2021 ALFA ROMEO STELVIO child seat
[x] Cancel search: child seatPage 174 of 280

SAFETY
172
damage by themselves are not good indicators
of whether or not an air bag should have
deployed.
Seat belts are necessary for your protection in
all collisions, and also are needed to help keep
you in position, away from an inflating air bag.
When the Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
detects a collision requiring the front air bags,
it signals the inflator units. A large quantity of
non-toxic gas is generated to inflate the front
air bags.
The steering wheel hub trim cover and the
upper passenger side of the instrument panel
separate and fold out of the way as the air
bags inflate to their full size. The front air bags
fully inflate in less time than it takes to blink
your eyes. The front air bags then quickly
deflate while helping to restrain the driver and
front passenger.
Knee Impact Bolsters
The Knee Impact Bolsters help protect the
knees of the driver and front passenger, and
position the front occupants for improved
interaction with the front air bags.
Supplemental Driver And Front Passenger
Knee Air Bags
This vehicle is equipped with a Supplemental
Driver Knee Air Bag mounted in the instrument
panel below the steering column and a
Supplemental Passenger Knee Air Bag
mounted in the instrument panel below the
glove compartment. The Supplemental Knee
Air Bags provide enhanced protection during a
frontal impact by working together with the
seat belts, pretensioners, and front air bags.
Supplemental Side Air Bags
Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air Bags
(SABs)
This vehicle is equipped with Supplemental
Seat-Mounted Side Air Bags (SABs).
Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air Bags
(SABs) are located in the outboard side of the
front seats. The SABs are marked with “SRS
AIRBAG” or “AIRBAG” on a label or on the seat
trim on the outboard side of the seats.
The SABs may help to reduce the risk of occu-
pant injury during certain side impacts, in addi-
tion to the injury reduction potential provided
by the seat belts and body structure. Front Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air
Bag
When the SAB deploys, it opens the seam on
the outboard side of the seatback’s trim cover.
The inflating SAB deploys through the seat
seam into the space between the occupant
and the door. The SAB moves at a very high
speed and with such a high force that it could
injure occupants if they are not seated prop -
erly, or if items are positioned in the area
where the SAB inflates. Children are at an
even greater risk of injury from a deploying air
bag.
WARNING!
Do not drill, cut, or tamper with the knee
impact bolsters in any way.
Do not mount any accessories to the knee
impact bolsters such as alarm lights,
stereos, citizen band radios, etc.
WARNING!
Do not use accessory seat covers or place
objects between you and the Side Air Bags;
the performance could be adversely
affected and/or objects could be pushed
into you, causing serious injury.
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 172
Page 175 of 280

173
(Continued)
Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable Curtains
(SABICs)
This vehicle is equipped with Supplemental
Side Air Bag Inflatable Curtains (SABICs).
Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable Curtains
(SABICs) are located above the side windows.
The trim covering the SABICs is labeled “SRS
AIRBAG” or “AIRBAG.”Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable Curtain (SABIC) Location SABICs may help reduce the risk of head and
other injuries to front and rear seat outboard
occupants in certain side impacts, in addition
to the injury reduction potential provided by
the seat belts and body structure.
The SABIC deploys downward, covering the
side windows. An inflating SABIC pushes the
outside edge of the headliner out of the way
and covers the window. The SABICs inflate
with enough force to injure occupants if they
are not belted and seated properly, or if items
are positioned in the area where the SABICs
inflate. Children are at an even greater risk of
injury from a deploying air bag.
The SABICs may help reduce the risk of partial
or complete ejection of vehicle occupants
through side windows in certain side impact
events.
Side Impacts
The Side Air Bags are designed to activate in
certain side impacts. The Occupant Restraint
Controller (ORC) determines whether the
deployment of the Side Air Bags in a particular
impact event is appropriate, based on the
severity and type of collision. The side impact
sensors aid the ORC in determining the appro
-
priate response to impact events. The system
is calibrated to deploy the Side Air Bags on the
impact side of the vehicle during impacts that
require Side Air Bag occupant protection. In
side impacts, the Side Air Bags deploy inde -
pendently; a left side impact deploys the left
Side Air Bags only and a right-side impact
deploys the right Side Air Bags only. Vehicle
damage by itself is not a good indicator of
whether or not Side Air Bags should have
deployed.
The Side Air Bags will not deploy in all side
collisions, including some collisions at certain
angles, or some side collisions that do not
impact the area of the passenger
WARNING!
Do not mount equipment, or stack luggage
or other cargo up high enough to block the
deployment of the SABICs. The trim
covering above the side windows where the
SABIC and its deployment path are located
should remain free from any obstructions.
In order for the SABICs to work as intended,
do not install any accessory items in your
vehicle which could alter the roof. Do not
add an aftermarket sunroof to your vehicle.
Do not add roof racks that require perma -
nent attachments (bolts or screws) for
installation on the vehicle roof. Do not drill
into the roof of the vehicle for any reason.
WARNING! (Continued)
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 173
Page 176 of 280

SAFETY
174
(Continued)
compartment. The Side Air Bags may deploy
during angled or offset frontal collisions where
the front air bags deploy.
Side Air Bags are a supplement to the seat belt
restraint system. Side Air Bags deploy in less
time than it takes to blink your eyes.
NOTE:
Air bag covers may not be obvious in the inte-
rior trim, but they will open during air bag
deployment.
Rollover Events
Side Air Bags and seat belt pretensioners are
designed to activate in certain rollover events.
The Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
determines whether deployment in a partic -
ular rollover event is appropriate, based on the
severity and type of collision. Vehicle damage
by itself is not a good indicator of whether or
not Side Air Bags and seat belt pretensioners
should have deployed.
The Side Air Bags and seat belt pretensioners
will not deploy in all rollover events. The roll -
over sensing system determines if a rollover
event may be in progress and whether deploy -
ment is appropriate. In the event the vehicle
experiences a rollover or near rollover event, and deployment is appropriate, the rollover
sensing system will deploy the side air bags
and seat belt pretensioners on both sides of
the vehicle.
The SABICs may help reduce the risk of partial
or complete ejection of vehicle occupants
through side windows in certain rollover or
side impact events.
Air Bag System Components
NOTE:
The Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC) moni
-
tors the internal circuits and interconnecting
wiring associated with electrical Air Bag
System Components listed below:
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
Air Bag Warning Light
Steering Wheel and Column
Instrument Panel
Knee Impact Bolsters
Driver and Front Passenger Air Bags
Seat Belt Buckle Switch
Supplemental Side Air Bags
Supplemental Knee Air Bags
Front and Side Impact Sensors
Seat Belt Pretensioners
Seat Track Position Sensors
WARNING!
Occupants, including children, who are up
against or very close to Side Air Bags can
be seriously injured or killed. Occupants,
including children, should never lean on or
sleep against the door, side windows, or
area where the side air bags inflate, even
if they are in an infant or child restraint.
Seat belts (and child restraints where appro -
priate) are necessary for your protection in
all collisions. They also help keep you in
position, away from an inflating Side Air Bag.
To get the best protection from the Side Air
Bags, occupants must wear their seat belts
properly and sit upright with their backs
against the seats. Children must be properly
restrained in a child restraint or booster seat
that is appropriate for the size of the child.
WARNING!
Side Air Bags need room to inflate. Do not
lean against the door or window. Sit
upright in the center of the seat.
Being too close to the Side Air Bags during
deployment could cause you to be
severely injured or killed.
Relying on the Side Air Bags alone could
lead to more severe injuries in a collision.
The Side Air Bags work with your seat belt
to restrain you properly. In some colli -
sions, Side Air Bags won’t deploy at all.
Always wear your seat belt even though
you have Side Air Bags.
WARNING! (Continued)
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 174
Page 180 of 280

SAFETY
178
Event Data Recorder (EDR)
This vehicle is equipped with an event data
recorder (EDR). The main purpose of an EDR is
to record, in certain crash or near crash-like
situations, such as an air bag deployment or
hitting a road obstacle, data that will assist in
understanding how a vehicle’s systems
performed. The EDR is designed to record data
related to vehicle dynamics and safety
systems for a short period of time, typically 30
seconds or less. The EDR in this vehicle is
designed to record such data as:
How various systems in your vehicle were
operating;
Whether or not the driver and passenger
safety belts were buckled/fastened;
How far (if at all) the driver was depressing
the accelerator and/or brake pedal; and,
How fast the vehicle was traveling.
These data can help provide a better under -
standing of the circumstances in which
crashes and injuries occur.
NOTE:
EDR data are recorded by your vehicle only if a
non-trivial crash situation occurs; no data are
recorded by the EDR under normal driving
conditions and no personal data (e.g., name,
gender, age, and crash location) are recorded.
However, other parties, such as law enforce -
ment, could combine the EDR data with the
type of personally identifying data routinely
acquired during a crash investigation. To read data recorded by an EDR, special
equipment is required, and access to the
vehicle or the EDR is needed. In addition to the
vehicle manufacturer, other parties, such as
law enforcement, that have the special equip
-
ment, can read the information if they have
access to the vehicle or the EDR.
Child Restraints
Everyone in your vehicle needs to be buckled
up at all times, including babies and children.
Every state in the United States, and every
Canadian province, requires that small chil -
dren ride in proper restraint systems. This is
the law, and you can be prosecuted for
ignoring it.
Children 12 years or younger should ride prop -
erly buckled up in a rear seat, if available.
According to crash statistics, children are
safer when properly restrained in the rear
seats rather than in the front. There are different sizes and types of
restraints for children from newborn size to
the child almost large enough for an adult
safety belt. Always check the child seat
Owner’s Manual to make sure you have the
correct seat for your child. Carefully read and
follow all the instructions and warnings in the
child restraint Owner’s Manual and on all the
labels attached to the child restraint.
Before buying any restraint system, make sure
that it has a label certifying that it meets all
applicable Safety Standards. You should also
make sure that you can install it in the vehicle
where you will use it.
NOTE:
For additional information, refer to
http://
www.nhtsa.gov/parents-and-caregivers
or
call: 1–888–327–4236
Canadian residents should refer to Trans -
port Canada’s website for additional infor -
mation:
https://www.tc.gc.ca/en/services/
road/child-car-seat-safety.html
WARNING!
In a collision, an unrestrained child can
become a projectile inside the vehicle. The
force required to hold even an infant on
your lap could become so great that you
could not hold the child, no matter how
strong you are. The child and others could
be badly injured or killed. Any child riding in
your vehicle should be in a proper restraint
for the child’s size.
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 178
Page 181 of 280

179
(Continued)
Summary Of Recommendations For Restraining Children In Vehicles
Infant And Child Restraints
Safety experts recommend that children ride
rear-facing in the vehicle until they are two
years old or until they reach either the height
or weight limit of their rear-facing child
restraint. Two types of child restraints can be
used rear-facing: infant carriers and convert
-
ible child seats.
The infant carrier is only used rear-facing in
the vehicle. It is recommended for children
from birth until they reach the weight or height
limit of the infant carrier. Convertible child
seats can be used either rear-facing or
forward-facing in the vehicle. Convertible child
seats often have a higher weight limit in the
rear-facing direction than infant carriers do, so
they can be used rear-facing by children who have outgrown their infant carrier but are still
less than at least two years old. Children
should remain rear-facing until they reach the
highest weight or height allowed by their
convertible child seat.
Older Children And Child Restraints
Children who are two years old or who have
outgrown their rear-facing convertible child
seat can ride forward-facing in the vehicle.
Forward-facing child seats and convertible
child seats used in the forward-facing direc
-
tion are for children who are over two years old
or who have outgrown the rear-facing weight
Child Size, Height, Weight Or AgeRecommended Type Of Child Restraint
Infants and Toddlers Children who are two years old or younger
and who have not reached the height or
weight limits of their child restraint Either an Infant Carrier or a Convertible Child
Restraint, facing rearward in a rear seat of the
vehicle
Small Children Children who are at least two years old or
who have outgrown the height or weight
limit of their rear-facing child restraint Forward-Facing Child Restraint with a
five-point Harness, facing forward in a rear
seat of the vehicle
Larger Children Children who have outgrown their
forward-facing child restraint, but are too
small to properly fit the vehicle’s seat belt Belt Positioning Booster Seat and the vehicle
seat belt, seated in a rear seat of the vehicle
Children Too Large for Child Restraints Children 12 years old or younger, who have
outgrown the height or weight limit of their
booster seat Vehicle Seat Belt, seated in a rear seat of the
vehicle
WARNING!
Never place a rear-facing child restraint in
front of an air bag. A deploying passenger
front air bag can cause death or serious
injury to a child 12 years or younger,
including a child in a rear-facing child
restraint.
Never install a rear-facing child restraint in
the front seat of a vehicle. Only use a
rear-facing child restraint in the rear seat.
If the vehicle does not have a rear seat, do
not transport a rear-facing child restraint
in that vehicle.
WARNING! (Continued)
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 179
Page 182 of 280

SAFETY
180
(Continued)
or height limit of their rear-facing convertible
child seat. Children should remain in a
forward-facing child seat with a harness for as
long as possible, up to the highest weight or
height allowed by the child seat.
All children whose weight or height is above
the forward-facing limit for the child seat
should use a belt-positioning booster seat
until the vehicle’s seat belts fit properly. If the
child cannot sit with knees bent over the
vehicle’s seat cushion while the child’s back is
against the seatback, they should use a
belt-positioning booster seat. The child and
belt-positioning booster seat are held in the
vehicle by the seat belt.
Children Too Large For Booster Seats
Children who are large enough to wear the
shoulder belt comfortably, and whose legs are
long enough to bend over the front of the seat
when their back is against the seatback,
should use the seat belt in a rear seat. Use thissimple 5-step test to decide whether the child
can use the vehicle’s seat belt alone:
1. Can the child sit all the way back against
the back of the vehicle seat?
2. Do the child’s knees bend comfortably over the front of the vehicle seat – while
the child is still sitting all the way back?
3. Does the shoulder belt cross the child’s shoulder between the neck and arm?
4. Is the lap part of the belt as low as possible, touching the child’s thighs and
not the stomach?
5. Can the child stay seated like this for the whole trip?
If the answer to any of these questions was
“no,” then the child still needs to use a booster
seat in this vehicle. If the child is using the lap/
shoulder belt, check seat belt fit periodically
and make sure the seat belt buckle is latched.
A child’s squirming or slouching can move the
belt out of position. If the shoulder belt
contacts the face or neck, move the child
closer to the center of the vehicle, or use a
booster seat to position the seat belt on the
child correctly.
WARNING!
Improper installation can lead to failure of
an infant or child restraint. It could come
loose in a collision. The child could be
badly injured or killed. Follow the child
restraint manufacturer’s directions
exactly when installing an infant or child
restraint.
After a child restraint is installed in the
vehicle, do not move the vehicle seat
forward or rearward because it can loosen
the child restraint attachments. Remove
the child restraint before adjusting the
vehicle seat position. When the vehicle
seat has been adjusted, reinstall the child
restraint.
When your child restraint is not in use,
secure it in the vehicle with the seat belt or
LATCH anchorages, or remove it from the
vehicle. Do not leave it loose in the
vehicle. In a sudden stop or accident, it
could strike the occupants or seatbacks
and cause serious personal injury.
WARNING! (Continued)
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 180
Page 183 of 280
181
Recommendations For Attaching Child Restraints
Lower Anchors And Tethers For CHildren
(LATCH) Restraint System
LATCH LabelYour vehicle is equipped with the child
restraint anchorage system called LATCH,
which stands for Lower Anchors and Tethers
for CHildren. The LATCH system has three
vehicle anchor points for installing
LATCH-equipped child seats. There are two
lower anchorages located at the back of the
seat cushion where it meets the seatback and
one top tether anchorage located behind the
seating position. These anchorages are used
to install LATCH-equipped child seats without
using the vehicle’s seat belts. Some seating
positions may have a top tether anchorage but
no lower anchorages. In these seating posi
-
tions, the seat belt must be used with the top
tether anchorage to install the child restraint.
Please see the following table for more infor -
mation.
WARNING!
Never allow a child to put the shoulder belt under an arm or behind their back. In a crash, the shoulder belt will not protect a child properly,
which may result in serious injury or death. A child must always wear both the lap and shoulder portions of the seat belt correctly.
Restraint Type
Combined Weight of the Child + Child RestraintUse Any Attachment Method Shown With An “X” Below
LATCH – Lower Anchors OnlySeat Belt Only
LATCH – Lower
Anchors + Top Tether AnchorSeat Belt + Top Tether Anchor
Rear-Facing Child Restraint Up to 65 lbs (29.5 kg)
XX
Rear-Facing Child Restraint More than 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) X
Forward-Facing Child Restraint Up to 65 lbs (29.5 kg)
XX
Forward-Facing Child Restraint More than 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) X
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 181
Page 184 of 280
SAFETY
182
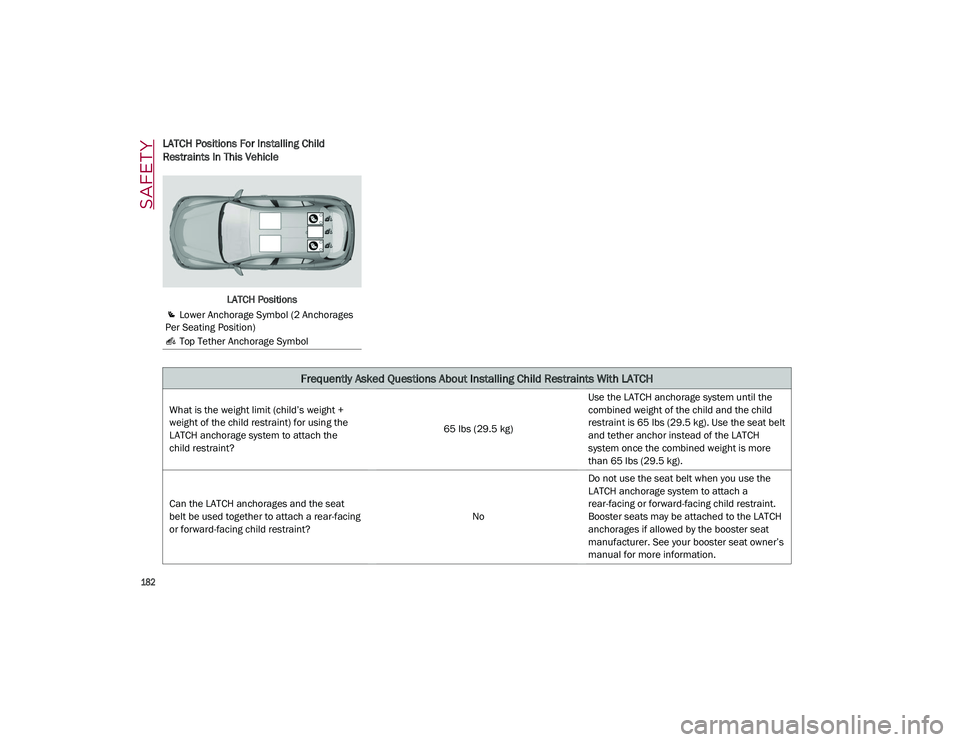
LATCH Positions For Installing Child
Restraints In This Vehicle
LATCH Positions
Lower Anchorage Symbol (2 Anchorages
Per Seating Position)
Top Tether Anchorage Symbol
Frequently Asked Questions About Installing Child Restraints With LATCH
What is the weight limit (child’s weight +
weight of the child restraint) for using the
LATCH anchorage system to attach the
child restraint? 65 lbs (29.5 kg)Use the LATCH anchorage system until the
combined weight of the child and the child
restraint is 65 lbs (29.5 kg). Use the seat belt
and tether anchor instead of the LATCH
system once the combined weight is more
than 65 lbs (29.5 kg).
Can the LATCH anchorages and the seat
belt be used together to attach a rear-facing
or forward-facing child restraint? NoDo not use the seat belt when you use the
LATCH anchorage system to attach a
rear-facing or forward-facing child restraint. Booster seats may be attached to the LATCH
anchorages if allowed by the booster seat
manufacturer. See your booster seat owner’s
manual for more information.
21_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 182