Page 121 of 212

WARNING (Continued)
● Children are exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an acci-
dent if they lean forward or adopt an incorrect seated position when the vehi-
cle is moving. This particularly applies to children who are transported on the
front passenger seat if the airbag system deploys in the event of an accident.
This can result in severe or even fatal injuries.
● It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts are
to offer their maximum protection ⇒
page 107, How are seat belts correctly
fastened?. Pay particular attention to the information provided by the manu-
facturer of the child safety seat regarding correct routing of the belt. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents.
● Safety belts must be checked to ensure that they are running properly.
One should also ensure that the belt is not damaged by sharp-edged fittings.
● It is essential to always switch off the front passenger front airbag when
attaching a child safety seat to the front passenger seat where the child is
seated with its back facing in direction of travel ⇒ page 116. If this is not done,
there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal injuries if the front
passenger front airbag is deployed. When transporting a child on the front
passenger seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations re-
garding the use of child safety seats.
Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat Child safety seats should always be attached to the rear seats.
Fig. 105 Sticker on the centre column of
the body on the front passenger side. We recommend, for safety reasons, that you always mount a child restraint sys-
tems on the rear seats whenever possible. If you still decide, however, to use a
child safety seat on the front passenger seat then you must pay attention to the
following warnings in connection with the use of the airbag system on the front
passenger seat. WARNING
● Warning - particular hazard! Never use a child safety seat on the front pas-
senger seat in which the child is seated with its back facing the direction of
travel. This child safety seat is positioned in the deployment area of the front
passenger airbag. The airbag may cause the child severe, or even fatal injuries,
in the event of it being deployed.
● This is also clearly stated on the sticker which is located on the centre col-
umn of the body on the front passenger side ⇒ fig. 105. The sticker is visible
upon opening the front passenger door. For some countries, the sticker is also
affixed to the sun visor of the front passenger.
● It is essential to always switch off the front passenger front airbag when a
child safety seat is nevertheless attached to the front passenger seat where
the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel ⇒
page 116, Deacti-
vating airbags. If this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or
even fatal injuries if the front passenger front airbag is deployed. When trans-
porting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with the appropri-
ate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
● If the front passenger front airbag has been switched off by a specialist
garage using the vehicle system tester, the side and head passenger airbag
remains switched on. Please comply with any differing national legal regula-
tions regarding the use of child safety seats.
● If a child safety seat in which the child faces in the direction of travel is
used on the front passenger seat, the front passenger seat must be moved
back and to the top fully. Move the seat backrest into the vertical position.
● You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just as
soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the front passenger seat. 119
Transporting children safely Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 122 of 212
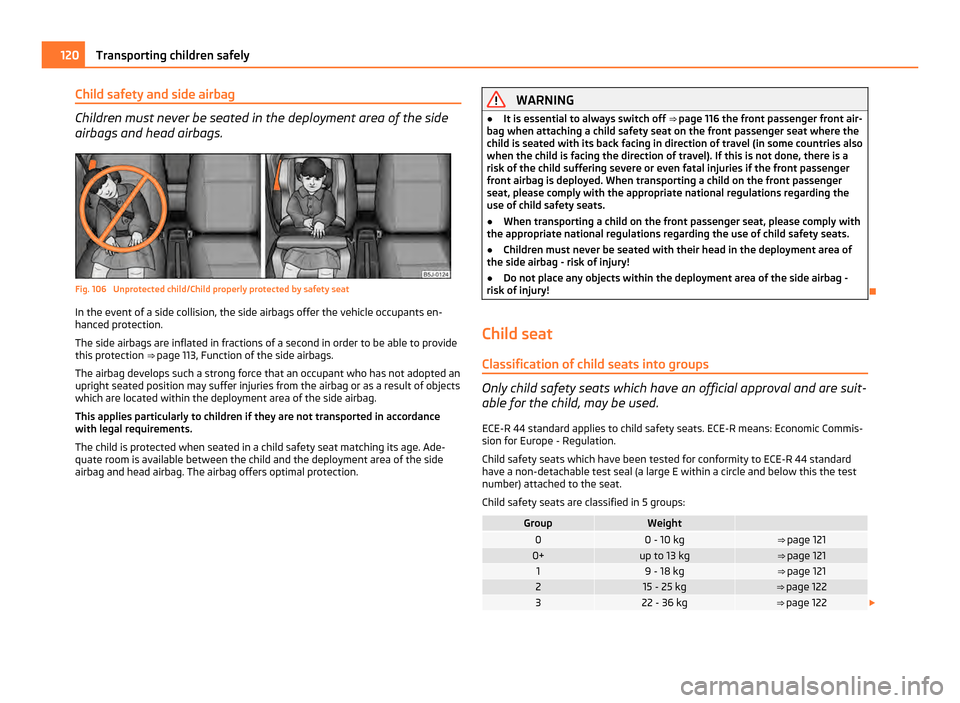
Child safety and side airbag
Children must never be seated in the deployment area of the side
airbags and head airbags.
Fig. 106 Unprotected child/Child properly protected by safety seat
In the event of a side collision, the side airbags offer the vehicle occupants en-
hanced protection.
The side airbags are inflated in fractions of a second in order to be able to provide
this protection
⇒
page 113, Function of the side airbags.
The airbag develops such a strong force that an occupant who has not adopted an
upright seated position may suffer injuries from the airbag or as a result of objects
which are located within the deployment area of the side airbag.
This applies particularly to children if they are not transported in accordance
with legal requirements.
The child is protected when seated in a child safety seat matching its age. Ade-
quate room is available between the child and the deployment area of the side
airbag and head airbag. The airbag offers optimal protection. WARNING
● It is essential to always switch off ⇒ page 116 the front passenger front air-
bag when attaching a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the
child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries also
when the child is facing the direction of travel). If this is not done, there is a
risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger
front airbag is deployed. When transporting a child on the front passenger
seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
● When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with
the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
● Children must never be seated with their head in the deployment area of
the side airbag - risk of injury!
● Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side airbag -
risk of injury!
Child seat Classification of child seats into groups Only child safety seats which have an official approval and are suit-
able for the child, may be used.
ECE-R 44 standard applies to child safety seats. ECE-R means: Economic Commis-
sion for Europe - Regulation.
Child safety seats which have been tested for conformity to ECE-R 44 standard
have a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below this the test
number) attached to the seat.
Child safety seats are classified in 5 groups: Group Weight
0 0 - 10 kg ⇒
page 121 0+ up to 13 kg ⇒
page 121 1 9 - 18 kg ⇒
page 121 2 15 - 25 kg ⇒
page 122 3 22 - 36 kg ⇒
page 122 £120
Transporting children safely
Page 123 of 212

Children who are more than 1.50 m in height or who weigh more than 36 kg can
use normal seat belts without a seat bolster.
Use of child seats An overview of the usefulness of child seats on each of the seats according to the
ECE-R 44 standard: Child seat of
the group Front passenger
seat Rear seat
outside Rear seat
middle 0 U U
+
T U
+ T
0+ U U
+
T U
+ T
1 U U
+
T U
+ T
2 and 3 U U U
Universal category - seat is suitable for all approved types of child safety
seats.
The seat can be fitted with fixing eyes for the
“ISOFIX ”system.
The seat is equipped as standard with the fixing system “Top Tether ”.
Child seats of group 0/0+ Fig. 107 Child seats of group 0/0+
The optimal solution for babies of up to about 9 months old weighing up to 10 kg
or children up to about 18 months old weighing up to 13 kg is a child safety seat
which is fastened in the opposite direction of travel ⇒
fig. 107.
U +
T Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of
travel should not be used on the front passenger seat when the vehicle is fitted
with a front passenger airbag
⇒
page 119, Use of child safety seats on the front
passenger seat. WARNING
● It is essential to always switch off the front passenger front airbag at a
specialist garage or with the switch for front passenger airbag when attaching
in exceptional circumstances a child safety seat on the front passenger seat
where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel ⇒
page 117.
● Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
● If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat may suffer
severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag or airbags are de-
ployed.
● You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just as
soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the front passenger seat.
Child safety seats in Group 1 Fig. 108 Child seat with padded table in
Group 1 installed on rear seat bench fac-
ing the direction of travel
Child seats in Group 1 are for babies and small children up to 4 years of age with a
weight of between 9 and 18 kilograms. It is best for children in the lower range of
this group, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit with its back to the di-
rection of travel. It is best for children in the upper range of the Group 0+, to use a
child seat which allows the child to sit ⇒ fig. 108 in the direction of travel. £ 121
Transporting children safely Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 124 of 212
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of
travel should not be used on the front passenger seat when the vehicle is fitted
with a front passenger airbag
⇒
page 119, Use of child safety seats on the front
passenger seat. WARNING
● It is essential to always switch off the front passenger front airbag at a
specialist garage or with the switch for front passenger airbag when attaching
in exceptional circumstances a child safety seat on the front passenger seat
where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel ⇒
page 117.
● Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
● If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat may suffer
severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag or airbags are de-
ployed.
● You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just as
soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the front passenger seat.
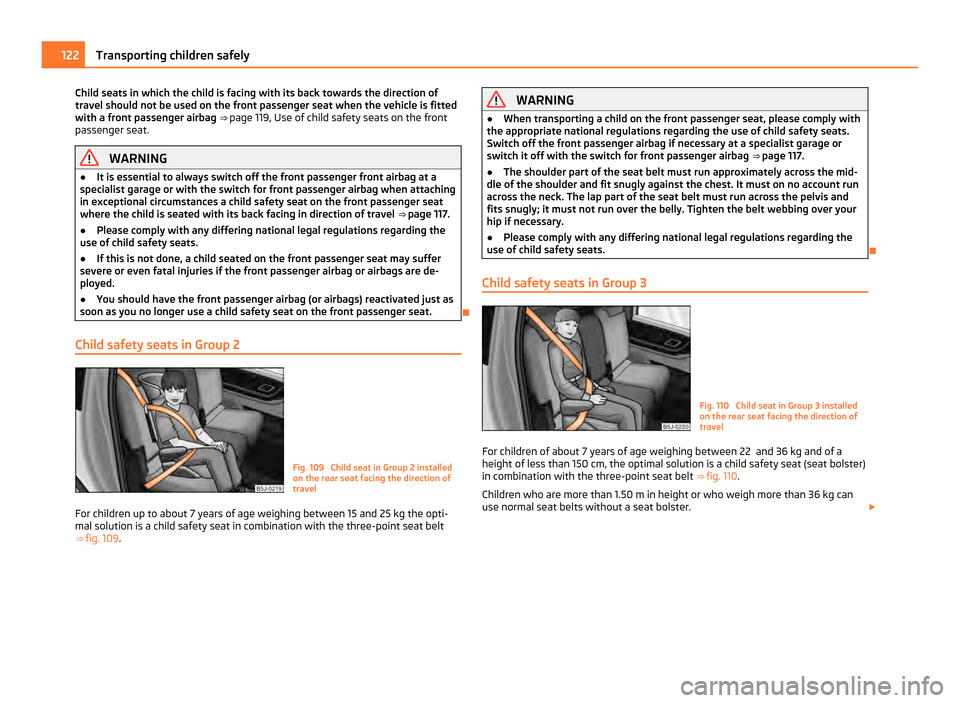
Child safety seats in Group 2 Fig. 109 Child seat in Group 2 installed
on the rear seat facing the direction of
travel
For children up to about 7 years of age weighing between 15 and 25 kg the opti-
mal solution is a child safety seat in combination with the three-point seat belt
⇒ fig. 109 . WARNING
● When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with
the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
Switch off the front passenger airbag if necessary at a specialist garage or
switch it off with the switch for front passenger airbag ⇒
page 117.
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately across the mid-
dle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest. It must on no account run
across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and
fits snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your
hip if necessary.
● Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
Child safety seats in Group 3 Fig. 110 Child seat in Group 3 installed
on the rear seat facing the direction of
travel
For children of about 7 years of age weighing between 22 and 36 kg and of a
height of less than 150
cm, the optimal solution is a child safety seat (seat bolster)
in combination with the three-point seat belt ⇒ fig. 110 .
Children who are more than 1.50 m in height or who weigh more than 36 kg can
use normal seat belts without a seat bolster. £122
Transporting children safely
Page 125 of 212

WARNING
● When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with
the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
Switch off the front passenger airbag if necessary at a specialist garage or
switch it off with the switch for front passenger airbag ⇒
page 117.
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately across the mid-
dle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest. It must on no account run
across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and
fits snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your
hip if necessary.
● Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
Attaching a child seat using the “ISOFIX” system Fig. 111 Push locking eyes (ISOFIX system)/ISOFIX child seat into the installed mounting fun-
nels
There are two locking eyes between the rear exterior seat backrest and the sur-
face of the seat itself on both sides for fixing the
“ISOFIX” system child seat in
place.
– Insert the mounting funnels A onto the locking eyes
B between the seat
backrest and the seat cushion ⇒
fig. 111.
– Push the notched arms of the child seat into the locking eyes until they are
heard to lock in place ⇒
fig. 111.
– Pull on both sides of the child seat! One can mount a child safety seat using the “ISOFIX” system quickly, easily and
reliably. Please pay close attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the
child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.
Child seats fitted with the
“ISOFIX” system can only be mounted and fixed in a ve-
hicle fitted with an “ISOFIX” system when these child seats have been released
for this type of vehicle according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
Child safety seats with the fixing system “ISOFIX” can be obtained from ŠKODA
Original Accessories.
Complete installation instructions are enclosed with the child safety seat. WARNING
● The locking eyes have just been developed for child safety seats which use
the
“ISOFIX” system. You should therefore never attach other child safety
seats, seat belts or objects to the locking eyes - hazard!
● Before using a child seat with an “ISOFIX” system that you bought for an-
other vehicle, it is recommended that you consult an authorised
ŠKODA Serv-
ice Partner whether the child seat is suitable for your vehicle.
● Certain child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system can be attached with
standard three-point seat belts. Please pay close attention to instructions
from the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing
the seat. Note
● Child seats which use the
“ISOFIX” system are currently available for children
weighing up to about 18 kg. This corresponds to an age range up to 4 years.
● The child seats can also be fitted with the “Top Tether” system ⇒
page 124. 123
Transporting children safely Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 126 of 212
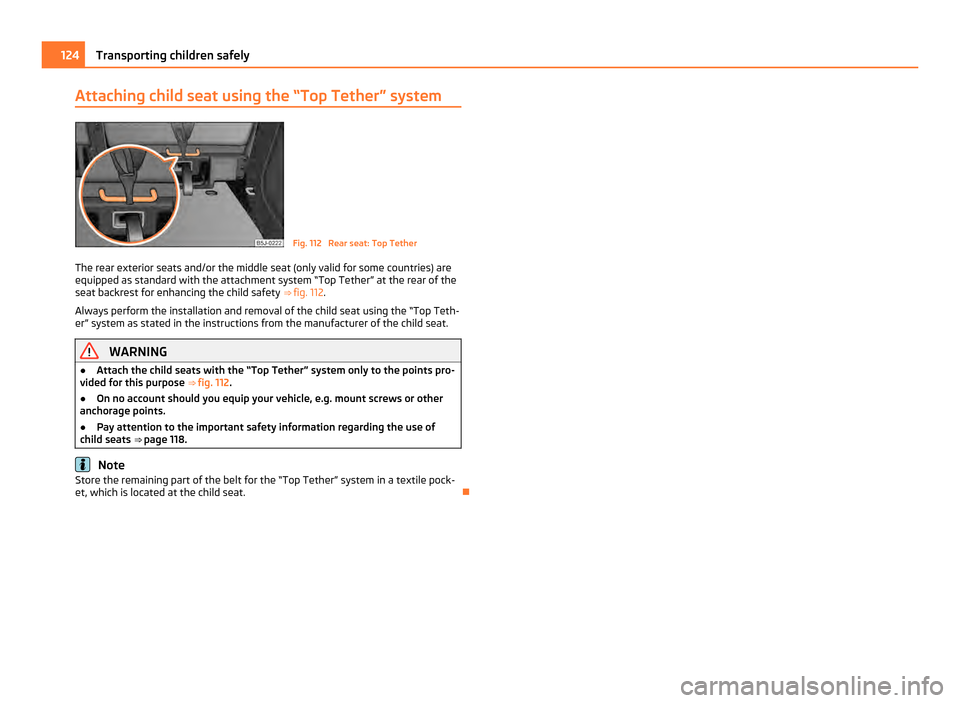
Attaching child seat using the “Top Tether” system
Fig. 112 Rear seat: Top Tether
The rear exterior seats and/or the middle seat (only valid for some countries) are
equipped as standard with the attachment system “Top Tether” at the rear of the
seat backrest for enhancing the child safety ⇒ fig. 112.
Always perform the installation and removal of the child seat using the “Top Teth-
er” system as stated in the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat. WARNING
● Attach the child seats with the
“Top Tether” system only to the points pro-
vided for this purpose ⇒ fig. 112.
● On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
anchorage points.
● Pay attention to the important safety information regarding the use of
child seats ⇒
page 118. Note
Store the remaining part of the belt for the “Top Tether” system in a textile pock-
et, which is located at the child seat. 124
Transporting children safely
Page 127 of 212

Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology Electronic stability programme (ESP)
General General
The ESP aids you in maintaining control of your vehicle in situations in which the
vehicle is driving at its dynamic limits, such as entering a curve fast. The risk of
skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on
the conditions of the road surface. The system operates at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
● Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
● Traction control system (TCS),
● Antilock brake system (ABS),
● Brake Assist,
● Uphill Start Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts
a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It al-
so processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive
sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle about its vertical axis, the lateral ac-
celeration of the vehicle, the braking pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual be-
haviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the car beginning to skid, the
ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is
braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front
wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle
to break away) while occurs this is on the inner rear wheel of a vehicle which
tends to understeer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle
is accompanied by noises. During an intervention of the system, the warning light
flashes quickly in the
instrument cluster.
The ESP system cannot be switched off, only the TCS system can be switched off
by pressing the button ⇒
fig. 113. The warning light ⇒ page 25 lights up if the
TCS system is switched off.
The warning light lights up permanently if there is a fault in the ESP system.
The fact that the ESP system operates together with the ABS means that the ESP
warning light will also come on if the ABS system is not operating properly.
If the warning light comes on immediately after starting the engine, the ESP
system can be switched off for technical reasons. In this case, the ESP system can
be switched on again by switching the ignition on and off. If the warning light
goes out, the ESP system is fully functional again. WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the vehi-
cle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your style of
driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation. This par-
ticularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident! Note
● All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve prob-
lem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can
lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒
page 166, Ac-
cessories, changes and replacement of parts. 125
Intelligent Technology Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 128 of 212

Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual wheel from
slipping.
Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part of the
driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sen-
sors. Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will
be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function
brakes the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to
the other driven wheel. This control process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in order to
avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being
braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as
a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down. WARNING
● Carefully depress the accelerator when accelerating on uniformly slippery
road surfaces, such as ice and snow. The driven wheels might still spin despite
the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
● You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road sur-
face and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL. The
increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than other-
wise - risk of an accident! Note
● If the ABS or ASR or, where applicable, ESP indicator light lights up, the EDl
may have a fault. Have the vehicle inspected by your specialist garage as soon as
you can.
● Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL ⇒
page 166,
Accessories, changes and replacement of parts.
Traction control system (TCS) The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spin-
ning when accelerating.
Fig. 113 TCS switch
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, acceler-
ate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavoura-
ble.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts
a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of
the ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force transmitted to the road sur-
face is automatically adapted by reducing the engine speed. The system operates
at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS ⇒ page 128, Antilock brake system
(ABS)
. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS system.
The TCS warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on
the TCS ⇒ page 24. £126
Intelligent Technology
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13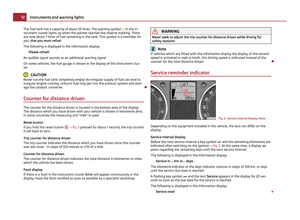 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44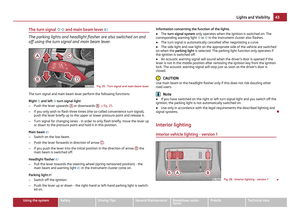 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53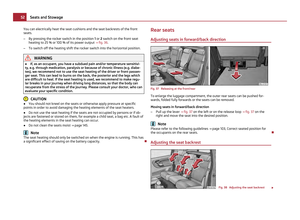 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60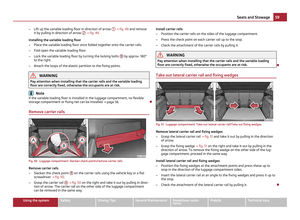 61
61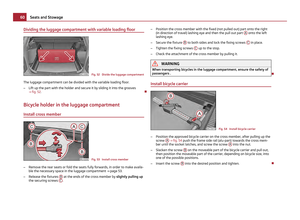 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65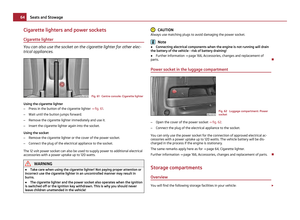 66
66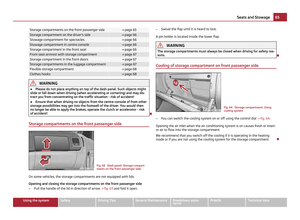 67
67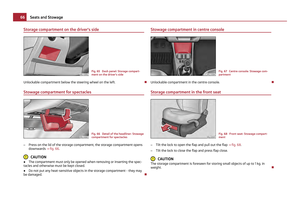 68
68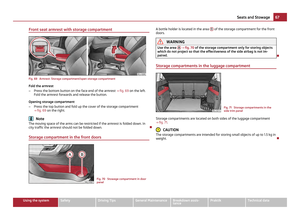 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97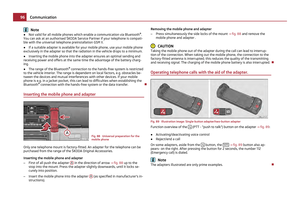 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106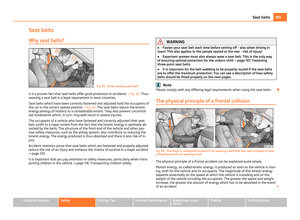 107
107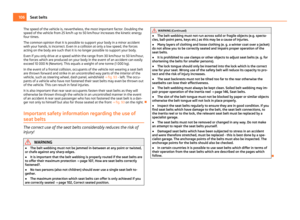 108
108 109
109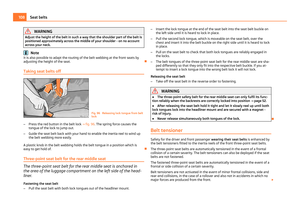 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114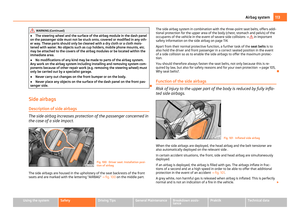 115
115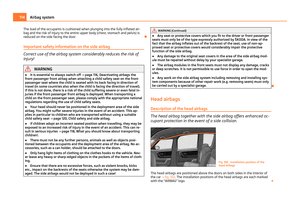 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121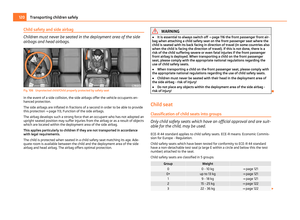 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132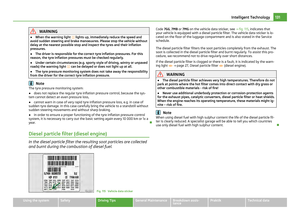 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143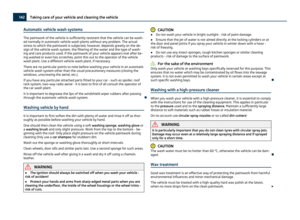 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168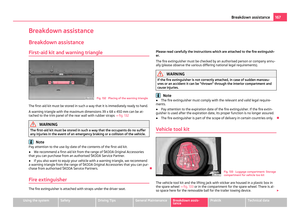 169
169 170
170 171
171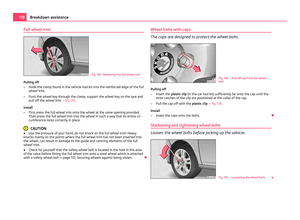 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183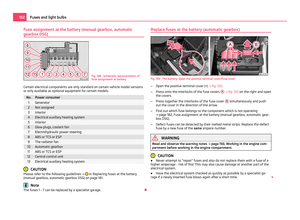 184
184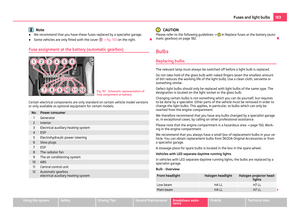 185
185 186
186 187
187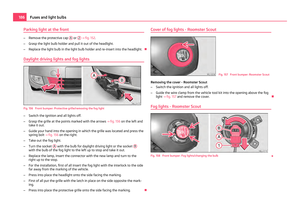 188
188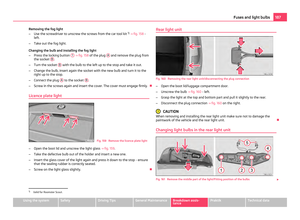 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192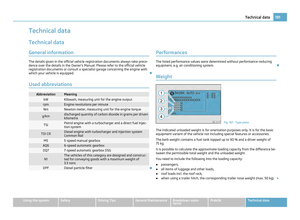 193
193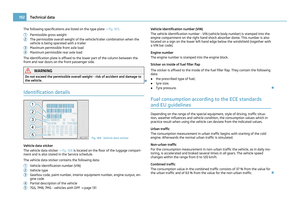 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211