2009 NISSAN LATIO ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 3153 of 4331
![NISSAN LATIO 2009 Service Repair Manual EM-206< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE]
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Position each ring with the gap as shown referring to the pis- ton front mark.
CAUTION:
Never contact the rail end gap under NISSAN LATIO 2009 Service Repair Manual EM-206< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE]
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Position each ring with the gap as shown referring to the pis- ton front mark.
CAUTION:
Never contact the rail end gap under](/manual-img/5/57359/w960_57359-3152.png)
EM-206< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE]
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Position each ring with the gap as shown referring to the pis- ton front mark.
CAUTION:
Never contact the rail end gap under the oil ring with the
oil drain cast groove of piston.
• Install second ring with the stamped surface facing upward.
20. Install connecting rod bearing upper (2) and lower (3) to con- necting rod (1) and connecting rod cap (4).
• Install the connecting rod in the dimension shown.
• Make sure that connecting rod bearing oil hole (A) is com- pletely in the inside of connecting rod oil hole chamfered area
(B).
• When installing connecting rod bearings, apply new engine oil to the bearing surface (inside). Do not apply new engine oil to
the back surface, but thoroughly clean it.
NOTE:
• There is no positioning tab.
• Install the connecting rod bearings in the center of connect-
ing rod and connecting rod bearing cap as shown. For ser-
vice operation, the center position can be checked, visually.
21. Install piston and connecting rod assembly to crankshaft. • Position crankshaft pin corresponding to connecting rod to be installed onto the bottom dead center.
• Apply new engine oil sufficiently to the cylinder bore, piston and crankshaft pin.
• Match the cylinder position with the cylinder number (C) on connecting rod to install.
• Install so that front mark (A) on the piston head faces the front of engine.A : Oil ring upper or lower rail gap
B : Front mark
C : Second ring and oil ring spacer gap
D : Top ring gap
E : Stamped mark PBIC3588J
C : Oil hole (connecting rod)
D : Arrow view
: Engine front PBIC4541E
B : Oil hole
D : Big end diameter grade
E : Small end diameter grade
F : Front mark (connecting rod bearing cap) PBIC3587J
Page 3160 of 4331
![NISSAN LATIO 2009 Service Repair Manual CYLINDER BLOCK
EM-213
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE] C
D E
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A EM
NP
O
1. “Main Bearing Selection Table” rows correspond to main bearing
housing grade on rear left side of cylinder NISSAN LATIO 2009 Service Repair Manual CYLINDER BLOCK
EM-213
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE] C
D E
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A EM
NP
O
1. “Main Bearing Selection Table” rows correspond to main bearing
housing grade on rear left side of cylinder](/manual-img/5/57359/w960_57359-3159.png)
CYLINDER BLOCK
EM-213
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
[MR18DE] C
D E
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A EM
NP
O
1. “Main Bearing Selection Table” rows correspond to main bearing
housing grade on rear left side of cylinder block (L).
• If there is a correction stamp ma rk on cylinder block, use it as
a correct reference.
2. Apply main journal diameter grade stamped on crankshaft front side to column in the “Main Bearing Selection Table”.
3. Read the symbol at the cross point of selected row and column in the “Main Bearing Selection Table”.
CAUTION:
There are two main bearing selection tables. One is for No. 1, 4 and 5 journals and the other is for
No. 2 and 3 journals. Make certain to use the approp riate table. This is due to differences in the
specified clearances.
4. Apply the symbol obtained to the “Main B earing Grade Table” to select main bearing.
NOTE:
Service part is available as a set of both upper and lower.
When Cylinder Block and Crankshaft are Reused 1. Measure the dimensions of the cylinder block ma in bearing housing inner diameter and crankshaft main
journal diameter individually. Refer to EM-216, " Inspection After Disassembly " and
EM-216, " Inspection
After Disassembly " .
2. Apply the measured dimension to t he “Main Bearing Selection Table”.
3. Read the symbol at the cross point of selected row and column in the “Main Bearing Selection Table”.
CAUTION:
There are two main bearing selection tables. One is for No. 1, 4 and 5 journals and the other is for
No. 2 and 3 journals. Make certain to use the ap propriate table. This is due to differences in the
specified clearances.
4. Apply the symbol obtained to the “Main B earing Grade Table” to select main bearing.
NOTE: A : Correction stamp
B : Standard stamp
C : Cylinder No. 1 bore grade
D : Cylinder No. 2 bore grade
E : Cylinder No. 3 bore grade
F : Cylinder No. 4 bore grade
G : No. 1 main bearing housing grade
H : No. 2 main bearing housing grade
I : No. 3 main bearing housing grade
J : No. 4 main bearing housing grade
K : No. 5 main bearing housing grade
: Engine front PBIC3264J
A : No. 1 pin journal diameter grade
B : No. 2 pin journal diameter grade
C : No. 3 pin journal diameter grade
D : No. 4 pin journal diameter grade
E : No. 1 main journal diameter grade
F : No. 2 main journal diameter grade
G : No. 3 main journal diameter grade
H : No. 4 main journal diameter grade
I : No. 5 main journal diameter grade PBIC3261J
Page 3230 of 4331
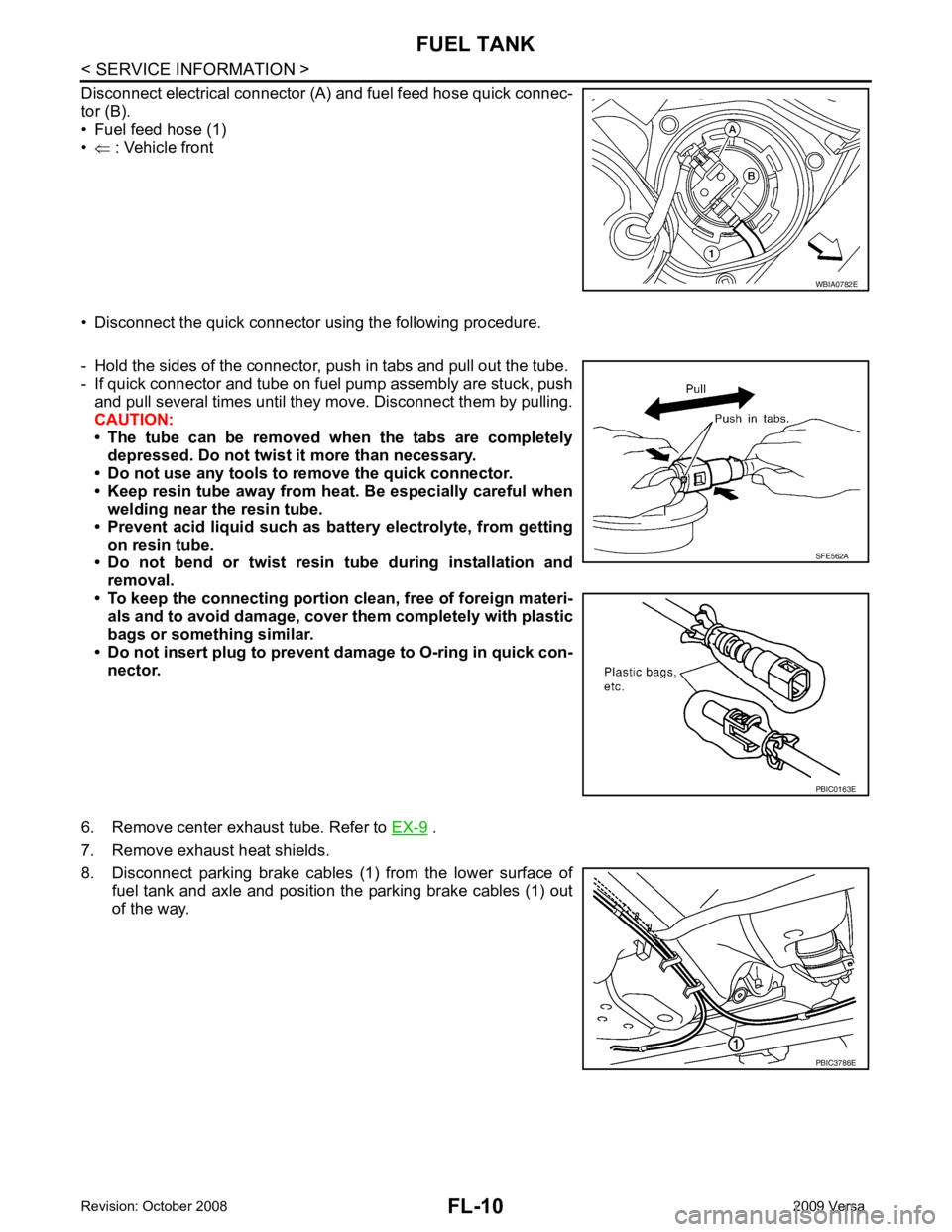
FL-10< SERVICE INFORMATION >
FUEL TANK
Disconnect electrical connector (A) and fuel feed hose quick connec-
tor (B).
• Fuel feed hose (1)
• ⇐ : Vehicle front
• Disconnect the quick connector using the following procedure.
- Hold the sides of the connector, push in tabs and pull out the tube.
- If quick connector and tube on fuel pump assembly are stuck, push
and pull several times until they move. Disconnect them by pulling.
CAUTION:
• The tube can be removed when the tabs are completely depressed. Do not twist it more than necessary.
• Do not use any tools to remove the quick connector.
• Keep resin tube away from h eat. Be especially careful when
welding near the resin tube.
• Prevent acid liquid such as ba ttery electrolyte, from getting
on resin tube.
• Do not bend or twist resin tube during installation and removal.
• To keep the connecting portion clean, free of foreign materi-
als and to avoid damage, cover them completely with plastic
bags or something similar.
• Do not insert plug to prevent damage to O-ring in quick con-
nector.
6. Remove center exhaust tube. Refer to EX-9 .
7. Remove exhaust heat shields.
8. Disconnect parking brake cables (1) from the lower surface of
fuel tank and axle and position the parking brake cables (1) out
of the way. WBIA0782E
SFE562A
PBIC0163E
PBIC3786E
Page 3231 of 4331
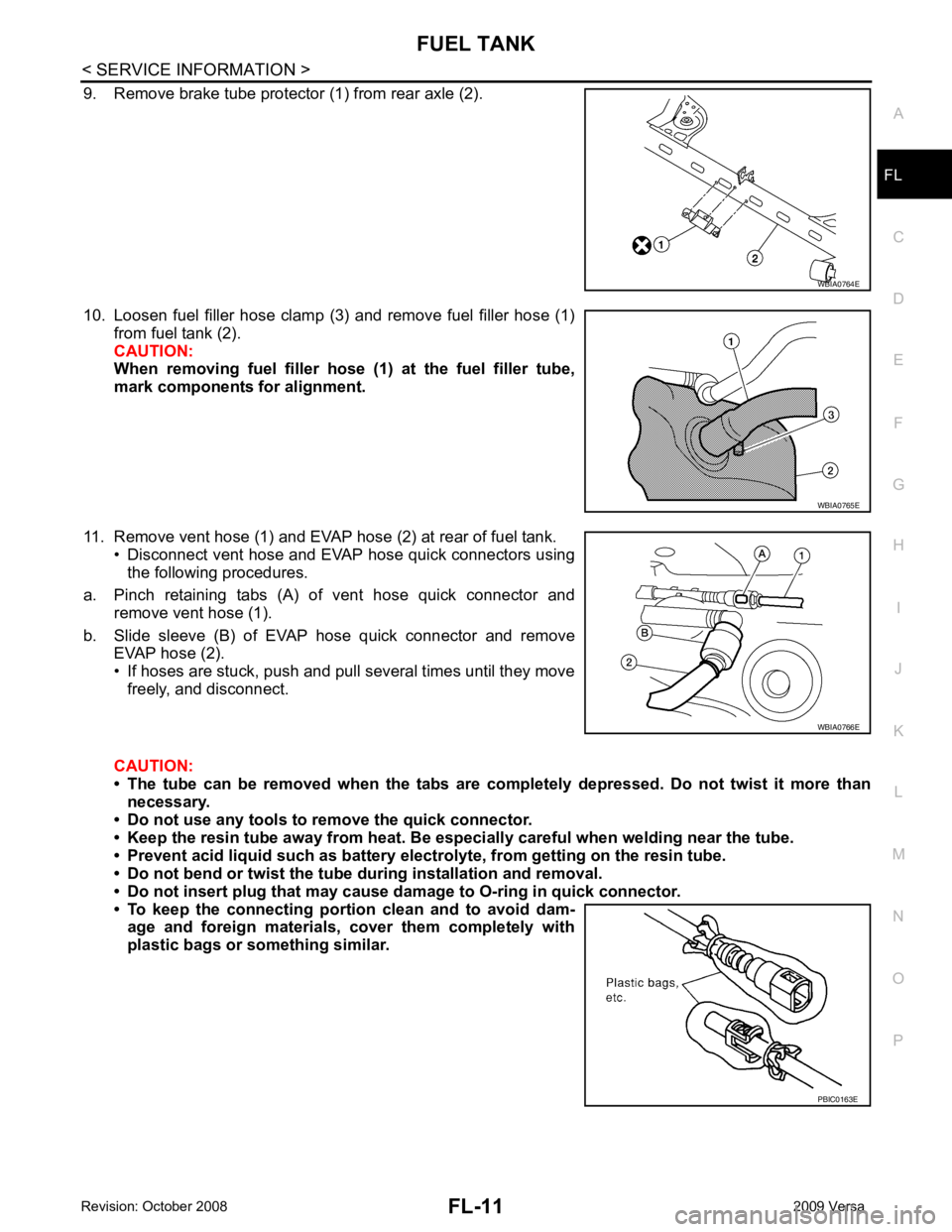
FL
NP
O
9. Remove brake tube protector (1) from rear axle (2).
10. Loosen fuel filler hose clamp (3) and remove fuel filler hose (1) from fuel tank (2).
CAUTION:
When removing fuel filler hose (1) at the fuel filler tube,
mark components for alignment.
11. Remove vent hose (1) and EVAP hose (2) at rear of fuel tank. • Disconnect vent hose and EVAP hose quick connectors usingthe following procedures.
a. Pinch retaining tabs (A) of vent hose quick connector and remove vent hose (1).
b. Slide sleeve (B) of EVAP hose quick connector and remove EVAP hose (2).
• If hoses are stuck, push and pull several times until they move freely, and disconnect.
CAUTION:
• The tube can be removed when the tabs are completely depressed. Do not twist it more than
necessary.
• Do not use any tools to remove the quick connector.
• Keep the resin tube away from heat. Be especi ally careful when welding near the tube.
• Prevent acid liquid such as battery elect rolyte, from getting on the resin tube.
• Do not bend or twist the tube during installation and removal.
• Do not insert plug that may cause dama ge to O-ring in quick connector.
• To keep the connecting portio n clean and to avoid dam-
age and foreign materials, cover them completely with
plastic bags or something similar. WBIA0765E
WBIA0766E
Page 3256 of 4331

GI
N
O P
2. Use the Intelligent Key or mechanical key to turn the ignition switch to the
″ACC ″ position. At this time, the
steering lock will be released.
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released and the steering wheel can be
rotated.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
5. When the repair work is completed, return the ignition switch to the ″LOCK ″ position before connecting
the battery cables. (At this time, the steering lock mechanism will engage.)
6. Perform a self-diagnosis check of al l control units using CONSULT-III.
General Precaution INFOID:0000000004307347
• Do not operate the engine for an extended period of time without proper exhaust ventilation.
Keep the work area well ventilated and free of any flammable
materials. Special care should be taken when handling any flam-
mable or poisonous materials, such as gasoline, refrigerant gas,
etc. When working in a pit or ot her enclosed area, be sure to prop-
erly ventilate the area before working with hazardous materials.
Do not smoke while working on the vehicle.
• Before jacking up the vehicle, apply wheel chocks or other tire blocks to the wheels to prevent t he vehicle from moving. After jack-
ing up the vehicle, support the vehicle weight with safety stands at
the points designated for proper lifting before working on the vehi-
cle.
These operations should be done on a level surface.
• When removing a heavy component such as the engine or tran-
saxle/transmission, be careful not to lose your balance and drop
them. Also, do not allow them to strike adjacent parts, especially
the brake tubes and master cylinder.
• Before starting repairs which do not require battery power: Turn off ignition switch.
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
• If the battery terminals are disconnected, recorded memory of
radio and each control unit is erased.
• Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds. Wash hands after handling.
• To prevent serious burns: Avoid contact with hot metal parts.
Do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot.
• Dispose of or recycle drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning
parts in an appropriate manner.
• Do not attempt to top off the fuel tank after the fuel pump nozzle shuts off automatically.
Continued refueling may cause fuel overflow, resulting in fuel spray
and possibly a fire.
• Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly. SGI231
SGI233
Page 3270 of 4331

GI
N
O P
Harness Indication 14 Wire color
• This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light Green BR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description • This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch • This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts • Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code • This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow • Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
• A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on circuit operation.
20 System branch • This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing • This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
• The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preceding pages.
22 Shielded line • The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23 Component box in
wave line • This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name • This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number • This shows the connector number.
• The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
• Example: M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in lo-
cating connectors.
26 Ground (GND) • The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the ground-
ed connector.
27 Ground (GND) • This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views • This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component • Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color • This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31 Fusible link and fuse
box • This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of "POW-
ER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area • This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details.
Num-
ber Item Description
Page 3309 of 4331
GW-6< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Work Flow INFOID:0000000004306847
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the c onditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to GW-10, " Diagnostic Worksheet " . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain all the facts and conditions that exist w hen the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise) Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include hi gh frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperat ure, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or lo cation of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair. SBT842
Page 3375 of 4331
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
IP-5
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
C
D E
F
G H
J
K L
M A
B IP
N
O P
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Work Flow INFOID:0000000004307244
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW Interview the customer, if possible, to determine the c onditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interv iew to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-9, " Diagnostic Worksheet " . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed descr iption or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by te st driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
- Squeak — (Like tennis shoes on a clean floor) Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
- Creak — (Like walking on an old wooden floor) Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
- Rattle — (Like shaking a baby rattle) Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
- Knock — (Like a knock on a door) Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
- Tick — (Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of li ght materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
- Thump — (Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
- Buzz — (Like a bumblebee) Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE SBT842