2010 JAGUAR XFR Engine
[x] Cancel search: EnginePage 1580 of 3039
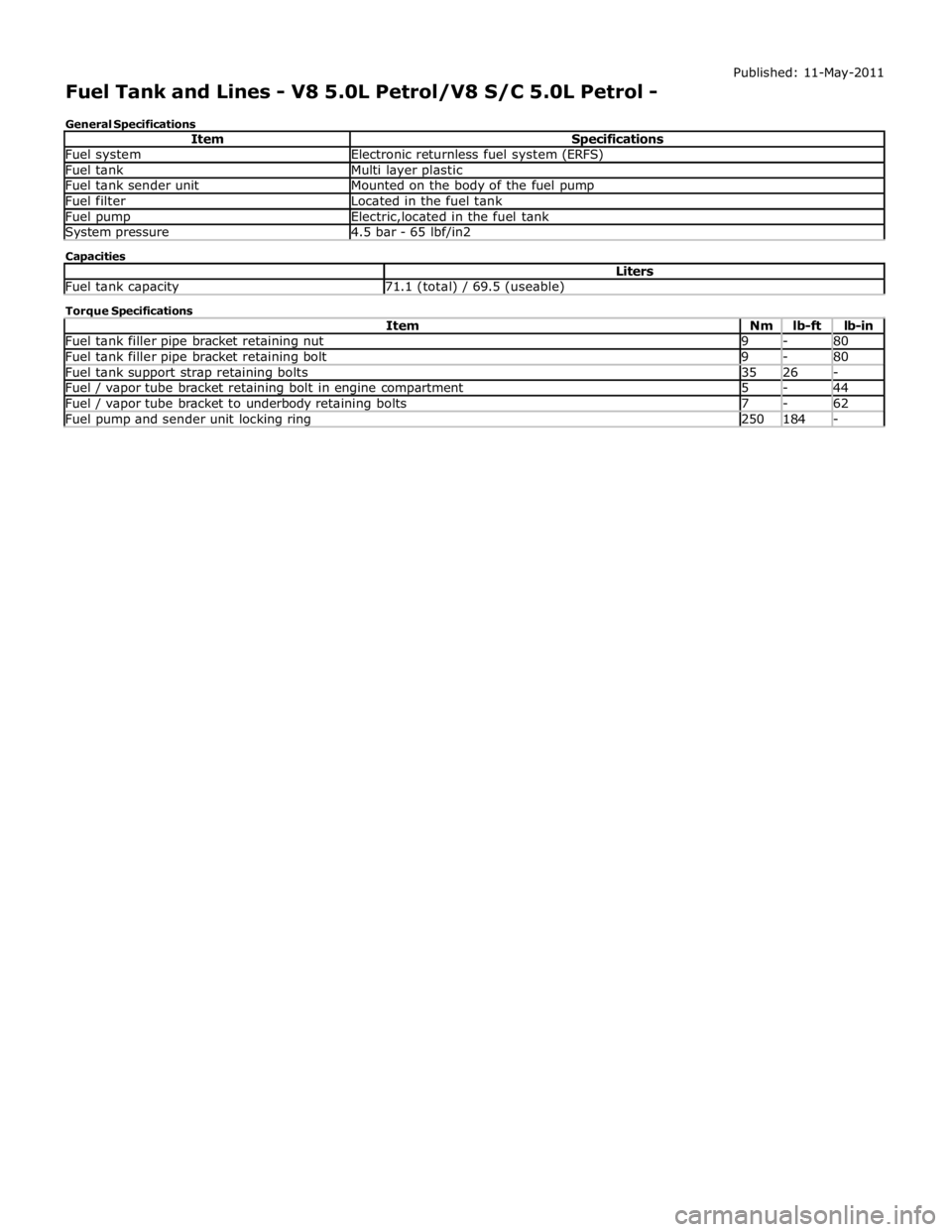
Fuel system Electronic returnless fuel system (ERFS) Fuel tank Multi layer plastic Fuel tank sender unit Mounted on the body of the fuel pump Fuel filter Located in the fuel tank Fuel pump Electric,located in the fuel tank System pressure 4.5 bar - 65 lbf/in2 Capacities Liters Fuel tank capacity 71.1 (total) / 69.5 (useable) Torque Specifications
Item Nm lb-ft lb-in Fuel tank filler pipe bracket retaining nut 9 - 80 Fuel tank filler pipe bracket retaining bolt 9 - 80 Fuel tank support strap retaining bolts 35 26 - Fuel / vapor tube bracket retaining bolt in engine compartment 5 - 44 Fuel / vapor tube bracket to underbody retaining bolts 7 - 62 Fuel pump and sender unit locking ring 250 184 -
Page 1584 of 3039

the flow and pressure supplied by controlling the operation of the fuel pump using a PWM (pulse width modulation) output. A
LP sensor is located in the fuel feed supply line to the engine and is monitored by the ECM for fuel pump control.
Two fuel level sensors are installed in either side of the saddle tank. The sensors are a MAPPS (magnetic passive position
sensor) which provide a variable resistance to ground for the output from the fuel gage.
The fuel system also incorporates an EVAP (evaporative emission) system which is part of the on-board refueling and vapor
recovery feature. The function and operation of the system is designed to meet EVAP requirements to minimize fuel vapor losses.
Page 1585 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Tank and Lines - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
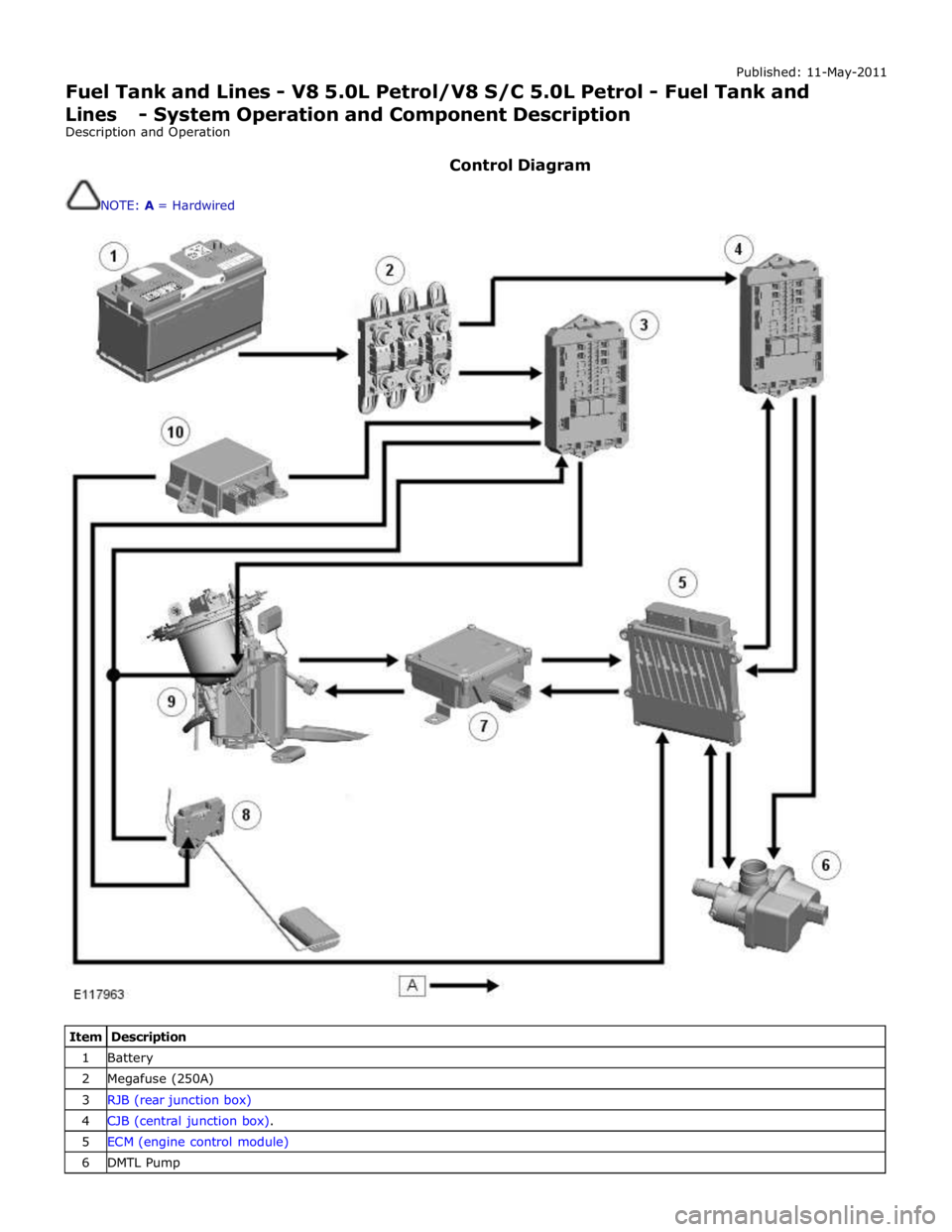
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 Megafuse (250A) 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 CJB (central junction box). 5 ECM (engine control module) 6 DMTL Pump
Page 1586 of 3039
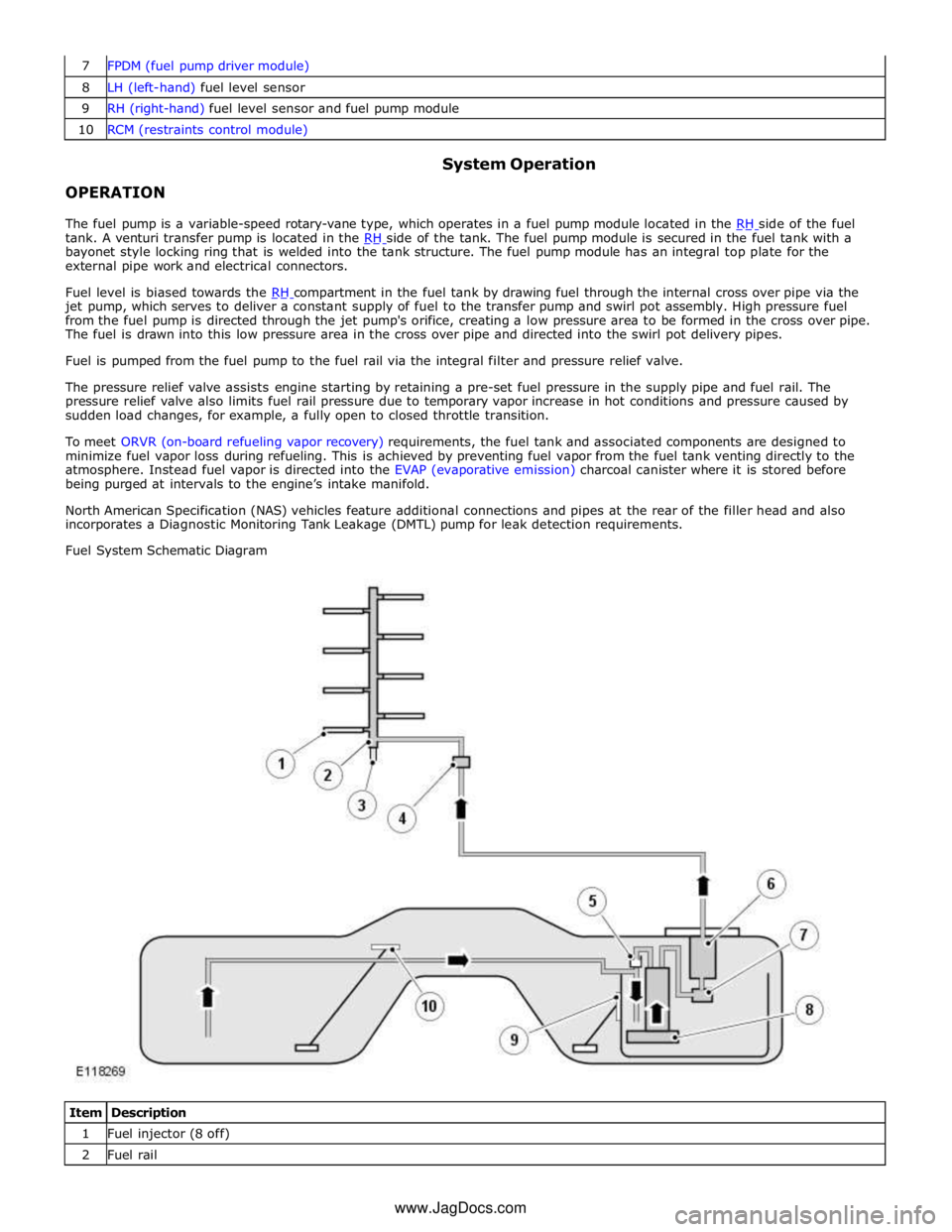
8 LH (left-hand) fuel level sensor 9 RH (right-hand) fuel level sensor and fuel pump module 10 RCM (restraints control module)
OPERATION System Operation
The fuel pump is a variable-speed rotary-vane type, which operates in a fuel pump module located in the RH side of the fuel tank. A venturi transfer pump is located in the RH side of the tank. The fuel pump module is secured in the fuel tank with a bayonet style locking ring that is welded into the tank structure. The fuel pump module has an integral top plate for the
external pipe work and electrical connectors.
Fuel level is biased towards the RH compartment in the fuel tank by drawing fuel through the internal cross over pipe via the jet pump, which serves to deliver a constant supply of fuel to the transfer pump and swirl pot assembly. High pressure fuel
from the fuel pump is directed through the jet pump's orifice, creating a low pressure area to be formed in the cross over pipe.
The fuel is drawn into this low pressure area in the cross over pipe and directed into the swirl pot delivery pipes.
Fuel is pumped from the fuel pump to the fuel rail via the integral filter and pressure relief valve.
The pressure relief valve assists engine starting by retaining a pre-set fuel pressure in the supply pipe and fuel rail. The
pressure relief valve also limits fuel rail pressure due to temporary vapor increase in hot conditions and pressure caused by
sudden load changes, for example, a fully open to closed throttle transition.
To meet ORVR (on-board refueling vapor recovery) requirements, the fuel tank and associated components are designed to
minimize fuel vapor loss during refueling. This is achieved by preventing fuel vapor from the fuel tank venting directly to the
atmosphere. Instead fuel vapor is directed into the EVAP (evaporative emission) charcoal canister where it is stored before
being purged at intervals to the engine’s intake manifold.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles feature additional connections and pipes at the rear of the filler head and also
incorporates a Diagnostic Monitoring Tank Leakage (DMTL) pump for leak detection requirements.
Fuel System Schematic Diagram
Item Description 1 Fuel injector (8 off) 2 Fuel rail www.JagDocs.com
Page 1587 of 3039
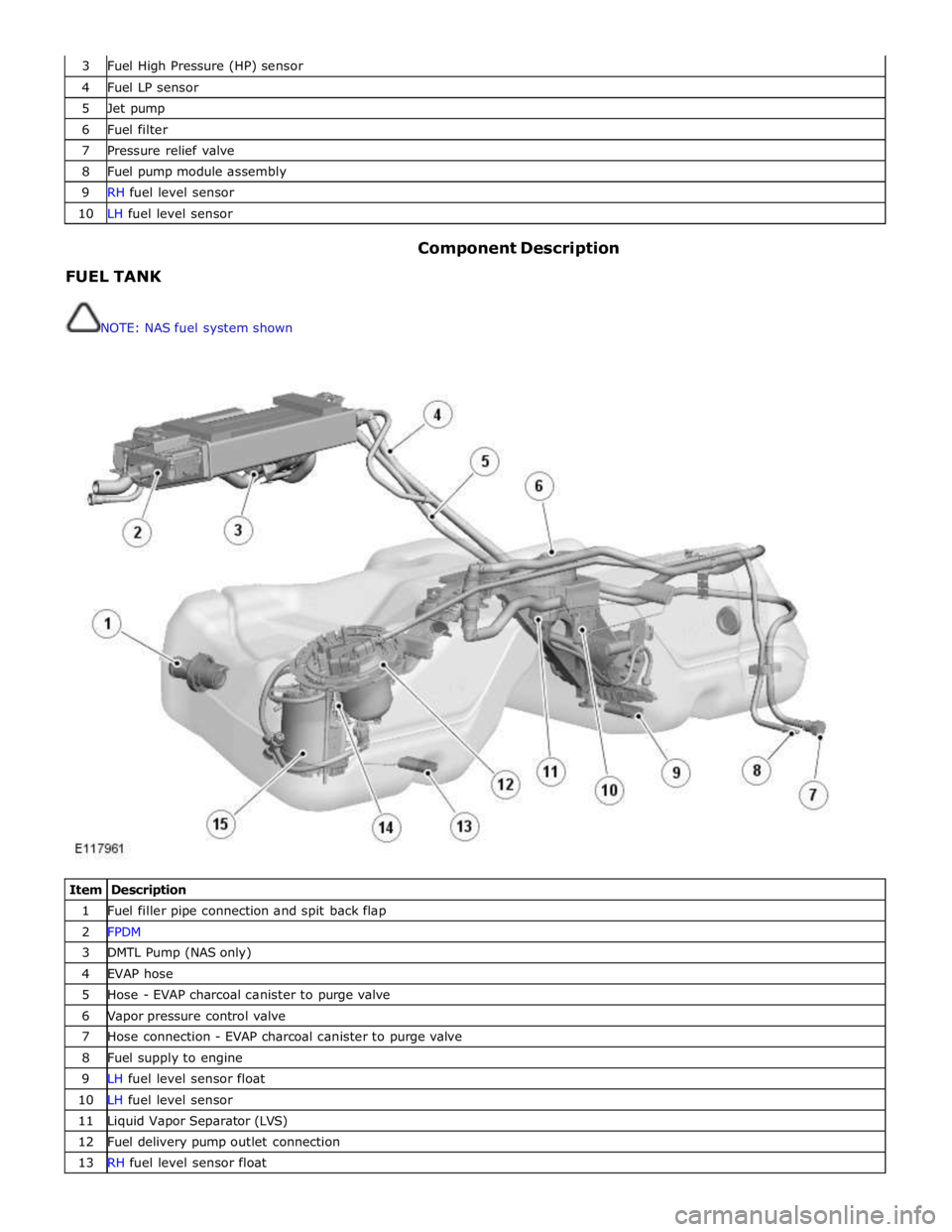
3 Fuel High Pressure (HP) sensor 4 Fuel LP sensor 5 Jet pump 6 Fuel filter 7 Pressure relief valve 8 Fuel pump module assembly 9 RH fuel level sensor 10 LH fuel level sensor
FUEL TANK
NOTE: NAS fuel system shown Component Description
Item Description 1 Fuel filler pipe connection and spit back flap 2 FPDM 3 DMTL Pump (NAS only) 4 EVAP hose 5 Hose - EVAP charcoal canister to purge valve 6 Vapor pressure control valve 7 Hose connection - EVAP charcoal canister to purge valve 8 Fuel supply to engine 9 LH fuel level sensor float 10 LH fuel level sensor 11 Liquid Vapor Separator (LVS) 12 Fuel delivery pump outlet connection 13 RH fuel level sensor float
Page 1589 of 3039
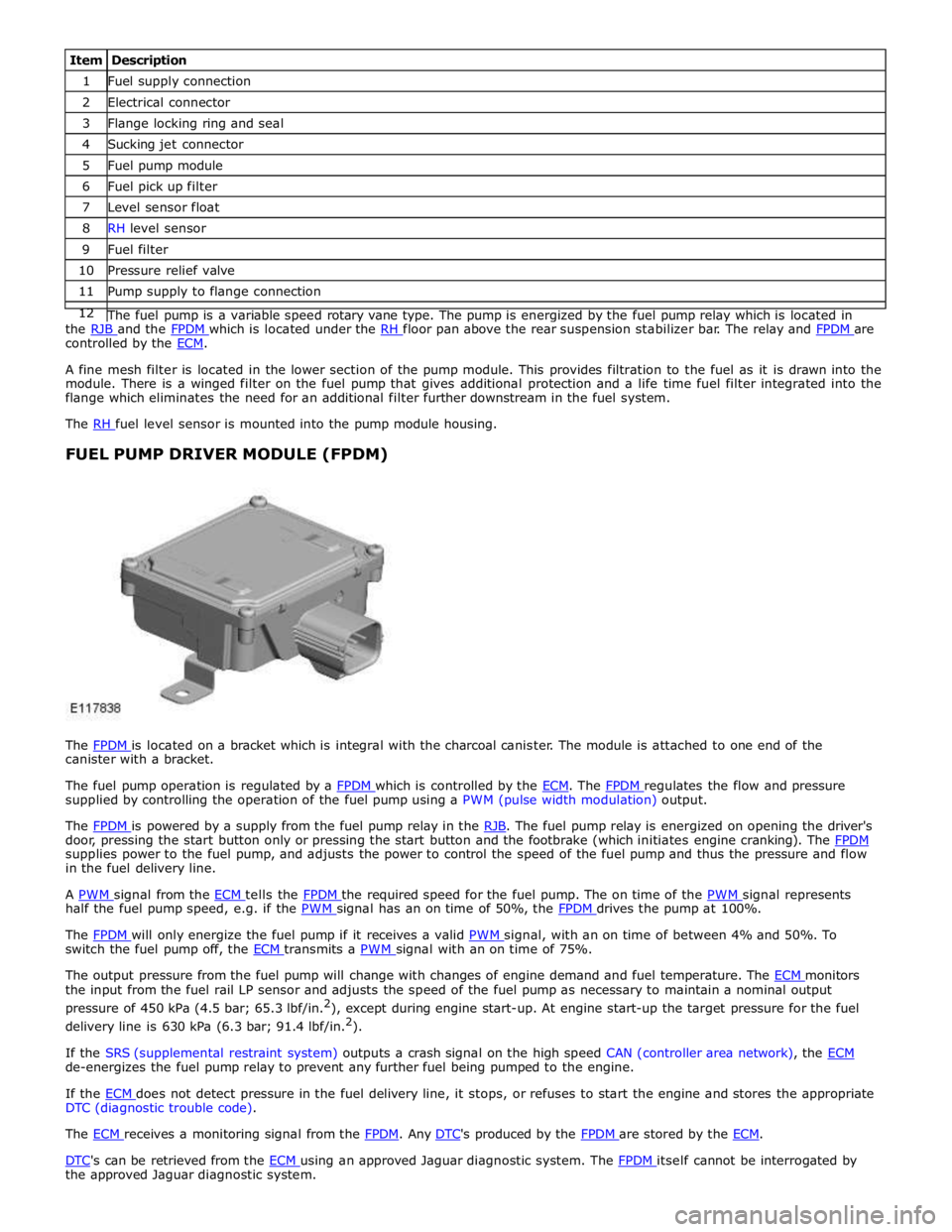
1 Fuel supply connection 2 Electrical connector 3 Flange locking ring and seal 4 Sucking jet connector 5 Fuel pump module 6 Fuel pick up filter 7 Level sensor float 8 RH level sensor 9 Fuel filter 10 Pressure relief valve 11 Pump supply to flange connection 12 The fuel pump is a variable speed rotary vane type. The pump is energized by the fuel pump relay which is located in the RJB and the FPDM which is located under the RH floor pan above the rear suspension stabilizer bar. The relay and FPDM are controlled by the ECM.
A fine mesh filter is located in the lower section of the pump module. This provides filtration to the fuel as it is drawn into the
module. There is a winged filter on the fuel pump that gives additional protection and a life time fuel filter integrated into the
flange which eliminates the need for an additional filter further downstream in the fuel system.
The RH fuel level sensor is mounted into the pump module housing.
FUEL PUMP DRIVER MODULE (FPDM)
The FPDM is located on a bracket which is integral with the charcoal canister. The module is attached to one end of the canister with a bracket.
The fuel pump operation is regulated by a FPDM which is controlled by the ECM. The FPDM regulates the flow and pressure supplied by controlling the operation of the fuel pump using a PWM (pulse width modulation) output.
The FPDM is powered by a supply from the fuel pump relay in the RJB. The fuel pump relay is energized on opening the driver's door, pressing the start button only or pressing the start button and the footbrake (which initiates engine cranking). The FPDM supplies power to the fuel pump, and adjusts the power to control the speed of the fuel pump and thus the pressure and flow
in the fuel delivery line.
A PWM signal from the ECM tells the FPDM the required speed for the fuel pump. The on time of the PWM signal represents half the fuel pump speed, e.g. if the PWM signal has an on time of 50%, the FPDM drives the pump at 100%.
The FPDM will only energize the fuel pump if it receives a valid PWM signal, with an on time of between 4% and 50%. To switch the fuel pump off, the ECM transmits a PWM signal with an on time of 75%.
The output pressure from the fuel pump will change with changes of engine demand and fuel temperature. The ECM monitors the input from the fuel rail LP sensor and adjusts the speed of the fuel pump as necessary to maintain a nominal output
pressure of 450 kPa (4.5 bar; 65.3 lbf/in.2
), except during engine start-up. At engine start-up the target pressure for the fuel
delivery line is 630 kPa (6.3 bar; 91.4 lbf/in.2
).
If the SRS (supplemental restraint system) outputs a crash signal on the high speed CAN (controller area network), the ECM de-energizes the fuel pump relay to prevent any further fuel being pumped to the engine.
If the ECM does not detect pressure in the fuel delivery line, it stops, or refuses to start the engine and stores the appropriate DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
The ECM receives a monitoring signal from the FPDM. Any DTC's produced by the FPDM are stored by the ECM.
DTC's can be retrieved from the ECM using an approved Jaguar diagnostic system. The FPDM itself cannot be interrogated by the approved Jaguar diagnostic system.
Page 1595 of 3039

Published: 28-Jul-2014
Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Tank and
Lines
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the fuel tank and lines system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (310-01C Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNINGS:
Eye protection must be worn at all times when working on or near any fuel related components. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
This procedure involves fuel handling. Be prepared for fuel spillage at all times and always observe fuel handling
precautions. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
After carrying out repairs, the fuel system must be checked visually for leaks. This should be done after the engine has
been run, but with the engine switched OFF. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
If taken internally, DO NOT induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention. Failure to follow this instruction may
result in personal injury.
If fuel contacts the eyes, flush the eyes with cold water or eyewash solution and seek medical attention. Failure to follow
this instruction may result in personal injury.
Wash hands thoroughly after handling, as prolonged contact may cause irritation. Should irritation develop, seek medical
attention. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
Before disconnecting any part of the system, it is imperative that all dust, dirt and debris is removed from around
components to prevent ingress of foreign matter into the fuel system. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to
the vehicle.
It is essential that absolute cleanliness is observed when working with these components. Always install blanking plugs
to any open orifices or lines. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to the vehicle.
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
When measuring fuel sender resistance values with a multimeter, it is critical to use the correct multimeter setting. The
multimeter should not be on the 'Auto' setting and must be set to 'Manual'. This will help prevent incorrect diagnosis and
unnecessary replacement of fuel senders. If the multimeter range is set at 'Auto' then, during a sweep of the sender from 50
Ohms to 998 Ohms, the multimeter has to change its measurement range. For approximately 1 second, during the range switch
over point, the multimeter display indicates an open circuit. This can lead to a mis-diagnosis of a fuel sender fault.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Page 1596 of 3039
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Low/contaminated fuel
Fuel supply/return line(s)
Fuel tank and filler pipe
Fuel leak(s)
Fuel filler cap
Fuel filter
Push connect fittings
Fuel pump
Fuses
Links
Relays
Fuel Pump Driver Module (FPDM)
Fuel pump module
Sensor(s)
Engine control module (ECM)
Rear Junction Box (RJB)
Restraints Control Module (RCM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and proceed to the DTC Index
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Engine cranks, but does not
fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine control
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for ignition system, fuel system and electronic
engine control DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Engine cranks and fires, but
will not start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
HT short to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Ignition system
Check for evaporative emissions, fuel system and
ignition system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Difficult cold start
Engine coolant level/anti-
freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Fuel pump
Purge valve
Check the engine coolant level and condition
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition
Check for electronic engine controls, engine
emissions, fuel system and evaporative emissions
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Difficult hot start
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative
emissions, fuel system, ignition system and engine
emission system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Difficult to start after hot
soak (vehicle standing,
engine off, after engine has
reached operating
temperature)
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative
emissions, fuel system, ignition system and engine
emission system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine stalls soon after start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
ECM relay
Electronic engine control
Ignition system
Air intake system restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for electronic engine control, ignition system
and fuel system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index
Check for blockage in air filter element and air
intake system
Check for air leakage in air intake system Engine hesitates/poor
acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Check for fuel system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required www.JagDocs.com