2016 NISSAN NOTE ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 2076 of 3641
IP-8
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
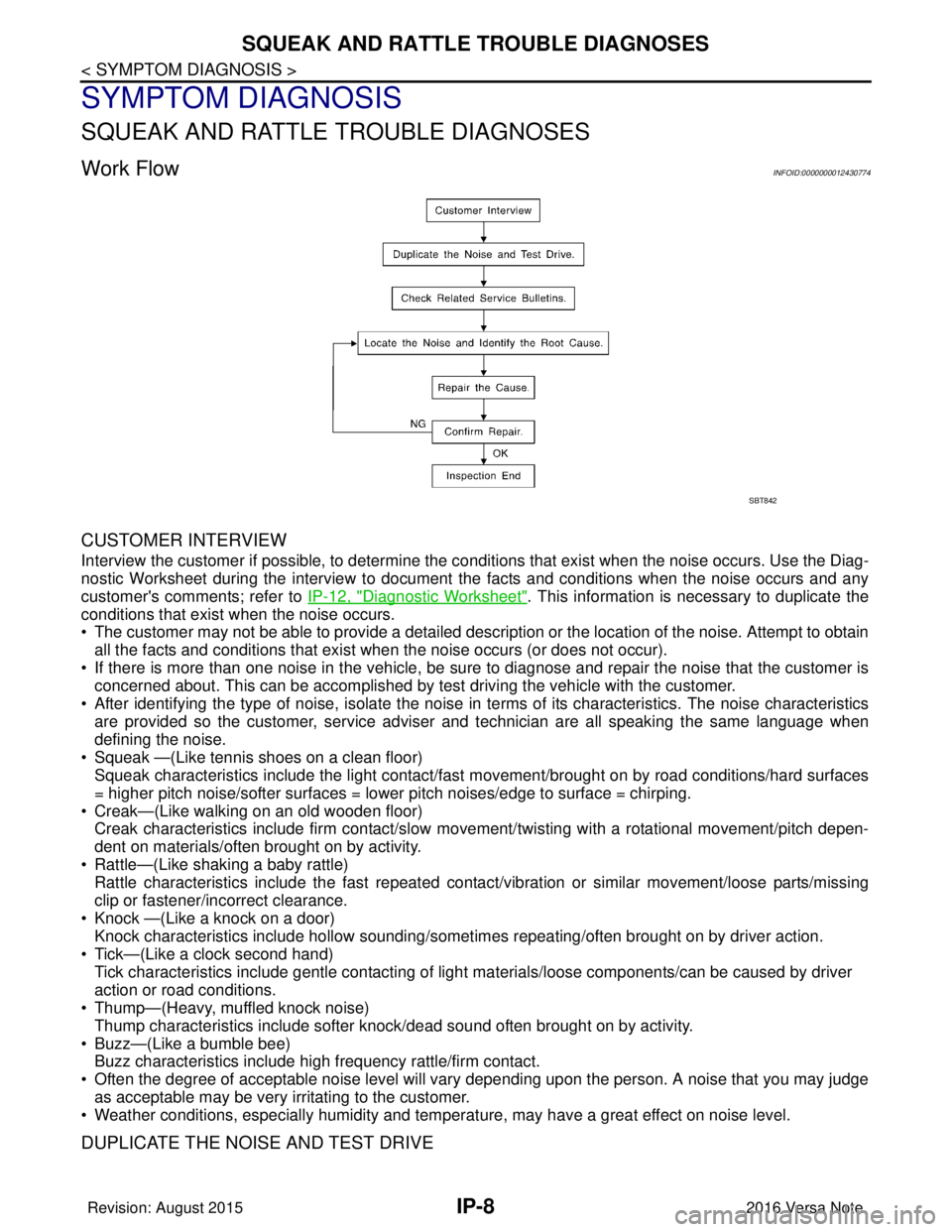
Work FlowINFOID:0000000012430774
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-12, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist w hen the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor) Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor) Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle) Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door) Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee) Buzz characteristics include hi gh frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperat ure, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
SBT842
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2160 of 3641
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESINT-9
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
C
DE
F
G H
I
K L
M A
B
INT
N
O P
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
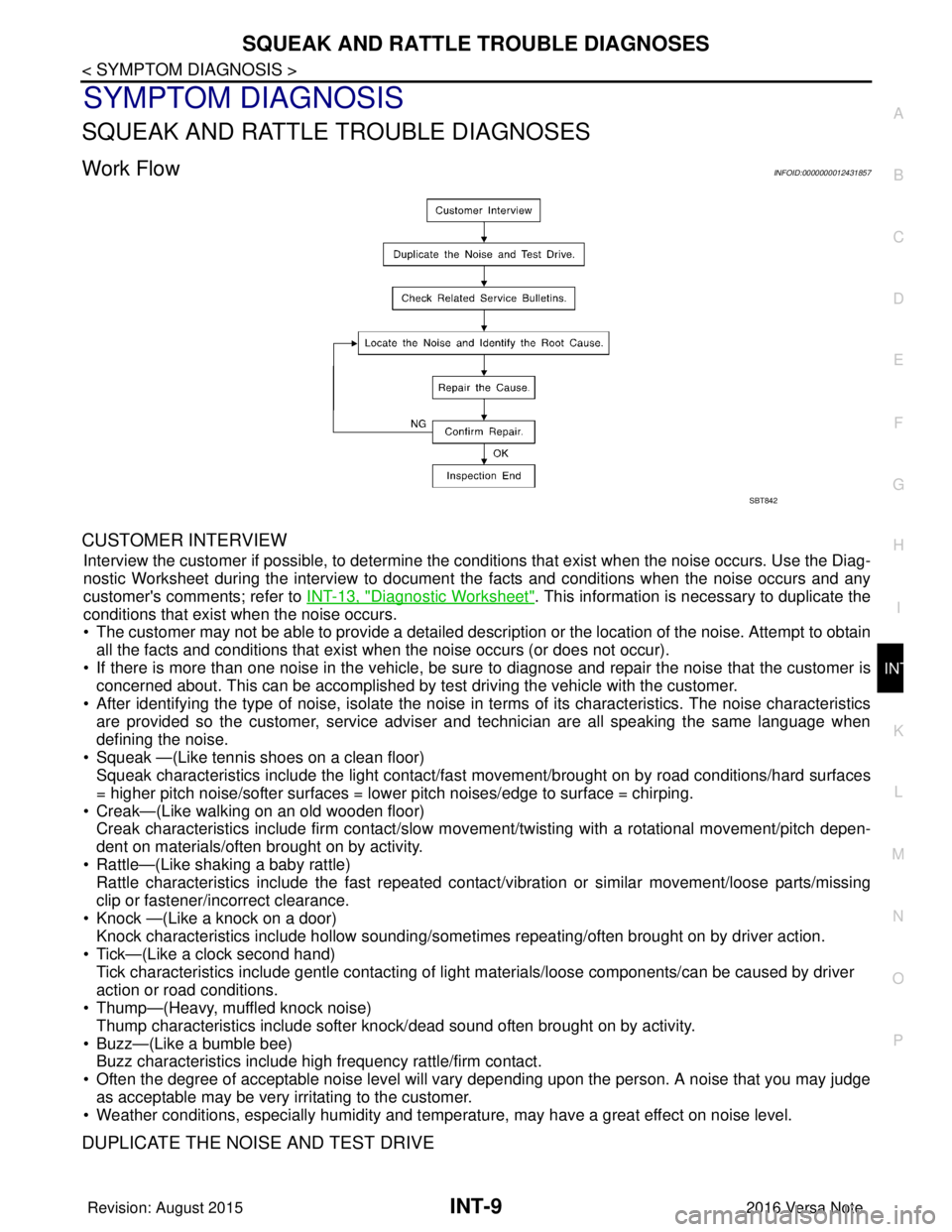
Work FlowINFOID:0000000012431857
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interv iew to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to INT-13, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed descr iption or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor) Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor) Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle) Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door) Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of li ght materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee) Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
SBT842
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2201 of 3641
![NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual LAN
TROUBLE DIAGNOSISLAN-13
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN FUNDAMENTAL]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
• Response to the system call
• Control unit diagnosis information
• Self-diagnosis
• CAN dia NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual LAN
TROUBLE DIAGNOSISLAN-13
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN FUNDAMENTAL]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
• Response to the system call
• Control unit diagnosis information
• Self-diagnosis
• CAN dia](/manual-img/5/57363/w960_57363-2200.png)
LAN
TROUBLE DIAGNOSISLAN-13
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN FUNDAMENTAL]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
• Response to the system call
• Control unit diagnosis information
• Self-diagnosis
• CAN diagnostic support monitor
Self-DiagnosisINFOID:0000000012433336
If communication signals cannot be transmitted or rece
ived among control units communicating via CAN com-
munication line, CAN communication-related DTC is displayed on the CONSULT “Self Diagnostic Result”
screen.
NOTE:
The following table shows examples of CAN communicati on-related DTC. For other DTC, refer to the applica-
ble sections.
CAN Diagnostic Support MonitorINFOID:0000000012433337
MONITOR ITEM (CONSULT)
Example: CAN DIAG SUPPORT MNTR indication
Without PAST
DTC Self-diagnosis item
(CONSULT indication) DTC detection condition
Inspection/Action
U1000 CAN COMM CIRCUIT ECM
When ECM is not transmitting or receiving CAN
communication signal of OBD (emission-relat-
ed diagnosis) for 2 seconds or more.
Start the inspection. Re-
fer to the applicable sec-
tion of the indicated
control unit.
Except
for ECM
When a control unit (except for ECM) is not
transmitting or receiving CAN communication
signal for 2 seconds or more.
U1001 CAN COMM CIRCUIT When ECM is not transmitting or receiving CAN communi-
cation signal other than OBD (emission-related diagnosis)
for 2 seconds or more.
U1002 SYSTEM COMM When a control unit is not transmitting or receiving CAN
communication signal for 2 seconds or less.
U1010 CONTROL UNIT(CAN) When an error is detected during the initial diagnosis for
CAN controller of each control unit. Replace the control unit
indicating “U1010”.
JSMIA0964GB
Item
PRESENT Description
Initial diagnosis OK Normal at present
NG Control unit e rror (Except for some control units)
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2215 of 3641
![NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual LAN
SYSTEMLAN-27
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
The CAN communication line is a twisted pair wire consisting of
strands of CAN-H (1) and CAN-L (2) and has noise immunity.
N NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual LAN
SYSTEMLAN-27
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
The CAN communication line is a twisted pair wire consisting of
strands of CAN-H (1) and CAN-L (2) and has noise immunity.
N](/manual-img/5/57363/w960_57363-2214.png)
LAN
SYSTEMLAN-27
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION > [CAN]
C
D
E
F
G H
I
J
K L
B A
O P
N
The CAN communication line is a twisted pair wire consisting of
strands of CAN-H (1) and CAN-L (2) and has noise immunity.
NOTE:
The CAN communication system has the characteristics of noise-resistant because this system produces dig-
ital signals by using the potential difference between
the CAN-H line and the CAN-L line and has the twisted
pair wire structure.
Since the CAN-H line and the CAN-L line are always adjacent to
each other, the same degree of noise occurs, respectively, when a
noise (1) occurs. Although the noise changes the voltage, the poten-
tial difference (2) between the CAN-H line and the CAN-L line is
insensitive to noise. Therefore, noise-resistant signals can be
obtained.
CAN Signal Communications
Each control unit of the CAN communication system transmits signals through the CAN communication con-
trol circuit included in the control unit and receives only necessary signals from each control unit to perform
various kinds of control.
• Example: Transmitted signals
JSMIA0382ZZ
JSMIA0383ZZ
JSMIA0576GB
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2482 of 3641
MIR-8
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
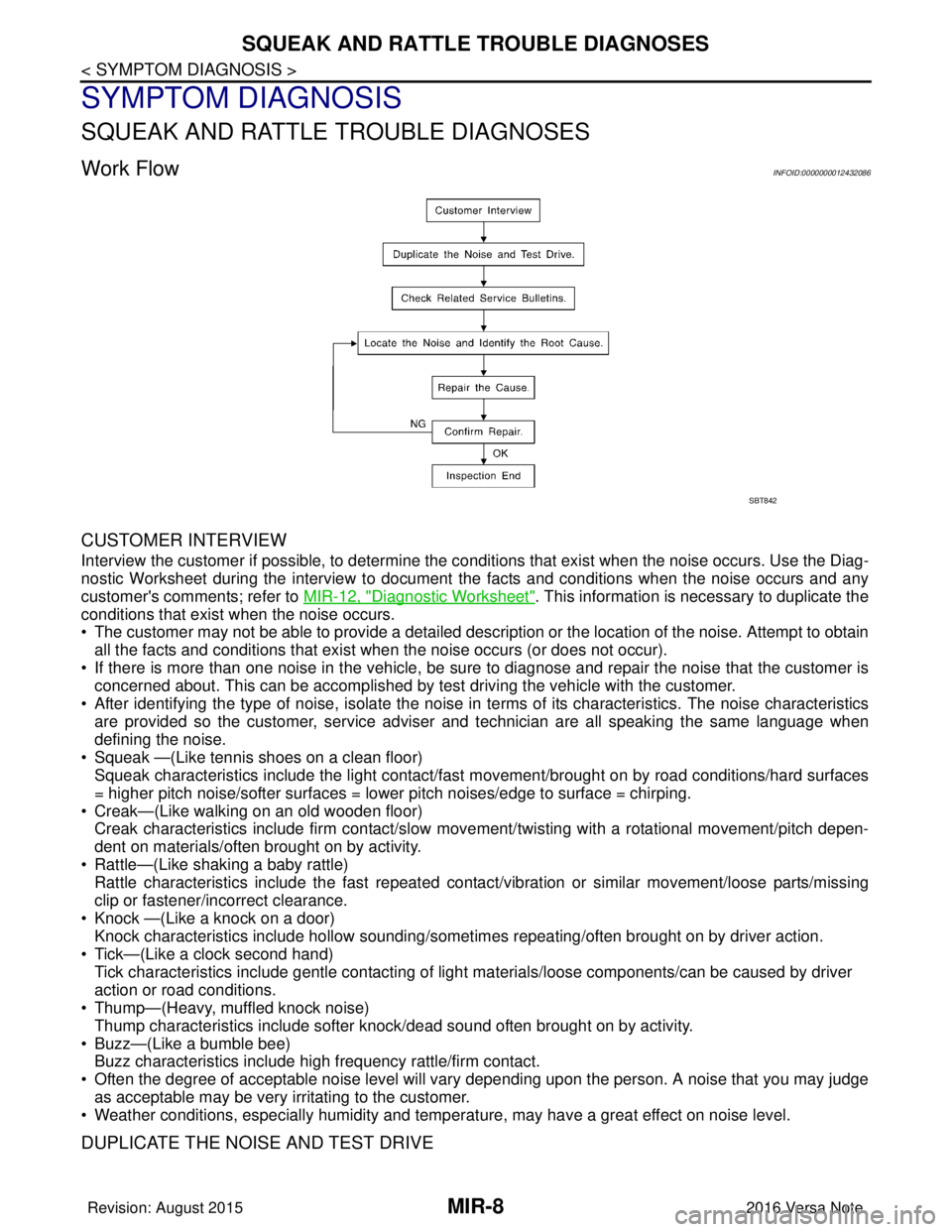
Work FlowINFOID:0000000012432086
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to MIR-12, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist w hen the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor) Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor) Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle) Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door) Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee) Buzz characteristics include hi gh frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperat ure, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
SBT842
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2559 of 3641
![NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-56
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433301
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERFORM SE NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-56
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433301
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERFORM SE](/manual-img/5/57363/w960_57363-2558.png)
PCS-56
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
B2614 ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433301
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERFORM SELF DIAGNOSTIC RESULT
1. Turn ignition switch to ACC, and wait for 1 second or more.
2. Check “Self Diagnostic Result” of “BCM” using CONSULT.
Is DTC B2614 detected?
YES >> Go to PCS-56, "Diagnosis Procedure".
NO >> Inspection End.
Diagnosis ProcedureINFOID:0000000012433302
Regarding Wiring Diagram information, refer to PCS-42, "Wiring Diagram".
1.CHECK ACCESSORY RELAY-2 CONTROL SIGNAL VOLTAGE
1. Disconnect accessory relay-2 connector.
2. Check voltage between accessory relay-2 connector M39 terminal 1 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> GO TO 3.
NO >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK ACCESSORY RELAY-2 CONTROL SIGNAL CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector M98.
3. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 96 and accessory relay-2 connector M39 terminal 1.
4. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 96 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> Replace BCM. Refer to BCS-74, "Removal and Installation".
NO >> Repair or replace harness or connectors.
CONSULT Display DTC detecting condition Possible cause
ACC RELAY CIRCUIT
[B2614] An immediate operation of accessory relay-2 is re-
quested by BCM, but there is no response for more
than 1 second. • Harness or connectors.
• Accessory relay-2.
•BCM.
Accessory relay-2
GroundCondition Vo l ta g e
(Approx.)
Connector Terminal
M39 1—Ignition: OFF
0 V
Ignition: ACC or ON Battery voltage
BCM Accessory relay-2
Continuity
Connector TerminalConnector Terminal
M 989 6M 39 1 Y es
BCM
GroundContinuity
Connector Terminal
M98 96 No
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2561 of 3641
![NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-58
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433303
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERF NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-58
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433303
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERF](/manual-img/5/57363/w960_57363-2560.png)
PCS-58
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
B2615 BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433303
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.PERFORM SELF DIAGNOSTIC RESULT
1. Turn ignition switch to ON, and wait for 1 second or more.
2. Check “Self Diagnostic Result” of “BCM” using CONSULT.
Is DTC B2615 detected?
YES >> Go to PCS-60, "Diagnosis Procedure".
NO >> Inspection End.
Diagnosis ProcedureINFOID:0000000012433304
Regarding Wiring Diagram information, refer to PCS-42, "Wiring Diagram".
1.CHECK BLOWER RELAY CONTROL SIGNAL VOLTAGE
1. Remove blower relay.
2. Check voltage between blower relay connector J-1 terminal 2 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> GO TO 3.
NO >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK BLOWER RELAY CONTROL SIGNAL CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector M98.
3. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 106 and blower relay connector J-1 terminal 2.
4. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 106 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> Replace BCM. Refer to BCS-74, "Removal and Installation".
NO >> Repair or replace harness or connectors.
CONSULT Display DTC Detection Condition Possible Cause
BLOWER RELAY CIRCUIT
[B2615] An immediate operation of blower relay is requested
by BCM, but there is no response for more than 1
second. • Harness or connectors.
• Blower relay.
• Fuse block J/B.
•BCM.
Blower relay
GroundCondition Vo l ta g e
(Approx.)
Connector Terminal
J-1 2—Ignition: OFF
0 V
Ignition: ON Battery voltage
BCM Blower relay
Continuity
Connector TerminalConnector Terminal
M98 106J-1 2Yes
BCM
GroundContinuity
Connector Terminal
M98 106 No
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 2563 of 3641
![NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-60
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433305
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1. NISSAN NOTE 2016 Service Repair Manual PCS-60
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433305
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1.](/manual-img/5/57363/w960_57363-2562.png)
PCS-60
< DTC/CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS >[POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM]
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
B2616 IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
DTC LogicINFOID:0000000012433305
DTC DETECTION LOGIC
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1. PERFORM SELF DIAGNOSTIC RESULT
1. Turn ignition switch to ON, and wait for 1 second or more.
2. Check “Self Diagnostic Result” of “BCM” using CONSULT.
Is DTC B2616 detected?
YES >> Refer to PCS-60, "Diagnosis Procedure".
NO >> Inspection End.
Diagnosis ProcedureINFOID:0000000012433306
Regarding Wiring Diagram information, refer to PCS-42, "Wiring Diagram".
1.CHECK IGNITION RELAY-2 CONTROL SIGNAL VOLTAGE
1. Remove ignition relay-2.
2. Check voltage between ignition relay-2 connector J-3 terminal 1 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> GO TO 3.
NO >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK IGNITION RELAY-2 CONTROL SIGNAL CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector M98.
3. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 99 and ignition relay-2 connector J-3 terminal 1.
4. Check continuity between BCM connector M98 terminal 99 and ground.
Is the inspection result normal?
YES >> Replace BCM. Refer to BCS-74, "Removal and Installation".
NO >> Repair or replace harness or connectors.
CONSULT Display DTC Detection Condition Possible Cause
IGNITION RELAY CIRCUIT
[B2616] An immediate operation of ignition relay-2 is re-
quested by BCM, but there is no response for more
than 1 second. • Harness or connectors.
• Ignition relay-2.
• Fuse block J/B.
•BCM.
Ignition relay-2
Ground Condition Vo l ta g e
(Approx.)
Connector Terminal
J-3 1—Ignition: OFF
0 V
Ignition: ON Battery voltage
BCM Ignition relay-2
Continuity
Connector TerminalConnector Terminal
M98 99J-3 1Yes
BCM
GroundContinuity
Connector Terminal
M98 99 No
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com