2009 NISSAN TIIDA key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 3256 of 4331

GI
N
O P
2. Use the Intelligent Key or mechanical key to turn the ignition switch to the
″ACC ″ position. At this time, the
steering lock will be released.
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released and the steering wheel can be
rotated.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
5. When the repair work is completed, return the ignition switch to the ″LOCK ″ position before connecting
the battery cables. (At this time, the steering lock mechanism will engage.)
6. Perform a self-diagnosis check of al l control units using CONSULT-III.
General Precaution INFOID:0000000004307347
• Do not operate the engine for an extended period of time without proper exhaust ventilation.
Keep the work area well ventilated and free of any flammable
materials. Special care should be taken when handling any flam-
mable or poisonous materials, such as gasoline, refrigerant gas,
etc. When working in a pit or ot her enclosed area, be sure to prop-
erly ventilate the area before working with hazardous materials.
Do not smoke while working on the vehicle.
• Before jacking up the vehicle, apply wheel chocks or other tire blocks to the wheels to prevent t he vehicle from moving. After jack-
ing up the vehicle, support the vehicle weight with safety stands at
the points designated for proper lifting before working on the vehi-
cle.
These operations should be done on a level surface.
• When removing a heavy component such as the engine or tran-
saxle/transmission, be careful not to lose your balance and drop
them. Also, do not allow them to strike adjacent parts, especially
the brake tubes and master cylinder.
• Before starting repairs which do not require battery power: Turn off ignition switch.
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
• If the battery terminals are disconnected, recorded memory of
radio and each control unit is erased.
• Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds. Wash hands after handling.
• To prevent serious burns: Avoid contact with hot metal parts.
Do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot.
• Dispose of or recycle drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning
parts in an appropriate manner.
• Do not attempt to top off the fuel tank after the fuel pump nozzle shuts off automatically.
Continued refueling may cause fuel overflow, resulting in fuel spray
and possibly a fire.
• Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly. SGI231
SGI233
Page 3257 of 4331
GI-4< SERVICE INFORMATION >
PRECAUTIONS
• Replace oil seals, gaskets, packings, O-rings, locking wa shers, cotter pins, self-locking nuts, etc. with new
ones.
• Replace inner and outer races of tapered roller bearings and needle bearings as a set.
• Arrange the disassembled parts in accordance with their assembled locations and sequence.
• Do not touch the terminals of electrical com ponents which use microcomputers (such as ECM).
Static electricity may damage internal electronic components.
• After disconnecting vacuum or air hoses, atta ch a tag to indicate the proper connection.
• Use only the fluids and lubricants specified in this manual.
• Use approved bonding agent, sealants or their equivalents when required.
• Use hand tools, power tools (disassembly only) and recommended
special tools where specified for safe and efficient service repairs.
• When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust systems, check all affected lines for leaks.
• Before servicing the vehicle: Protect fenders, upholstery and carpeting with appropriate covers.
Take caution that keys, buckles or buttons do not scratch paint.
WARNING:
To prevent ECM from storing the diagnostic tro uble codes, do not carelessly disconnect the harness
connectors which are related to the engine cont rol system and TCM (transmission control module)
system. The connectors should be disconnected on ly when working according to the WORK FLOW of
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES in EC, CVT, and AT sections.
Precaution for Three Way Catalyst INFOID:0000000004307348
If a large amount of unburned fuel flows into the catalyst , the catalyst temperature will be excessively high. To
prevent this, follow the instructions.
• Use unleaded gasoline only. Leaded gasoline will seriously damage the three way catalyst.
• When checking for ignition spark or measuring engine compression, make tests quickly and only when nec-
essary.
• Do not run engine when the fuel tank level is low, otherwise the engine may misfire, causing damage to the
catalyst.
Do not place the vehicle on flammable material. Keep flammable material off the exhaust pipe and the three
way catalyst.
Precaution for Fuel (Unleade d Regular Gasoline Recommended) INFOID:0000000004307349
Use unleaded regular gasoline with an octane rating of at least 87 AKI (Anti-Knock Index) number (Research
octane number 91).
CAUTION:
Do not use leaded gasoline. Using leaded gasoline will damage the three way catalyst. Do not use E-85
fuel (85% fuel ethanol, 15% unl eaded gasoline) unless the vehicle is specifically designed for E-85 fuel PBIC0190E
SGI234
Page 3282 of 4331
GI
N
O P
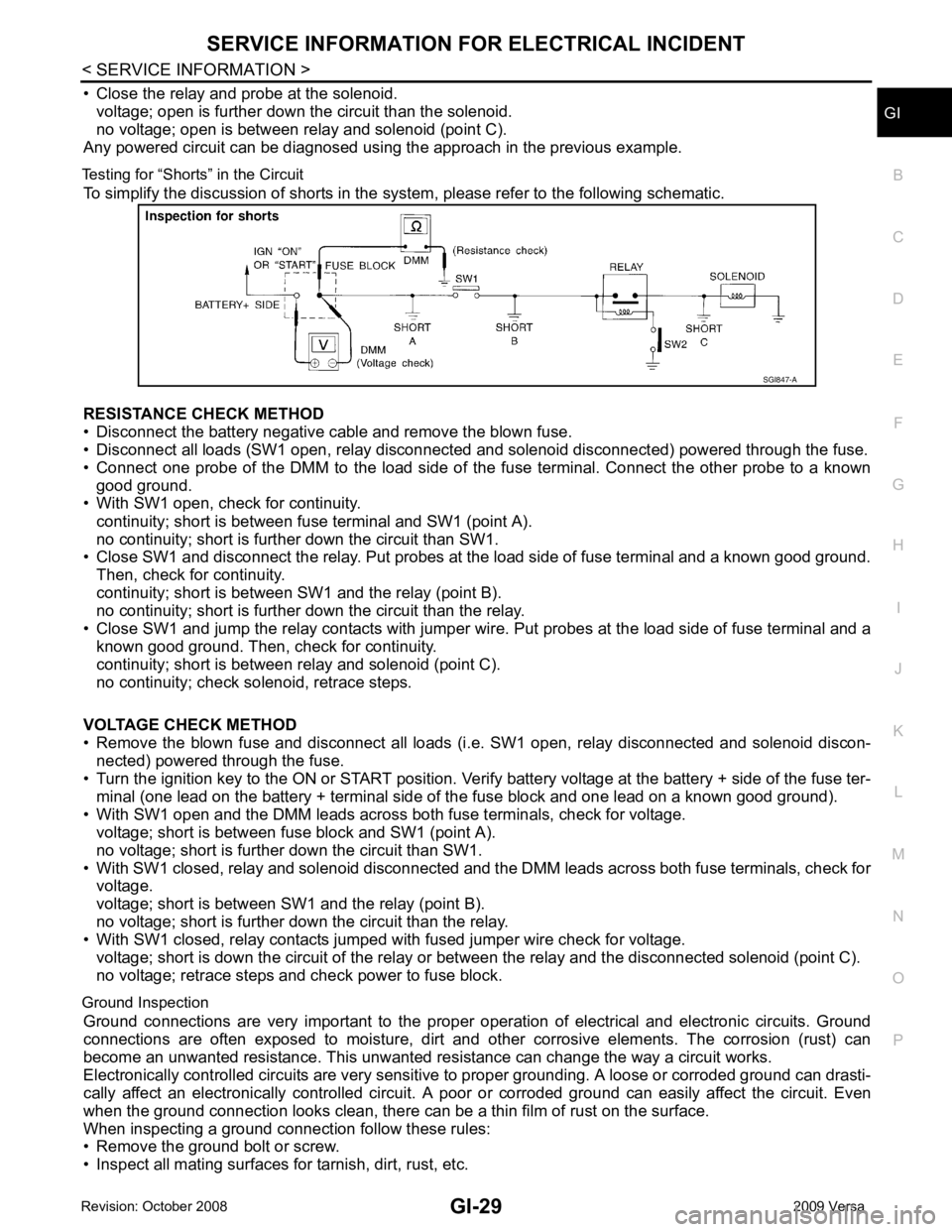
• Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
• Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
• Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
• Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
• With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good ground.
Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wir e. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a
known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
• Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i .e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
• Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Veri fy battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
• With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and t he DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for
voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection Ground connections are very important to the proper oper ation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted re sistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
• Remove the ground bolt or screw.
• Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
Page 3288 of 4331

GI
N
O P
CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
Description INFOID:0000000004307366
• CONSULT-III is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the vehicle side, it will communicate with the contro l unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various kinds
of diagnostic tests.
• Refer to CONSULT-III Operator's Manual for more information.
Function and System Application INFOID:0000000004307367
x: Applicable.
*1: If equipped.
*2: With automatic transmission (A/T).
*3: With continuously variable transmission (CVT).
*4: With security card installed. Diagnostic test mode FunctionENGINE
ABS* 1
AIR BAG EPS
IPDM E/R BCM
METER/M&A
INTELLIGENT KEY* 1
TRANSMISSION* 2
TRANSMISSION* 3
Work support This mode enables a technician to adjust some devices faster and
more accurately by following indications on CONSULT-III. x - - - - x - x x x
Self-diagnostic results Self-diagnostic results can be read and erased quickly. x x x x x x x x x x
Trouble diagnostic record Current self-diagnostic results and all trouble diagnostic records
previously stored can be read. - - x - - - - - - -
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. x x x x x x x x x x
CAN diagnostic support
monitor The communication condition of CAN communication line can be
read. x x - x x x x x x x
Calibration data* 2
Shows unit calibration IDs, offsets and gains. This data is stored in
the ECU memory. - - - - - - - - - x
Active test Diagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-III drives actuators apart
from ECU shifting some parameters in a specified range. x x - - x x - x - -
Function test This mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU with either
"OK" or "NG". For engines, more practical tests regarding sensors/
switches and/or actuators are available. x x x - - - - - x x
DTC & SRT confirmation The results of SRT (System Readiness Test) and the self-diagno-
sis status/result can be confirmed. x - - - - - - - x -
DTC work support The operating condition to confirm Diagnosis Trouble Codes can
be selected. x - - - - - - - x -
ECM/ECU part number ECM/ECU part number can be read. x x - x - x - x x x
ECU discriminated No. Classification number of a replacement ECU can be read to pre-
vent an incorrect ECU from being installed. - - x - - - - - - -
Passenger airbag Displays the STATUS (readiness) of front passenger air bag. - - x - - - - - - -
Configuration Sets control module parameters to match vehicle options. - - - - - x - - - -
Control unit initialization *4
All registered ignition key IDs in NATS components can be initial-
ized and new IDs can be registered. - - - - - x - - - -
PIN Read *4
This mode enables technician to get BCM-specific 5-digit code. - - - - - x - - - -
Page 3306 of 4331

GW
N
O P
SERVICE INFORMATION
PRECAUTIONS
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER" INFOID:0000000004306843
The Supplemental Restraint System such as “A IR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along
with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severi ty of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. This system includes seat belt switch inputs and dual stage front air bag modules. The SRS
system uses the seat belt switches to determine the front air bag deployment, and may only deploy one front
air bag, depending on the severity of a collision and w hether the front occupants are belted or unbelted.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in the SRS and SB section of this Service Man-
ual.
WARNING:
• To avoid rendering the SRS inoper ative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death in
the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed by
an authorized NISSAN/INFINITI dealer.
• Improper maintenance, including in correct removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to personal
injury caused by unintentional act ivation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air Bag
Module, see the SRS section.
• Do not use electrical test equipm ent on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses can be identi fied by yellow and/or orange harnesses or har-
ness connectors.
Precaution Necessary for Steering Wh eel Rotation After Battery Disconnect
INFOID:0000000004687763
NOTE:
• This Procedure is applied only to models with Inte lligent Key system and NATS (NISSAN ANTI-THEFT SYS-
TEM).
• Remove and install all control units after disconnecti ng both battery cables with the ignition knob in the
″ LOCK ″ position.
• Always use CONSULT-III to perform self-diagnosis as a part of each function inspection after finishing work.
If DTC is detected, perform trouble diagnosis according to self-diagnostic results.
For models equipped with the Intelligent Key system and NATS , an electrically controlled steering lock mech-
anism is adopted on the key cylinder.
For this reason, if the battery is disconnected or if the battery is discharged, the steering wheel will lock and
steering wheel rotation will become impossible.
If steering wheel rotation is required when battery pow er is interrupted, follow the procedure below before
starting the repair operation.
OPERATION PROCEDURE 1. Connect both battery cables. NOTE:
Supply power using jumper cables if battery is discharged.
2. Use the Intelligent Key or mechanical key to turn the ignition switch to the ″ACC ″ position. At this time, the
steering lock will be released.
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released and the steering wheel can be
rotated.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
5. When the repair work is completed, return the ignition switch to the ″LOCK ″ position before connecting
the battery cables. (At this time, the steering lock mechanism will engage.)
6. Perform a self-diagnosis check of al l control units using CONSULT-III.
Page 3400 of 4331

LAN
N
O P
Diagnosis Procedure ...........................................
..
161
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..162
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..162
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...................... ..163
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..163
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..164
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..164
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..165
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..165
I-KEY BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..................... ..166
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..166
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...................... ..167
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..167
ABS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..168
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..168
TCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..169
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..169
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .................. ..170
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..170
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ................ ..171
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..171
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 13)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................173
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..173
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..173
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...................... ..174
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..174
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..175
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..175
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... ..176
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..176
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...................... ..177
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..177
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .................. ..178
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..178
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ................ ..179
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..179
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 14)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................181
MAIN LINE BETWEEN DLC AND ABS CIR-
CUIT ................................................................ ..
181
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..181 ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .......................
182
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..182
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 183
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..183
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 184
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..184
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 185
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..185
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 186
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..186
ABS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 187
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..187
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ................... 188
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..188
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ................. 189
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..189
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 15)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................191
MAIN LINE BETWEEN DLC AND TCM CIR-
CUIT ................................................................ 191
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..191
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 192
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..192
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 193
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..193
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 194
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..194
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 195
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..195
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 196
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..196
TCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................ 197
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..197
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ................... 198
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..198
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ................. 199
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..199
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 16)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................
201
MAIN LINE BETWEEN DLC AND ABS CIR-
CUIT ................................................................ 201
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..201
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ....................... 202
Page 3417 of 4331

Trouble Diagnosis Procedure " .
Abbreviation List INFOID:0000000004306697
Unit name abbreviations in CONSULT-III CAN diagnosis and in this section are as per the following list.
Abbreviation Unit name A-BAG Air bag diagnosis sensor unitABS ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit)
BCM BCM DLC Data link connector
ECM ECM EPS EPS control unit
I-KEY Intelligent Key unit
IPDM-E IPDM E/R M&A Combination meter
TCM TCM
Page 3421 of 4331
Trouble Diagnosis Procedure " for how to use CAN system specification chart.
× : Applicable
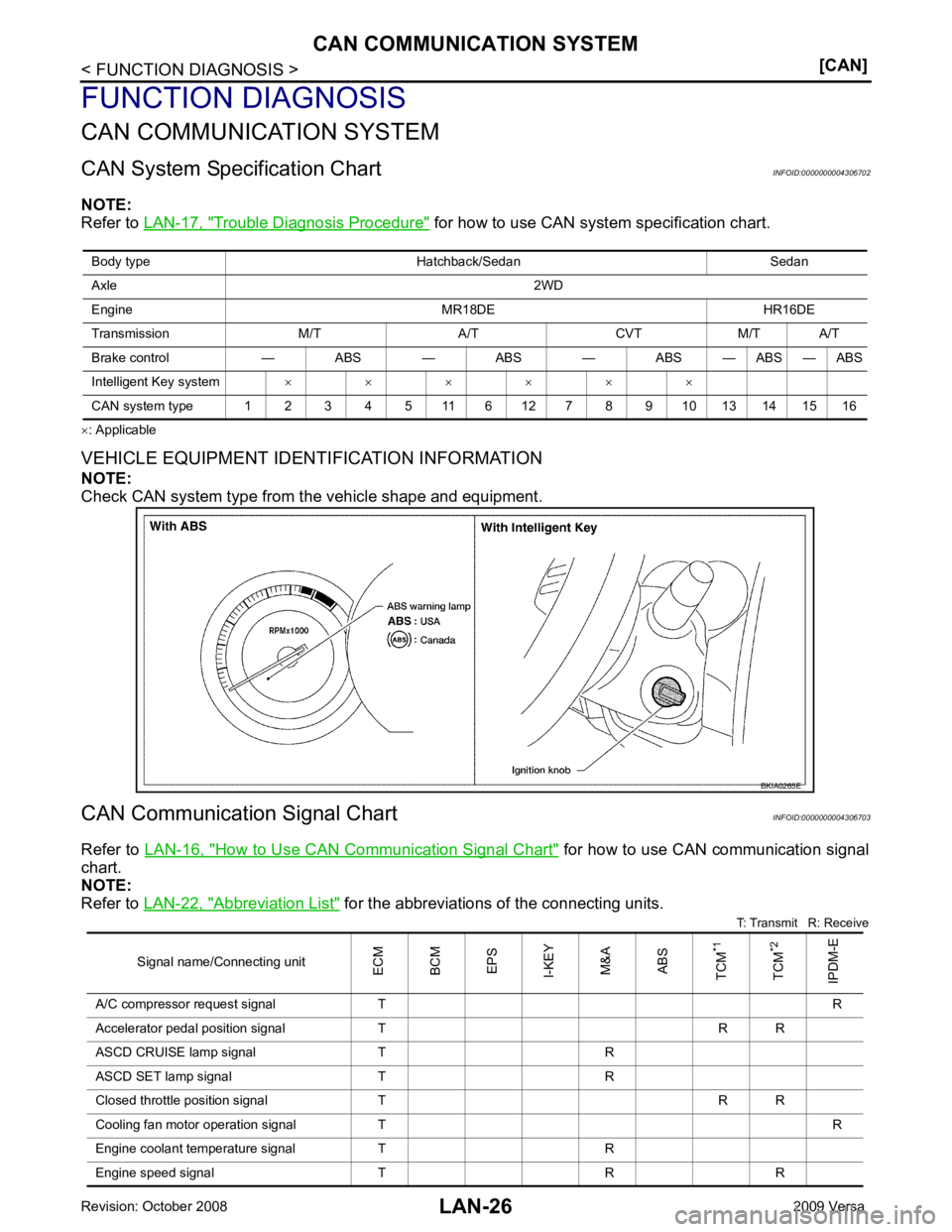
VEHICLE EQUIPMENT IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
NOTE:
Check CAN system type from the vehicle shape and equipment.
CAN Communication Signal Chart INFOID:0000000004306703
Refer to LAN-16, " How to Use CAN Communication Signal Chart " for how to use CAN communication signal
chart.
NOTE:
Refer to LAN-22, " Abbreviation List " for the abbreviations of the connecting units.
T: Transmit R: Receive
Body type Hatchback/Sedan Sedan
Axle 2WD
Engine MR18DE HR16DE
Transmission M/T A/T CVT M/T A/T
Brake control — ABS — ABS — ABS — ABS — ABS
Intelligent Key system × × × × × ×
CAN system type 1 2 3 4 5 11 6 12 7 8 9 10 13 14 15 16