COUNTRIES
lccS1235 Fig. 148 look for the API oil identification
Non-detergent motor oils or straight mineral
label when choosing your enaine oil oils should not be used in your engine.
When adding oil to the crankcase or changing the
0 Nil or filter, it is important that oil of an equal quality
I original equipment be used in your car. The use of
. tc mtenor 011s may void the warranty, damage your en-
gine, or both. __
The SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) grade
number of oil indicates the viscosity of the oil (its
ability to lubricate at a given temperature). The lower
Fig. 149 Grasp the oil level dipstick and pull
upward to remove it from the dipstick
tube
The API (American Petroleum Institute) designa-
tions, also found on the oil container, indicates the
classification of engine oil used under certain given
operating conditions. Only oils designated for use
Service SJ heavy duty detergent should be used in
your car. Oils of the SJ type perform may functions If you plan to drive your car outside the United
States or Canada, there is a possibility that fuels will
be too low in anti-knock quality and could produce
engine damage. It is wise to consult with local au-
thorities upon arrival in a foreign country to deter-
mine the best fuels available.
inside the engine besides their basic lubrication.
Through a balanced system of metallic detergents
and polymeric dispersants, the oil prevents high and
low temperature deposits and also keeps sludge and
dirt particles in suspension. Acids, particularly sulfu-
OILLEVELCHECK ric acid, as well as other by-products of engine com-
bustion are neutralized by the oil. If these acids are
# See Figures 149, 150, and 151
allowed to concentrate, thev can cause corrosion and
rapid wear of the internal engine parts.
Synthetic Oil
There are many excellent synthetic and fuel-effi-
cient oils currently available that can provide better
gas mileage, longer service life and, in some cases,
better engine protection. These benefits do not come
without a few hitches, however; the main one being
the price of synthetic oil, which is significantly more
expensive than conventional oil.
.
The EPA warns that urolonoed contact with used engine oil ma; cause-a number of skin
disorders, including cancer! You should
make every effort to minimize your exposure
to
used engine oil. Protective gloves should
be worn when changing the oil. Wash your
hands and any other exposed skin areas as
soon as possible after exposure to used en-
gine oil. Soap and water, or waterless hand
cleaner should be used.
Fig. 150 Wipe the dipstick clean and rein-
sert it into the dipstick
tube to get the cor-
rect oil level The engine oil dipstick is typically located in the
Fig. 151 The oil level should be between the
marks/notches on the dipstick
Page 33 of 408
.
l-34 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Engine oil level should be checked every time you
put fuel in the vehicle or are under the hood perform- miles of highway driving. Fluid which is warmed to
normal operating temperature will flow faster, drain
ing other maintenance.
1. Park the vehicle on a level surface.
2. The enaine mav be either hot or cold when
, if it is hot, wait a few min- checking oil level. The EPA warns that prolonged contact with
used engine oil may cause a num’ * * *
dianrAnrr inrldinn ranrnrl V#lll more completely and remove more contaminants
frnm tho clnnine
utes after the engine has been turned OFF to allow the
oil to drain back into the crankcase. If the engine is
cold, do not start it before checking the oil level. point on the oil pan. If not, you may have to raise the
vehicle slightly higher on one jackstand (side) than
3. Open the hood and locate the engine oil dip-
stick. Pull the dipstick from its tube, wipe it clean,
and reinsert it. Make sure the diDstick is fullv in-
serted.
4. Pull the dipstick from its tube again. Holding it to used engin
be worn whet
handsandan
so*m ..#a . . . . .
IDer 01 SKlll u,yu,u=,+, ,,,u,uu,,,u uu,,u=, i , vu should
uff art to minimize your exposure
le oil. Protective gloves should
1 changing the oil. Wash your
y other exposed skin areas as
111 aJ vv4ble after exposure to used en-
m nil St-mn mwl w&or nr umtarlncr hand gin Y “II. ““up “ll” .,U.“I, “rn W.Y.“. .““I .I....” cleaner should be used.
horizontally, read the oil level. The oilshould be be-
tween the MIN and MAX marks or the notches on the
dipstick. If the oil is below the MIN mark or lower
notch, add oil of the proper viscosity through the
capped opening of the valve cover. *The engine oil and oil filter should be
changed at the recommended intervals on
the Maintenance Chart. Though some manu-
facturers have at times recommended chang-
ing the filter only at every other oil change, ’
Chilton recommends that you always change
ll”,,, Cl>” ““y”‘“. 1. Raise and support the vehicle safely on jack-
stands. Make sure the oil drain olua is at the lowest
the other.
2. Before you crawl under the vehicle, take a look
at where you will be working and gather all the nec-
essary tools, such as a few wrenches or a ratchet and
strip of sockets, the drain pan, some clean rags and,
if the oil filter is more accessible from underneath the
vehicle, you will also want to grab a bottle of oil, the
new filter and a filter wrench at this time.
5. Reolace the diostick. and check the level aaain
. The benefit of fresh oil
p See Figures 152 thru 153
The oil and filter should be changed every 7,500
miles (12,000 km) under normal service and every
3,000 miles (5,000 km) under severe service.
93151p-55 Fig. 152 loosen the drain plug on the en-
a wrench. The drain plug’s 3. Position the drain pan beneath the oil pan
drain plug. Keep in mind that the fast flowing oil,
which will spill out as you pull the plug from the pan,
will flow with enough force that it could miss the pan.
Position the drain pan accordingly and be ready to
move the pan more directly beneath the plug as the
oil flow lessens to a trickle.
4. Loosen the drain ~lua with a wrench (or socket
and driver), then carefuliy unscrew the plug with your
fingers. Use a rag to shield your fingers from the
heat. Push in on the plug as you unscrew it so you
draining the oil, make sure that the engine is at oper- can feel when all of the screw threads are out of the
ating temperature. Hot oil will hold more impurities hole (and so you will keep the oil from seeping past
in suspension and will flow better, allowing the re- the threads until you are ready to remove the plug).
moval of more oil and dirt. You can then remove the plug quickly to avoid hav-
It is a good idea to warm the engine oil first so it ing hot oil run down your arm. This will also help as-
will flow better. This can be accomolished bv 15-20 sure that have the plug in your hand, not in the bot-
tom of a pan of hot oil.
Fig. 153 When loosened sufficiently, slowly
turn the drain plug by hand, keeping con- Fig. 154 When you are ready, carefully pull
Fig. 156 Also inspect the drain plug th
before installing it back into the oil
Fig. 155 Clean and inspect the threads on
the oil pan Make sure the gasket on the drain plug is
in place and does not require replacement Fig. 157 A plier-type filter wrench Is used
here to loosen the filter
Page 42 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-43
l Special car washing detergent is the best to
use. Liquid dishwashing detergent can remove wax
and leave the car’s paint unprotected and in addition
some liquid detergents contains abrasives which can
scratch the paint.
l Bird droppings should be removed from the
paintwork as soon as possible, otherwise the finish
may be permanently stained.
When the car is driven immediately after be-
ing washed, apply the brakes several times
93151p14 93151p12 Fig. 215 Twist the reservoir cap, then lift up
I I
in order to remove any moisture from the
Fig. 216 Wipe the dipstick off, reinsert it braking surfaces.
on the integral cap/dipstick assembly
into the reservoir and check the level
I
Engine cleaning agents should not be used
when the engine is warm, a fire risk is pre-
sent as most engine cleaning agents are
highly flammable.
sition of the fluid against the mark on the dipstick,
Add fluid to the reservoir if the fluid does not reach
the appropriate full line.
On most models, the manufacturer doesn’t install
lubrication fittings on lube points on the steering
linkage or suspension. However, if the lubrication
point does have a grease fitting, lubricate with multi-
purpose NLGI No. 2 (Lithium base) grease.
CAR WASHING
The car should be washed at regular intervals to
remove dirt, dust, insects, and tar and other possibly
damaging stains that can adhere to the paint and may
cause damage. Proper exterior maintenance also
helps in the resale value of the vehicle by maintaining
its like-new appearance.
Mt is particularly important ta frequentiy
wash the car in the wintertime to prevent cor-
rosion, when salt has been used on the roads.
There are many precautions and tips on washing,
including the following:
l When washing the car, do not expose it do di-
rect sunlight.
. Use lukewarm water to soften the dirt before
you wash with a sponge, and plenty of water, to avoid
scratching.
l A detergent can be used to facilitate the soften-
ing of dirt and oil. * A water-soluble grease solvent may be used in
cases of sticky dirt. However, use a washplace with a
drainage separator.
l Dry the car with a clean chamois and remem-
ber to clean the drain holes in the doors and rocker
panels.
l If equipped with a power radio antenna, it must
be dried after washing.
Never clean the bumpers with gasoline or
paint thinner, always use the same agent as
used on the painted surfaces of the vehicle.
l Tar spots can be removed with tar remover or
kerosene after the car has been washed.
l A stiff-bristle brush and lukewarm soapy water
can be used to clean the wiper blades. Frequent
cleaning improves visibility when using the wipers
considerably.
l Wash off the did from the underside (wheel
housings, fenders, etc.).
l In areas of high industrial fallout, more fre-
quent washing is recommended.
During high pressure washing the spray nonle
must never be closer to the vehicle than 13
inches (30cm). Do not spray into the locks.
l When washing or steam cleaning the engine,
avoid spraying water or steam directly on the electri-
cal components or near the distributor or ignition
components. After cleaning the engine, the spark
plug wells should be inspected for water and blown
dry if necessary. Automatic car washing is a simple and quick way
to clean your car, but it is worth remembering that it
is not as thorough as when you yourself clean the
car. Keeping the underbody clean is vitally important,
and some automatic washers do not contain equip-
ment for washing the underside of the car.
When driving into an automatic was, make sure
the following precautions have been taken:
l Make sure all windows are up, and no objects
that you do not want to get wet are exposed.
l In some cases, rotating the side view mirrors
in can help to avoid possible damage.
l If your car is equipped with a power antenna,
lower it. If your vehicle has a solid mounted, non-
power antenna, it is best to remove it, but this is not
always practical. Inspect the surroundings to reduce
the risk of possible damage, and check to see if the
antenna can be manually lowered.
Most manufacturers do not recommend auto-
matic car washing in the first six months due
to the possibility of insufficient paint curing;
a safe bet is to wait until after six months of
ownership (when purchased new) to use an
automatic car wash.
WAXING
eBefore applying wax, the vehicle must be
washed and thoroughly dried.
Waxing a vehicle can help to preserve the appear-
ante of your vehicle. A wide range of polymer-based
car waxes are available today. These waxes are easy
to use and produce a long-lasting, high gloss finish
that protects the body and paint against oxidation,
road dirt, and fading.
Sometimes, waxing a neglected vehicle, or one
that has sustained chemical or natural element dam-
age (such as acid rain) require more than waxing,
and a light-duty compound can be applied. For se-
verely damaged surfaces, it is best to consult a pro-
fessional to see what would be required to repair the
damage.
Waxing procedures differ according to manufac-
turer, type, and ingredients, so it is best to consult
the directions on the wax and/or polish purchased.
Page 46 of 408
GENERAL INFORMATION AND MAINTENANCE 1-47
ramps are also a handy and safe way to both raise l When the drive wheels are to remain on the
and support the vehicle. Be careful though, some ground, leave the vehicle in gear to help prevent it
ramps may be too steep to drive your vehicle onto
The following safety points cannot be overempha- from rolling.
without scraping the front bottom panels. Never sup-
sized:
l Always use jackstands to support the vehicle
port the vehicle on any suspension member (unless l Always block the opposite wheel or wheels to when you are working underneath. Place the stands
specifically instructed to do so by a repair manual) or
keep the vehicle from rolling off the jack. beneath the vehrcle’s jacking brackets Before climb-
by an underbody panel.
l When raising the front of the vehicle, firmly ap- ing underneath, rock the vehicle a bit to make sure it
ply the parking brake. is firmly supported.
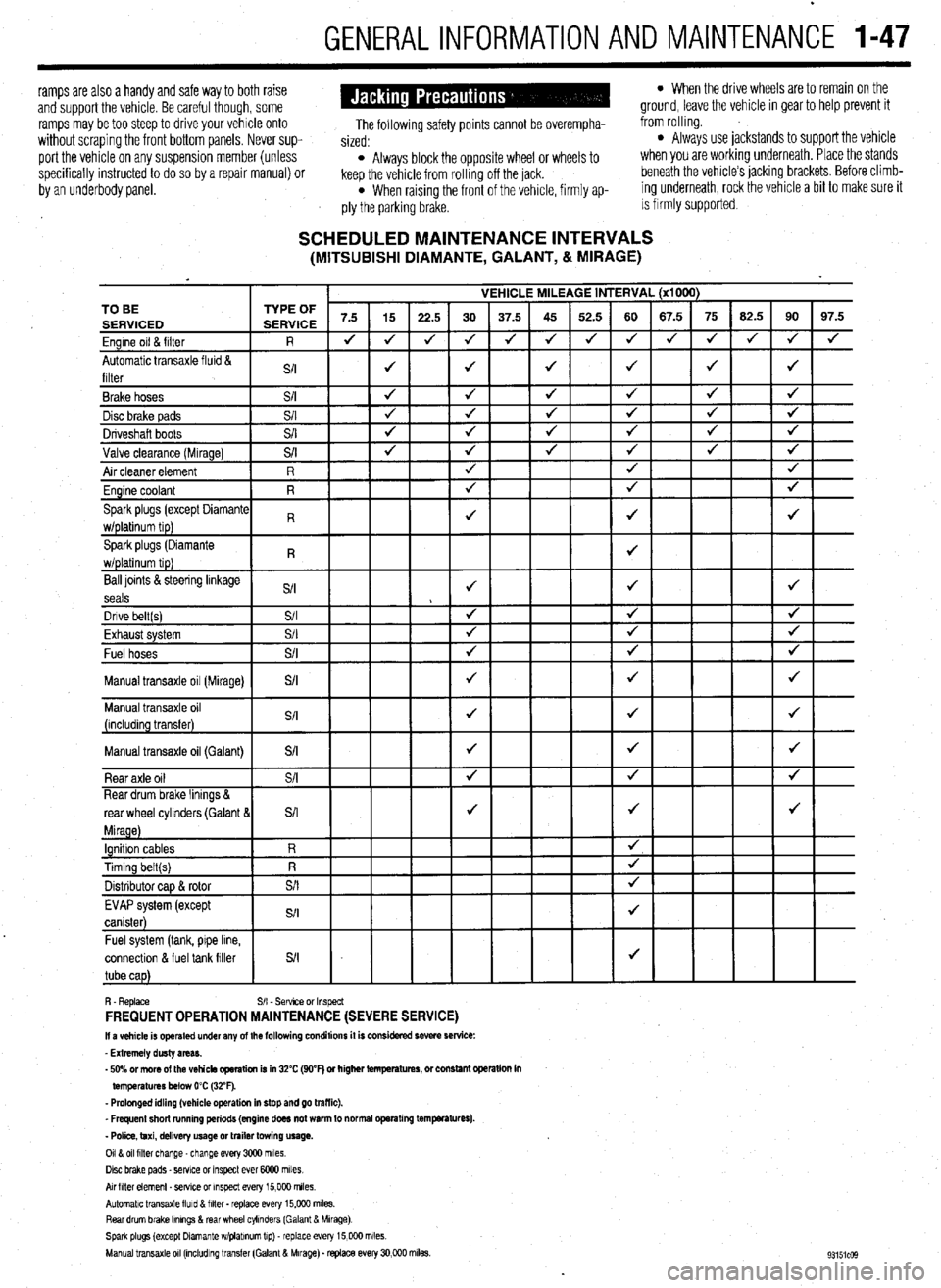
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE INTERVALS (MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE, GALANT, & MIRAGE)
VEHICLE MILEAGE INTERVAL (x1000)
7.5 15
22.5 30 37.5 45 52.5 60 67.5 75 62.5 90 97.5
J J
J 4 J J 4 4 4 J J
J 4
4
J J J J 4 TO BE
Ball loints &steering linkage
S/I J J J
seals
Dnve belt(s) S/I 4 4 J
Fvha,,rt cvctom $/I
J J J LmI,..“w. “,YL”,‘. Fuel hoses
+
Manual transaxle oil (Galant)
connectlon & fuel tank filler
R. Replace S/I - Sefwce or Inspect FREQUENT OPERATION MAINTENANCE (SEVERE SERVICE) II a vehicle is operated under any of the following conditions it is considered severe service:
- Extremely dusty areas.
- 50% or more of the vehicle operation is in 32% (WF) or higher temperatures, or constant opsralion in
temperatures below 0% (32°F).
- Prolonged idling (vehicle operation in stop and go traffic).
_ Frequent short running periods (engine does not warm to normal operating temfwatures).
- Police, taxi, delivery usage or trailer towing usage.
0118 011 filter change-change every 3CQO miles.
Disc brake pads - sewce or Inspect ever 6COO miles
AN hlter element _ setwe or inspect every 15,000 miles.
Automatic transaxle lluld 8 filter . replace every 15,COO m&s.
Rear drum brake Ikmngs & rear wheel cylinders (Galant & Mirage)
Spark plugs (except Dlamante wlplabnum tip) - replace every 15,COO miles.
Manual transaxle 011 (mcludlng transfer (Galant & Mirage). replace every 30,000 miles.
Page 58 of 408

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 2-11
l.unVeMlil(GSflWtWJ
2.Gwwator harness con- connectk,,,
3. Engme OS, level d,pst,&
4 Generator
Fig. 51 Alternator mounting -3.51 engine
The starting system includes the battery, starter
motor, solenoid, ignition switch, circuit protection
and wiring connecting the components. An inhibitor
switch located in the park/neutral safety switch or
Transmission Range (TR) sensor is included in the
starting system to prevent the vehicle from being
started with the vehicle in gear.
When the ignition key is turned to the START po-
sition, current flows and energizes the starters sole-
noid coil. The solenoid plunger and clutch shift lever
are activated and the clutch pinion engages the ring
gear on the flywheel. The switch contacts close and
the starter cranks the engine until it starts.
To prevent damage caused by excessive starter ar-
mature rotation when the engine starts, the starter in-
corporates an over-running clutch in the pinion gear. 2. Connect a voltmeter between the positive ter-
minal of the battery and the starter B+ circuit.
3. Turn the ignition key to the START position
and note the voltage on the meter.
4. If voltage reads 0.5 volts or more, there is high
resistance in the starter cables or the cable ground,
repair as necessary. If the voltage reading is ok pro-
teed to the next step.
5. Connect a voltmeter between the positive ter-
minal of the battery and the starter M circuit,
6. Turn the ignition key to the START position
and note the voltage on the meter.
7. If voltage reads 0.5 volts or more, there is high
resistance in the starter. Repair or replace the starter
as necessary.
*Many automotive parts stores have starter
bench testers available for use by customers.
A starter bench test is the most definitive
way to determine the condition of your
starter. 3. Remove the resonator retaining nuts and re-
move the air intake hose and resonator assembly as
required.
rllse care when removing the air cleaner
cover because the air-flow sensor is attached
and is a sensitive component.
4. If equipped with Active-ECS suspension, re-
move the air compressor as follows:
a. Detach the two electrical connectors, from
the compressor.
b. Disconnect the air line at the compressor.
c. Remove the three mounting bolts, securing
the compressor to the chassis.
5. Raise the vehicle and support safely.
6. Remove the engine undercover.
7. Remove the heat shield from beneath the in-
take manifold on the 1.5L engine.
8. If necessary, detach the speedometer cable
connector at the transaxle end.
9. Detach the starter motor electrical connac-
TESTING
Voltage Drop Test
*The battery must be in good condition and
fully charged prior to performing this test. REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
# See Figures 52 and 53
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Detach the air-flow sensor assembly connec-
tor and remove the breather hose.
1. Disable the ignition system by unplugging the
coil pack. Verify that the vehicle will not start. tions.
10. Remove the starter motor mounting bolts and
remove the starter.
11. The installation is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Tighten the starter mounting bolts to 22 ft.
Ibs. (31 Nm).
12. Connect the negative battery cable and check
the starter for proper operation.
9315zp19 Fig. 53 Location of the two starter retaining bolts