2010 JAGUAR XFR Engine
[x] Cancel search: EnginePage 1640 of 3039
Published: 29-Sep-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - System
Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
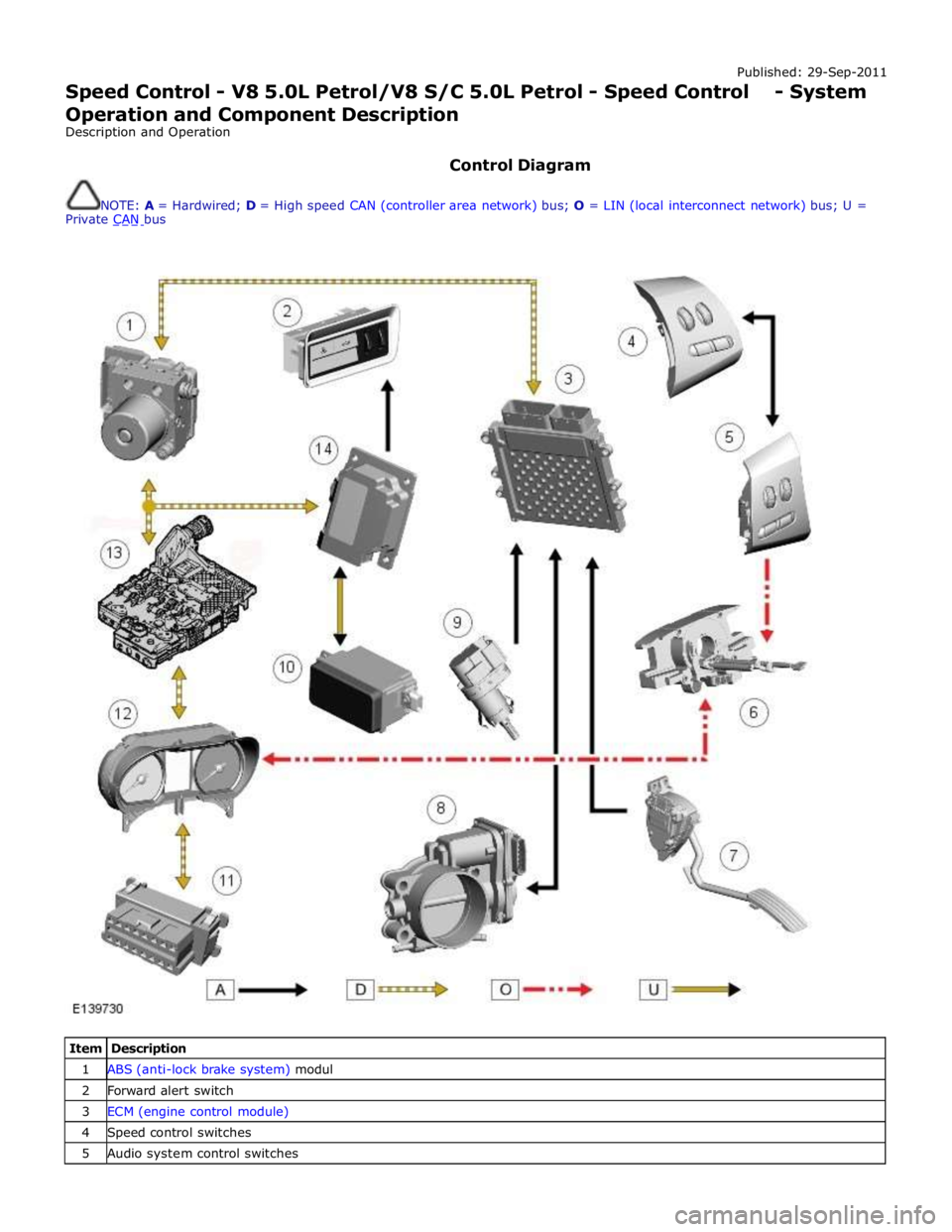
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN (controller area network) bus; O = LIN (local interconnect network) bus; U =
Private CAN bus
Item Description 1 ABS (anti-lock brake system) modul 2 Forward alert switch 3 ECM (engine control module) 4 Speed control switches 5 Audio system control switches
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the
Page 1646 of 3039

Published: 08-Nov-2013
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the speed control system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Speed control sensor
Ensure the speed control sensor is free from obstructions
Speed control module
Brake switch
Fuses
Wiring harness
Electrical connector(s)
Steering wheel switches
Brake switch
Speed control sensor
Speed control module
Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively, check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Speed Control Sensor Adjustment (vehicles with adaptive system installed)
An incorrectly aligned speed control sensor can cause incorrect system operation. Before starting any repair work on the speed
control system, on vehicles with the adaptive system installed, check speed control sensor for correct vertical alignment, and
carry out speed control sensor alignment procedure using manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Speed control inhibited or
disabled
Power or ground supply to
speed control module or speed
control sensor
Steering wheel speed control
switch/circuits
Throttle sensors
Brake switch
Anti-Lock Brake System fault
Check for DTCs that could be caused by power or
ground failure to the module or sensor and refer to
DTC Index
Check for sticking, jammed and broken speed control
switches. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short, open
circuit
For throttle position sensor tests. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls - 3.0L Diesel (303-14
Electronic Engine Controls - 3.0L Diesel, Diagnosis and
Testing),
Electronic Engine Controls - 3.0L (303-14B Electronic Engine Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and
Testing),
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14 Electronic Engine
Controls - V8 4.2L Petrol/V8 S/C 4.2L Petrol, Diagnosis
and Testing).
Check for correct installation and adjustment of brake
switch. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check brake switch circuits for short, open circuit
Check ABS system for related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Unable to regulate/adjust
vehicle speed
Steering wheel switch
malfunction
Check for sticking, jammed and broken speed control
switches. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short, open
circuit
Page 1649 of 3039
DTC Description Possible Causes Action U0401-00
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A - No
sub type information
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
cancel or auto brake
cancel request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-67
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Signal incorrect after
event
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
resume request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-81
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid data received
from engine control
module
Bus signal/message
failure
Speed control inhibited
by ECM
Check the Engine Control Module for related DTCs
and refer to relevant DTC Index. If U040181 is
logged as historic but no other DTCs have logged in
the engine control module at the same time and
distance, it may be caused by cranking with low
voltage conditions. Check battery and charging
system according to instructions in the battery care
manual. Install the latest Engine Control Module
software using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, contact Dealer Technical Support before
replacing components U0415-53
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-Lock Braking
System (ABS) Control
Module - De-activated
Event information
Deactivated
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0415-81
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-lock Brake
System (ABS) Control
Module - Invalid serial
data received
Stability assist fault
Check ABS module for related DTCs and refer to
relevant DTC Index U0417-67
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module - Signal
incorrect after event
Parking brake module did
not respond properly to
apply request
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0417-81
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by parking brake module
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0418-68
Invalid Data Received
From Brake System
Control Module - Event
information
Event information
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0421-81
Invalid Data Received
From Suspension
Control Module 'A' -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid serial data
received
Check the Suspension Control Module for related
DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0423-81
Invalid Data Received
From Instrument Panel
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by instrument cluster
Check instrument cluster, CJB and RJB for related
DTCs and refer to relevant DTC Index U1A00-88
Private Communication
Network - Bus off
Bus off
The module setting this code has disabled CAN
transmission. Check for other bus off codes. Check
the module and circuits. Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams. Clear all DTCs and road test the vehicle. If
the concern reoccurs contact Dealer Technical
Support for further advice. Under no circumstance
should any parts be replaced to overcome this issue U1A14-49
CAN Initialisation
Failure - Internal
electronic failure
Internal electronic failure
Suspect the speed control module. Check and install
a new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index U2101-00
Control Module
Configuration
Incompatible - No sub
type information
Data sent from RJB is
invalid
Check/amend Car Configuration File using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system, clear DTC
and re-test. If DTC remains, re-configure RJB using
manufacturer approved diagnostic system, clear DTC
and re-test. If DTC remains check RJB for DTCs and
Page 1651 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action for further assistance P0501-62
Vehicle Speed Sensor A
Range/Performance - Signal
compare failure
Vehicle speed - range
performance
Check ABS/TCM for related DTCs and refer
to relevant DTC Index P0504-00 Brake Switch A / B Correlation
- No sub type information
The brake pressure reading
does not agree with the
brake light switch value
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check brake switch
circuits for short, open circuit, high
resistance P0504-01 Brake Switch A / B Correlation
- General electrical failure
Brake switch high fault:
- Brake lights stuck
on
- Gearshift interlock
inoperative
- Speed control
inoperative
Brake switch low fault:
- Brake lights
inoperative
- Gearshift stuck in
Park
- Reduced engine
braking
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check brake switch
circuits for short, open circuit, high
resistance P0566-00
Cruise Control OFF Signal - No
sub type information
Speed control Cancel
switch 2 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0567-00
Cruise Control DECREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Resume
switch 7 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0568-00
Cruise Control INCREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Accel Set
Plus Switch 6 stuck closed
Check and install a new speed control
switch as required P0569-00
Cruise Control COAST Signal -
No sub type information
Speed control Coast Set
Minus switch 3 stuck
closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P056A-00
Cruise Control INCREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Headway
Plus switch 4 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P056B-00
Cruise Control DECREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Headway
Minus switch 5 stuck
closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0571-62
Brake Switch A Circuit - Signal
compare failure
Plausibility error
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check brake light switch signal circuits for
short, open circuit. Check and install a new
brake light switch as required P0575-01
Cruise Control Input Circuit -
General electrical failure
General electrical failure
Check speed control system for related
DTCs and refer to relevant DTC Index. Carry
out CAN network integrity tests using the
Page 1663 of 3039
Climate Control System - General Information -
Lubricants, Fluids, Sealers and Adhesives
NOTE: NAS vehicles. Published: 29-Jan-2014
Description Specification Air conditioning (A/C) refrigerant R-1234yf A/C compressor oil SPA2
NOTE: ROW vehicles.
Description Specification Air conditioning (A/C) refrigerant R-134a A/C compressor oil SPA2
NOTE: EU vehicles.
Description Specification Air conditioning (A/C) refrigerant R-1234yf A/C compressor oil SPA2 Capacities
Description Grammes A/C refrigerant - all engine variants 700 Refrigerant Oil Adding Capacities
NOTE: Rotate the A/C compressor shaft at least 6 to 8 turns when draining the refrigerant oil.
Item Milliliters A/C condenser core and desiccant bag Add 25ml oil A/C evaporator Add 30ml oil A/C compressor
1. Drain old A/C compressor. With drain plug removed and ports uncapped, rotate
shaft to remove A/C compressor oil and measure the amount of oil captured. 2. Drain
new A/C compressor into a clean vessel. With drain plug removed and ports
uncapped, rotate shaft to remove oil. Then add back a quantity of the new oil that is
identical to the quantity of oil removed from the old A/C compressor. However, if this quantity is less than 30ml, then make it up to 30ml. A/C lines - if air conditioning has been operational. Add 5ml oil per A/C line A/C system after flushing - with new compressor installed No oil should be used- new oil in new compressor is sufficient A/C system after flushing - without a
new compressor installed - remaining
A/C compressor oil is to be drained.
Compressor and expansion valve must
not be flushed (removed from the circuit) Add 80ml oil A/C compressor drain plug Torque 12Nm www.JagDocs.com
Page 1665 of 3039

Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Air conditioning performance poor or
inoperative
Refrigerant undercharged
Refrigerant overcharged
Thermostatic expansion valve
faulty
Receiver drier restricted
Water in refrigerant
GO to Pinpoint Test A. Air conditioning operates briefly and
then switches off
Electric cooling fan inoperative
Air conditioning condenser
airflow obstructed
Test the operation of the electric cooling
fan
Check the air conditioning condenser for
external obstructions Pinpoint Tests
PINPOINT TEST A : PRELIMINARY TESTS TEST CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS A1: PRELIMINARY TEST 1 NOTES:
This test is performed with the engine not running.
Normal pressure for a correctly charged and switched off system is approximately 4.5 bar on both gauges (system
equalised). 1 Close the valves on the air conditioning station 2 Connect the air conditioning station to the vehicle charging ports 3 Check the pressure values Is a pressure registered on both gauges? Yes
GO to Pinpoint Test B. No
GO to Pinpoint Test D.
PINPOINT TEST B : FUNCTIONALITY TESTS TEST CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS B1: FUNCTIONALITY TEST 1 NOTES:
Normal pressures for a correctly charged and working system are 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar (low) and 11.0 bar to 15.0 bar (high).
Normal temperature (measured at the center air vent) for a correctly charged and working system is -7°C to -2°C when
ambient temperature is 20°C. 1 Close the valves on the air conditioning station 2 Connect the air conditioning station to the vehicle charging ports 3 Open all doors and the tailgate 4 Start the engine 5 Set the temperature to the lowest setting (all zones) 6 Set the fan speed to maximum 7 Set the recirculate switch to off 8 Insert a temperature probe into the centre air vent 9 Raise engine speed to 1500rpm and maintain this speed for 5 minutes 10 Check the temperature value 11 Check the pressure values Are the pressure readings stable and in the green 'normal' region of the gauge? Yes
Air conditioning system operating normally No
Air conditioning system fault present. GO to Pinpoint Test C.
PINPOINT TEST C : GAUGE TESTS
Page 1666 of 3039

TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS C1: GAUGE TEST 1
NOTE: This test is performed with the engine running and the air conditioning set to on. 1 Check the pressure values Did the gauges register a change in pressure when the air conditioning was switched on? Yes
GO to C2. No
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, check the Automatic Temperature Control Module (ATCM) for related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index C2: GAUGE TEST 2
NOTE: This test is performed with the engine running and the air conditioning set to on. 1 Check the pressure values Are the pressure gauge readings fluctuating? Yes
Moisture present in the air conditioning system. Recover the refrigerant. Install a new receiver drier.
Refer to the relevant section of the workshop manual and evacuate and recharge the air conditioning
system. GO to Pinpoint Test B. No
GO to C3. C3: GAUGE TEST 3 NOTES:
This test is performed with the engine running and the air conditioning set to on.
Normal pressures for a correctly charged and working system are 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar (low) and 11.0 bar to 15.0 bar (high). 1 Check the pressure values Are the pressure gauge readings too low? Yes
GO to C4. No
GO to C6. C4: GAUGE TEST 4
NOTE: This test is performed with the engine not running. 1 Stop the engine 2 Using the manufacturer approved refrigerant leak detector, check for a refrigerant leak Was a refrigerant leak detected? Yes
Refer to the relevant section of the workshop manual and recover the refrigerant. Repair as necessary.
Evacuate and recharge the air conditioning system. GO to Pinpoint Test B. No
GO to C5. C5: GAUGE TEST 5
NOTE: This test is performed with the engine not running. 1 Refer to the relevant section of the workshop manual and recover the refrigerant Was the weight of the recovered refrigerant less than specified for the air conditioning system? Yes
Refer to the relevant section of the workshop manual and evacuate and recharge the air conditioning
system. GO to Pinpoint Test B. No
Install a new receiver drier. Refer to the relevant section of the workshop manual and evacuate and recharge the air conditioning system. GO to Pinpoint Test B. C6: GAUGE TEST 6 NOTES:
This test is performed with the engine running and the air conditioning set to on.
Normal pressures for a correctly charged and working system are 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar (low) and 11.0 bar to 15.0 bar (high).